Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit II
Unit II
Uploaded by
miteshbargadiya.sageOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit II
Unit II
Uploaded by
miteshbargadiya.sageCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
**Color Fundamentals:**
- Color is the visual perception of different wavelengths of light.
- The three primary colors are red, green, and blue (RGB).
- Secondary colors are formed by mixing primary colors: cyan (green + blue), magenta (red +
blue), and yellow (red + green).
- Color perception is influenced by factors like illumination and human vision.
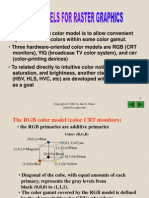
2. **Color Models:**
- RGB Model: Represents colors using additive mixing of red, green, and blue channels.
Common in digital displays.
- CMY Model: Used in subtractive color mixing, primarily in color printing, based on cyan,
magenta, and yellow.
- HSL/HSV Model: Represents colors in terms of Hue, Saturation, and Lightness/Value,
providing more intuitive control over color adjustments.
- LAB Model: A perceptually uniform color space where L represents lightness, and AB
represents color information.
- YUV/YCbCr Model: Used for image and video compression, separating luminance (Y) and
chrominance (UV/CbCr) information.
3. **Converting Colors to Different Models:**
- Converting between color models involves mathematical transformations.
- For example, to convert RGB to CMY, you can subtract the RGB values from 255 to get
CMY values.
- To convert RGB to HSL/HSV, you'll need to calculate the hue, saturation, and lightness/value
based on the RGB values.
4. **Color Transformation:**
- Color transformations are used for various image processing tasks, such as color correction,
enhancement, and manipulation.
- Techniques like histogram equalization can adjust the distribution of colors in an image to
improve contrast.
- Color balance adjustments can correct color casts and ensure natural-looking colors.
- Color filters and color mapping can be applied to change the overall color tone of an image.
5. **Applications:**
- Color image processing is crucial in various fields, including photography, graphic design,
computer vision, and medical imaging.
- It plays a significant role in tasks like object recognition, image segmentation, and enhancing
visual content.
6. **Challenges:**
- Color processing may face challenges due to variations in lighting conditions, color
calibration, and human perception differences.
You might also like
- IppptDocument15 pagesIppptFind the hero in youNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument95 pagesUntitledapi-251901021No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Vision: CIE Chromaticity Diagram and Color GamutDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Computer Vision: CIE Chromaticity Diagram and Color GamutDiego AntonioNo ratings yet
- Colouring: Types of ColoursDocument26 pagesColouring: Types of ColoursgowthamNo ratings yet
- Color Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya NitinDocument4 pagesColor Model: Submitted by Jagtap Aishwarya Nitinshriyash jagtapNo ratings yet
- Color Space and Color Image ProcessingDocument15 pagesColor Space and Color Image ProcessingmsmayoNo ratings yet
- CG - Chapter 6 Color ModelsDocument19 pagesCG - Chapter 6 Color Modelstyv89783No ratings yet
- Digital ImageProcessing-color Image ProcessingDocument115 pagesDigital ImageProcessing-color Image Processingcareer Point BastiNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 - RGB and CMY Color ModelDocument22 pagesLec-11 - RGB and CMY Color Modelbijoystudent481No ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesColor Image ProcessingSarthak MokalNo ratings yet
- Digital MidddddddDocument4 pagesDigital MidddddddAl Sabid (191014053)No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4dixit.ramani7773No ratings yet
- Color Image Processing 26-7-2012 PDFDocument27 pagesColor Image Processing 26-7-2012 PDFU.Ida PerciaNo ratings yet
- Digital ImageProcessing-color Image ProcessingDocument89 pagesDigital ImageProcessing-color Image Processingcareer Point BastiNo ratings yet
- 2 Color ImagesDocument17 pages2 Color ImagesABHIJITHNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5Document4 pagesExperiment No.5Tejas PatilNo ratings yet
- 2015 Chapter 4 MMS ITencryptedDocument29 pages2015 Chapter 4 MMS ITencryptedMercy DegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Digital Image Processing: Bachelor of Science (Computer Science) Session (2020-2024) Submitted byDocument5 pagesAssignment of Digital Image Processing: Bachelor of Science (Computer Science) Session (2020-2024) Submitted bysumanafzal1212No ratings yet
- Color Space Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesColor Space Image ProcessingSushant SawantNo ratings yet
- Colour (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesColour (Compatibility Mode)PradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Key Terms in Graphic DesignDocument13 pagesKey Terms in Graphic DesignResty FloresNo ratings yet
- RGB Color ModelDocument15 pagesRGB Color ModelkavitaNo ratings yet
- 03 Color Space Lecture NoteDocument65 pages03 Color Space Lecture Notethuandvt97No ratings yet
- Cvdip AssignmentDocument12 pagesCvdip AssignmentJagadeesh NarendraNo ratings yet
- NIP24 CMYKRGB 7color Mei-ChunDocument7 pagesNIP24 CMYKRGB 7color Mei-ChunMichael PetersNo ratings yet
- RgbcmyDocument12 pagesRgbcmyAnonymous XybLZfNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument189 pagesColor Image ProcessingruikarsachinNo ratings yet
- RGB &cmy Color ModelDocument24 pagesRGB &cmy Color ModelCh Anas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Color ModelDocument10 pagesColor ModelVISHNUKUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit6ColorImageFundamentalspdf 2022 11-09-14!46!50Document71 pagesUnit6ColorImageFundamentalspdf 2022 11-09-14!46!50SUSAN KHADKANo ratings yet
- CMYK and RGBDocument2 pagesCMYK and RGBPrisha BansalNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument11 pagesDigital Image ProcessingAlina RehmanNo ratings yet
- Machine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Document6 pagesMachine Vision Exp 2 (Mumbai Univesrity)Om BhamareNo ratings yet
- Color Model 1Document20 pagesColor Model 1sharmilaNo ratings yet
- RGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)Document9 pagesRGB (Used in Computer Graphics) Yiq, Yuv or Ycbcr (Used in Video Systems)Mera KaramNo ratings yet
- 1: Bitmap: Explanation of Different Color Modes in PhotoshopDocument12 pages1: Bitmap: Explanation of Different Color Modes in PhotoshopMcheaven NojramNo ratings yet
- Various Colour Spaces and Colour Space Conversion Algorithms 44 48Document5 pagesVarious Colour Spaces and Colour Space Conversion Algorithms 44 48Ali Musilim TemamNo ratings yet
- Sugita & Takahashi - Computational RYB Color Model and Its ApplicationsDocument13 pagesSugita & Takahashi - Computational RYB Color Model and Its ApplicationsGuilherme BiancarelliNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDDocument55 pagesPengolahan Citra Berwarna: Kuliah Ke-3 PPCDaditya nur johansyahNo ratings yet
- Color SystemsDocument6 pagesColor Systemsbsnt.a7md23No ratings yet
- Introduction To Color SpacesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Color Spacesabdullah saifNo ratings yet
- Color Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduDocument60 pagesColor Image Processing: Prepared by T. Ravi Kumar NaiduRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- CGMM 3Document3 pagesCGMM 3nishita patidarNo ratings yet
- Chap1 2 3Document27 pagesChap1 2 3Hàng Không Mẫu HạmNo ratings yet
- Color Image To Grayscale Image ConversionDocument4 pagesColor Image To Grayscale Image ConversionBudi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Irfan Sawar 3026Document5 pagesIrfan Sawar 3026Ahmad Aslam MajhianaNo ratings yet
- Quiz DIPDocument7 pagesQuiz DIPayesha bashirNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument15 pagesColor Image ProcessingRaviteja UdumudiNo ratings yet
- Color Image ProcessingDocument13 pagesColor Image ProcessingBrijesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Graphic Editor XDocument15 pagesGraphic Editor XClaudea Pramesdila MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Hue Is One of The Main Properties (Called: Color Appearance Parameters ColorDocument5 pagesHue Is One of The Main Properties (Called: Color Appearance Parameters ColorRobert Kite ClementeNo ratings yet
- Color in Image and VideoDocument5 pagesColor in Image and VideoNii LaryeaNo ratings yet
- CAT1 Computer Vision SyllabusDocument24 pagesCAT1 Computer Vision SyllabusLuckyNo ratings yet
- Color Model: TeacherDocument16 pagesColor Model: TeacherNikhil WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Color Image ProcessingDocument17 pagesUNIT-4 Color Image ProcessingShravani ChettineniNo ratings yet
- Grayscale Image Coloring by Using Ycbcr and HSV Color SpacesDocument7 pagesGrayscale Image Coloring by Using Ycbcr and HSV Color SpacesSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Image Retrieval Based On Color and Texture FeaturesDocument3 pagesImage Retrieval Based On Color and Texture FeaturesKarthik SurabathulaNo ratings yet
- 10about Color Models PDFDocument2 pages10about Color Models PDF65paulosalesNo ratings yet
- RgbcmyDocument12 pagesRgbcmybhariprasad_mscNo ratings yet