Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 (Ict)
Unit 1 (Ict)
Uploaded by
moresurya87Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Computer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12Document136 pagesComputer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12MeAnnLarrosa86% (50)
- Chapter 7 LabDocument5 pagesChapter 7 LabDuluth MarketsNo ratings yet
- DVR 450H SDocument172 pagesDVR 450H SNewfieFixerNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit 1 NotesDocument104 pagesCoa Unit 1 NotesNilavazhagan GunaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 FCPDocument52 pagesUnit - 1 FCPHemanth Kumar100% (1)
- EIT NOTES ConsolidatedDocument143 pagesEIT NOTES ConsolidatedAdnan HamadNo ratings yet
- Unit I IctDocument59 pagesUnit I IctYogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- GEE2Document15 pagesGEE2Ronimarie Nicole ZapataNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalDocument9 pagesComputer Fundamentalprinceisrael332No ratings yet
- Oswaal CBSE Class 9 Computer Applications Revision Notes For 2023 ExamDocument11 pagesOswaal CBSE Class 9 Computer Applications Revision Notes For 2023 Examrajuchakraborti253No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Inside The ComputerDocument58 pagesLESSON 3 Inside The ComputerBelle BeautyNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Computer-Converted DR SuriyaDocument11 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer-Converted DR SuriyaMegacable MegacableNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Document24 pagesUnit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Ujjwal KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Itt ProjectDocument78 pagesItt ProjectLokesh Patidar100% (3)
- Elements of Computer SystemDocument39 pagesElements of Computer SystemMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Task One Cheptoo MercyDocument5 pagesTask One Cheptoo MercybonfaceNo ratings yet
- Computer PDFDocument12 pagesComputer PDFrocma guindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1patel.ved98795No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer PDFDocument121 pagesIntroduction To Computer PDFAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- ITB Notes (OU BBA 3rd Sem)Document82 pagesITB Notes (OU BBA 3rd Sem)Saba TaherNo ratings yet
- Ce Workshop Lab ManualDocument140 pagesCe Workshop Lab Manualvamsi raviNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems HARDWARE L2Document102 pagesComputer Systems HARDWARE L2trevorNo ratings yet
- Complete CP NotesDocument91 pagesComplete CP NotesAnonymous 1HlNy6nNo ratings yet
- Estrada - Assignment 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEstrada - Assignment 1 PDFAsia EstradaNo ratings yet
- Aefunaicsc101 Lect1Document21 pagesAefunaicsc101 Lect1favourlucky2.aNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Fundamentals of A PCDocument36 pagesInformation Technology Fundamentals of A PCMykayla LindsayNo ratings yet
- Computer DocumentDocument7 pagesComputer DocumentTatuh PerryNo ratings yet
- Icps Module 1 Part 1 of 5Document19 pagesIcps Module 1 Part 1 of 5fevay55076No ratings yet
- Day 1Document5 pagesDay 1emadeeuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lighting and ShadowsDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Lighting and Shadowsnickmcklin7No ratings yet
- 1basic Computer OrganizationDocument13 pages1basic Computer OrganizationAdrija SinghNo ratings yet
- Ict Lecture 1Document16 pagesIct Lecture 1Sufyan UllahNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessDocument31 pagesComputer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessADITYA KUMAR0% (2)
- IT Assignments 1-13Document34 pagesIT Assignments 1-13ASHISHNo ratings yet
- Reading - Material - On ITDocument37 pagesReading - Material - On ITKISHORETNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer SystemDocument61 pagesBasics of Computer Systemshahiddange05No ratings yet
- Module 1-Computer - ComponentsDocument131 pagesModule 1-Computer - ComponentsEliza Jiann B. BualanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Structure of Computers - Functional UnitsDocument3 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Structure of Computers - Functional UnitsGdsg DsgNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 (GST 100) PDFDocument35 pagesLecture - 2 (GST 100) PDFPaschal ErukayifeNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations of A Computer SystemDocument11 pagesBasic Operations of A Computer SystemJanus Michael FaustoNo ratings yet
- ICT & Multimedia Fundamentals: Computer Hardware Block Diagram (Above)Document31 pagesICT & Multimedia Fundamentals: Computer Hardware Block Diagram (Above)Khidir MansorNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument45 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALNanny BoppanaNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument145 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALAvinash TalapulaNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument42 pagesComputer Applicationriya wadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Computer HarwareDocument22 pagesLesson 1 - Computer HarwarePaul DefensorNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer TrainingDocument12 pagesBasic Computer Trainingtemesgen fuliNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument16 pagesComputer Notesmunaxemimosa8No ratings yet
- ICDL Module 1 FinalDocument131 pagesICDL Module 1 Finalyousef100% (1)
- Computer Manual: Compiled by S KiturDocument43 pagesComputer Manual: Compiled by S KiturAlexNo ratings yet
- COA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90Document89 pagesCOA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90BOBAN05No ratings yet
- ITE101 - Living in The IT Era - Week 1 2Document10 pagesITE101 - Living in The IT Era - Week 1 2Maybelle Bernal100% (1)
- Basic Power PointDocument10 pagesBasic Power PointPaul Anthony Gerona JacerNo ratings yet
- I CTM Su Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesI CTM Su Lecture NotesGabriel R. AboNo ratings yet
- Computer System & Organization: Unit-IDocument58 pagesComputer System & Organization: Unit-I8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- FCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer ProgrammingDocument54 pagesFCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer Programmingsoni2.officialNo ratings yet
- Resource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsDocument257 pagesResource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- What Is A ComputerDocument19 pagesWhat Is A ComputerFuad TalNo ratings yet
- Data: Data Is A Raw Material of Information. Information: Proper Collection of The Data Is Called InformationDocument13 pagesData: Data Is A Raw Material of Information. Information: Proper Collection of The Data Is Called InformationAnubhav sirohiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ComputersLaira LicudineNo ratings yet
- Computr Appltion 1 and 2Document46 pagesComputr Appltion 1 and 2george manNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument19 pagesComputer FundamentalsPaneendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Document 206Document2 pagesDocument 206moresurya87No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document10 pagesTutorial 3moresurya87No ratings yet
- Question Bank CT II Sem-IDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank CT II Sem-Imoresurya87No ratings yet
- ICT Practical No 7 Semester 1Document5 pagesICT Practical No 7 Semester 1moresurya87No ratings yet
- Eagle Server IntroDocument39 pagesEagle Server IntroDavid Fernando Arquez BeltranNo ratings yet
- Perform Computer Operations QuizDocument2 pagesPerform Computer Operations QuizArt Dollosa100% (1)
- Disks, Memories & Buffer Management: "The Two Offices of Memory Are Collection and Distribution." - Samuel JohnsonDocument28 pagesDisks, Memories & Buffer Management: "The Two Offices of Memory Are Collection and Distribution." - Samuel JohnsonGilbert HeßNo ratings yet
- Computer Boot-Up Troubleshoot FlowchartDocument21 pagesComputer Boot-Up Troubleshoot FlowchartCheAzahariCheAhmad100% (1)
- HCI BR P HCI-BrochureDocument12 pagesHCI BR P HCI-BrochureHafizalZainalNo ratings yet
- Melc Competency Code Tle - Iacss9-12Iccs-Iiif-J-32: Burning or Testing Installed Equipment/DevicesDocument4 pagesMelc Competency Code Tle - Iacss9-12Iccs-Iiif-J-32: Burning or Testing Installed Equipment/DevicesIzaak CabigonNo ratings yet
- How To Install Linux Mint On VMWare WorkstationDocument16 pagesHow To Install Linux Mint On VMWare WorkstationAhmed ShuvoNo ratings yet
- DLL in CSS 11 - Q2, W1Document3 pagesDLL in CSS 11 - Q2, W1Diaz100% (3)
- HDD GURU FORUMS - View Topic - Dumping Micron M500 SSD Firmware MU05Document12 pagesHDD GURU FORUMS - View Topic - Dumping Micron M500 SSD Firmware MU05Nauka SolutionNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Intelligent Storage ComponentsDocument62 pages2-1 Intelligent Storage ComponentsAlberto SantosNo ratings yet
- Báo Giá VANTECH - Dau Ghi - T10Document24 pagesBáo Giá VANTECH - Dau Ghi - T10Car Toys Sao ViệtNo ratings yet
- Vess R2000-J2000 Series PM v2.2Document704 pagesVess R2000-J2000 Series PM v2.2power kacang1No ratings yet
- DHI NVR1104HS S3H - DatasheetDocument2 pagesDHI NVR1104HS S3H - DatasheetKairos TvNo ratings yet
- Poweredge r740 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesPoweredge r740 Spec SheetDinu MoraruNo ratings yet
- DVR Alarm Supply PDFDocument70 pagesDVR Alarm Supply PDFAndres Duque100% (1)
- Quick User Manual For DVR V1.0Document13 pagesQuick User Manual For DVR V1.0Elenilto Oliveira de AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Welland ME-602J ManualDocument8 pagesWelland ME-602J ManualCarlos A C PiresNo ratings yet
- Oceanstor S3900 PDFDocument2 pagesOceanstor S3900 PDFJhon ALexander Caldas LesmesNo ratings yet
- Mans io-2D0KiJ3gDocument259 pagesMans io-2D0KiJ3gRy RicardoNo ratings yet
- History of NseDocument9 pagesHistory of NseadesloopNo ratings yet
- LINUXDocument140 pagesLINUXsivavadde150No ratings yet
- IBM Lenovo Think Centre M58M58p DatasheetDocument4 pagesIBM Lenovo Think Centre M58M58p DatasheetMarko MarkovicNo ratings yet
- 4mag 1 Q2 2013 (22 36) PDFDocument15 pages4mag 1 Q2 2013 (22 36) PDFAndres MaciasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12 May/June 2020Document9 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12 May/June 2020Zaki JrNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On CybercrimeDocument16 pagesTerm Paper On CybercrimeML GamingNo ratings yet
- Advent 4211B NetbookDocument8 pagesAdvent 4211B NetbookCarlos ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Samsung NP300V4ADocument136 pagesSamsung NP300V4AAlan ChavezNo ratings yet
Unit 1 (Ict)
Unit 1 (Ict)
Uploaded by
moresurya87Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 (Ict)
Unit 1 (Ict)
Uploaded by
moresurya87Copyright:
Available Formats
Fundamental of ICT 1
Unit 1- Introduction to Computer System
Definition of a computer
➢ By definition, a computer is an electronic device that inputs data, processes
data(converting it into information that is useful to people) outputs and stores
information.
➢ Computers are controlled by programmed instructions that transform the data
into meaningful information.
➢ Generally a Computer is a device that accepts input, processes it, stores data,
and produces output.
Information Processing Cycle
Steps followed to process data
▪ Input
▪ Processing
▪ Output
▪ Storage
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 2
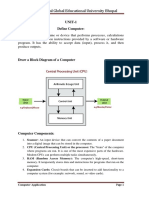
Block Diagram of Computer System
Input Unit
➢ Input: Information provided to the computer by a person, the environment, or
another computer. Typical input devices include the keyboard, floppy disks,
mouse, microphone, light pen, joy stick, magnetic tapes etc.
Examples of Input
➢ words and symbols, numbers, pictures, audio signals from a microphone,
signals from another computer, temperature, speed, pressures, etc. from
sensors The functions of the input unit are :
➢ Accept information (data) and programs.
➢ Convert the data in a form which the computer can accept.
➢ Provide this converted data to the computer for further processing.
The Central Processing Unit
This is the brain of any computer system. The central processing unit or CPU is made
of three parts:
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 3
➢ The control unit.
➢ The arithmetic logic unit
➢ The primary storage unit / Memory Unit
The Central Processing Unit
1. The Control Unit :
The Control Unit controls the operations of the entire computer system. The control
unit gets the instructions from the programs stored in primary storage unit interprets
these instruction an subsequently directs the other units to execute the instructions.
Thus it manages and coordinates the entire computer system.
2. The Arithmetic Logic Unit:
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) actually executes the instructions and performs
all the calculations and decisions. The data is held in the primary storage unit and
transferred to the ALU whenever needed. Data can be moved from the primary
storage to the arithmetic logic unit a number of times before the entire processing is
complete. After the completion, the results are sent to the output storage section and
the output devices
3. The Primary Storage Unit:
This is also called as Main Memory. Before the actual processing starts the data and
the instructions fed to the computer through the input units are stored in this primary
storage unit. Similarly, the data which
is to be output from the computer system is also temporarily stored in the primary
memory. It is also the area where intermediate results of calculations are stored. The
main memory has the storage section that holds the computer programs during
execution.
Thus the primary unit:
• Stores data and programs during actual processing.
• Stores temporary results of intermediate processing.
• Stores results of execution temporarily.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 4
Output Unit
➢ Output - the result produced by a computer after processing the data.
➢ Output device –displays, prints, or transmits the results after processing.
➢ The output devices give the results of the process and computations to the
outside world. The output units accept the results produced by the computer,
convert them into a human readable form and supply them to the users. The
more common output devices are printers, plotters, display screens, magnetic
tape drives etc
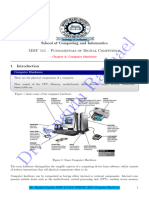
Internal Components
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 5
Motherboard
➢ The motherboard is the main circuit board that all other computer components
either sit in or are connected to. The motherboard type will determine what
kind of processor and memory chips can be installed on the computer, along
with what kind of external connections, such as USB, are natively supported.
Some motherboards also will include onboard video and sound, removing the
need for expansion cards.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 6
Processor
➢ The processor is probably the most important internal part of your computer,
as it is where almost all of the computations required to run the computer take
place. The processor sits inside of a small socket near the middle of the
motherboard, and on top of executing code for your programs, it also controls
how the other computer components communicate and operate. The
processor's power is measured in megahertz, and more recently gigahertz,
with a higher number representing more processing power.
RAM
➢ When the processor needs information for a particular program or task, it first
loads that data into random access memory. or RAM. RAM is short-term
memory, meaning that it gets wiped out every time the computer loses power
or gets reset, but its speed of access makes it ideal for being the computer's
primary storage.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 7
Hard Drive
➢ Hard drives are slowly accessed, long-term storage. Any file or piece of
information that may be needed more than once is stored on the hard drive.
➢ When the processor needs a file or set of files to run a program, it copies them
from the hard drive and loads those copies into RAM. Hard drive capacities
are measured in gigabytes, or sometimes terabytes, with the larger numbers
representing more capacity.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 8
ROM
➢ read-only memory, ROM is a storage medium that is used with computers and
other electronic devices. As the name indicates, data stored in ROM may only
be read.
➢ Unlike RAM (random access memory), ROM is non-volatile, which means
it keeps its contents regardless of whether or not it has power.
Video Card
➢ While some older motherboards have built-in video, most modern systems
require a separate video card to output graphics. The pure computational
power required to render modern graphics require a separate processor and
cooling unit that is housed on this video card. The card itself is connected to
the motherboard using an expansion slot.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 9
External Components
Input Devices
The devices which are used to give data and instructions to the computer are
called Input Devices. Various types of input devices can be used with the
computer depending upon the type of data you want to enter in the computer,
e.g., keyboard, mouse, joystick, light pen, etc
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 10
Keyboard
1. A simple device comprising keys and each key denotes either an alphabet,
number or number commands which can be given to a computer for various
actions to be performed
➢ It has a modified version of typewriter keys
➢ The keyboard is an essential input device and computer and laptops both use
keyboards to give commands to the computer
Mouse
➢ It is also known as a pointing device
➢ Using mouse we can directly click on the various icons present on the system
and open up various files and programs
➢ A mouse comprises 3 buttons on the top and one trackball at the bottom which
helps in selecting and moving the mouse around, respectively
➢ In case of laptops, the touchpad is given as a replacement of mouse which
helps in the movement of the mouse pointer.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 11
Joystick and Game-pad
➢ Joystick and game-pad are also input devices which are also input devices
which are used to control the movement of object on the screen.
➢ Just like mouse, these are also pointing devices. Mostly they are used for
playing games on the computer.
Light Pen
➢ Light pen is another pointing type input device.
➢ It is a pen shaped device which can be used by directly pointing the objects
on the screen.
➢ It can also be used for making drawings directly on the monitor screen.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 12
Scanner
➢ We can store pictures, photographs, diagrams into the computer with the help
of scanner.
➢ This device can scan images or text and convert it into a digital signal
➢ When we place any piece of document on a scanner, it converts it into a digital
signal and displays it on the computer screen.
Output Devices
The devices which are used to display the results or information are called Output
Devices. You can view the output on the monitor or you can print it on a paper
using a printer. Monitor and the printer are the commonly used output devices.
E.g. monitor, printer, plotter, speakers, headphones, projector etc.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 13
Monitor
➢ The device which displays all the icons, text, images, etc. over a screen is
called the Monitor
➢ When we ask the computer to perform an action, the result of that action is
displayed on the monitor
➢ Various types of monitors have also been developed over the years.
Printer
➢ A device which makes a copy of the pictorial or textual content, usually over
a paper is called a printer
➢ For example, an author types the entire book on his/her computer and later
gets a print out of it which is in the form of paper and is later published
➢ Multiple types of printers are also available in the market, which can serve
different purposes.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 14
Dot Matrix Printer
➢ This type of printer works like a typewriter.
➢ It creates an impression on the paper by pressing the end of pins fixed in its
print heads, against an inked ribbon.
➢ This printer is noisy with a low print quality. Its speed is measured in
CPS(Characters Per Second).
Inkjet Printer
➢ This type of printer prints by spraying tiny ink droplets on the paper. It can
print in both, color as well as black and white.
➢ The print quality of this printer is better than that of Dot Matrix Printer and it
prints without making any noise.
➢ Its speed is measured in PPM(Pages Per Minute).
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 15
Plotter
➢ We can get the print of a photograph, drawing, image stored in the computer,
by using a plotter.
➢ Instead of toner, plotters use a pen, pencil, marker, or another writing tool to
draw multiple, continuous lines onto paper rather than a series of dots like a
traditional printer.
➢ It is an output device which provides a high quality of printed output. It is
generally used by engineers and architects.
Speakers
➢ A device through which we can listen to a sound as an outcome of what we
command a computer to do is called a speaker
➢ Speakers are attached with a computer system and also are a hardware device
which can be attached separately
➢ With the advancement in technology, speakers are now available which are
wireless and can be connected using bluetooth or other applications.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 16
External Storage Devices
CD/DVD
➢ CDs, DVDs disks are used as storage devices, and collectively they’re known
as optical storage devices or optical disk media.
➢ A DVD allow to store more data despite being the same size than a CD and a
finer red laser is used in DVD drives than CD drives.
External HDDs and SSDs
➢ You can get both HDD and SSD devices as external drives. These generally
offer the largest storage capacity among external options, with external HDDs
offering up to 20 TB of storage and (reasonably-priced) external SSDs
offering up to 8 TB of storage.
➢ External HDDs and SSDs work in the exact same way that their internal
counterparts do. Most external drives can be connected to any computer;
they’re not tied to one device, so they’re a decent
➢ solution for transferring files across devices.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 17
Pen Drive
➢ USB pen drive emulates a small disk drive and allows data to be transferred
easily from one device to another. The way it works is very simple. It also
works very fast. Since it is a relatively newer device,Manufacturers are
launching it with added capabilities and higher storage power.
Parts of a Computer System
Computer hardware:
1. A computer's hardware consists of electronic devices; the parts you can see
and touch.
2. In other words these are tangible parts of a computer.
3. The term "device" refers to any piece of hardware used by the computer, such
as a keyboard, monitor, modem, mouse, etc.
4. These are mechanical devices that make up the computer.
Computer Software
➢ Is the set of instructions that makes the computer perform tasks.
➢ The software is a part of the computer you cannot touch but is very important.
➢ The software is all the programming that makes the computer run; controlling
everything that the computer does.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 18
➢ For any computer to function, it needs to have software installed on it.
➢ Software is a set of instructions that drive a computer to perform specific
tasks.
➢ These instructions tell the machine’s physical components what to do.
➢ A set of instructions is often called a program.
➢ When a computer is using a particular program, it is said to be running or
executing the program.
The two most common types of programs are :
1. system software
2. application software
1. System Software
➢ System software is any program that controls the computer’s hardware or that
can be used to maintain the computer in some way so that it runs more
efficiently.
➢ System Software provides a platform for running application software.
➢ There are three basic types of system software:
a) Operating System
➢ An operating system tells the computer how to use its own components. All
computers require an operating system.
➢ The OS tells the computer how to interact with the user and its own devices.
➢ Examples of operating systems include Windows, Macintosh operating
system and Linux.
b) Device Drivers
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 19
➢ Driver software is a type of system software which brings computer devices
and peripherals to life. Drivers make it possible for all connected components
and external add-ons perform their intended tasks and as directed by the OS.
Without drivers, the OS would not assign any duties.
c) Utilities
➢ A utility is a program that makes the computer system easier to use or
performs highly specialized functions.
➢ Utilities are used to manage disks, troubleshoot hardware problems, and
perform other tasks that the operating system itself may not be able to do. For
example a Symantec antivirus, Partition Magic etc.
d) Programming language translators (Compilers &Interpreters)
➢ These are intermediate programs used to translate high-level language source
code to machine language code.
➢ Popular language translators include assemblers, compilers, and interpreters.
➢ They may be used to perform complete translation of program codes or they
may translate each instruction one at a time
Application Software
Applications software is capable of dealing with user inputs and helps the user to
complete the task. It is also called end-user programs or only an app. It resides above
system software.
Some of the major categories of these applications include:
1. Word Processing Software
2. Spreadsheet Software
3. Database Software
4. Multimedia Software
5. Presentation Software etc.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 20
Application Software
1. Word Processing Software
➢ Word Processing software is used to manipulate, format the text, to create
memos, letters, faxes and documents. Processing Software is used to format
and beautify the text.
➢ It provides a list of features. The option provides synonyms, antonyms and
related words for chosen word or phrase. Find and replace feature enables
users to scan and replace selected words or phrases in the document.
➢ Font option provides font colour, font style, font effect, font size to modify
the txt. Word Art option to modify or animated titles, hyphens, columns and
text boxes in documents.
➢ Grammar and Spelling check option available for checking errors. Many
more option is listed here in software.
➢ For example Microsoft Word, Lotus Word Pro, Word pad and Corel
WordPerfect.
2) Spreadsheet Software
➢ Spreadsheet software is used to perform manipulate and calculations. In
spreadsheet software data is stored in intersection row and column. The
intersection of row and column is known as a cell. The cell labelled with the
row and column label like A1, A2 etc. While entering data into the cell, we
can also define the data value like text, date, time, number.
➢ It provides many formula and function to perform calculations like arithmetic
operations, logical operations, text operation etc. It provides charts, graphs to
display data graphically.
➢ For example Microsoft Excel, lotus 1-2-3 for windows and number for MAC
OS
3) Database Software
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 21
➢ Database is a collection of data related to any applications. Today is
environment every application has some database where data regarding users
stored. For this purpose, we used database software. When we operate the
application data is accessed from the database, and after manipulation, it gets
back stored in the database.
➢ Database Management System (DBMS) software tool used for storing,
modifying extracting and searching for information within a database.
MySQL, MS Access, Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle is the example of
database application Software.
4) Multimedia Software
➢ Multimedia is a combination of text, graphics, audio and Multimedia
software used in the editing of video, audio and text.
➢ Multimedia software used in the growth of business, educations, information,
remote system and entertainment.
➢ For example, video editing software, photo editing software, graphics
manipulation software etc.
5) Presentation Software
➢ Presentation program is a program to show the information in the form of
slides. We can add text, graphics video and images to slides to make them
more informative.
➢ The software has three components:
1) Text editor for inputting and formatting text.
2) Inserting graphics, text, video and other multimedia files.
3) Slideshow to display the information.
➢ Presentation software helps the presenter to present their ideas with ease and
visual information easy to understand. Example of presentation software:
Microsoft’s PowerPoint and Apple’s Keynote.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 22
Network Environments
Network Interface Card (NIC)
➢ A network interface card (NIC) is a hardware component, typically a circuit
board or chip, which is installed on a computer so that it can connect to a
network.
➢ The network card operates as a middleman between a computer and a data
network.
➢ The term network interface card is often considered interchangeable with the
terms network interface controller, network adapter and LAN adapter.
Hub
➢ Hubs connect multiple computer networking devices together. A hub also acts
as a repeater in that it amplifies signals that deteriorate after traveling long
distances over connecting cables.
➢ Hubs do not perform packet filtering or addressing functions; they just send
data packets to all connected devices.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 23
Switch
➢ Switches generally have a more intelligent role than hubs.
➢ A switch is a multiport device that improves network efficiency. The switch
maintains limited routing information about nodes in the internal network, and
it allows connections to systems like hubs or routers.
➢ Strands of LANs are usually connected using switches. Generally, switches
can read the hardware addresses of incoming packets to transmit them to the
appropriate destination.
Router
➢ Routers help transmit packets to their destinations by charting a path through
the sea of interconnected networking devices using different network
topologies.
➢ Routers are intelligent devices, and they store information about the networks
they’re connected to.
➢ Router are also used to divide internal networks into two or more sub
networks.
Modem
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 24
➢ Modems (modulators-demodulators) are used to transmit digital signals over
analog telephone lines.
➢ Thus, digital signals are converted by the modem into analog signals of
different frequencies and transmitted to a modem at the receiving location.
➢ The receiving modem performs the reverse transformation and provides a
digital output to a device connected to a modem, usually a computer.
Local Area Network (LAN)
➢ A local area network (LAN) is a computer network covering a small physical
area, like a home, office, or small group of buildings, such as a school, or an
airport.
➢ On a typical LAN application, softwares and users' data files are stored on a
central computer called a file server (SERVER).
➢ Each computer on a LAN is called a workstation.
➢ To connet to a LAN, a workstation must have a network card. This is a device
through which computers communicate which each other.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 25
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
➢ A wireless LAN (WLAN) links two or more computers or devices using
spread-spectrum or OFDM modulation technology based to enable
communication between devices in a limited area.
➢ This gives users the mobility to move around within a broad coverage area
and still be connected to the network.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 26
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
➢ MAN network covers larger area by connections LANs to a larger network
of computers.
➢ In Metropolitan area network various Local area networks are connected with
each other through telephone lines.
➢ The size of the Metropolitan area network is larger than LANs and smaller
than WANs(wide area networks), a MANs covers the larger area of a city or
town.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
➢ A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a broad area
(i.e. any network whose communications links cross metropolitan, regional,
or national boundaries). Less formally, a WAN is a network that uses routers
and public communications links.
➢ The computers in a WAN are not permanently connected to each other with
data cables. They communicate with each other through telephone lines, radio
signals and satellite links.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 27
Working With Operating System
Data and Information
➢ Data are the words, numbers, symbols and graphics that describe people,
events, things, and ideas.
➢ Data becomes information when it is used as the basis for initiating some
action or for making a decision.
➢ Information are the words, numbers, and graphics used as the basis for human
actions and decisions.
➢ A set of data that has been given a name is called a file.
➢ A file that a user can open and use is called document.
➢ A folder is a place where groups of computer files and other folders can be
kept and organized.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
Fundamental of ICT 28
Files
➢ A file is a named collection of data, stored on a storage medium such as a
hard disk.
➢ There are two types of files
➢ Data files contains text, images, or other data that can be used by a program.
➢ Executable files contains programs or instructions that tell the computer how
to perform a task.
➢ Filename extensions describe a file’s contents. For example Executable files
usually end in .exe, word files end in .doc, adobe acrobat documents end in
.pdf etc.
Extensions and Formats
➢ A filename might be followed by a filename extension that further describes
the file contents.
➢ Word files end in .doc
➢ Excel files end in .xls
➢ The file format is the arrangement of data in a file and the coding scheme that
is used to represent the data.
➢ The native file format is the format that is saved by the application that
created it.
Sandip Polytechnic Computer Department Prof. K. M. Kamale
You might also like
- Computer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12Document136 pagesComputer Systems Servicing Learning Module K To 12MeAnnLarrosa86% (50)
- Chapter 7 LabDocument5 pagesChapter 7 LabDuluth MarketsNo ratings yet
- DVR 450H SDocument172 pagesDVR 450H SNewfieFixerNo ratings yet
- Coa Unit 1 NotesDocument104 pagesCoa Unit 1 NotesNilavazhagan GunaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 FCPDocument52 pagesUnit - 1 FCPHemanth Kumar100% (1)
- EIT NOTES ConsolidatedDocument143 pagesEIT NOTES ConsolidatedAdnan HamadNo ratings yet
- Unit I IctDocument59 pagesUnit I IctYogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- GEE2Document15 pagesGEE2Ronimarie Nicole ZapataNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalDocument9 pagesComputer Fundamentalprinceisrael332No ratings yet
- Oswaal CBSE Class 9 Computer Applications Revision Notes For 2023 ExamDocument11 pagesOswaal CBSE Class 9 Computer Applications Revision Notes For 2023 Examrajuchakraborti253No ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Inside The ComputerDocument58 pagesLESSON 3 Inside The ComputerBelle BeautyNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Computer-Converted DR SuriyaDocument11 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer-Converted DR SuriyaMegacable MegacableNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Document24 pagesUnit 1-Lecture Note-1, 2Ujjwal KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Itt ProjectDocument78 pagesItt ProjectLokesh Patidar100% (3)
- Elements of Computer SystemDocument39 pagesElements of Computer SystemMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Task One Cheptoo MercyDocument5 pagesTask One Cheptoo MercybonfaceNo ratings yet
- Computer PDFDocument12 pagesComputer PDFrocma guindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1patel.ved98795No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer PDFDocument121 pagesIntroduction To Computer PDFAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- ITB Notes (OU BBA 3rd Sem)Document82 pagesITB Notes (OU BBA 3rd Sem)Saba TaherNo ratings yet
- Ce Workshop Lab ManualDocument140 pagesCe Workshop Lab Manualvamsi raviNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems HARDWARE L2Document102 pagesComputer Systems HARDWARE L2trevorNo ratings yet
- Complete CP NotesDocument91 pagesComplete CP NotesAnonymous 1HlNy6nNo ratings yet
- Estrada - Assignment 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEstrada - Assignment 1 PDFAsia EstradaNo ratings yet
- Aefunaicsc101 Lect1Document21 pagesAefunaicsc101 Lect1favourlucky2.aNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Fundamentals of A PCDocument36 pagesInformation Technology Fundamentals of A PCMykayla LindsayNo ratings yet
- Computer DocumentDocument7 pagesComputer DocumentTatuh PerryNo ratings yet
- Icps Module 1 Part 1 of 5Document19 pagesIcps Module 1 Part 1 of 5fevay55076No ratings yet
- Day 1Document5 pagesDay 1emadeeuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lighting and ShadowsDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Lighting and Shadowsnickmcklin7No ratings yet
- 1basic Computer OrganizationDocument13 pages1basic Computer OrganizationAdrija SinghNo ratings yet
- Ict Lecture 1Document16 pagesIct Lecture 1Sufyan UllahNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessDocument31 pagesComputer Basics: Analytical Ability and Digital AwarenessADITYA KUMAR0% (2)
- IT Assignments 1-13Document34 pagesIT Assignments 1-13ASHISHNo ratings yet
- Reading - Material - On ITDocument37 pagesReading - Material - On ITKISHORETNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer SystemDocument61 pagesBasics of Computer Systemshahiddange05No ratings yet
- Module 1-Computer - ComponentsDocument131 pagesModule 1-Computer - ComponentsEliza Jiann B. BualanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Structure of Computers - Functional UnitsDocument3 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Structure of Computers - Functional UnitsGdsg DsgNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 (GST 100) PDFDocument35 pagesLecture - 2 (GST 100) PDFPaschal ErukayifeNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations of A Computer SystemDocument11 pagesBasic Operations of A Computer SystemJanus Michael FaustoNo ratings yet
- ICT & Multimedia Fundamentals: Computer Hardware Block Diagram (Above)Document31 pagesICT & Multimedia Fundamentals: Computer Hardware Block Diagram (Above)Khidir MansorNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument45 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALNanny BoppanaNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument145 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALAvinash TalapulaNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument42 pagesComputer Applicationriya wadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Computer HarwareDocument22 pagesLesson 1 - Computer HarwarePaul DefensorNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer TrainingDocument12 pagesBasic Computer Trainingtemesgen fuliNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument16 pagesComputer Notesmunaxemimosa8No ratings yet
- ICDL Module 1 FinalDocument131 pagesICDL Module 1 Finalyousef100% (1)
- Computer Manual: Compiled by S KiturDocument43 pagesComputer Manual: Compiled by S KiturAlexNo ratings yet
- COA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90Document89 pagesCOA NOTESmod118EC35-2-90BOBAN05No ratings yet
- ITE101 - Living in The IT Era - Week 1 2Document10 pagesITE101 - Living in The IT Era - Week 1 2Maybelle Bernal100% (1)
- Basic Power PointDocument10 pagesBasic Power PointPaul Anthony Gerona JacerNo ratings yet
- I CTM Su Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesI CTM Su Lecture NotesGabriel R. AboNo ratings yet
- Computer System & Organization: Unit-IDocument58 pagesComputer System & Organization: Unit-I8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- FCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer ProgrammingDocument54 pagesFCP-L2 Fundamentals of Computer Programmingsoni2.officialNo ratings yet
- Resource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsDocument257 pagesResource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- What Is A ComputerDocument19 pagesWhat Is A ComputerFuad TalNo ratings yet
- Data: Data Is A Raw Material of Information. Information: Proper Collection of The Data Is Called InformationDocument13 pagesData: Data Is A Raw Material of Information. Information: Proper Collection of The Data Is Called InformationAnubhav sirohiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ComputersLaira LicudineNo ratings yet
- Computr Appltion 1 and 2Document46 pagesComputr Appltion 1 and 2george manNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument19 pagesComputer FundamentalsPaneendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Document 206Document2 pagesDocument 206moresurya87No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document10 pagesTutorial 3moresurya87No ratings yet
- Question Bank CT II Sem-IDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank CT II Sem-Imoresurya87No ratings yet
- ICT Practical No 7 Semester 1Document5 pagesICT Practical No 7 Semester 1moresurya87No ratings yet
- Eagle Server IntroDocument39 pagesEagle Server IntroDavid Fernando Arquez BeltranNo ratings yet
- Perform Computer Operations QuizDocument2 pagesPerform Computer Operations QuizArt Dollosa100% (1)
- Disks, Memories & Buffer Management: "The Two Offices of Memory Are Collection and Distribution." - Samuel JohnsonDocument28 pagesDisks, Memories & Buffer Management: "The Two Offices of Memory Are Collection and Distribution." - Samuel JohnsonGilbert HeßNo ratings yet
- Computer Boot-Up Troubleshoot FlowchartDocument21 pagesComputer Boot-Up Troubleshoot FlowchartCheAzahariCheAhmad100% (1)
- HCI BR P HCI-BrochureDocument12 pagesHCI BR P HCI-BrochureHafizalZainalNo ratings yet
- Melc Competency Code Tle - Iacss9-12Iccs-Iiif-J-32: Burning or Testing Installed Equipment/DevicesDocument4 pagesMelc Competency Code Tle - Iacss9-12Iccs-Iiif-J-32: Burning or Testing Installed Equipment/DevicesIzaak CabigonNo ratings yet
- How To Install Linux Mint On VMWare WorkstationDocument16 pagesHow To Install Linux Mint On VMWare WorkstationAhmed ShuvoNo ratings yet
- DLL in CSS 11 - Q2, W1Document3 pagesDLL in CSS 11 - Q2, W1Diaz100% (3)
- HDD GURU FORUMS - View Topic - Dumping Micron M500 SSD Firmware MU05Document12 pagesHDD GURU FORUMS - View Topic - Dumping Micron M500 SSD Firmware MU05Nauka SolutionNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Intelligent Storage ComponentsDocument62 pages2-1 Intelligent Storage ComponentsAlberto SantosNo ratings yet
- Báo Giá VANTECH - Dau Ghi - T10Document24 pagesBáo Giá VANTECH - Dau Ghi - T10Car Toys Sao ViệtNo ratings yet
- Vess R2000-J2000 Series PM v2.2Document704 pagesVess R2000-J2000 Series PM v2.2power kacang1No ratings yet
- DHI NVR1104HS S3H - DatasheetDocument2 pagesDHI NVR1104HS S3H - DatasheetKairos TvNo ratings yet
- Poweredge r740 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesPoweredge r740 Spec SheetDinu MoraruNo ratings yet
- DVR Alarm Supply PDFDocument70 pagesDVR Alarm Supply PDFAndres Duque100% (1)
- Quick User Manual For DVR V1.0Document13 pagesQuick User Manual For DVR V1.0Elenilto Oliveira de AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Welland ME-602J ManualDocument8 pagesWelland ME-602J ManualCarlos A C PiresNo ratings yet
- Oceanstor S3900 PDFDocument2 pagesOceanstor S3900 PDFJhon ALexander Caldas LesmesNo ratings yet
- Mans io-2D0KiJ3gDocument259 pagesMans io-2D0KiJ3gRy RicardoNo ratings yet
- History of NseDocument9 pagesHistory of NseadesloopNo ratings yet
- LINUXDocument140 pagesLINUXsivavadde150No ratings yet
- IBM Lenovo Think Centre M58M58p DatasheetDocument4 pagesIBM Lenovo Think Centre M58M58p DatasheetMarko MarkovicNo ratings yet
- 4mag 1 Q2 2013 (22 36) PDFDocument15 pages4mag 1 Q2 2013 (22 36) PDFAndres MaciasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12 May/June 2020Document9 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12 May/June 2020Zaki JrNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On CybercrimeDocument16 pagesTerm Paper On CybercrimeML GamingNo ratings yet
- Advent 4211B NetbookDocument8 pagesAdvent 4211B NetbookCarlos ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Samsung NP300V4ADocument136 pagesSamsung NP300V4AAlan ChavezNo ratings yet