Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Os Frontale
Os Frontale
Uploaded by
LBllb lblOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Os Frontale
Os Frontale
Uploaded by
LBllb lblCopyright:
Available Formats
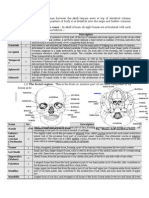
Os Frontale: The Frontal Bone
The os frontale, or frontal bone, is a critical element of the human skull, forming the forehead and the
superior part of the orbit. Positioned at the anterior portion of the cranium, this flat, bone plays a
pivotal role in both protection and aesthetic features. Understanding its anatomy and functions is
crucial in comprehending the importance of the frontal bone in human physiology and overall well-
being.
Anatomy and Structure
The os frontale consists of a single bone that comprises the majority of the cranial vault's anterior
portion. Key structural features include:
Frontal Squama: The large, flat, and curved portion of the frontal bone that forms the forehead. The
surface of the frontal squama is marked by the presence of numerous frontal sinuses, which are air-
filled cavities that help reduce the weight of the skull.
Supraorbital Foramen or Notch: Located just above the orbits (eye sockets), this small opening allows
the passage of the supraorbital nerve and vessels, which provide sensory innervation to the forehead.
Glabella: A smooth, slightly raised area between the eyebrows, which is an important anatomical
landmark in medical and anthropological studies.
Coronal Suture: The point where the frontal bone articulates with the parietal bones. This suture plays
a crucial role in the overall structure of the skull.
Functions
Protection: The os frontale serves as a protective barrier for the brain, providing a robust, solid layer at
the anterior aspect of the cranial vault. It acts as a safeguard against injuries, such as blows to the
head, by dispersing and absorbing the force, thus helping to minimize potential damage to the
delicate brain tissue.
Aesthetic and Facial Structure: The frontal bone contributes significantly to the overall appearance of
the face. It forms the forehead, which varies in contour and prominence among individuals and plays a
role in facial aesthetics.
Frontal Sinuses: The frontal sinuses within the frontal squama are part of the paranasal sinuses
system. They help humidify and filter inhaled air, reduce the weight of the skull, and resonate the
voice.Supraorbital Foramen/Notch: This anatomical feature provides a passage for the supraorbital
nerve and vessels, allowing for sensory innervation of the forehead and helping to maintain proper
sensory function.
Clinical Significance The os frontale is crucial in various medical and forensic contexts. Medical
imaging techniques, such as X-rays and CT scans, can reveal abnormalities in the frontal bone, aiding in
the diagnosis of head injuries, congenital disorders, or structural abnormalities. In forensic
anthropology, the size and shape of the frontal bone can be used for age, sex, and ancestry
estimation.
You might also like
- Cosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBDocument11 pagesCosmetic Otoplasty 2018 DBcirugia plastica uisNo ratings yet
- Fetal Skull - Madam JustinaDocument11 pagesFetal Skull - Madam JustinaNana Yunus67% (3)
- Short Syngo - Via - EngDocument5 pagesShort Syngo - Via - EngCeoĐứcTrườngNo ratings yet
- CarQuest Wearever Brake Parts Cleaner WES W5089 PDFDocument1 pageCarQuest Wearever Brake Parts Cleaner WES W5089 PDFYoutube For EducationNo ratings yet
- Studying Human SkullDocument6 pagesStudying Human SkullDianaLabsYou ChannelNo ratings yet
- Camadas MusculosDocument8 pagesCamadas MusculosTathianefreitasNo ratings yet
- Os TemporaleDocument1 pageOs TemporaleLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- CraniumDocument20 pagesCraniumDifa ZafiraNo ratings yet
- The Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesDocument25 pagesThe Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesFrozen Pandora MahayaNo ratings yet
- The Bones of The SkullDocument5 pagesThe Bones of The Skullnknm40No ratings yet
- Questions For The Practical Exam 1 (Dentistry) : Head, Neck and Central Nerve System BonesDocument15 pagesQuestions For The Practical Exam 1 (Dentistry) : Head, Neck and Central Nerve System BonesNiousha pajoohandehNo ratings yet
- Basis CraniiDocument11 pagesBasis Craniicharlesy TNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Document17 pagesThe Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Leo Cordel Jr.No ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument17 pagesAnaphy ReportingKIA KHYTE FLORESNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument18 pagesANAPHYRaiza Abegail RoxasNo ratings yet
- Craneo Sobotta PDFDocument111 pagesCraneo Sobotta PDFMaria Teresa AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- The Skull-1Document46 pagesThe Skull-1renzvalorant28No ratings yet
- 5the SkeletonDocument24 pages5the SkeletonIza ShaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument17 pagesBones of The Skull Author Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeryمدونة الأحترافNo ratings yet
- Name No. Description Frontal Parietals OccipitalDocument2 pagesName No. Description Frontal Parietals OccipitalyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDocument4 pagesAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Functions of The Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Functions of The Muscles of Facial Expressionpaolahn14No ratings yet
- Anatomy FACEDocument11 pagesAnatomy FACEMilton quisbert paredesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsemmanuelNo ratings yet
- The SkullDocument28 pagesThe SkullAyethNo ratings yet
- The A To Z of Bones of The SkullDocument102 pagesThe A To Z of Bones of The SkullDr. Santorini100% (1)
- Anat NotesDocument94 pagesAnat NotesCarineHugz (CarineHugz)No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesHuman Anatomy 4th Edition Saladin Solutions Manual DownloadArturo Thomas100% (29)
- Fetal SkullDocument4 pagesFetal Skullsubashik0% (1)
- What Is The Function of The Frontal Bone ?Document1 pageWhat Is The Function of The Frontal Bone ?assiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Chapter3Document29 pagesAnatomy Chapter3jules BlasabasNo ratings yet
- Found 903128372 4535Document2 pagesFound 903128372 4535Bogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human OsteologyDocument131 pagesIntroduction To Human OsteologyMiguel Angel Soto Gutierrez100% (1)
- Nursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonDocument29 pagesNursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- CC CCC C C C CCCCCCC CCCCCCC CCCCCC CCCCCCCC CCC CDocument12 pagesCC CCC C C C CCCCCCC CCCCCCC CCCCCC CCCCCCCC CCC CBrian GenesisNo ratings yet
- Anatomia Facial 2018Document11 pagesAnatomia Facial 2018Isnelda EricesNo ratings yet
- Section15 Chapter8EarAnatomyDocument29 pagesSection15 Chapter8EarAnatomyBudi Darmawan DiswanNo ratings yet
- Finals TopicDocument22 pagesFinals TopicAbegail B. ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Maimoona, Maryam, Bushra, Husna Submitted To: Ms. Sadia Sharif Topic: Meninges & SkullDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Maimoona, Maryam, Bushra, Husna Submitted To: Ms. Sadia Sharif Topic: Meninges & SkullMaryam IftikharNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lesson 8Document22 pagesAnaphy Lesson 8Richee LunnayNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument13 pagesAxial Skeletonfhkb7ymzbqNo ratings yet
- The Parts Skeletal SystemDocument16 pagesThe Parts Skeletal SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- 1.translate Sumber Dan Materi Hafalan (AutoRecovered)Document19 pages1.translate Sumber Dan Materi Hafalan (AutoRecovered)raden chandrajaya listiandokoNo ratings yet
- Viswass School & College of Nursing GNM 1 Year Anatomy and Physiology UNIT-13 The Skeletal System Long Questions and AnswersDocument33 pagesViswass School & College of Nursing GNM 1 Year Anatomy and Physiology UNIT-13 The Skeletal System Long Questions and Answersshubham vermaNo ratings yet
- The Skull: Endang E.W. Kukun Djemi B. PenuDocument7 pagesThe Skull: Endang E.W. Kukun Djemi B. PenualfridusNo ratings yet
- Skull Base NROSDocument3 pagesSkull Base NROSXavier de lucaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology EditedDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology EditedAya BantuasNo ratings yet
- Anatomski Atlas KOSTI GLAVEDocument19 pagesAnatomski Atlas KOSTI GLAVEVesna StevanovicNo ratings yet
- Forehead AnatomyDocument4 pagesForehead Anatomyenglish-exactly100% (1)
- Bing MentahanDocument15 pagesBing Mentahansecondfery2021No ratings yet
- Anatomy, Head and Neck Frontalis Muscle ArticleDocument7 pagesAnatomy, Head and Neck Frontalis Muscle ArticleWindsurfingFinnNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton Second LectureDocument23 pagesAxial Skeleton Second LectureRichard BidalNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Projectsoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- HeadDocument503 pagesHeadpilot abdi baariNo ratings yet
- Frontal Bone: External and Internal SurfaceDocument18 pagesFrontal Bone: External and Internal SurfaceCamille MagdirilaNo ratings yet
- BetiDocument4 pagesBetiBiruk HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Cranium PDFDocument24 pagesAnatomi Cranium PDFVelrones TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure QuizzDocument2 pagesProtein Structure QuizzLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Os TemporaleDocument1 pageOs TemporaleLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Diverse Wildlife in National ParksDocument2 pagesDiverse Wildlife in National ParksLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Facts NotesDocument1 pageFacts NotesLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument2 pagesMeasurementLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Energy GlandsDocument14 pagesEnergy GlandsLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Concept and Structure of Scientific Explanation Types of Explanations High School KruševacDocument14 pagesConcept and Structure of Scientific Explanation Types of Explanations High School KruševacLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- History WWII Q&A High SchoolDocument2 pagesHistory WWII Q&A High SchoolLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- How Do We Hear High School KruševacDocument10 pagesHow Do We Hear High School KruševacLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Emphasis - InversionDocument2 pagesEmphasis - InversionLBllb lblNo ratings yet
- Luna RogersDocument2 pagesLuna RogersamyNo ratings yet
- Interview Techniques: General Hints & GuidelinesDocument6 pagesInterview Techniques: General Hints & GuidelinesDininhoNo ratings yet
- CSF RhinorrheaDocument34 pagesCSF RhinorrheaAnoop SinghNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Solution 30 - 54 MX ENDocument15 pagesSodium Hydroxide Solution 30 - 54 MX ENChe RomeroNo ratings yet
- Farhana AssignmentDocument4 pagesFarhana AssignmentMuhammad NadilNo ratings yet
- Economically DisadvantagedDocument7 pagesEconomically DisadvantagedAhm SamNo ratings yet
- GEPjuly Oct 2014Document16 pagesGEPjuly Oct 2014Joy Bernadette TanchingcoNo ratings yet
- Othmer Bab 3Document54 pagesOthmer Bab 3JHWNo ratings yet
- Ay Home Remedies by Sri Swami Sivananda SaraswatiDocument283 pagesAy Home Remedies by Sri Swami Sivananda Saraswatirajat gupta100% (2)
- Knowledge:: Knowledge Attitude and Practice Regarding Hypertension in General Population of IslamabadDocument2 pagesKnowledge:: Knowledge Attitude and Practice Regarding Hypertension in General Population of IslamabadAneesUrRahmanNo ratings yet
- Blasting Certification InitialDocument1 pageBlasting Certification InitialraidrobbyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Asian Natural FarmingDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Asian Natural Farminggeen201No ratings yet
- Mayrink2020 2Document7 pagesMayrink2020 2Stella AraujoNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Sustainability ReportDocument42 pagesCoca Cola Sustainability ReportbagepNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Pressure Ulcer Prevention Strategies For Adult Patients in Intensive Care Units: A Systematic ReviewDocument13 pagesEffectiveness of Pressure Ulcer Prevention Strategies For Adult Patients in Intensive Care Units: A Systematic ReviewKayam SinghNo ratings yet
- First Half Science of Happines SummaryDocument25 pagesFirst Half Science of Happines SummaryFarid DKNo ratings yet
- Ellie Lochner: Work ExperienceDocument4 pagesEllie Lochner: Work Experienceapi-571942009No ratings yet
- The Xay Fye Farms PDFDocument1 pageThe Xay Fye Farms PDFSene, PapaNo ratings yet
- PIT IKA XI Final AnnouncementDocument40 pagesPIT IKA XI Final AnnouncementAsviandri IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Emotion and MotivationDocument15 pagesEmotion and MotivationRichard HubbardNo ratings yet
- Halloween Should Be Spooky, Not Scary!Document2 pagesHalloween Should Be Spooky, Not Scary!NewsChannel 9No ratings yet
- Laboratory Procedure Manual: Alanine Amino Transferase (ALT) Refrigerated SerumDocument9 pagesLaboratory Procedure Manual: Alanine Amino Transferase (ALT) Refrigerated Serumحيدر كاملNo ratings yet
- Workbook 2Document5 pagesWorkbook 2Мария ДьяченкоNo ratings yet
- Stok Opname 2020Document63 pagesStok Opname 2020Hafizh JhunkoNo ratings yet
- Sharing Earth's ResourcesDocument3 pagesSharing Earth's ResourcesRussell Hill50% (2)
- Positive Guidance TechniquesDocument5 pagesPositive Guidance TechniquesChrismoonNo ratings yet
- 20 Sample Essays Vol 1 Ielts9proDocument25 pages20 Sample Essays Vol 1 Ielts9proKevinAnthonyDeanNo ratings yet
- Cafeteria Worker ResumeDocument8 pagesCafeteria Worker Resumewajhnzwhf100% (1)