Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
Uploaded by
rabinoadrian24Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 718 MP111 Individual Assignment S2 2022 Part 1Document23 pages718 MP111 Individual Assignment S2 2022 Part 1Rosalie BachillerNo ratings yet
- 2017 Fac1501 Answers PDFDocument77 pages2017 Fac1501 Answers PDFdevashneeNo ratings yet
- Heidi Jara Opened Jara's Cleaning Service On July 1, 2014. During July, The Following Transactions Were CompletedDocument6 pagesHeidi Jara Opened Jara's Cleaning Service On July 1, 2014. During July, The Following Transactions Were Completedlaale dijaan100% (1)
- Acct Project Question 4Document15 pagesAcct Project Question 4graceNo ratings yet
- Kieso Chapter 10Document6 pagesKieso Chapter 10Dian Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Statement of Accounts: Today's StatementsDocument1 pageStatement of Accounts: Today's StatementsAnonymous 1oW40srJJ2No ratings yet
- Business Accounting 1A - Assignment 1 - 0Document4 pagesBusiness Accounting 1A - Assignment 1 - 0DxdNo ratings yet
- CH 8 LiabilitiesDocument10 pagesCH 8 LiabilitiesKrizia Oliva100% (1)
- Unit 6 Achievement TestDocument9 pagesUnit 6 Achievement TestPablo Silva AriasNo ratings yet
- The Power of Virtual Distance Free Summary by Richard R. Reilly and Karen Sobel LojeskiDocument9 pagesThe Power of Virtual Distance Free Summary by Richard R. Reilly and Karen Sobel Lojeskiyogstr1No ratings yet
- Tugas Minggu 1Document5 pagesTugas Minggu 1Anti BastianNo ratings yet
- General Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation CreditDocument4 pagesGeneral Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation CreditHarriane Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Alfarizi - 142200278 - Ea-J - Tugas 2 Ap2Document4 pagesMuhammad Alfarizi - 142200278 - Ea-J - Tugas 2 Ap2Muhammad AlfariziNo ratings yet
- Pacalna - Accounting Cycle ActivityDocument35 pagesPacalna - Accounting Cycle ActivityAnifahchannie PacalnaNo ratings yet
- (ANSWER) - 02 - The Recording ProcessDocument12 pages(ANSWER) - 02 - The Recording ProcessdeltakoNo ratings yet
- Sales Journal Purcase Journal Cash Receipt Journal Cash Disbursement Journal General JournalDocument15 pagesSales Journal Purcase Journal Cash Receipt Journal Cash Disbursement Journal General JournalNathalia Alexandra PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Yusril Nur Amin_PR2Document7 pagesYusril Nur Amin_PR2Ahmad SandiNo ratings yet
- Soal 2-3ADocument5 pagesSoal 2-3Atrinanda ajiNo ratings yet
- Tricky Widgets AssumptionsDocument34 pagesTricky Widgets AssumptionsOvidiu NimigeanNo ratings yet
- Shujat Ali Khan - Assignment # 2Document7 pagesShujat Ali Khan - Assignment # 2Shujat AliNo ratings yet
- Arief Siklus-AkuntansiDocument70 pagesArief Siklus-AkuntansiArief FadilahNo ratings yet
- Question No 8: Cost Overhauling Depreciatoin Reducing Bal Method Sold DR Truck A/C Date Details Amount DateDocument6 pagesQuestion No 8: Cost Overhauling Depreciatoin Reducing Bal Method Sold DR Truck A/C Date Details Amount DateEducatry FamNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402Document4 pagesTugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402marhandega10No ratings yet
- Tugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402Document5 pagesTugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402marhandega10No ratings yet
- The Schram Academy: Accounts ProjectDocument17 pagesThe Schram Academy: Accounts ProjectVarshini KNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 Chapter - 8Document8 pagesFAR 1 Chapter - 8Klaus DoNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 Chapter - 8Document8 pagesFAR 1 Chapter - 8Klaus DoNo ratings yet
- Soal Apj 5Document8 pagesSoal Apj 5Najwa mutiara jasmineNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Chapter 11 AnswersDocument4 pagesCoursebook Chapter 11 AnswersAhmed Zeeshan100% (9)
- POA - mt.01 SolutionDocument7 pagesPOA - mt.01 SolutionHường Đoàn ThịNo ratings yet
- Tugas Part 3Document10 pagesTugas Part 3Mas AbiNo ratings yet
- Richardo PanganDocument19 pagesRichardo PanganLowel PayawanNo ratings yet
- GJ No. 1Document6 pagesGJ No. 1AN AdeNo ratings yet
- Accounting ExampleDocument19 pagesAccounting ExampleKevin GalindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Accounting For Receivables: Exercise 1Document45 pagesChapter 8: Accounting For Receivables: Exercise 1jokerightwegmail.com joke1233No ratings yet
- Prelim Exercises Partnership Operation 28Document5 pagesPrelim Exercises Partnership Operation 28Garp BarrocaNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 FARDocument6 pagesCh-10 FARSatchie L. ESPINOSANo ratings yet
- NaderaBrian FabmDocument91 pagesNaderaBrian FabmBrian NaderaNo ratings yet
- There Is No Transfer of Ownership Over The P3M Receivables.: Disclosure OnlyDocument8 pagesThere Is No Transfer of Ownership Over The P3M Receivables.: Disclosure OnlyCrizel DarioNo ratings yet
- 07 Receivable Financing 2 SolvingDocument3 pages07 Receivable Financing 2 Solvingkyle mandaresioNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICES-answer KeyDocument7 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICES-answer KeyLiaNo ratings yet
- May 2018 and 2017 SolutionsDocument43 pagesMay 2018 and 2017 SolutionsgNo ratings yet
- Answers To Practice Set I: AR RentalsDocument13 pagesAnswers To Practice Set I: AR RentalsDin Rose Gonzales100% (1)
- Quiz 2B - Bank Reconciliation and Proof of CashDocument5 pagesQuiz 2B - Bank Reconciliation and Proof of CashLorence Ibañez100% (2)
- Classroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersDocument4 pagesClassroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersJohn Cedfrey Narne100% (1)
- Class Exercise SolutionDocument10 pagesClass Exercise SolutionChristina KaukareNo ratings yet
- Books of Accounts TemplatesDocument18 pagesBooks of Accounts TemplatesMc Clent CervantesNo ratings yet
- Arce - Chan Accounting FirmDocument38 pagesArce - Chan Accounting FirmshaneNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Kasus PT - BERKARYA TOKO BANGUNANDocument26 pagesLembar Kerja Kasus PT - BERKARYA TOKO BANGUNANBunga JoitoNo ratings yet
- Test SolutionDocument4 pagesTest SolutionDibyani DashNo ratings yet
- HW Chap 10Document9 pagesHW Chap 10uong huonglyNo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument8 pagesReceivable FinancingHannah Pearl Flores VillarNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 EditedDocument18 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 EditedApril Mae LomboyNo ratings yet
- Soal PraktikDocument9 pagesSoal Praktikm habiburrahman55No ratings yet
- Completing The Accounting ProcessDocument23 pagesCompleting The Accounting ProcessFretchie Anne C. LauroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akt Perusahaan DagangDocument4 pagesTugas Akt Perusahaan DagangRizkita Sukma Gayanti0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Practice KEYDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Practice KEYmartinmuebejayiNo ratings yet
- DateDocument3 pagesDatejadarangelNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assignment Bilal 18798Document4 pagesAccounting Assignment Bilal 18798Muhammad Shahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Quiz Audit of ReceivablesDocument4 pagesQuiz Audit of ReceivableswesNo ratings yet
- Cash Book ProjectDocument2 pagesCash Book ProjectInspired IndianNo ratings yet
- 1.3 PAS 1 Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument65 pages1.3 PAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statementsrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- 2.1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument38 pages2.1 Cash and Cash Equivalentsrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- 2.2 Petty Cash FundDocument16 pages2.2 Petty Cash Fundrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 3 - Merchandising Transactions - Class Ex - Freight - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesFDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 3 - Merchandising Transactions - Class Ex - Freight - Answer Keyrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 1 - Analyzing Business Transactions - Class Ex - Answer KeyDocument1 pageFDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 1 - Analyzing Business Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Keyrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- Gunjan ProjectDocument85 pagesGunjan ProjectAshok Kumar Fandiya100% (3)
- Quran and PhysicsDocument2 pagesQuran and PhysicsShahzad Shameem50% (2)
- Woman in The Story, 2nd EditionDocument49 pagesWoman in The Story, 2nd EditionMichael Wiese Productions75% (4)
- Lawrence Kohlberg For SPDocument13 pagesLawrence Kohlberg For SPBea RamosNo ratings yet
- Development of Hot Cells and Their Embedded PartsDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Hot Cells and Their Embedded PartsK. JayarajanNo ratings yet
- Ten Questions About AnnulmentsDocument3 pagesTen Questions About AnnulmentsganneborjaNo ratings yet
- Answer - Tutorial - Record Business TransactionDocument10 pagesAnswer - Tutorial - Record Business TransactiondenixngNo ratings yet
- CBSE SolutionDocument80 pagesCBSE SolutionMuktara LisaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsuifjzvrifNo ratings yet
- Northern Christian College: The Institution For Better LifeDocument22 pagesNorthern Christian College: The Institution For Better Lifenananana123No ratings yet
- Edward Broughton v. Russell A. Courtney, Donald A. D'Lugos, 861 F.2d 639, 11th Cir. (1988)Document8 pagesEdward Broughton v. Russell A. Courtney, Donald A. D'Lugos, 861 F.2d 639, 11th Cir. (1988)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Neilsen SentencingDocument9 pagesNeilsen SentencingYTOLeaderNo ratings yet
- Packet TracerDocument11 pagesPacket TracerFauzan FiqriansyahNo ratings yet
- Apl Apollo Annual Report 2017-18Document216 pagesApl Apollo Annual Report 2017-18Nitin PatidarNo ratings yet
- Customer Value ManagementDocument31 pagesCustomer Value ManagementP RAGHU VAMSYNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb WorksheetDocument3 pagesIrregular Verb WorksheetVIPNo ratings yet
- IAP GuidebookDocument21 pagesIAP Guidebooksuheena.CNo ratings yet
- Weekly Meal Plan - Three-Year-Old (Vegetarian) : Breakfast Lunch Evening Snack DinnerDocument1 pageWeekly Meal Plan - Three-Year-Old (Vegetarian) : Breakfast Lunch Evening Snack DinnerPallavi SonalNo ratings yet
- Gilgit BaltistanDocument4 pagesGilgit BaltistanJunaid HassanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 The Enduring VisionDocument29 pagesCh. 2 The Enduring VisionDiar16No ratings yet
- DOJ CRT Press Release FINAL 7-12-13 Pdf0Document3 pagesDOJ CRT Press Release FINAL 7-12-13 Pdf0jchristianadamsNo ratings yet
- 33 Al Ahzab TranslationDocument18 pages33 Al Ahzab TranslationAbbey IshaqNo ratings yet
- Recruiting, Interviewing, Selecting and Orienting New EmployeesDocument19 pagesRecruiting, Interviewing, Selecting and Orienting New EmployeesRaluca Bosînceanu0% (1)
- Digital Evidence and AdmissibilityDocument14 pagesDigital Evidence and AdmissibilityTerence ClaerNo ratings yet
- Transcript of Evidence - Maitland 25.10.11Document47 pagesTranscript of Evidence - Maitland 25.10.11Wade WheelerNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Uti Mutual Funds: Kunal Agrawal Bba 5 Semester, September (08-11) Isb & M, KolkataDocument38 pagesTraining Report On Uti Mutual Funds: Kunal Agrawal Bba 5 Semester, September (08-11) Isb & M, KolkataArhum JalilNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Forensic Accounting and Fraud Examination 2nd Edition All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Forensic Accounting and Fraud Examination 2nd Edition All Chapterguurhawk9100% (7)
- Stock Screener, Technical Analysis ScannerDocument82 pagesStock Screener, Technical Analysis Scannerravi kumarNo ratings yet
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
Uploaded by
rabinoadrian24Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 2 - Journalizing Promissory Notes Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Key
Uploaded by
rabinoadrian24Copyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4_Part 2 - Journalizing promissory notes transactions_Class Exercise
I. Tolliver: Notes Payable
During 20x1, Tolliver Company borrowed money from Natchez Provincial Bank and Trust on two ocassions.
One June 8, the company borrowed $60,000, giving a 120-day, 5% note and
on September 8, the company borrowed $120,000, giving a 3-month, 7% note.
1. Give entries in general journal form to record issuance of each of these notes.
2. Give entries in general journal form to record issuance of a check to pay each of these notes.
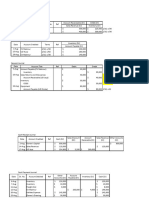
Date Particulars Dr Cr
8-Jun Cash 60,000
Notes Payable 60,000 Face value
5%, 120-day note
8-Sep Cash 120,000 Face value - prt
Notes Payable 120,000 Face value
7%, 3-month note
6-Oct Notes Payable 60,000 Face value
Interest expense 1,000 prt
Cash 61,000 MV = Face + prt
paid note
8-Dec Notes Payable 120,000 Face value
Interest expense 2,100 prt
Cash 122,100 MV = Face + prt
paid note
prt = principal X rate X (term / relevant denominator)
MV = Maturity value
30 days in June Issue date, June 8
June 30 - 8 22 30 - 8
July 31 31 days in July
Aug 31 31 days in August
Sept 30 30 days in September total = 114
Oct 6 120 - 114
120 term of the note
Issue date, Sept 8
Sept 8
Oct 8 1 month
Nov 8 1
Dec 8 1
3
II. Keler: Interest and maturity value
The following notes were received by Keller Company during 20x1:
Note # Date Face Amount Period Interest Rate
21 Jan 5 $ 30,000 3 months 8%
22 June 3 $ 15,000 90 days 10%
23 Sept 28 $ 20,000 3 months 9%
1. Compute the maturity value of each note.
2. Compute the total interest income of these notes.
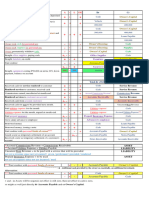
Note Face Interest Maturity
No. Value Value
21 30,000 600 30,600
22 15,000 375 15,375
23 20,000 450 20,450
1,425
III. Georgia: Notes Receivable
On July 15, 20x1, Georgia Company received the following notes:
- a $10,400, 45-day, 10% note from Sampson, a customer, for service rendered.
- a $20,000, 2-month, 12% note from Griffin, a customer whose account was past due.
On maturity date, Sampson dishonored the note while Griffin paid Georgia Company.
1. Record in the general journal the receipt of the notes.
2. Record in the general journal the dishonor of note by Sampson.
3. Record in the general journal the collection from Griffin.
Date Particulars Dr Cr
15-Jul Notes Receivable - Sampson 10,400 Face value
Service Income 10,400
10%, 45-day note
15-Jul Notes Receivable - Griffin 20,000 Face value
Accounts Receivable - Griffin 20,000
12%, 3-month note
29-Aug Accounts Receivable - Sampson 10,530 MV = Face + prt
Notes Receivable - Sampson 10,400 Face value
Interest Income 130 prt
Sampson dishonored the note
15-Sep Cash 20,400 MV = Face + prt
Notes Receivable - Griffin 20,000 Face value
Interest Income 400 prt
Sampson dishonored the note
31 days in July Receipt date, July 15
July 31 - 15 16 31 - 15
Aug 29 45 - 16
45 term of the note
Receipt date, July 15
Jul 15
Aug 15 1 month
Sept 15 1
2
You might also like
- 718 MP111 Individual Assignment S2 2022 Part 1Document23 pages718 MP111 Individual Assignment S2 2022 Part 1Rosalie BachillerNo ratings yet
- 2017 Fac1501 Answers PDFDocument77 pages2017 Fac1501 Answers PDFdevashneeNo ratings yet
- Heidi Jara Opened Jara's Cleaning Service On July 1, 2014. During July, The Following Transactions Were CompletedDocument6 pagesHeidi Jara Opened Jara's Cleaning Service On July 1, 2014. During July, The Following Transactions Were Completedlaale dijaan100% (1)
- Acct Project Question 4Document15 pagesAcct Project Question 4graceNo ratings yet
- Kieso Chapter 10Document6 pagesKieso Chapter 10Dian Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Statement of Accounts: Today's StatementsDocument1 pageStatement of Accounts: Today's StatementsAnonymous 1oW40srJJ2No ratings yet
- Business Accounting 1A - Assignment 1 - 0Document4 pagesBusiness Accounting 1A - Assignment 1 - 0DxdNo ratings yet
- CH 8 LiabilitiesDocument10 pagesCH 8 LiabilitiesKrizia Oliva100% (1)
- Unit 6 Achievement TestDocument9 pagesUnit 6 Achievement TestPablo Silva AriasNo ratings yet
- The Power of Virtual Distance Free Summary by Richard R. Reilly and Karen Sobel LojeskiDocument9 pagesThe Power of Virtual Distance Free Summary by Richard R. Reilly and Karen Sobel Lojeskiyogstr1No ratings yet
- Tugas Minggu 1Document5 pagesTugas Minggu 1Anti BastianNo ratings yet
- General Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation CreditDocument4 pagesGeneral Journal: Date Account Titles and Explanation CreditHarriane Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Alfarizi - 142200278 - Ea-J - Tugas 2 Ap2Document4 pagesMuhammad Alfarizi - 142200278 - Ea-J - Tugas 2 Ap2Muhammad AlfariziNo ratings yet
- Pacalna - Accounting Cycle ActivityDocument35 pagesPacalna - Accounting Cycle ActivityAnifahchannie PacalnaNo ratings yet
- (ANSWER) - 02 - The Recording ProcessDocument12 pages(ANSWER) - 02 - The Recording ProcessdeltakoNo ratings yet
- Sales Journal Purcase Journal Cash Receipt Journal Cash Disbursement Journal General JournalDocument15 pagesSales Journal Purcase Journal Cash Receipt Journal Cash Disbursement Journal General JournalNathalia Alexandra PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Yusril Nur Amin_PR2Document7 pagesYusril Nur Amin_PR2Ahmad SandiNo ratings yet
- Soal 2-3ADocument5 pagesSoal 2-3Atrinanda ajiNo ratings yet
- Tricky Widgets AssumptionsDocument34 pagesTricky Widgets AssumptionsOvidiu NimigeanNo ratings yet
- Shujat Ali Khan - Assignment # 2Document7 pagesShujat Ali Khan - Assignment # 2Shujat AliNo ratings yet
- Arief Siklus-AkuntansiDocument70 pagesArief Siklus-AkuntansiArief FadilahNo ratings yet
- Question No 8: Cost Overhauling Depreciatoin Reducing Bal Method Sold DR Truck A/C Date Details Amount DateDocument6 pagesQuestion No 8: Cost Overhauling Depreciatoin Reducing Bal Method Sold DR Truck A/C Date Details Amount DateEducatry FamNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402Document4 pagesTugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402marhandega10No ratings yet
- Tugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402Document5 pagesTugas 4 Akuntansi Bisnis Muhammad Marhandega Wijaya (1402204284) - AK4402marhandega10No ratings yet
- The Schram Academy: Accounts ProjectDocument17 pagesThe Schram Academy: Accounts ProjectVarshini KNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 Chapter - 8Document8 pagesFAR 1 Chapter - 8Klaus DoNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 Chapter - 8Document8 pagesFAR 1 Chapter - 8Klaus DoNo ratings yet
- Soal Apj 5Document8 pagesSoal Apj 5Najwa mutiara jasmineNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Chapter 11 AnswersDocument4 pagesCoursebook Chapter 11 AnswersAhmed Zeeshan100% (9)
- POA - mt.01 SolutionDocument7 pagesPOA - mt.01 SolutionHường Đoàn ThịNo ratings yet
- Tugas Part 3Document10 pagesTugas Part 3Mas AbiNo ratings yet
- Richardo PanganDocument19 pagesRichardo PanganLowel PayawanNo ratings yet
- GJ No. 1Document6 pagesGJ No. 1AN AdeNo ratings yet
- Accounting ExampleDocument19 pagesAccounting ExampleKevin GalindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Accounting For Receivables: Exercise 1Document45 pagesChapter 8: Accounting For Receivables: Exercise 1jokerightwegmail.com joke1233No ratings yet
- Prelim Exercises Partnership Operation 28Document5 pagesPrelim Exercises Partnership Operation 28Garp BarrocaNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 FARDocument6 pagesCh-10 FARSatchie L. ESPINOSANo ratings yet
- NaderaBrian FabmDocument91 pagesNaderaBrian FabmBrian NaderaNo ratings yet
- There Is No Transfer of Ownership Over The P3M Receivables.: Disclosure OnlyDocument8 pagesThere Is No Transfer of Ownership Over The P3M Receivables.: Disclosure OnlyCrizel DarioNo ratings yet
- 07 Receivable Financing 2 SolvingDocument3 pages07 Receivable Financing 2 Solvingkyle mandaresioNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICES-answer KeyDocument7 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICES-answer KeyLiaNo ratings yet
- May 2018 and 2017 SolutionsDocument43 pagesMay 2018 and 2017 SolutionsgNo ratings yet
- Answers To Practice Set I: AR RentalsDocument13 pagesAnswers To Practice Set I: AR RentalsDin Rose Gonzales100% (1)
- Quiz 2B - Bank Reconciliation and Proof of CashDocument5 pagesQuiz 2B - Bank Reconciliation and Proof of CashLorence Ibañez100% (2)
- Classroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersDocument4 pagesClassroom Exercises On Receivables AnswersJohn Cedfrey Narne100% (1)
- Class Exercise SolutionDocument10 pagesClass Exercise SolutionChristina KaukareNo ratings yet
- Books of Accounts TemplatesDocument18 pagesBooks of Accounts TemplatesMc Clent CervantesNo ratings yet
- Arce - Chan Accounting FirmDocument38 pagesArce - Chan Accounting FirmshaneNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Kasus PT - BERKARYA TOKO BANGUNANDocument26 pagesLembar Kerja Kasus PT - BERKARYA TOKO BANGUNANBunga JoitoNo ratings yet
- Test SolutionDocument4 pagesTest SolutionDibyani DashNo ratings yet
- HW Chap 10Document9 pagesHW Chap 10uong huonglyNo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument8 pagesReceivable FinancingHannah Pearl Flores VillarNo ratings yet
- INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 EditedDocument18 pagesINTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 1 EditedApril Mae LomboyNo ratings yet
- Soal PraktikDocument9 pagesSoal Praktikm habiburrahman55No ratings yet
- Completing The Accounting ProcessDocument23 pagesCompleting The Accounting ProcessFretchie Anne C. LauroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Akt Perusahaan DagangDocument4 pagesTugas Akt Perusahaan DagangRizkita Sukma Gayanti0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Practice KEYDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Practice KEYmartinmuebejayiNo ratings yet
- DateDocument3 pagesDatejadarangelNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assignment Bilal 18798Document4 pagesAccounting Assignment Bilal 18798Muhammad Shahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Quiz Audit of ReceivablesDocument4 pagesQuiz Audit of ReceivableswesNo ratings yet
- Cash Book ProjectDocument2 pagesCash Book ProjectInspired IndianNo ratings yet
- 1.3 PAS 1 Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument65 pages1.3 PAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statementsrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- 2.1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument38 pages2.1 Cash and Cash Equivalentsrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- 2.2 Petty Cash FundDocument16 pages2.2 Petty Cash Fundrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 3 - Merchandising Transactions - Class Ex - Freight - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesFDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 3 - Merchandising Transactions - Class Ex - Freight - Answer Keyrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- FDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 1 - Analyzing Business Transactions - Class Ex - Answer KeyDocument1 pageFDNACCT Unit 4 - Part 1 - Analyzing Business Transactions - Class Ex - Answer Keyrabinoadrian24No ratings yet
- Gunjan ProjectDocument85 pagesGunjan ProjectAshok Kumar Fandiya100% (3)
- Quran and PhysicsDocument2 pagesQuran and PhysicsShahzad Shameem50% (2)
- Woman in The Story, 2nd EditionDocument49 pagesWoman in The Story, 2nd EditionMichael Wiese Productions75% (4)
- Lawrence Kohlberg For SPDocument13 pagesLawrence Kohlberg For SPBea RamosNo ratings yet
- Development of Hot Cells and Their Embedded PartsDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Hot Cells and Their Embedded PartsK. JayarajanNo ratings yet
- Ten Questions About AnnulmentsDocument3 pagesTen Questions About AnnulmentsganneborjaNo ratings yet
- Answer - Tutorial - Record Business TransactionDocument10 pagesAnswer - Tutorial - Record Business TransactiondenixngNo ratings yet
- CBSE SolutionDocument80 pagesCBSE SolutionMuktara LisaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsuifjzvrifNo ratings yet
- Northern Christian College: The Institution For Better LifeDocument22 pagesNorthern Christian College: The Institution For Better Lifenananana123No ratings yet
- Edward Broughton v. Russell A. Courtney, Donald A. D'Lugos, 861 F.2d 639, 11th Cir. (1988)Document8 pagesEdward Broughton v. Russell A. Courtney, Donald A. D'Lugos, 861 F.2d 639, 11th Cir. (1988)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Neilsen SentencingDocument9 pagesNeilsen SentencingYTOLeaderNo ratings yet
- Packet TracerDocument11 pagesPacket TracerFauzan FiqriansyahNo ratings yet
- Apl Apollo Annual Report 2017-18Document216 pagesApl Apollo Annual Report 2017-18Nitin PatidarNo ratings yet
- Customer Value ManagementDocument31 pagesCustomer Value ManagementP RAGHU VAMSYNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb WorksheetDocument3 pagesIrregular Verb WorksheetVIPNo ratings yet
- IAP GuidebookDocument21 pagesIAP Guidebooksuheena.CNo ratings yet
- Weekly Meal Plan - Three-Year-Old (Vegetarian) : Breakfast Lunch Evening Snack DinnerDocument1 pageWeekly Meal Plan - Three-Year-Old (Vegetarian) : Breakfast Lunch Evening Snack DinnerPallavi SonalNo ratings yet
- Gilgit BaltistanDocument4 pagesGilgit BaltistanJunaid HassanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 The Enduring VisionDocument29 pagesCh. 2 The Enduring VisionDiar16No ratings yet
- DOJ CRT Press Release FINAL 7-12-13 Pdf0Document3 pagesDOJ CRT Press Release FINAL 7-12-13 Pdf0jchristianadamsNo ratings yet
- 33 Al Ahzab TranslationDocument18 pages33 Al Ahzab TranslationAbbey IshaqNo ratings yet
- Recruiting, Interviewing, Selecting and Orienting New EmployeesDocument19 pagesRecruiting, Interviewing, Selecting and Orienting New EmployeesRaluca Bosînceanu0% (1)
- Digital Evidence and AdmissibilityDocument14 pagesDigital Evidence and AdmissibilityTerence ClaerNo ratings yet
- Transcript of Evidence - Maitland 25.10.11Document47 pagesTranscript of Evidence - Maitland 25.10.11Wade WheelerNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Uti Mutual Funds: Kunal Agrawal Bba 5 Semester, September (08-11) Isb & M, KolkataDocument38 pagesTraining Report On Uti Mutual Funds: Kunal Agrawal Bba 5 Semester, September (08-11) Isb & M, KolkataArhum JalilNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Forensic Accounting and Fraud Examination 2nd Edition All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Forensic Accounting and Fraud Examination 2nd Edition All Chapterguurhawk9100% (7)
- Stock Screener, Technical Analysis ScannerDocument82 pagesStock Screener, Technical Analysis Scannerravi kumarNo ratings yet