Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt 4 Physic
Expt 4 Physic
Uploaded by
•Mr Ravi•Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt 4 Physic
Expt 4 Physic
Uploaded by
•Mr Ravi•Copyright:
Available Formats
LABORATORY MANUAL
Ig = kN
if n represents the actual deflection in the converted galvanometer,
then the total current will be
IO
I=n .
N
P ROCEDURE
1. Determine the galvanometer resistance G and figure of merit k as
per the procedure given in experiment 6.
2. Count the total number of divisions N on either side of zero of the
galvanometer scale.
3. Calculate the current I g for full scale deflection in the
galvanometer by using the relation Ig = Nk, where k is the figure
of merit of the galvanometer.
4. Calculate the shunt resistance S using the
I G
formula S = g .
I0 − I g
5. Measure the radius r of the wire and from
the given value of the specific resistance ρ,
calculate the length of the wire l, for resistance
S πr 2
S [use the formula l = ].
ρ
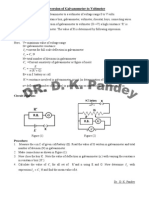
Fig. E 7.1 Circuit to verify conversion of
6. Let the calculated length of the wire be 10
galvanometer into an ammeter cm. Then cut 3-4 cm extra and put it in
parallel to the galvanometer and complete
the circuit as shown in Fig. E 7.1.
7. Adjust the length of the wire so that when we see full scale
deflection in the galvanometer, the current in the ammeter is
30 mA.
8. Thus the galvanometer is now converted to an ammeter whose
range is 30 mA.
9. Now measure the exact length of the shunt wire and calculate its
resistance by using the previously measured value of radius and
the known value of specific resistance.
10. Compare the above value of resistance to the one calculated using
l×ρ
the formula S = .
πr 2
60
24/04/2018
You might also like
- Conversion of Galvanometer To Ammeter PracticalDocument4 pagesConversion of Galvanometer To Ammeter Practicaldipu21250% (2)
- Galvanometer To Ammeter PDFDocument2 pagesGalvanometer To Ammeter PDFMegha SaranNo ratings yet
- Vigilance MattersDocument6 pagesVigilance MattersAnonymous CVKDY65OGNo ratings yet
- Practical 11Document4 pagesPractical 11Piyush Jain0% (1)
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsshuvanita2006dasNo ratings yet
- 12th Experiment-3pDocument4 pages12th Experiment-3pkrishnaraghu327No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual Part 01Document37 pagesPhysics Lab Manual Part 01Dr U S MirdhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual - eDocument30 pagesPhysics Lab Manual - eMurukeshwari S SaravananNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Specific Resistance of The Given Wires, Using Ohm's LawDocument13 pagesTo Determine The Specific Resistance of The Given Wires, Using Ohm's LawSivaRamaKrishnan R.No ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Kabir AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- S.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IIDocument2 pagesS.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IINeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical March 2022-1Document20 pagesPhysics Practical March 2022-1deepakrambhakt07No ratings yet
- Super Conduct AmmeterDocument4 pagesSuper Conduct Ammetertritium325No ratings yet
- Galvanometer To VoltmeterDocument2 pagesGalvanometer To Voltmeterfaizmustafa67No ratings yet
- Sensitivity TestDocument12 pagesSensitivity Testratnaraj_kanungoeNo ratings yet
- To Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Document4 pagesTo Convert A Weston Type Galvanometer Into An Ammeter of Range 0Sulman Abbasi0% (2)
- PHYS 106: Practical Physics II Second Semester: University of GhanaDocument4 pagesPHYS 106: Practical Physics II Second Semester: University of Ghanakaleab mebratuNo ratings yet
- Experiments After BTDocument11 pagesExperiments After BTArkaprava MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- IC 211 Lab Manual 2018-2019Document102 pagesIC 211 Lab Manual 2018-2019AdityaSoniNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical ReadingsDocument49 pagesPhysics Practical ReadingsKaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge - Principle and Working Experiment - Embibe (HTTPSWWW - Embibe.comexamsmeter-Bridge)Document15 pagesMeter Bridge - Principle and Working Experiment - Embibe (HTTPSWWW - Embibe.comexamsmeter-Bridge)subrata kumar nandiNo ratings yet
- GalvanometerDocument8 pagesGalvanometerAnkit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer Ammeter by Dr. Gaurav KarnatakDocument14 pagesGalvanometer Ammeter by Dr. Gaurav KarnatakRose ytNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Obs Booklet 2021-22Document59 pagesClass 12 Obs Booklet 2021-22nooraNo ratings yet
- Lab Phy 1Document14 pagesLab Phy 1sarath1234567No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Edited Labmanual 1 8 1683724296Document24 pagesClass 12 Physics Edited Labmanual 1 8 1683724296Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Combination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredDocument4 pagesCombination of Resistances: Circuit Diagram: Series Combination Experiment No.:7A Date: Aim: - Apparatus RequiredRonda StewartNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical List - Class Xii: Exp. No. Name of ExperimentsDocument1 pagePhysics Practical List - Class Xii: Exp. No. Name of ExperimentsSoumyashis BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaDocument6 pagesConversion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaCharis Israel Ancha50% (2)
- Physics PracticalDocument8 pagesPhysics Practicalcvpranav1104No ratings yet
- Physics Practical'sDocument43 pagesPhysics Practical'sTvara PatelNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report #3Document6 pagesPhysics Lab Report #3231152No ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument24 pagesPhysics PracticalPeddini Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353Document145 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353NishaKamarajNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiments Topic For Class 12Document27 pagesPhysics Experiments Topic For Class 12Aditya Chakraborty100% (2)
- Thermistor PracDocument7 pagesThermistor PracSekh AsifNo ratings yet
- 12th Lab ManualDocument82 pages12th Lab ManualUdithyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual XII 2021-22Document20 pagesPhysics Lab Manual XII 2021-22kangan nagiNo ratings yet
- Class-12 Lab Manual PhysicsDocument29 pagesClass-12 Lab Manual PhysicsV.R. MuruganNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 3Document5 pagesPhysics Lab Report 3usmanNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Iv-Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Ziet Chandigarh: Practice Paper Unit-Iv-Moving Charges and Magnetismanime loverNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 2-1Document14 pagesPhysics Project 2-1Saul NathNo ratings yet
- IMG - 0521 EE PreBoard Exam 2 Jan 2014Document1 pageIMG - 0521 EE PreBoard Exam 2 Jan 2014rii amosNo ratings yet
- 07 Galvanometer - 2Document2 pages07 Galvanometer - 2Muhammad SufyanNo ratings yet
- To Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half DeflectionDocument4 pagesTo Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half DeflectionPriyojit MondalNo ratings yet
- ConversionDocument2 pagesConversionmurugeshkasthuri786No ratings yet
- XII - Physics Practical 2023-24Document38 pagesXII - Physics Practical 2023-24Aadil0% (1)
- EMI 3rd PDFDocument53 pagesEMI 3rd PDFKeshav Kumar Pushpam100% (1)
- G12 Physics Experiment 23-24Document43 pagesG12 Physics Experiment 23-24anonymous3256tNo ratings yet
- Y11 Electrical QuantitiesDocument12 pagesY11 Electrical QuantitiesWu YiruiNo ratings yet
- Sure Short Question For Physics 3-Marks AnswerDocument16 pagesSure Short Question For Physics 3-Marks AnswerSantoshi PandeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 & 2Document5 pagesExperiment 1 & 2POWERMAN YTNo ratings yet
- 1 Meter BridgeDocument2 pages1 Meter BridgeDinesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- II PUC ManualDocument31 pagesII PUC Manuals2263001No ratings yet
- X L R L L: Thus Resistivity of The Given Wire IsDocument2 pagesX L R L L: Thus Resistivity of The Given Wire IsPalash VermaNo ratings yet
- Physics All IndiaDocument17 pagesPhysics All IndiahiNo ratings yet
- Physics 1st YearDocument64 pagesPhysics 1st YearManishNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument25 pagesPhysics PracticalYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- II PU New ExptsDocument6 pagesII PU New ExptsAdvaithNo ratings yet