Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsLearningjourney 10H
Learningjourney 10H
Uploaded by
jryjh8s2s5This document outlines the learning objectives and Mathswatch resources for a Year 10 student over the 2021-22 school year. It is divided into 6 terms covering topics including equations, inequalities, graphs, trigonometry, statistics, and multiplicative reasoning. Some key objectives are solving simultaneous equations, quadratic functions, circle theorems, conditional probability, and growth/decay problems. Mathswatch resources are provided to support learning objectives for each term.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Full Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full Chapterrabate.toiler.vv5s091% (23)
- Bowie, Lorrainne - Platinum Mathematics. 7Document297 pagesBowie, Lorrainne - Platinum Mathematics. 7herman willie100% (3)
- John Bird Published by Taylor and FrancisDocument9 pagesJohn Bird Published by Taylor and FrancisromwamaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Geometry of Algebrai - C. G. Gibson PDFDocument268 pagesElementary Geometry of Algebrai - C. G. Gibson PDFLucius Thales da Silva100% (1)
- Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Document2 pagesPre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Book A: Essential Mathematics 1Document336 pagesBook A: Essential Mathematics 1Juan Diego100% (1)
- CURRICULUM MAP Math 9Document16 pagesCURRICULUM MAP Math 9Lourdes de Jesus92% (24)
- Module 6.9 TLEDocument115 pagesModule 6.9 TLEroseavy90% (10)
- Smoke Extraction System Sample CalculationDocument5 pagesSmoke Extraction System Sample Calculationsmcsaminda100% (3)
- Y10 LJFDocument6 pagesY10 LJFjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- A Course of Elementary Mathematics PDFDocument654 pagesA Course of Elementary Mathematics PDFSelf-DeveloperNo ratings yet
- GRD 8 MX Yearly OverviewDocument2 pagesGRD 8 MX Yearly OverviewSmoky SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Complete: Pure MathematicsDocument28 pagesComplete: Pure MathematicsZira Grey100% (1)
- Math 9 Bow Q1Document2 pagesMath 9 Bow Q1Hans Jhayson CuadraNo ratings yet
- A. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardDocument7 pagesA. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 8Document3 pagesBOW in MATH 8Eric ManotaNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 EOS1 LO BookletDocument46 pagesMaths Year 10 EOS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 8Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 8EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsDocument6 pagesEdexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsWandaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 9 Feb 2024Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 9 Feb 2024Muhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsDocument3 pagesPivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsMarife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 9Document2 pagesBOW in MATH 9Joshua ServitoNo ratings yet
- JSU Paper 1-Form 1Document3 pagesJSU Paper 1-Form 1surayaothmanNo ratings yet
- 2019 After Exam ChecklistDocument3 pages2019 After Exam Checklistkuanyo yoNo ratings yet
- Aqa Further Maths WorkbookDocument58 pagesAqa Further Maths Workbook18mckenzieaNo ratings yet
- Topic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsDocument4 pagesTopic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsmosulNo ratings yet
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Document4 pagesYear 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Mahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Grade Quarter Content TopicsDocument2 pagesGrade Quarter Content TopicsKen Matthew OlivaNo ratings yet
- Budget or WorkDocument3 pagesBudget or WorkMAFIL GAY BABERANo ratings yet
- MPM2D Self AssessmentDocument11 pagesMPM2D Self AssessmentRudrashish JassalNo ratings yet
- 2021 Maths ATP Grade 11Document3 pages2021 Maths ATP Grade 11sharolsmadzimureNo ratings yet
- Math, Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesMath, Q1 ReviewerPrime JavateNo ratings yet
- (Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Document477 pages(Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Jesús Eduardo Dimas Ramírez100% (1)
- 0908微積分期末Document12 pages0908微積分期末JunYiNo ratings yet
- Notes (Section # 3 (SETS, CONST) )Document2 pagesNotes (Section # 3 (SETS, CONST) )A.BensonNo ratings yet
- Year 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous ListsDocument4 pagesYear 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous Listslyang1No ratings yet
- Sow F4Document10 pagesSow F4Girl and Mwila CholaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermDocument3 pagesScheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- RPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017Document9 pagesRPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017sitihajar88No ratings yet
- Grade 10 - MathematicsDocument1 pageGrade 10 - MathematicsApril Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermDocument3 pagesScheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Complec Vector Spaces - LarsonDocument42 pagesComplec Vector Spaces - LarsonAgung ManaluNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument7 pagesSyllabusFransiska KNo ratings yet
- MIRA18Apr2019 PDFDocument399 pagesMIRA18Apr2019 PDFToghrul KarimovNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 1Document4 pagesChapter-9 1durgakalyani.dNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents Template Word 03Document3 pagesTable of Contents Template Word 03Kevin DanyNo ratings yet
- 2022 23 DIVISION ASSESSMENT TESTQ2 With TOSDocument5 pages2022 23 DIVISION ASSESSMENT TESTQ2 With TOSnemarlije siladaNo ratings yet
- A. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardDocument17 pagesA. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Level 3 Pure Mathematics 2018 2019Document5 pagesCourse Outline Level 3 Pure Mathematics 2018 2019SandoNo ratings yet
- U017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2Document1 pageU017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2al-gazNo ratings yet
- MATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFDocument81 pagesMATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFMarcus John Vincent C. KeNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition by Richard N. Aufmann All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition by Richard N. Aufmann All Chaptermalcrinadiha100% (11)
- Introducing Pure MathematicsDocument580 pagesIntroducing Pure Mathematicsganesh jamankarNo ratings yet
- Ss 2 Mathematics First Term e NoteDocument72 pagesSs 2 Mathematics First Term e Noteomolajaezekiel60No ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 9Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 9EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Ixl-Nwea-Map-Growth-6-Plus 1 1 1Document17 pagesIxl-Nwea-Map-Growth-6-Plus 1 1 1api-436017583No ratings yet
- Ixl Nwea Map Growth 6 PlusDocument17 pagesIxl Nwea Map Growth 6 Plusapi-329194538No ratings yet
- v6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFDocument21 pagesv6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFnoneofyourbusinessNo ratings yet
- Algebra HandbookDocument187 pagesAlgebra HandbookPrince BoaheneNo ratings yet
- Higher-Checklist (1)Document3 pagesHigher-Checklist (1)Ricky JacobNo ratings yet
- Year Planner For Form 2Document3 pagesYear Planner For Form 2Muhammad Yusof AbdullahNo ratings yet
- School Term Dates 2022 2023Document1 pageSchool Term Dates 2022 2023jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Year 11 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 3Document1 pageYear 11 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 3jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Roald Dahl Day 2021 - Form AnnouncementDocument5 pagesRoald Dahl Day 2021 - Form Announcementjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Higher Topic List For Assessment On 4th FebDocument1 pageHigher Topic List For Assessment On 4th Febjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Whole School Letter 21.06.21Document2 pagesWhole School Letter 21.06.21jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Year 8 RE Overview With Dispositions RADocument3 pagesYear 8 RE Overview With Dispositions RAjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument1 pageHomeworkjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- P2.5 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Thermal ConductivityDocument3 pagesP2.5 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Thermal Conductivityjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet - Easter Holiday ResearchDocument3 pagesRomeo and Juliet - Easter Holiday Researchjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Computer Networks ChecklistDocument2 pagesComputer Networks Checklistjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- C3 Food Chains and Food WebsDocument16 pagesC3 Food Chains and Food Websjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Volcano Comp Poster 2021Document1 pageVolcano Comp Poster 2021jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Ppe Topic List Higher 2Document1 pagePpe Topic List Higher 2jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Spelling Punctuation and Grammar Revision GuideDocument49 pagesSpelling Punctuation and Grammar Revision Guidejryjh8s2s5100% (1)
- Year 8 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 2Document1 pageYear 8 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 2jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Work-Done Clue-Sheet Yr 7Document1 pageWork-Done Clue-Sheet Yr 7jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument35 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Track ListDocument1 pageTrack ListTiago LopesNo ratings yet
- The Pre-Production Process EvaluationDocument8 pagesThe Pre-Production Process EvaluationMC_Onnell100% (1)
- Sunil Panda Commerce Classes: Before Exam Practice Questions For Term 2 Boards Accounts-Not For Profit OrganisationDocument3 pagesSunil Panda Commerce Classes: Before Exam Practice Questions For Term 2 Boards Accounts-Not For Profit OrganisationHigi SNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aDocument16 pagesGroup 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aJan TheGamerNo ratings yet
- FOSFA Technical Manual Oils and FatsDocument15 pagesFOSFA Technical Manual Oils and FatsNurhayati SurbaktiNo ratings yet
- JLTR, 02Document8 pagesJLTR, 02Junalyn Villegas FerbesNo ratings yet
- Forget No MoreDocument14 pagesForget No MoreSheeqin Mn100% (2)
- Marketing Plan: GoldilocksDocument18 pagesMarketing Plan: GoldilocksAkhia Visitacion100% (1)
- Christopher MontoyaDocument1 pageChristopher MontoyaUF Student GovernmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 LectureDocument29 pagesChapter 9 Lectureinam vf100% (6)
- The Outlaw (1871)Document21 pagesThe Outlaw (1871)ViannisoNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quizes Al-JaberDocument21 pagesTake Home Quizes Al-JaberalfredomedardoNo ratings yet
- Plug Valves To API 599Document11 pagesPlug Valves To API 599Marten HaneNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data SheetDocument6 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data Sheetjulio100% (1)
- Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus Exposure of PlasticsDocument6 pagesFluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus Exposure of PlasticsFlor Areli Reyes HernándezNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Document5 pagesBlockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Chiraz Elhog0% (1)
- Group 3 - Strategies For Classroom ManagementDocument25 pagesGroup 3 - Strategies For Classroom ManagementSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument8 pagesHardness TestlvasuthavanNo ratings yet
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document1 pageIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Jay ParkheNo ratings yet
- Assessing Digital Skills and Competencies For Different Groups and Devising A Conceptual Model To Support Teaching and TrainingDocument14 pagesAssessing Digital Skills and Competencies For Different Groups and Devising A Conceptual Model To Support Teaching and TrainingMuhammad Ilyas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- Expt. 8 Salivary DigestionDocument25 pagesExpt. 8 Salivary DigestionLESLIE JANE BALUYOS JALANo ratings yet
- Powermax45 Despiece AntorchaDocument5 pagesPowermax45 Despiece AntorchaWall OmarNo ratings yet
- Opsrey - Acre 1291Document97 pagesOpsrey - Acre 1291Hieronymus Sousa PintoNo ratings yet
- LSP 401 Ip S1 12-13Document4 pagesLSP 401 Ip S1 12-13Mary TeohNo ratings yet
Learningjourney 10H
Learningjourney 10H
Uploaded by
jryjh8s2s50 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThis document outlines the learning objectives and Mathswatch resources for a Year 10 student over the 2021-22 school year. It is divided into 6 terms covering topics including equations, inequalities, graphs, trigonometry, statistics, and multiplicative reasoning. Some key objectives are solving simultaneous equations, quadratic functions, circle theorems, conditional probability, and growth/decay problems. Mathswatch resources are provided to support learning objectives for each term.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the learning objectives and Mathswatch resources for a Year 10 student over the 2021-22 school year. It is divided into 6 terms covering topics including equations, inequalities, graphs, trigonometry, statistics, and multiplicative reasoning. Some key objectives are solving simultaneous equations, quadratic functions, circle theorems, conditional probability, and growth/decay problems. Mathswatch resources are provided to support learning objectives for each term.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageLearningjourney 10H
Learningjourney 10H
Uploaded by
jryjh8s2s5This document outlines the learning objectives and Mathswatch resources for a Year 10 student over the 2021-22 school year. It is divided into 6 terms covering topics including equations, inequalities, graphs, trigonometry, statistics, and multiplicative reasoning. Some key objectives are solving simultaneous equations, quadratic functions, circle theorems, conditional probability, and growth/decay problems. Mathswatch resources are provided to support learning objectives for each term.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
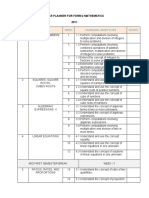
YEAR 10: HIGHER: LEARNING JOURNEY : 2021-22
TERM OBJECTIVES MATHSWATCH TERM OBJECTIVES MATHSWATCH
AUTUMN 1 9 Equations and inequalities SUMMER 1 17 More algebra
Find the roots of quadratic functions. 160 Change the subject of a formula where the power of the subject appears. 136
Rearrange and solve simple quadratic equations. 157 Change the subject of a formula where the subject appears twice. 190
Solve more complex quadratic equations. 192 Add and subtract algebraic fractions. 210b
Use the quadratic formula to solve a quadratic equation. 191 Multiply and divide algebraic fractions. 210b
Complete the square for a quadratic expression. 209 Change the subject of a formula involving fractions where all the variables are in the 190
denominators.
Solve quadratic equations by completing the square. 209 Simplify algebraic fractions. 210a
Solve simple simultaneous equations. 140 Add and subtract more complex algebraic fractions. 210b
Solve simultaneous equations for real-life situations. Multiply and divide more complex algebraic fractions. 210b
Use simultaneous equations to find the equation of a straight line. 162 Simplify expressions involving surds. 207b
Solve linear simultaneous equations where both equations are multiplied. Expand expressions involving surds. 207b
Interpret real-life situations involving two unknowns and solve them. Rationalise the denominator of a fraction. 207c
Solve simultaneous equations with one quadratic equation. 211 Solve equations that involve algebraic fractions.
Use real-life situations to construct quadratic and linear equations and solve them. Use function notation. 36
Solve inequalities and show the solution on a number line and using set notation. 212 Find composite functions. 215
AUTUMN 2 15 Equations and graphs Find inverse functions. 214
Solve simultaneous equations graphically. 140 Prove a result using algebra. 193
Represent inequalities on graphs. 138 SUMMER 2 16 Circle theorems
Interpret graphs of inequalities. 198 Solve problems involving angles, triangles and circles.
Recognise and draw quadratic functions. 98 Understand and use facts about chords and their distance from the centre of a circle. 116
Find approximate solutions to quadratic equations graphically. 98 Solve problems involving chords and radii.
Solve quadratic equations using an iterative process. 180 Understand and use facts about tangents at a point and from a point. 149
13 More trigonometry Give reasons for angle and length calculations involving tangents. 149
Understand and use upper and lower bounds in calculations involving trigonometry. 206 Understand, prove and use facts about angles subtended at the centre and the 183
circumference of circles.
Understand how to find the sine of any angle. 168 Understand, prove and use facts about the angle in a semicircle being a right angle. 184
Know the graph of the sine function and use it to solve equations. 195a Find missing angles using these theorems and give reasons for answers. 183
Understand how to find the cosine of any angle. 168 Understand, prove and use facts about angles subtended at the circumference of a circle. 184
Know the graph of the cosine function and use it to solve equations. 195a Understand, prove and use facts about cyclic quadrilaterals. 183
Understand how to fi nd the tangent of any angle. 168 Prove the alternate segment theorem. 184
Know the graph of the tangent function and use it to solve equations. 195b Solve angle problems using circle theorems.
Find the area of a triangle and a segment of a circle. 203 Give reasons for angle sizes using mathematical language.
Use the sine rule to solve 2D problems. 201 Find the equation of the tangent to a circle at a given point. 197
Use the cosine rule to solve 2D problems. 202
Solve bearings problems using trigonometry. 124
Use Pythagoras’ theorem in 3D. 217
Use trigonometry in 3D. 218
Recognise how changes in a function affect trigonometric graphs. 196b
Recognise how changes in a function affect trigonometric graphs. 196b
SPRING 1 14 Further statistics
Understand how to take a simple random sample. 152
Understand how to take a stratifi ed sample. 176
Draw and interpret cumulative frequency tables and diagrams. 186
Work out the median, quartiles and interquartile range from a cumulative frequency diagram. 186
Find the quartiles and the interquartile range from stem-and-leaf diagrams. 186
Draw and interpret box plots. 187
Understand frequency density. 205
Draw histograms. 205
Interpret histograms. 205
Decide if two events are independent.
Draw and use tree diagrams to calculate conditional probability. 175
Draw and use tree diagrams without replacement. 151
Use two-way tables to calculate conditional probability. 61
Use Venn diagrams to calculate conditional probability. 185
Use set notation. 185
SPRING 2 11 Multiplicative reasoning
Find an amount after repeated percentage changes.
Solve growth and decay problems. 164
Calculate rates.
Convert between metric speed measures. 142
Use a formula to calculate speed and acceleration.
Solve problems involving compound measures.
Use relationships involving ratio. 106
Use direct and indirect proportion. 199
You might also like
- Full Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Discrete Mathematics With Applications 5th Edition Susanna S Epp PDF Full Chapterrabate.toiler.vv5s091% (23)
- Bowie, Lorrainne - Platinum Mathematics. 7Document297 pagesBowie, Lorrainne - Platinum Mathematics. 7herman willie100% (3)
- John Bird Published by Taylor and FrancisDocument9 pagesJohn Bird Published by Taylor and FrancisromwamaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Geometry of Algebrai - C. G. Gibson PDFDocument268 pagesElementary Geometry of Algebrai - C. G. Gibson PDFLucius Thales da Silva100% (1)
- Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Document2 pagesPre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Book A: Essential Mathematics 1Document336 pagesBook A: Essential Mathematics 1Juan Diego100% (1)
- CURRICULUM MAP Math 9Document16 pagesCURRICULUM MAP Math 9Lourdes de Jesus92% (24)
- Module 6.9 TLEDocument115 pagesModule 6.9 TLEroseavy90% (10)
- Smoke Extraction System Sample CalculationDocument5 pagesSmoke Extraction System Sample Calculationsmcsaminda100% (3)
- Y10 LJFDocument6 pagesY10 LJFjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- A Course of Elementary Mathematics PDFDocument654 pagesA Course of Elementary Mathematics PDFSelf-DeveloperNo ratings yet
- GRD 8 MX Yearly OverviewDocument2 pagesGRD 8 MX Yearly OverviewSmoky SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Complete: Pure MathematicsDocument28 pagesComplete: Pure MathematicsZira Grey100% (1)
- Math 9 Bow Q1Document2 pagesMath 9 Bow Q1Hans Jhayson CuadraNo ratings yet
- A. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardDocument7 pagesA. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 8Document3 pagesBOW in MATH 8Eric ManotaNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 EOS1 LO BookletDocument46 pagesMaths Year 10 EOS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 8Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 8EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsDocument6 pagesEdexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsWandaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 9 Feb 2024Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 9 Feb 2024Muhammad AsimNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsDocument3 pagesPivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsMarife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 9Document2 pagesBOW in MATH 9Joshua ServitoNo ratings yet
- JSU Paper 1-Form 1Document3 pagesJSU Paper 1-Form 1surayaothmanNo ratings yet
- 2019 After Exam ChecklistDocument3 pages2019 After Exam Checklistkuanyo yoNo ratings yet
- Aqa Further Maths WorkbookDocument58 pagesAqa Further Maths Workbook18mckenzieaNo ratings yet
- Topic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsDocument4 pagesTopic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsmosulNo ratings yet
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Document4 pagesYear 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Mahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Grade Quarter Content TopicsDocument2 pagesGrade Quarter Content TopicsKen Matthew OlivaNo ratings yet
- Budget or WorkDocument3 pagesBudget or WorkMAFIL GAY BABERANo ratings yet
- MPM2D Self AssessmentDocument11 pagesMPM2D Self AssessmentRudrashish JassalNo ratings yet
- 2021 Maths ATP Grade 11Document3 pages2021 Maths ATP Grade 11sharolsmadzimureNo ratings yet
- Math, Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesMath, Q1 ReviewerPrime JavateNo ratings yet
- (Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Document477 pages(Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Jesús Eduardo Dimas Ramírez100% (1)
- 0908微積分期末Document12 pages0908微積分期末JunYiNo ratings yet
- Notes (Section # 3 (SETS, CONST) )Document2 pagesNotes (Section # 3 (SETS, CONST) )A.BensonNo ratings yet
- Year 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous ListsDocument4 pagesYear 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous Listslyang1No ratings yet
- Sow F4Document10 pagesSow F4Girl and Mwila CholaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermDocument3 pagesScheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- RPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017Document9 pagesRPH Maths Form 2 DLP 2017sitihajar88No ratings yet
- Grade 10 - MathematicsDocument1 pageGrade 10 - MathematicsApril Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermDocument3 pagesScheme of Work - JSS3 - First TermFranca OkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Complec Vector Spaces - LarsonDocument42 pagesComplec Vector Spaces - LarsonAgung ManaluNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument7 pagesSyllabusFransiska KNo ratings yet
- MIRA18Apr2019 PDFDocument399 pagesMIRA18Apr2019 PDFToghrul KarimovNo ratings yet
- Chapter-9 1Document4 pagesChapter-9 1durgakalyani.dNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents Template Word 03Document3 pagesTable of Contents Template Word 03Kevin DanyNo ratings yet
- 2022 23 DIVISION ASSESSMENT TESTQ2 With TOSDocument5 pages2022 23 DIVISION ASSESSMENT TESTQ2 With TOSnemarlije siladaNo ratings yet
- A. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardDocument17 pagesA. Find The Dimention of The Bulletin BoardLourdes de JesusNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Level 3 Pure Mathematics 2018 2019Document5 pagesCourse Outline Level 3 Pure Mathematics 2018 2019SandoNo ratings yet
- U017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2Document1 pageU017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2al-gazNo ratings yet
- MATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFDocument81 pagesMATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFMarcus John Vincent C. KeNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition by Richard N. Aufmann All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) Intermediate Algebra 8th Edition by Richard N. Aufmann All Chaptermalcrinadiha100% (11)
- Introducing Pure MathematicsDocument580 pagesIntroducing Pure Mathematicsganesh jamankarNo ratings yet
- Ss 2 Mathematics First Term e NoteDocument72 pagesSs 2 Mathematics First Term e Noteomolajaezekiel60No ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 9Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 9EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Ixl-Nwea-Map-Growth-6-Plus 1 1 1Document17 pagesIxl-Nwea-Map-Growth-6-Plus 1 1 1api-436017583No ratings yet
- Ixl Nwea Map Growth 6 PlusDocument17 pagesIxl Nwea Map Growth 6 Plusapi-329194538No ratings yet
- v6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFDocument21 pagesv6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFnoneofyourbusinessNo ratings yet
- Algebra HandbookDocument187 pagesAlgebra HandbookPrince BoaheneNo ratings yet
- Higher-Checklist (1)Document3 pagesHigher-Checklist (1)Ricky JacobNo ratings yet
- Year Planner For Form 2Document3 pagesYear Planner For Form 2Muhammad Yusof AbdullahNo ratings yet
- School Term Dates 2022 2023Document1 pageSchool Term Dates 2022 2023jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Year 11 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 3Document1 pageYear 11 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 3jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Roald Dahl Day 2021 - Form AnnouncementDocument5 pagesRoald Dahl Day 2021 - Form Announcementjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Higher Topic List For Assessment On 4th FebDocument1 pageHigher Topic List For Assessment On 4th Febjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Whole School Letter 21.06.21Document2 pagesWhole School Letter 21.06.21jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Year 8 RE Overview With Dispositions RADocument3 pagesYear 8 RE Overview With Dispositions RAjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument1 pageHomeworkjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- P2.5 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Thermal ConductivityDocument3 pagesP2.5 Student Bump Up Your Grade: Thermal Conductivityjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Romeo and Juliet - Easter Holiday ResearchDocument3 pagesRomeo and Juliet - Easter Holiday Researchjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Computer Networks ChecklistDocument2 pagesComputer Networks Checklistjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- C3 Food Chains and Food WebsDocument16 pagesC3 Food Chains and Food Websjryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Volcano Comp Poster 2021Document1 pageVolcano Comp Poster 2021jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Ppe Topic List Higher 2Document1 pagePpe Topic List Higher 2jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Spelling Punctuation and Grammar Revision GuideDocument49 pagesSpelling Punctuation and Grammar Revision Guidejryjh8s2s5100% (1)
- Year 8 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 2Document1 pageYear 8 Return To School in September For Covid 19 Testing 2jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- Work-Done Clue-Sheet Yr 7Document1 pageWork-Done Clue-Sheet Yr 7jryjh8s2s5No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument35 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Track ListDocument1 pageTrack ListTiago LopesNo ratings yet
- The Pre-Production Process EvaluationDocument8 pagesThe Pre-Production Process EvaluationMC_Onnell100% (1)
- Sunil Panda Commerce Classes: Before Exam Practice Questions For Term 2 Boards Accounts-Not For Profit OrganisationDocument3 pagesSunil Panda Commerce Classes: Before Exam Practice Questions For Term 2 Boards Accounts-Not For Profit OrganisationHigi SNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aDocument16 pagesGroup 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aJan TheGamerNo ratings yet
- FOSFA Technical Manual Oils and FatsDocument15 pagesFOSFA Technical Manual Oils and FatsNurhayati SurbaktiNo ratings yet
- JLTR, 02Document8 pagesJLTR, 02Junalyn Villegas FerbesNo ratings yet
- Forget No MoreDocument14 pagesForget No MoreSheeqin Mn100% (2)
- Marketing Plan: GoldilocksDocument18 pagesMarketing Plan: GoldilocksAkhia Visitacion100% (1)
- Christopher MontoyaDocument1 pageChristopher MontoyaUF Student GovernmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 LectureDocument29 pagesChapter 9 Lectureinam vf100% (6)
- The Outlaw (1871)Document21 pagesThe Outlaw (1871)ViannisoNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quizes Al-JaberDocument21 pagesTake Home Quizes Al-JaberalfredomedardoNo ratings yet
- Plug Valves To API 599Document11 pagesPlug Valves To API 599Marten HaneNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data SheetDocument6 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage: Data Sheetjulio100% (1)
- Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus Exposure of PlasticsDocument6 pagesFluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus Exposure of PlasticsFlor Areli Reyes HernándezNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Document5 pagesBlockchain Based Car-Sharing Platform: September 2019Chiraz Elhog0% (1)
- Group 3 - Strategies For Classroom ManagementDocument25 pagesGroup 3 - Strategies For Classroom ManagementSiti AisyahNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument8 pagesHardness TestlvasuthavanNo ratings yet
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document1 pageIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Jay ParkheNo ratings yet
- Assessing Digital Skills and Competencies For Different Groups and Devising A Conceptual Model To Support Teaching and TrainingDocument14 pagesAssessing Digital Skills and Competencies For Different Groups and Devising A Conceptual Model To Support Teaching and TrainingMuhammad Ilyas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportDocument7 pagesThe Brain and Nervous System (Psychology) Unit 14: An Academic ReportOlatokunbo SinaayomiNo ratings yet
- Expt. 8 Salivary DigestionDocument25 pagesExpt. 8 Salivary DigestionLESLIE JANE BALUYOS JALANo ratings yet
- Powermax45 Despiece AntorchaDocument5 pagesPowermax45 Despiece AntorchaWall OmarNo ratings yet
- Opsrey - Acre 1291Document97 pagesOpsrey - Acre 1291Hieronymus Sousa PintoNo ratings yet
- LSP 401 Ip S1 12-13Document4 pagesLSP 401 Ip S1 12-13Mary TeohNo ratings yet