Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SG5 Integration
SG5 Integration
Uploaded by
Fate VargasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SG5 Integration
SG5 Integration
Uploaded by
Fate VargasCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.
105-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 5: Unit 5-- Integration
Module No. 5
Unit 5- Integration
MODULE OVERVIEW
Learner-centered psychological principles are widely shared and implicitly recognized in
many good programs found in today’s schools and are consistent with more than a century of study
on teaching and learning. They also combine research and practice in developmental, educational,
experimental, social, clinical, organizational, community, and school psychology, among other
fields. Furthermore, these ideas are based on conventional and scientific knowledge. They include
not only learner-centered ideas that can lead to good schooling, but also principles that can
contribute to positive mental health and productivity in our nation’s children, teachers, and the
systems that support them.
Learner-centered psychological concepts provide a framework for designing and
integrating the elements of new schooling approaches. The active and reflective aspect of learning
and learners is emphasized by these ideas. From this standpoint, educational practice will most
likely improve if the educational system is restructured with the student as the major focus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
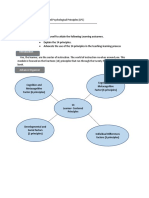
A. Integrate the 14 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles to the concepts previously learned in this course;
B. Cite the importance of learning the 14 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles in Facilitating Learning.
LEARNING CONTENTS
COGNITIVE AND METACOGNITIVE FACTOR
1. Nature of Learning Process
Learning complicated subject matter is most effective when it is a collaborative international
process of generating meaning from information and experience.
2. Goals of the Learning Process
Over time, with assistance and instructional supervision, a successful learner can construct
meaningful, coherent representations of knowledge.
3. Construction of Knowledge
A successful learner may make meaningful connections between new material and previous
knowledge. As students continue to make connections between new information and
experiences and their existing knowledge base, their knowledge expands and deepens.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY PAGE \* MERGEFORMAT 1
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.105-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 5: Unit 5-- Integration
4. Strategic Thinking
To attain complicated learning goals, a successful learner can develop and employ a repertoire of
thinking and reasoning skills. In their approach to learning, successful learners use reasoning,
problem solving, and concept learning.
5. Thinking about thinking
Successful learners can examine how they think and learn, set realistic learning or performance
goals, choose possibly appropriate learning tactics or methods, and track their progress toward
these objectives.
6. Context of Learning
Environmental elements, such as culture, technology, and instructional approaches, have an
impact on learning.
MOTIVATIONAL AND AFFECTIVE FACTOR
7. Motivational and emotional influences on learning
The learner’s rich internal world of thoughts, beliefs, aspirations, and expectations for success or
failure can either improve or hinder his or her ability to think and process information.
8. Intrinsic motivation to learn
Intrinsic motivation is sparked by tasks that are both unique and challenging, relevant to
personal interests, and allow for personal choice and control.
9. Effects of motivation on effort
Another important predictor of motivation to learn is effort. The acquisition of complicated
knowledge and abilities necessitates a significant amount of energy and purposeful effort on the
part of the learner, as well as tenacity throughout time.
DEVELOPMENTAL AND SOCIAL FACTOR
10. Developmental influences on learning
Learning is most effective when differences in development are considered within and across the
physical, intellectual, emotional, and social domains. Individuals learn best when material is
tailored to their developmental stage and delivered in a fun and engaging manner.
11. Social influences on learning
When a learner gets the opportunity to communicate and work with others on instructional
assignments, their learning is boosted.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY PAGE \* MERGEFORMAT 1
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.105-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 5: Unit 5-- Integration
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES FACTOR
12. Individual differences in learning
Individuals are born with their own traits and talents, which they develop over time. Educators
must assist students in examining their learning preferences and, if required, expanding or
modifying them.
13. Learning and diversity
All learners share the same core principles of learning, motivation, and effective instruction.
14. Standards and assessment
At every level of the learning process, assessment gives crucial information to both the learner
and the teacher.
LEARNING POINTS
The learner and the learning process are addressed by the 14 psychological principles.
Rather than conditioned habits or physiological causes, they concentrate on psychological
elements that are essentially internal to and under the control of the learner. The principles, on
the other hand, attempt to take into account the external environment or contextual elements
that interact with these internal components. The concepts are designed to deal with learners
holistically in real-world learning contexts. As a result, they're best comprehended as a collection
of principles; no one premise should be considered in isolation. The 14 principles are organized
into four categories that influence learners and learning: cognitive and metacognitive,
motivational and affective, developmental and social, and individual differences. Finally, the
principles are designed to apply to all learners in our educational system, including children,
teachers, administrators, parents, and community members.
LEARNING ACTIVITIES
Accomplish the following: (45 pts.)
1. Device a mnemonic to easily remember the 14 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles. (10 pts.)
2. Integrate the 14 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles to the concepts previously learned in this course by
citing examples under each. (28 pts.)
3. Cite the importance of learning the 14 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles in Facilitating Learning. (7 pts.)
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY PAGE \* MERGEFORMAT 1
Study Guide in Prof.Ed.105-Facilitating Learner Centered-Teaching Module 5: Unit 5-- Integration
REFERENCE
APA Work Group of the Board of Educational Affairs (1997, November). Learner-centered
psychological principles: A framework for school reform and redesign. Washington, D.C.:
American Psychological Association.
PANGASINAN STATE UNIVERSITY PAGE \* MERGEFORMAT 1
You might also like
- Short Stories in Brazilian Portuguese For BeginnersDocument211 pagesShort Stories in Brazilian Portuguese For BeginnersMarina AngelidouNo ratings yet
- Kaplan QuicksheetsDocument27 pagesKaplan Quicksheetschanheejung024No ratings yet
- Prof Ed 1 Lecture 1 Learner Centered PrinciplesDocument65 pagesProf Ed 1 Lecture 1 Learner Centered PrinciplesDee Em87% (52)
- The Child and Adolescent LearnersDocument179 pagesThe Child and Adolescent LearnersMyla Guab100% (1)
- Course Title Course Code Number of UnitsDocument6 pagesCourse Title Course Code Number of UnitsMingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LearnerDocument9 pagesModule 2 LearnerJayson PalmaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 FaciDocument5 pagesModule 5 FaciAngelo CaoileNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Integration: Module OverviewDocument5 pagesUnit 5-Integration: Module OverviewMAYLENE CALICDANNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 The Child and Adoloscent LearnersMyla GuabNo ratings yet
- Module-Child and Adolescent LearnerDocument85 pagesModule-Child and Adolescent LearnerAira Jane BaliquiaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Frances Bea Abarado100% (1)
- 01 Learner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pages01 Learner - Centered Psychological PrinciplesKristine Saron GalaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Ped 1 - 18 - Assignment 1 - 2Document5 pagesPed 1 - 18 - Assignment 1 - 2erick tahelNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument14 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesShechem JonesNo ratings yet
- PED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMDocument43 pagesPED01 Learning Module PRELIMINARY TERMMicah Esteban OngpaucoNo ratings yet
- MODULE FACILITATING LEARNING FOR STUDENTS WordDocument217 pagesMODULE FACILITATING LEARNING FOR STUDENTS WordHANEYZIL LARANGJONo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument13 pagesUNIT 4 - Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesZarry ZackNo ratings yet
- 14 Learner-Centered Principle: Cmcacalda19 OCTOBER 23, 2017Document3 pages14 Learner-Centered Principle: Cmcacalda19 OCTOBER 23, 2017Mary Cherish FerrerNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachingDocument5 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered TeachingHelna CachilaNo ratings yet
- The LearnerDocument11 pagesThe LearnerAlexa Khrystal Eve GorgodNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Facilitating LearnerDocument9 pagesWeek 2 Facilitating LearnerNoemi PachocoNo ratings yet
- Module Child and Ado Lesson 1 PDFDocument12 pagesModule Child and Ado Lesson 1 PDFDominic Julius RamosNo ratings yet
- Educ 101Document35 pagesEduc 101Cyrell Joshua Salas100% (1)
- Revisiting the-WPS OfficeDocument22 pagesRevisiting the-WPS OfficeJa Sarmiento67% (3)
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles: BackgroundDocument2 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles: BackgroundMajoy TurcolasNo ratings yet
- Ed 1 Introduction LCPDocument27 pagesEd 1 Introduction LCPJimeniah Ignacio RoyoNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6313653169777345964Document7 pagesInbound 6313653169777345964Reina Mae PorcareNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Document13 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles Module 1Rea Jane OrnedoNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument2 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesKatkatNo ratings yet
- Module Child and Ado Lesson 1Document9 pagesModule Child and Ado Lesson 1Lanie Ballesteros TiuNo ratings yet
- 14 Learning Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument3 pages14 Learning Centered Psychological PrinciplesLean Dominic BorlazaNo ratings yet
- Learner - Centered Psychological Principles: Bernardo Fernandez II, MSP, CHRP, CLSSYBDocument35 pagesLearner - Centered Psychological Principles: Bernardo Fernandez II, MSP, CHRP, CLSSYBBernardNo ratings yet
- Learner - Centered Psychological Principles: Reporter: Gerardo M. Altamia Jr. CherylDocument17 pagesLearner - Centered Psychological Principles: Reporter: Gerardo M. Altamia Jr. CherylZtik PeraltaNo ratings yet
- ED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Document9 pagesED123 Unit 1 Lesson 3Yogine M BarongNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaDocument6 pagesModule 2. Daphne B. Abonita and Monneth MatayaGeorgie AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Fourteen Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument9 pagesFourteen Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesKimay DanielNo ratings yet
- 14 PsychologicalPrinciplesDocument23 pages14 PsychologicalPrinciplesJane AgripaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument39 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching 02 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJonathan AysonNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument3 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesMichael NatividadNo ratings yet
- Why Are Psychological Principles ImportantDocument3 pagesWhy Are Psychological Principles ImportantIYF Region llNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed ReviewerDocument54 pagesProf Ed ReviewerAniah OdinNo ratings yet
- St. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Document8 pagesSt. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800JESS ARCEONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Unit 2Document9 pagesChapter 1 Unit 2DELA CRUZ KRISTINE Y.No ratings yet
- The LearnerDocument2 pagesThe LearnerChe WalaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Document6 pagesActivity 1 Module 1 FLCT The Learning Principles.Juedy Lala PostreroNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Learning PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Learning PrinciplesJohn Mark NovenoNo ratings yet
- WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document5 pagesWMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00: Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)My Home100% (1)
- Learner CenteredDocument7 pagesLearner Centeredapi-302157367No ratings yet
- 14 LEARNER-CENTERED e - 1Document6 pages14 LEARNER-CENTERED e - 1Angelito S. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1Dhaze OjanoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument9 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesCecelien Salgado AntonioNo ratings yet
- 2prof Ed 02Document17 pages2prof Ed 02airen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Part IDocument17 pagesPart Iairen bandolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Ed123Document7 pagesLesson 5 Ed123Julie Ann Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- Written Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aDocument13 pagesWritten Report Unit 2 Bsed Fil 1aaira mambagNo ratings yet
- Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument34 pagesLearner Centered Psychological PrinciplesPaulgarcia AngelesNo ratings yet
- Classroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- Learning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualFrom EverandLearning & Study Guide for Adult Students: Teacher's ManualNo ratings yet
- From Struggle to Success: Practical Study Techniques for Every StudentFrom EverandFrom Struggle to Success: Practical Study Techniques for Every StudentNo ratings yet
- The Adult Learners Handbook: Step-By-Step to Deliberate Practice, Active Recall And a Growth MindsetFrom EverandThe Adult Learners Handbook: Step-By-Step to Deliberate Practice, Active Recall And a Growth MindsetNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG4Document11 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG4Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG1-1Document6 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG1-1Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 108 SG2Document7 pagesProf. Ed. 108 SG2Fate VargasNo ratings yet
- SG1 Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument5 pagesSG1 Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesFate VargasNo ratings yet
- Q1 W1 MtbmleDocument10 pagesQ1 W1 MtbmleMaria Cristina AguantaNo ratings yet
- TABLIZO. Pricniples of Teaching-Learning Styles. PPT. The Teaching of Lit & CompositionDocument17 pagesTABLIZO. Pricniples of Teaching-Learning Styles. PPT. The Teaching of Lit & CompositionJiwon ParkNo ratings yet
- Educational Psychology 5th EditionDocument9 pagesEducational Psychology 5th EditionDiary Vlog100% (1)
- Cognitive Biases in A Nutshell Understanding The Common Mental Shortcuts We Use Everyday (Thinknetic) (Z-Library)Document141 pagesCognitive Biases in A Nutshell Understanding The Common Mental Shortcuts We Use Everyday (Thinknetic) (Z-Library)Alwin BennyNo ratings yet
- AI Session 2 SlidesDocument47 pagesAI Session 2 SlidesShame BopeNo ratings yet
- Language Across The Currriculum - English - For PrintingDocument216 pagesLanguage Across The Currriculum - English - For PrintingPriyadharsinee jayakumarNo ratings yet
- What Is AIDocument3 pagesWhat Is AISiju V SomanNo ratings yet
- Motor Control Models: Learning and Performance: Pietro G Morasso, Italian Institute of Technology, Genoa, ItalyDocument8 pagesMotor Control Models: Learning and Performance: Pietro G Morasso, Italian Institute of Technology, Genoa, Italytanvir anwarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Countries and Origins (3º Ano)Document3 pagesLesson Plan - Countries and Origins (3º Ano)Jéssica FernandesNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Value: A Literature ReviewDocument26 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Business Value: A Literature ReviewDalal MouaniNo ratings yet
- Pp2 Schemes of Work Psychomotor SkillsDocument7 pagesPp2 Schemes of Work Psychomotor Skillsvincent mugendiNo ratings yet
- Shyterria Redd - Module 05 Written Assignment - 070523Document5 pagesShyterria Redd - Module 05 Written Assignment - 070523BrianNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument93 pagesPreviewpdfjaime luque lopezNo ratings yet
- History of Psychology Slide ShowDocument20 pagesHistory of Psychology Slide ShowJohn Alldrin Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- L&T HarshitaDocument17 pagesL&T HarshitaNikita JainNo ratings yet
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument19 pagesCognitive PsychologyyoucanseemarizflyNo ratings yet
- CSCS24 Paper 42 yDocument6 pagesCSCS24 Paper 42 yDaniela HossuNo ratings yet
- Husserl'S Concept of Categorial Intuition: Dieter LohmarDocument2 pagesHusserl'S Concept of Categorial Intuition: Dieter LohmarDavis Kaspars SprogisNo ratings yet
- The Expertise Reversal EffectDocument10 pagesThe Expertise Reversal EffectPablo RuisotoNo ratings yet
- PSC 100 Lec 3 Perception NotesDocument2 pagesPSC 100 Lec 3 Perception NotesAsher OlsonNo ratings yet
- Q4 MathDocument11 pagesQ4 MathMAE HERNANDEZ100% (1)
- Canonical Word Order in TagalogDocument55 pagesCanonical Word Order in Tagalogsevilla.laurenceNo ratings yet
- 4.advance Organizer Model - David Ausubel's.pptx2Document15 pages4.advance Organizer Model - David Ausubel's.pptx2Ashmi DarwinNo ratings yet
- EDA 5 Activity 5-Job-Interviews Cuarto 2023Document2 pagesEDA 5 Activity 5-Job-Interviews Cuarto 2023PEREZ BANDINI DE PALOMINO SUSANA MILAGROSNo ratings yet
- Illustrations in Children's BooksDocument3 pagesIllustrations in Children's BooksAisha RahatNo ratings yet
- The Importance, Meaning, and Assumptions of ArtDocument6 pagesThe Importance, Meaning, and Assumptions of ArtRyan Paul CaalemNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Metacognition A Textbook For Cognitive Educational Lifespan and Applied Psychology PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Metacognition A Textbook For Cognitive Educational Lifespan and Applied Psychology PDFmitchell.clinard764100% (43)
- Sarah Evans SubmissionDocument8 pagesSarah Evans SubmissionJovana MarNo ratings yet