Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsNotes
Notes
Uploaded by
mishrakumkum526The document discusses contingent contracts and quasi contracts under Indian contract law. It defines contingent contracts as contracts that depend on an uncertain future event outside the parties' control. Insurance, indemnity, and guarantee contracts are examples. Quasi contracts are not true contracts as they lack elements like offer, acceptance and consideration, but courts will enforce obligations that arise from principles of equity and justice. The key differences between contingent contracts, quasi contracts and regular contracts are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Contract of GuaranteeDocument26 pagesContract of GuaranteeSrishti Jain100% (1)
- 18 Disciplines of NinjutsuDocument1 page18 Disciplines of NinjutsutakedashindenNo ratings yet
- FLOATEL SUPERIOR SPECIFICATION DetailsDocument2 pagesFLOATEL SUPERIOR SPECIFICATION DetailsIsmail ZainolNo ratings yet
- Asking The People For Their MoneyDocument13 pagesAsking The People For Their MoneyTCFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6agarwalpawan1No ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument7 pagesContingent ContractsTanvir Sadik AkashNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument6 pagesContingent ContractsHemant AroraNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument3 pagesContingent ContractsRaza ZeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 - Quasi Contract and Chapter-13 - Unjust EnrichmentDocument3 pagesChapter - 12 - Quasi Contract and Chapter-13 - Unjust EnrichmentManish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heritage Law CollegeDocument8 pagesHeritage Law CollegeMUSKAN AGARWALNo ratings yet
- CONTIGENT - ASSIGNMENT - Sagar 47Document15 pagesCONTIGENT - ASSIGNMENT - Sagar 47Sagar JoonNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument9 pagesContingent ContractAli ShahNo ratings yet
- CHINNAYA VDocument20 pagesCHINNAYA VAshwin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Ica Unit 2 PDFDocument6 pagesIca Unit 2 PDFvxnyrxoheNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act Chapter - 6Document4 pagesIndian Contract Act Chapter - 6basraniharsh916No ratings yet
- Contingent Contracts (Section 31 in The Indian Contract Act, 1872)Document17 pagesContingent Contracts (Section 31 in The Indian Contract Act, 1872)harish_100_inNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument40 pagesContingent ContractSAUMYA GIRINo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document25 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872sjkushwaha21100% (1)
- Contract First DraftDocument9 pagesContract First DraftVishalNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument43 pagesContingent ContractJayanth Prakash100% (1)
- Contingent ContractDocument20 pagesContingent ContractKrutika AshtikarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: Contract of Indemnity v. Contract of GuaranteeDocument23 pagesIntroduction To: Contract of Indemnity v. Contract of GuaranteeStuti BaradiaNo ratings yet
- BL 1Document32 pagesBL 1Varesh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Frustration of ContractDocument4 pagesDoctrine of Frustration of ContractRaghavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Contingent ContractsDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Contingent ContractsPratyusha DashNo ratings yet
- BR 2Document65 pagesBR 2shashankd2804No ratings yet
- Contingent Contract-Event Based ContractDocument2 pagesContingent Contract-Event Based ContractSIIB SURATNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument4 pagesConsiderationSOUMYA SUCHARITA TRIPATHYNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation Law Colourful Summary NotesDocument113 pagesCa Foundation Law Colourful Summary Notesprerana sharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Legal AspectsDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Legal AspectsNurarief Affendy100% (1)
- Agreements Expressly Declared VoidDocument7 pagesAgreements Expressly Declared VoidAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wagering Agreement Amp Contingent Contract PDF PDF FreeDocument9 pagesWagering Agreement Amp Contingent Contract PDF PDF FreeSlakrkeNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6: Contingent and Quasi Contracts: Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesUnit - 6: Contingent and Quasi Contracts: Learning OutcomesE20PA063 MAHALAKSHMI.BNo ratings yet
- Intro To Contract ActDocument28 pagesIntro To Contract ActRahulNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract Under Contract Act 1872Document37 pagesLaw of Contract Under Contract Act 1872Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Problems Insurance 2Document13 pagesFinal Problems Insurance 2CloieRjNo ratings yet
- Contract of IndemnityDocument11 pagesContract of IndemnitySuresh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Contracts - Question and AnswersDocument9 pagesContracts - Question and Answersbbtqwrws78No ratings yet
- Contract of Guaranty and SuretyshipDocument6 pagesContract of Guaranty and SuretyshipNicole Reign EscusaNo ratings yet
- LLM - Iv Semester Law of Contract - Ii: Study MaterialDocument20 pagesLLM - Iv Semester Law of Contract - Ii: Study MaterialSuman sharmaNo ratings yet
- Contingent Contract: Presented byDocument28 pagesContingent Contract: Presented byIqra AfsarNo ratings yet
- Essentials of ContractDocument7 pagesEssentials of Contractsolitary soulNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument4 pagesDefinitionsGulka TandonNo ratings yet
- Contract of GuaranteeDocument9 pagesContract of Guarantee23.divyansh.kNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872: Unit - 1Document7 pagesThe Indian Contract Act, 1872: Unit - 1Raj DasNo ratings yet
- Contingent Contract: Chapter III: of Contingent Contracts Sections 31 To 36Document13 pagesContingent Contract: Chapter III: of Contingent Contracts Sections 31 To 36PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon PDFDocument37 pagesOblicon PDFDiana Grace SierraNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract - Roll No. 213112Document26 pagesLaw of Contract - Roll No. 213112Anita SudalaimaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Law For EngineersDocument40 pagesBasic Law For EngineersBhargav SarvepalliNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872Document9 pagesThe Indian Contract Act, 1872Venugopal PandeyNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument16 pagesContingent ContractPratik Raj100% (1)
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow 2019-2020Document11 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow 2019-2020sakshi barfalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6: Contingent and Quasi ContractsDocument11 pagesUnit - 6: Contingent and Quasi ContractsRahulNo ratings yet
- 74585bos60476 FND p2 Nset cp2 U6Document15 pages74585bos60476 FND p2 Nset cp2 U6Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Prudential Bank vs. Intermediate Appellate CourtDocument20 pagesPrudential Bank vs. Intermediate Appellate CourtAaron CariñoNo ratings yet
- Week 3-5 GuaranteeDocument108 pagesWeek 3-5 GuaranteeRamkumaar MadhavanNo ratings yet
- The Phrase Indemnity MeansDocument9 pagesThe Phrase Indemnity MeansArushiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture ThreeDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture Threesimangalisokhoza37No ratings yet
- 7 Gilat Satellite VS United Coconut Planters BankDocument17 pages7 Gilat Satellite VS United Coconut Planters BankKyla Ellen CalelaoNo ratings yet
- Contract of Indemnity Case Laws: Ankita Toppo, Sanchita TiwariDocument4 pagesContract of Indemnity Case Laws: Ankita Toppo, Sanchita TiwariSruti BansalNo ratings yet
- BR Study MaterialDocument5 pagesBR Study Materialal isra veliyancodeNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawFrom EverandBigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Act 1 Scene 5Document8 pagesYear 10 Act 1 Scene 5Zachary ConcessioNo ratings yet
- He Imes Eader: House Oks Debt DealDocument44 pagesHe Imes Eader: House Oks Debt DealThe Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Masoud AlamDocument1 pageMohammed Masoud AlamGokulam ExportsNo ratings yet
- The Israel Lobby in GermanyDocument8 pagesThe Israel Lobby in GermanyChrist Is BackNo ratings yet
- Sample Position PaperDocument19 pagesSample Position PaperWayne C.No ratings yet
- The History of The Mauryan Empire in IndiaDocument13 pagesThe History of The Mauryan Empire in Indiapurinaresh85No ratings yet
- Case Analysis Paper - Code of Conduct V2Document4 pagesCase Analysis Paper - Code of Conduct V2Charven VillamorNo ratings yet
- Shell V NLU Translated VersionDocument5 pagesShell V NLU Translated Versionmccm92No ratings yet
- Eucharistic Celebration and The Rite of Marriage PDFDocument25 pagesEucharistic Celebration and The Rite of Marriage PDFjoeyalmelorNo ratings yet
- Indeterminate Sentence LawDocument2 pagesIndeterminate Sentence LawMarlouis U. Planas100% (1)
- Everyone Is Beautiful and No One Is Horny - Blood KnifeDocument13 pagesEveryone Is Beautiful and No One Is Horny - Blood Knifestellarastrology646No ratings yet
- Essay of MacbethDocument9 pagesEssay of MacbethMaria Ximena Romero GaravitoNo ratings yet
- Berlin Airlift To Baader MeinhofDocument5 pagesBerlin Airlift To Baader MeinhofNick ShepleyNo ratings yet
- "El Filibusterismo, Resignation, and Exit": Jhonel E. Pido Bsed 4-9Document39 pages"El Filibusterismo, Resignation, and Exit": Jhonel E. Pido Bsed 4-9Shannen PabunanNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Administrative Order No. 95-19Document5 pagesSupreme Court Administrative Order No. 95-19jimmyNo ratings yet
- Civil Law vs. Criminal Law - A - Day - in - A - Civil - CourtDocument22 pagesCivil Law vs. Criminal Law - A - Day - in - A - Civil - CourtSpring MNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Speech and Assembly: Prior Restraint Near v. Minnesota 238 US 697Document25 pagesFreedom of Speech and Assembly: Prior Restraint Near v. Minnesota 238 US 697Earl Justine OcuamanNo ratings yet
- The People and The Nation: Home False FlagsDocument5 pagesThe People and The Nation: Home False FlagsGeovani Hernandez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Activity Design: Province of Surigao Del Norte City of Surigao Barangay WashingtonDocument4 pagesActivity Design: Province of Surigao Del Norte City of Surigao Barangay WashingtonKho Kent JohnNo ratings yet
- AP Human Geography 2015 Scoring Guidelines: Part A: (1 Point Total)Document8 pagesAP Human Geography 2015 Scoring Guidelines: Part A: (1 Point Total)Anand KancharlaNo ratings yet
- Company Law and Secretrial PracticeDocument3 pagesCompany Law and Secretrial PracticeGuruKPONo ratings yet
- Format For Filing Complaint Under The Protection of Women From Domestic Violence Act, 2005Document9 pagesFormat For Filing Complaint Under The Protection of Women From Domestic Violence Act, 2005tamalmukhNo ratings yet
- Batangas City v. Pilipinas Shell Petroleum Corp.Document2 pagesBatangas City v. Pilipinas Shell Petroleum Corp.Noreenesse Santos100% (1)
- BONSU v. FORSON (Ghana Case Law)Document6 pagesBONSU v. FORSON (Ghana Case Law)leonappiagyeiNo ratings yet
- Lore. Praetors of Dorn Space Marines ChapterDocument3 pagesLore. Praetors of Dorn Space Marines ChapterArjan Hoogervorst0% (1)
- Cam Hi ADocument4 pagesCam Hi AalexhwangNo ratings yet
- Corporate AccountingDocument79 pagesCorporate Accountingakshrajput2005No ratings yet
Notes
Notes
Uploaded by
mishrakumkum5260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThe document discusses contingent contracts and quasi contracts under Indian contract law. It defines contingent contracts as contracts that depend on an uncertain future event outside the parties' control. Insurance, indemnity, and guarantee contracts are examples. Quasi contracts are not true contracts as they lack elements like offer, acceptance and consideration, but courts will enforce obligations that arise from principles of equity and justice. The key differences between contingent contracts, quasi contracts and regular contracts are also summarized.
Original Description:
These are very helpful notes for students
Original Title
notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses contingent contracts and quasi contracts under Indian contract law. It defines contingent contracts as contracts that depend on an uncertain future event outside the parties' control. Insurance, indemnity, and guarantee contracts are examples. Quasi contracts are not true contracts as they lack elements like offer, acceptance and consideration, but courts will enforce obligations that arise from principles of equity and justice. The key differences between contingent contracts, quasi contracts and regular contracts are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesNotes
Notes
Uploaded by
mishrakumkum526The document discusses contingent contracts and quasi contracts under Indian contract law. It defines contingent contracts as contracts that depend on an uncertain future event outside the parties' control. Insurance, indemnity, and guarantee contracts are examples. Quasi contracts are not true contracts as they lack elements like offer, acceptance and consideration, but courts will enforce obligations that arise from principles of equity and justice. The key differences between contingent contracts, quasi contracts and regular contracts are also summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
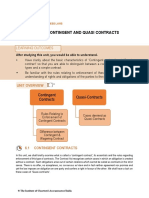
THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872
UNIT 6:- CONTIGENT CONTRACT AND QUASI
CONTRACT
DEFINATION OF CONTIGENT CONTRACT: “A contract to do or not to
do something, if some event, collateral to such contract, does or
does not happen”.
Contract of insurance, indemnity and guarantee fall under this category.
MEANING OF COLLATERAL EVENT: “An event which is neither a
performance directly promised as part of the contract, nor the
whole of the consideration for a promise”.
ESSENTIALS OF A CONTIGENT CONTRACT
The performance of a contingent contract would depend
upon the happening or non-happening of some event or condition.
The event referred to is collateral to the contract: the event is not part of the
contract.
The contingent event should not be a mere ‘will’ of the promisor.
The event must be uncertain: where the event is certain or bound to happen, the
contract is due to be performed, then it is not contingent contract.
RULES RELATING TO ENFORCEMENT
ENFORCEMENT OF CONTRACT CONTINGENT ON AN EVENT HAPPENING: Where a
contingent contract is made to do or not to do anything if an uncertain future
event happens, it cannot be enforced by law unless and until that event has
happened. If the event becomes impossible, such contract becomes void.
ENFORCEMENT OF CONTRACT CONTINGENT ON AN EVENT NOT HAPPENING:
Where a contingent contract is made to do or not do anything if an uncertain
future event does not happen, it can be enforced only when the happening of that
event becomes impossible and not before.
A CONTRACT WOULD CEASE TO BE ENFORCEABLE IF IT IS CONTINGENT UPON THE
CONDUCT OF A LIVING PERSON WHEN THAT LIVING PERSON DOES SOME THING TO
MAKE THE ‘EVENT’ OR ‘CONDUCT’ AS IMPOSSIBLE OF HAPPENING: If a contract is
contingent upon as to how a person will act at an unspecified time, the event shall
be considered to have become impossible when such person does anything which
renders it impossible that he should so act within any definite time or otherwise
than under further contingencies.
CONTINGENT ON HAPPENING OF SPECIFIED EVENT WITHIN THE FIXED TIME:
Contingent contracts to do or not to do anything, if a specified uncertain event
happens within a fixed time, becomes void if, at the expiration of time fixed, such
event has not happened, or it, before the time fixed, such event becomes
impossible.
CONTINGENT ON SPECIFIED EVENT NOT HAPPENING WITHIN FIXED TIME:
Contingent contracts to do or not to do anything, if a specified uncertain event
does not happen within a fixed time, may be enforced by law when the time fixed
has expired, and such event has not happened or before the time fixed has expired,
if it becomes certain that such event will not happen.
ARHAM INSTITUTE, CA VARDHAMAN DAGA, 9039600091 Page 29
THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872
CONTINGENT ON AN IMPOSSIBLE EVENT: Contingent contract to do or not to do
anything, if an impossible event happens are void.
DIFFERNCE BETWEEN CONTINGENT CONTRACT AND A WAGERING CONTRACT
BASIS CONTINGENT CONTRACT WAGERING CONTRACT
MEANING Is a contract to do or not to do
Is a promise to give money or
something with reference to a
money’s worth with reference
collateral event happening or not
to an uncertain event
happening. happening or not happening.
RECIPROCAL PROMISE May not contain reciprocal
It consists of reciprocal
promise. promise.
UNCERTAIN EVENT The event is collateral.
The uncertain event is the
core factor.
NATURE OF CONTRACT May not be wagering nature Is essential contingent in
nature
DOCTRINE OF Is not based on doctrine of It is a game, losing and
MUTAILITY OF LOSE mutability of lose and gain. gaining alone matters.
AND GAIN
EFFECT OF CONTRACT Valid Void
QUASI CONTRACTS
Sometimes the law implies a promise obligations on one party and conferring right in
favour of the other even when there is no offer, no acceptance, no genuine consent,
lawful consideration, etc. And in fact neither agreement nor promise. Such cases are not
contracts in the strict sense, but the court recognises them as RELATIONS RESEMBLING
THOSE OF CONTRACTS and enforce them as if they are contracts. Quasi contracts are
based on principles of equity, justice and good conscience. A quasi or constructive
contracts rests upon the maxims, “No man just grow rich out of another person loss”. In
India it is called as “CERTAIN RELATION RESEMBLING THOSE CREATED BY CONTRACTS”.
FEATURES OF QUASI CONTRACTS:
In the first place, such a right is always a right to money and generally, through not
always, to a liquidated sum of money.
Secondly, it does not arise from any agreement of the parties concerned, but is
imposed by the law; and
Thirdly, it is a right which is available not against all the world, but against a
particular person or persons only, so that in this respect it resembles a contractual
right.
CASES DEEMED AS QUASI CONTRACT
CLAIM FOR NECESSARIES SUPPLIED TO PERSONS INCAPABLE OF CONTRACTING: The
person who has furnished such supplies is entitled to be reimbursed from the
property of such incapable person.
ARHAM INSTITUTE, CA VARDHAMAN DAGA, 9039600091 Page 30
THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872
PAYMENT BY AN INTERESTED PERSON: A person who is interested in the payment
of money which another is bound by law to pay, and who therefore pays it, is
entitled to be reimbursed by the other.
OBLIGATION OF A PERSON ENJOYING BENEFITS OF NON-GRATUITOUS ACT: Where
a person lawfully does anything for another person, or delivers anything to him not
intending to do gratuitously and such other person enjoys the benefits thereof, the
latter is bound to pay compensation to the former in respect of, or to restore, the
things so done or delivered.
RESPONSIBILITY OF FINDER OF GOODS:
i) To take proper care of the property as man of ordinary prudence would
take.
ii) No right to appropriate the goods and
iii) To restore the goods if the owner is found.
MONEY PAID BY MISTAKE OR UNDER COERCION: A person to whom money has
been paid or anything delivered by mistake or under coercion, must repay or
return it.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN QUASI CONTRACTS AND CONTRACTS
BASIS QUASI CONTRACT CONTRACT
ESSENTIAL FOR THE Absent Present
VALID CONTRACTS
OBLIGATIONS Imposed by law Created by the consent of the
parties
ARHAM INSTITUTE, CA VARDHAMAN DAGA, 9039600091 Page 31
You might also like
- Contract of GuaranteeDocument26 pagesContract of GuaranteeSrishti Jain100% (1)
- 18 Disciplines of NinjutsuDocument1 page18 Disciplines of NinjutsutakedashindenNo ratings yet
- FLOATEL SUPERIOR SPECIFICATION DetailsDocument2 pagesFLOATEL SUPERIOR SPECIFICATION DetailsIsmail ZainolNo ratings yet
- Asking The People For Their MoneyDocument13 pagesAsking The People For Their MoneyTCFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6agarwalpawan1No ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument7 pagesContingent ContractsTanvir Sadik AkashNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument6 pagesContingent ContractsHemant AroraNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractsDocument3 pagesContingent ContractsRaza ZeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 - Quasi Contract and Chapter-13 - Unjust EnrichmentDocument3 pagesChapter - 12 - Quasi Contract and Chapter-13 - Unjust EnrichmentManish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heritage Law CollegeDocument8 pagesHeritage Law CollegeMUSKAN AGARWALNo ratings yet
- CONTIGENT - ASSIGNMENT - Sagar 47Document15 pagesCONTIGENT - ASSIGNMENT - Sagar 47Sagar JoonNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument9 pagesContingent ContractAli ShahNo ratings yet
- CHINNAYA VDocument20 pagesCHINNAYA VAshwin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Ica Unit 2 PDFDocument6 pagesIca Unit 2 PDFvxnyrxoheNo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act Chapter - 6Document4 pagesIndian Contract Act Chapter - 6basraniharsh916No ratings yet
- Contingent Contracts (Section 31 in The Indian Contract Act, 1872)Document17 pagesContingent Contracts (Section 31 in The Indian Contract Act, 1872)harish_100_inNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument40 pagesContingent ContractSAUMYA GIRINo ratings yet
- Indian Contract Act 1872Document25 pagesIndian Contract Act 1872sjkushwaha21100% (1)
- Contract First DraftDocument9 pagesContract First DraftVishalNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument43 pagesContingent ContractJayanth Prakash100% (1)
- Contingent ContractDocument20 pagesContingent ContractKrutika AshtikarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: Contract of Indemnity v. Contract of GuaranteeDocument23 pagesIntroduction To: Contract of Indemnity v. Contract of GuaranteeStuti BaradiaNo ratings yet
- BL 1Document32 pagesBL 1Varesh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Frustration of ContractDocument4 pagesDoctrine of Frustration of ContractRaghavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Contingent ContractsDocument2 pagesChapter 8: Contingent ContractsPratyusha DashNo ratings yet
- BR 2Document65 pagesBR 2shashankd2804No ratings yet
- Contingent Contract-Event Based ContractDocument2 pagesContingent Contract-Event Based ContractSIIB SURATNo ratings yet
- ConsiderationDocument4 pagesConsiderationSOUMYA SUCHARITA TRIPATHYNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation Law Colourful Summary NotesDocument113 pagesCa Foundation Law Colourful Summary Notesprerana sharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Legal AspectsDocument58 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Legal AspectsNurarief Affendy100% (1)
- Agreements Expressly Declared VoidDocument7 pagesAgreements Expressly Declared VoidAdeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wagering Agreement Amp Contingent Contract PDF PDF FreeDocument9 pagesWagering Agreement Amp Contingent Contract PDF PDF FreeSlakrkeNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6: Contingent and Quasi Contracts: Learning OutcomesDocument11 pagesUnit - 6: Contingent and Quasi Contracts: Learning OutcomesE20PA063 MAHALAKSHMI.BNo ratings yet
- Intro To Contract ActDocument28 pagesIntro To Contract ActRahulNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract Under Contract Act 1872Document37 pagesLaw of Contract Under Contract Act 1872Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Problems Insurance 2Document13 pagesFinal Problems Insurance 2CloieRjNo ratings yet
- Contract of IndemnityDocument11 pagesContract of IndemnitySuresh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Contracts - Question and AnswersDocument9 pagesContracts - Question and Answersbbtqwrws78No ratings yet
- Contract of Guaranty and SuretyshipDocument6 pagesContract of Guaranty and SuretyshipNicole Reign EscusaNo ratings yet
- LLM - Iv Semester Law of Contract - Ii: Study MaterialDocument20 pagesLLM - Iv Semester Law of Contract - Ii: Study MaterialSuman sharmaNo ratings yet
- Contingent Contract: Presented byDocument28 pagesContingent Contract: Presented byIqra AfsarNo ratings yet
- Essentials of ContractDocument7 pagesEssentials of Contractsolitary soulNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument4 pagesDefinitionsGulka TandonNo ratings yet
- Contract of GuaranteeDocument9 pagesContract of Guarantee23.divyansh.kNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872: Unit - 1Document7 pagesThe Indian Contract Act, 1872: Unit - 1Raj DasNo ratings yet
- Contingent Contract: Chapter III: of Contingent Contracts Sections 31 To 36Document13 pagesContingent Contract: Chapter III: of Contingent Contracts Sections 31 To 36PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon PDFDocument37 pagesOblicon PDFDiana Grace SierraNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract - Roll No. 213112Document26 pagesLaw of Contract - Roll No. 213112Anita SudalaimaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Law For EngineersDocument40 pagesBasic Law For EngineersBhargav SarvepalliNo ratings yet
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872Document9 pagesThe Indian Contract Act, 1872Venugopal PandeyNo ratings yet
- Contingent ContractDocument16 pagesContingent ContractPratik Raj100% (1)
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow 2019-2020Document11 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow 2019-2020sakshi barfalNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6: Contingent and Quasi ContractsDocument11 pagesUnit - 6: Contingent and Quasi ContractsRahulNo ratings yet
- 74585bos60476 FND p2 Nset cp2 U6Document15 pages74585bos60476 FND p2 Nset cp2 U6Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Prudential Bank vs. Intermediate Appellate CourtDocument20 pagesPrudential Bank vs. Intermediate Appellate CourtAaron CariñoNo ratings yet
- Week 3-5 GuaranteeDocument108 pagesWeek 3-5 GuaranteeRamkumaar MadhavanNo ratings yet
- The Phrase Indemnity MeansDocument9 pagesThe Phrase Indemnity MeansArushiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture ThreeDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 6 Minors Cont... Lecture Threesimangalisokhoza37No ratings yet
- 7 Gilat Satellite VS United Coconut Planters BankDocument17 pages7 Gilat Satellite VS United Coconut Planters BankKyla Ellen CalelaoNo ratings yet
- Contract of Indemnity Case Laws: Ankita Toppo, Sanchita TiwariDocument4 pagesContract of Indemnity Case Laws: Ankita Toppo, Sanchita TiwariSruti BansalNo ratings yet
- BR Study MaterialDocument5 pagesBR Study Materialal isra veliyancodeNo ratings yet
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesFrom EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawFrom EverandBigger Problems: Major Concepts for Understanding Transactions under Islamic lawNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Act 1 Scene 5Document8 pagesYear 10 Act 1 Scene 5Zachary ConcessioNo ratings yet
- He Imes Eader: House Oks Debt DealDocument44 pagesHe Imes Eader: House Oks Debt DealThe Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Masoud AlamDocument1 pageMohammed Masoud AlamGokulam ExportsNo ratings yet
- The Israel Lobby in GermanyDocument8 pagesThe Israel Lobby in GermanyChrist Is BackNo ratings yet
- Sample Position PaperDocument19 pagesSample Position PaperWayne C.No ratings yet
- The History of The Mauryan Empire in IndiaDocument13 pagesThe History of The Mauryan Empire in Indiapurinaresh85No ratings yet
- Case Analysis Paper - Code of Conduct V2Document4 pagesCase Analysis Paper - Code of Conduct V2Charven VillamorNo ratings yet
- Shell V NLU Translated VersionDocument5 pagesShell V NLU Translated Versionmccm92No ratings yet
- Eucharistic Celebration and The Rite of Marriage PDFDocument25 pagesEucharistic Celebration and The Rite of Marriage PDFjoeyalmelorNo ratings yet
- Indeterminate Sentence LawDocument2 pagesIndeterminate Sentence LawMarlouis U. Planas100% (1)
- Everyone Is Beautiful and No One Is Horny - Blood KnifeDocument13 pagesEveryone Is Beautiful and No One Is Horny - Blood Knifestellarastrology646No ratings yet
- Essay of MacbethDocument9 pagesEssay of MacbethMaria Ximena Romero GaravitoNo ratings yet
- Berlin Airlift To Baader MeinhofDocument5 pagesBerlin Airlift To Baader MeinhofNick ShepleyNo ratings yet
- "El Filibusterismo, Resignation, and Exit": Jhonel E. Pido Bsed 4-9Document39 pages"El Filibusterismo, Resignation, and Exit": Jhonel E. Pido Bsed 4-9Shannen PabunanNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Administrative Order No. 95-19Document5 pagesSupreme Court Administrative Order No. 95-19jimmyNo ratings yet
- Civil Law vs. Criminal Law - A - Day - in - A - Civil - CourtDocument22 pagesCivil Law vs. Criminal Law - A - Day - in - A - Civil - CourtSpring MNo ratings yet
- Freedom of Speech and Assembly: Prior Restraint Near v. Minnesota 238 US 697Document25 pagesFreedom of Speech and Assembly: Prior Restraint Near v. Minnesota 238 US 697Earl Justine OcuamanNo ratings yet
- The People and The Nation: Home False FlagsDocument5 pagesThe People and The Nation: Home False FlagsGeovani Hernandez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Activity Design: Province of Surigao Del Norte City of Surigao Barangay WashingtonDocument4 pagesActivity Design: Province of Surigao Del Norte City of Surigao Barangay WashingtonKho Kent JohnNo ratings yet
- AP Human Geography 2015 Scoring Guidelines: Part A: (1 Point Total)Document8 pagesAP Human Geography 2015 Scoring Guidelines: Part A: (1 Point Total)Anand KancharlaNo ratings yet
- Company Law and Secretrial PracticeDocument3 pagesCompany Law and Secretrial PracticeGuruKPONo ratings yet
- Format For Filing Complaint Under The Protection of Women From Domestic Violence Act, 2005Document9 pagesFormat For Filing Complaint Under The Protection of Women From Domestic Violence Act, 2005tamalmukhNo ratings yet
- Batangas City v. Pilipinas Shell Petroleum Corp.Document2 pagesBatangas City v. Pilipinas Shell Petroleum Corp.Noreenesse Santos100% (1)
- BONSU v. FORSON (Ghana Case Law)Document6 pagesBONSU v. FORSON (Ghana Case Law)leonappiagyeiNo ratings yet
- Lore. Praetors of Dorn Space Marines ChapterDocument3 pagesLore. Praetors of Dorn Space Marines ChapterArjan Hoogervorst0% (1)
- Cam Hi ADocument4 pagesCam Hi AalexhwangNo ratings yet
- Corporate AccountingDocument79 pagesCorporate Accountingakshrajput2005No ratings yet