Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NUCLEI Mind Map
NUCLEI Mind Map
Uploaded by
sarthakyedlawar04Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NUCLEI Mind Map
NUCLEI Mind Map
Uploaded by
sarthakyedlawar04Copyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear fission Nuclear fusion Nuclear Fusion
. Splitting of a heavy nucleus . Combining two lighter nuclei to form a heavy nucle us.
into or more lighter nucler. Nuclear 1 1
→ 21 H +e + +v +0.42 (energy )
235 n1 141 92 n1 1H+ 1H
e.g ⇒ 92 U +0 → 56 Ba + 36 kr + 30 + 200Mev
Application
. Uncontrolled chain reaction: principle of atomic bank. Nuclear fussion is the source of energy in the sun and stars.
. Contralled chain reation: principle of nuclear reactors.
Fusion
Nuclear of an atom onsists of proton and
Nuclear Fission neutrons collectively called nucleons. Nuclei can be
. Isotoper (same Z but different A)
Representation . Isobars (same A but different Z)
. Isotores (same N but different A) discoverd by henri
Becquerel in 1896
zxA
A = mass number
z = Atomic number
Radio activity
Nuclear Force theory
. Nuclear force is a force which
holds the nucleons together. Phenomenon of Disintegrakon
of heavy elements into
n
comparatively lighter elements
Rodius of a nucleus by emission of α, β, & γ radiations.
R = R0 A 1/3 { R0 = 1-2fm}
Binding Energy of Nucleus
. Density of Nucleus (S)
⇒ B .E = Dmc 2
⇒ B .E = [zmp + (A - Z ) m n - m n ]c 2 Mass Mass of 1 nucleon × A α decay β− decay γ decay
=
Volume 4 1 . radiations are the two types
(Where, c is the speed of light π R 3 = π R 03A z γ -decay office an α or
3 2 helium nuclei. These
c = 3 × 108 m/sec) - decay, nucleus vibrates
. Nuclear density is constant its . For atomic number < 20, most are emitted as β + (positron) β (Electrons)
B .E with the energy shared
⇒ B .E per nucleon = value is nearly 2.38 × 1017 kg/m3 stable nuclei have n:p ratio A-4 A →0 β + A Y + ν by it and electromagnetic
No . of nucleons A 4 z X
z X → 2 He + z − 2 Y
nearly 1:1 −1 z+1 ↓
waves of very high
. Mass of nucleus is measured . For atomic number > 83, there (electron) (antineutrina)
Nuclear binding energy is maximum for α-particle frequency (α-radition) are
in atomic mass unit (u) or (amu) are no stable nuclei. (Product)
mass number 50-60. Daughter emitted
1 amu (or u) = 1/12 (mass of C12) atom . A nucleus is stable when its A
→ +01 β + zA− 1 Y + V
nuclei z X least ionizing power but
= 1.6 × 10-27 kg Binding energy per nucleus (nutrino)
(Position) highest penetrating power.
value is around 8 mev per . highest ionizing power
nucleon or more. but least penetrating . less ionizing power than α
. Mass defect
. Following are observations from power. -particle and moderate
The difference (∆m) between mars of
Binding energy per penetrating power.
constituent nucleons and nucleus is
called mass defect of nucleus. nucleon versus mass number cerve.
Mass and energy [∆m = sum of the masles of nucleons
. Mass m of a particle is equivalent ∆Ebn
- mass of nucleus]
to energy given by E = mc2 Law of radio activity
= {zmp + (A - Z)mn} – Mn
. Also known as rest mass energy.
− dn
4He = λn
dt
7Li N = n 0e - λ t
mean life or any life
Q-Value
56 z 1 T1/2
A+B - C + D + Energy τ = = = 1.44 T1/2
mA mB mc md λ 0.693
Reactants product + Q- Value . B.E. per nucleon is more for some
Fraction of nuclei left
Q value = B.E of product - B.E. OF reactants nuclei than their neighbours.
undcayed after n half
Q-value = [(mA + mB) - (mC + mD)] C2 This andicates a shell type structure
Half - life lives is
Q-value = [(k.EC + k.ED) -(K.EA + K.EB)] of nucleus. N t decay rate or activity
. B.E. per nucleon is around 8meV N N 1 1 t1 2
where N = 0 = = dn
FOR 30 ∠A ∠120, these are 2 N0 2 2 R=-
dt
stable elements. ln 2 0.693
T1 = = Where, t = nT1/2
2 λ λ R = λ N 0 e - λt or R = R 0 e - λt
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- SemiConductor - Mind MapDocument1 pageSemiConductor - Mind Mapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AIATS For First Step JEE (ADV) - Phase-3&4 Test-2A-P2 Code-H Sol 10-03-2024Document7 pagesAIATS For First Step JEE (ADV) - Phase-3&4 Test-2A-P2 Code-H Sol 10-03-2024sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- P - Ch-28 - Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesP - Ch-28 - Communication Systemssarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- CLS ENG 23 24 XI Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2Document36 pagesCLS ENG 23 24 XI Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument1 pageChemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Newton - S LawDocument1 pageNewton - S Lawsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument1 pageRotational Motionsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument1 pageEquilibriumsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Electromagnatic Induction.Document1 pageElectromagnatic Induction.sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-1 MindmapDocument1 pageThermodynamics-1 Mindmapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Oscillations MindmapDocument1 pageOscillations Mindmapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
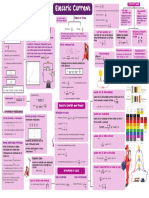
- Electric CurrentDocument1 pageElectric Currentsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
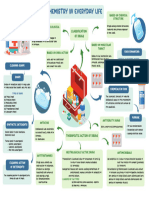
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument1 pageChemistry in Everyday Lifesarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
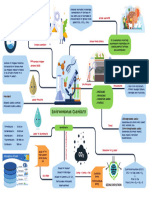
- Environmental Chemistry.Document1 pageEnvironmental Chemistry.sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Section - E: Subjective Type: G V T GT VDocument32 pagesSection - E: Subjective Type: G V T GT Vsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Section - C: Linked Comprehension Type: DV KVG DTDocument19 pagesSection - C: Linked Comprehension Type: DV KVG DTsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol - EthersDocument1 pageAlcohol, Phenol - Etherssarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Mechanics-I: Section - ADocument50 pagesMechanics-I: Section - Asarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet