Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul EFB Unit 1
Modul EFB Unit 1
Uploaded by
Evi RachmawatiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul EFB Unit 1
Modul EFB Unit 1
Uploaded by
Evi RachmawatiCopyright:
Available Formats
MODUL PERKULIAHAN
Mata Kuliah English For Business
Module 1:
Business, Commerce, and
Trade
Mahasiswa mampu memahami berbagai terminologi bisnis dan perdagangan
internasional serta menerapkannya dalam kalimat atau dialog berbahasa Inggris.
program tatap muka
fakultas kode mk disusun oleh
studi
ilmu budaya program cdp
studi
inggris s1
bahasa
01
Abstract Kompetensi
Bab ini mengeksplorasi Mahasiswa memiliki kemampuan
kemampuan dan keterampilan memahami dan berlatih menerapkan
berkomunikasi mahasiswa terminologi bisnis dan perdagangan
dalam dunia bisnis dan internasional dalam kalimat
perdagangan internasional. berbahasa Inggris.
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
1 CDP
MODULE 1
1 Business, Commerce, and Trade
Business, Commerce, and Trade
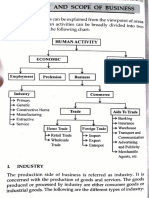
A. Difference Between Business, Commerce, and Trade
Commerce and trade are two distinct terms involved in business activities. Trade is a subpart of
commerce and carries narrow scope in comparison to commerce.
In simple terms, trade refers to buying and selling of goods between customers and sellers in return
for money. Whereas, commerce in addition to buying and selling of goods also includes all those
activities needed for completing exchange of goods between producers to ultimate consumers. It
includes various services which aid trade such as transportation, insurance, warehouses,
advertising, banking and many more.
Trading activities bring association between seller and buyers. Commerce links together the
producer of goods and end consumers by facilitating the exchange. Trade is a social activity as it
aims at satisfying the needs of buyers and sellers.
But commerce focuses on earning profits for several parties involved in its services and thereby is
an economic activity. Dissimilarities between the trade and commerce can be well-understood
more clearly from comparison chart given below.
Difference Between Business, Commerce, and Trade
(Commercemates.com, 2022)
Basis of
Business Commerce Trade
Difference
Commerce refers to all Trade refers to
Business refers to all
activities which exchange of products
those activities which are
Meaning facilitates the exchange or services among
done with the aim of
of goods from producer buyers and sellers in
earning profits.
to end consumer. return for money.
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
2 CDP
Basis of
Business Commerce Trade
Difference
Narrower as is
Wider. It includes both Wider than trade, as it
concerned with only
Scope trade and commerce comprises of activities
buying and selling of
within its activities. which supports trade.
goods.
Between owner and Between producer and Between buyer and
Connectivity
clients. consumer. seller.
Huge amount of capital is More amount of
Capital needed Requires less capital.
needed. capital needed.
Side Supply side of the Both demand and
Only demand side.
represented product. supply side.
Riskier than trade and
Risk level Riskier than trade. Low risk
commerce.
Transactions
Regular Regular Isolated
frequency
More employment
Large number of
opportunities as large
Employment opportunities due to
number of people are Very few.
Opportunities presence of many
required for performing
activities.
different tasks.
B. International Commerce and Global Trade
International commerce is the practice of buying and selling goods and services between nations.
With international commerce, sovereign states leverage competitive advantages of their home
countries to buy and sell elsewhere. A competitive advantage could be an extra-long coastline,
like Chile has; proximity to certain natural resources, like lumber (Canada) or fish (Portugal); or a
highly educated, technically trained workforce (South Korea, Sweden, Israel).
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
3 CDP
With all of these different countries participating in the international commercial system, each with
its own set of sovereign laws, it is important that global regulatory agencies exist to create some
legal cohesion. The two main organizations overseeing international commerce are the
International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and World Trade Organization (WTO). The WTO
does have a hand in regulating international commerce, despite there being a difference between
commerce and trade.
There is a technical distinction between international commerce and global trade. Trade refers to
the basic economic activity of buying, selling, and/or exchanging goods and services between two
or more parties in a marketplace. Commerce encompasses all activities that promote the exchange
of goods and services—from the point of manufacture to the moment a customer purchases a
product in a store.
Questions
1. Using your own words, what is the difference between business, commerce, and trade?
2. Find definition and meaning of the following business terms:
a. Customer
b. Seller
c. Goods
d. Service
e. Profit
f. Capital
g. Banking
h. Freight
i. Advertising
j. Marketing
k. Warehousing
l. Insurance
C. Reading
Getting started
Discuss the questions below with your group and then do the exercise which follows them.
1. What are the different types of trade discussed so far?
2. Who are the different people involved in this trade?
3. What role would they play in the process?
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
4 CDP
Vocabulary
Look at the terms below. Using what you have learnt about definitions, can you write one for each
term? Write the definitions for the following terms in your own words. Then check your answers
as you read the text. Do not use the text to find the definitions.
Term Definition
1 Export trading company
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
2 Export management
company
______________________________________________
3 Distributor ______________________________________________
______________________________________________
4 Retailer ______________________________________________
______________________________________________
5 Import export agent ______________________________________________
______________________________________________
6 Sales representative ______________________________________________
EXPORT TRADER
Trade has existed ever since Man recognized the need to look for and obtain resources to
fulfill his needs. From early man trading skins and salt with neighbouring tribes to Marco Polo
bringing silks, spices and technology from the Far East to the Western world, to modern
conglomerates trading millions of dollars on the stock exchange, trade has been an essential part
of our lives. Countries engage in trade for many reasons. These include product availability,
competitive prices and product image. But for the goods to reach the customer, they must go
through the import/export process and pass through the hands of different players along the way.
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
5 CDP
The word import comes from the Medieval Latin importare which means to bring in which, in
essence, is done when goods are brought in from a foreign country, while export is the process by
which goods are shipped from one country to another. There are two main methods of export:
direct and indirect exporting. In direct exporting, the manufacturer, assembler or processor of an
exported good is in charge of the entire marketing and distribution of the product and sells directly
to companies, known as direct merchants, in the foreign market. The direct merchant then sells
these goods on their domestic market. These merchants usually offer complementary services
such as maintenance, spare parts and technical support to their customers.
However, a cheaper and less risky export route is through indirect export where the manufacturer
hires a local agent to find and deliver its goods to buyers abroad. An example of indirect exporting
is through an Export management company (EMC) which handles trade for a domestic company
which wants to sell its product abroad. The EMC hires the dealers, distributors and representatives,
manages the advertising, marketing and promoting of the product, oversees marking and
packaging, and arranges the shipping. An Export management company can specialize in one type
of product, foreign market or both and is usually paid by commission, salary or a retainer plus
commission.
Another type of indirect trading agent is the Export trading company (ETC) which looks for
potential buyers by identifying the needs of the foreign market and then supplying domestic
sources willing to fill this need. It can either take title to the goods or work on a commission basis.
An Import/Export company, on the other hand, purchases goods directly from a domestic or
international client and then packs, ships and resells these goods.
There are also a number of intermediary players. For example, an import export agent is one
who rarely invests capital in inventory or deals in the merchandise, products or services directly.
Instead, this agent acts as an intermediary between manufacturers and distributors in one country
and buyers in another, finding the appropriate market for the goods, making a solid connection
and solidifying a business relationship between both parties. They are paid a commission which
is usually 10% of the transaction. Manufacturers may also decide to have their own representative
who is an expert in their particular industry and can give technical support. This specialization
may differentiate them from the sales representative who simply promotes the product and then
passes the sale to the seller. A distributor buys the imported product and then sells it to another
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
6 CDP
for further distribution to the buying public. Finally, there is the retailer who then sells the
merchandise to the customer.
There are many different kinds of agents involved in the import and export trade and the best type
would depend on the needs, and capabilities of the manufacturer who wishes to place his product
on an international market. From export management companies to individual sales
representatives, there is a group of qualified individuals able to help in this process.
Checking your understanding of the text
Form three groups. Each group has to do the following:
1. Write six (6) questions based on the text. Remember to check the grammatical structure of
your question.
2. Give your questions to members of the 2nd group for them to answer.
3. Give the answers to members of the 3rd group for them to be corrected.
4. Discuss the answers with the entire class.
References
1. Cruz, Didier J.C. “Introduction to International Trade”. accessed August 11, 2022
https://www.academia.edu/29941691/ENGLISH_FOR_INTERNATIONAL_TRADE_1_
Material_researched_and_adapted_by_Introduction_to_International_trade
2. Shopify. April 8, 2022. “International Commerce”. Accessed August 8, 2022.
https://www.shopify.com/blog/international-commerce
3. Commercemates.com “Difference Between Business, Commerce, and Trade”. Accessed
August 8, 2022. https://commercemates.com/difference-between-business-commerce-
trade/
4. http://www.entrepreneur.com/startingabusiness/businessideas/startupkits/article41846.ht
ml
English For Business Biro Akademik dan Pembelajaran http://www.widyatama.ac.id
7 CDP
You might also like
- ASAL Business Worksheet AnswersDocument53 pagesASAL Business Worksheet Answersdesrescott100% (1)
- Mattec Integration Technical Reference 2021.1Document283 pagesMattec Integration Technical Reference 2021.1Royston Da CostaNo ratings yet
- Modul EFB Unit 1Document7 pagesModul EFB Unit 1alziraanindia30No ratings yet
- Modul EFB Unit 1Document7 pagesModul EFB Unit 1Vidya AstriutamiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Trade and CommerceDocument7 pagesDifference Between Trade and CommerceAlessia RaviolaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Different Markets To Markets and Differentiate Those Markets From ONE AnotherDocument4 pagesIdentifying Different Markets To Markets and Differentiate Those Markets From ONE AnotherYathu MathuNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Learning ObjectivesDocument31 pagesHapter: Learning ObjectivesRichaNo ratings yet
- Firms Production Purchase Marketing R&D Finance B2C CustomersDocument6 pagesFirms Production Purchase Marketing R&D Finance B2C CustomersPratiksha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Reading 2Document10 pagesReading 2Muhammad Bilal MakhdoomNo ratings yet
- kebs110Document31 pageskebs110Raghav GulyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document31 pagesChapter 10Mohd shayaanNo ratings yet
- Bes Abm12 L1 - L2Document5 pagesBes Abm12 L1 - L2Jerwin SamsonNo ratings yet
- 228 Business Studies: HapterDocument30 pages228 Business Studies: HapterSomnath ChandaNo ratings yet
- Internal TradeDocument30 pagesInternal TradeRahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Market: MARKET' - Derived From The Latin Word MERCATUS' - Means To Trade'Document171 pagesMarket: MARKET' - Derived From The Latin Word MERCATUS' - Means To Trade'Seema GawaiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Introduction of Commerce For Economic & Finance PDFDocument7 pagesSyllabus of Introduction of Commerce For Economic & Finance PDFNaveed Whatsapp StatusNo ratings yet
- S.3 and S.4 Commerce Questions Answers 1Document43 pagesS.3 and S.4 Commerce Questions Answers 1zakNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 1 Rhin FrancineDocument85 pagesAccounting 1 1 Rhin FrancineKaysiah Jane Gapongli ApilNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2 - Customer Service Karen OrtizDocument8 pagesWorkshop 2 - Customer Service Karen OrtizOlga Lucia Escobar SernaNo ratings yet
- BA302-International Business and Trade I. Identification. Write Iin All Upper Case LetterDocument4 pagesBA302-International Business and Trade I. Identification. Write Iin All Upper Case LetterMary Grace BatalNo ratings yet
- B.ST CH 1Document24 pagesB.ST CH 1SaarthNo ratings yet
- Business-to-Business Marketing Session1-2: Introduction To The ConceptsDocument38 pagesBusiness-to-Business Marketing Session1-2: Introduction To The ConceptsurvigulatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To B2BDocument28 pagesIntroduction To B2BShreya KadamNo ratings yet
- Levitt (1980) Marketing Success Through Differentiation  of AnythingDocument10 pagesLevitt (1980) Marketing Success Through Differentiation  of AnythingWeronikaNo ratings yet
- Httpsncert - nic.Intextbookpdfkebs104.PDF 2Document34 pagesHttpsncert - nic.Intextbookpdfkebs104.PDF 2Divya ChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Module-I: Meaning and Definition of SaleDocument4 pagesModule-I: Meaning and Definition of Sale1220675007No ratings yet
- Difference Between Commerce, Trade & IndustryDocument4 pagesDifference Between Commerce, Trade & IndustrybeenishNo ratings yet
- CommodityTradingHubs. SingaporeDocument20 pagesCommodityTradingHubs. SingaporeSaumya Raizada100% (1)
- Chapter 7-8 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 7-8 ReviewerUnknownNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handout No. 1-Introduction To AccountingDocument9 pagesLecture Handout No. 1-Introduction To AccountingAngie BobierNo ratings yet
- Scope and Types of BusinessDocument9 pagesScope and Types of BusinessSam Nirmal PandianNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit 1 Notesanshu kushwahNo ratings yet
- ECO 01 Solved Assignments 2016Document11 pagesECO 01 Solved Assignments 2016Rahul RawatNo ratings yet
- Binge 4.0Document26 pagesBinge 4.0Royston NazarethNo ratings yet
- Business Trade and CommerceDocument25 pagesBusiness Trade and CommerceNinida AgroNo ratings yet
- Economics in Everyday Life Final ProjectDocument11 pagesEconomics in Everyday Life Final ProjectEsha AimenNo ratings yet
- CCP104Document12 pagesCCP104api-3849444No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2lâm nhã trúcNo ratings yet
- BCK ICAI Study Mat (Nov 21)Document218 pagesBCK ICAI Study Mat (Nov 21)Isha BavdechaNo ratings yet
- Advancing Trade Marketing in The Digital WorldDocument11 pagesAdvancing Trade Marketing in The Digital WorldgautamsaraswatNo ratings yet
- l22 - Internal TradeDocument29 pagesl22 - Internal TradeTeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- Laura Bolívar Karina Ospina Diana RodríguezDocument10 pagesLaura Bolívar Karina Ospina Diana RodríguezLaura Bolivar BNo ratings yet
- Commercial Transaction Documents: Module 2-2Document33 pagesCommercial Transaction Documents: Module 2-2Rafael TavaresNo ratings yet
- IBT Reviewer MDTDocument5 pagesIBT Reviewer MDTKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Bus Marktg 2023 Day 1 - Second HalfDocument38 pagesBus Marktg 2023 Day 1 - Second Halfrachitgandhi1101No ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2SylviaNo ratings yet
- Department of Economic Sciences and Commercial and Science of ManagementDocument3 pagesDepartment of Economic Sciences and Commercial and Science of ManagementKairi ShawolNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Retail ManagementDocument13 pagesRetail Management Retail ManagementshaikhamunafNo ratings yet
- Best Practices On Trade Marketing PDFDocument10 pagesBest Practices On Trade Marketing PDFSammy WilsonNo ratings yet
- B2B-All ModulesDocument483 pagesB2B-All ModulesakbarNo ratings yet
- Fashion - Productg Development Responsive - and - Profitable - Apparel - BusinessDocument5 pagesFashion - Productg Development Responsive - and - Profitable - Apparel - BusinessAmnon ArmoniNo ratings yet
- 2024 04 25 - #10 Pengantar Perpajakan InternasionalDocument65 pages2024 04 25 - #10 Pengantar Perpajakan Internasionalrotelematika.lemhannasNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Module 1 NotesDocument2 pagesRetail Management Module 1 NotesFrankie CordovaNo ratings yet
- Intro To RetailingDocument23 pagesIntro To RetailingSarju MoirangthemNo ratings yet
- Difference Between B2B and B2CDocument2 pagesDifference Between B2B and B2CDanica CantojaNo ratings yet
- b2c PDFDocument5 pagesb2c PDFAnonymous l7iBM68mBPNo ratings yet
- Business ESRDocument8 pagesBusiness ESRYsa belNo ratings yet
- Kebs 101Document25 pagesKebs 101Aarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- CB - XI - XII - Subject - Chapter - HOTS ASDocument11 pagesCB - XI - XII - Subject - Chapter - HOTS ASHetvi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Taller en Idioma Inglés Sobre Sistema de DistribuciónDocument6 pagesTaller en Idioma Inglés Sobre Sistema de Distribuciónyuliana quinteroNo ratings yet
- Representative Assessee - An Overview and Future OutlookDocument63 pagesRepresentative Assessee - An Overview and Future Outlookjoseph davidNo ratings yet
- 4 Judicial Affidavit RuleDocument4 pages4 Judicial Affidavit RuleHanifa Shereen Biston AliNo ratings yet
- Msds AcetyleneDocument7 pagesMsds AcetyleneSyaifuddin Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- RealEstate SingaporeDocument2 pagesRealEstate SingaporeKyaw Kyaw AungNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe's Economic Crisis Driving Homeless Boys Into Illegal Gay Sex TradeDocument4 pagesZimbabwe's Economic Crisis Driving Homeless Boys Into Illegal Gay Sex TradeColbert JohnesNo ratings yet
- Arce Vs Capital InsuranceDocument1 pageArce Vs Capital InsurancePam Otic-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice On ConsultationDocument16 pagesCode of Practice On Consultationaeo9898No ratings yet
- Mortgage Broker AgreementDocument2 pagesMortgage Broker Agreementolboy92No ratings yet
- Case 119 - First United Vs BayanihanDocument6 pagesCase 119 - First United Vs BayanihanGlance CruzNo ratings yet
- ESAB - Cored Wire Electrodes - Data Book PDFDocument210 pagesESAB - Cored Wire Electrodes - Data Book PDFBurag Hamparyan100% (1)
- Four Types of Vocation: Follow HimDocument15 pagesFour Types of Vocation: Follow HimJeanette FormenteraNo ratings yet
- History of Burma 01 PhayDocument362 pagesHistory of Burma 01 PhayMalem NingthoujaNo ratings yet
- Changing Seats Re-Domiciliation To Curaçao FinalDocument2 pagesChanging Seats Re-Domiciliation To Curaçao FinalRicardo NavaNo ratings yet
- Air 2003 Supreme Court 2987Document7 pagesAir 2003 Supreme Court 2987Kedar BhasmeNo ratings yet
- Limkhawpui: N. Hlimen Huan Neitu Pawl HriattirnaDocument2 pagesLimkhawpui: N. Hlimen Huan Neitu Pawl HriattirnaJC LalthanfalaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Corruption in IndiaDocument16 pagesCorporate Corruption in IndiaNAGARAJA M RNo ratings yet
- Fire Evacuation ProcedureDocument4 pagesFire Evacuation ProcedureJessica SimsNo ratings yet
- Modesto Leoveras vs. Casimero ValdezDocument4 pagesModesto Leoveras vs. Casimero ValdezMitchi BarrancoNo ratings yet
- Investment AlternativesDocument19 pagesInvestment AlternativesJagrityTalwarNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Health, Safety, Environment (Hse) Objective and Target Pt. Imr Arc SteelDocument26 pagesMonitoring Health, Safety, Environment (Hse) Objective and Target Pt. Imr Arc SteelArip Adi CandraNo ratings yet
- International Financial Management 13 Edition: by Jeff MaduraDocument39 pagesInternational Financial Management 13 Edition: by Jeff MaduraJaime SerranoNo ratings yet
- Verilog Digital Systems Design (Navabi) PDFDocument477 pagesVerilog Digital Systems Design (Navabi) PDFanupama vedharthamNo ratings yet
- 201-Chevron Phillips Marlex 9006 Polyethylene SDS 10-14-2019Document12 pages201-Chevron Phillips Marlex 9006 Polyethylene SDS 10-14-2019obeckoneNo ratings yet
- Accounting Research Part 1Document2 pagesAccounting Research Part 1Leonard CañamoNo ratings yet
- Liham - Pahintulot: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division of PalawanDocument12 pagesLiham - Pahintulot: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division of PalawanMarbert GarganzaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Type Certificate: Department of Transportation Federal Aviation AdministrationDocument2 pagesSupplemental Type Certificate: Department of Transportation Federal Aviation AdministrationDavid Samaniego PánchezNo ratings yet
- United Food Imports V Baroody ImportsDocument13 pagesUnited Food Imports V Baroody ImportspropertyintangibleNo ratings yet
- Ndian Apital Arket: 25-1 Excel Books Business Environment Suresh BediDocument12 pagesNdian Apital Arket: 25-1 Excel Books Business Environment Suresh BediSebin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Asnake InternshipDocument36 pagesAsnake Internshipkassahungedefaye3120% (1)