Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TP1 Kinetic Theory of Matter
TP1 Kinetic Theory of Matter
Uploaded by
Thabang Sbo PhokontsiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TP1 Kinetic Theory of Matter
TP1 Kinetic Theory of Matter
Uploaded by
Thabang Sbo PhokontsiCopyright:
Available Formats
1
KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER
Matter is made up of small particles called atoms or a group of chemically combined
atoms called molecules. The size of each particle is different for different materials.
The distance between molecules can change depending on the Internal Energy
(kinetic + potential) of the molecule or atom.
Particles are always in motion (moving). The higher the temperature the faster the
molecules move/vibrates.
At the same temperature, all molecules have the same energy. Small particles move
faster while heavy particles moves slowly.
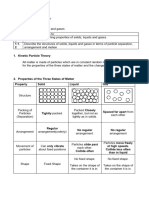
States Of Matter
States of
SOLIDS LIQUIDS GASES
matter
Have no definite shape
Have a definite volume
Have a definite or volume. (wholly fills
but no definite shape
volume and definite up the container and
Properties (takes the shape of the
shape. takes the shape of the
container).
Not compressible container).
Slightly compressible
Highly compressible
Particles slightly further Particles are much further
Distance
Particles are very close apart than in solids but still apart. So gases can be
between
to each other close together to have a compressed or squeezed in
particles
definite volume. smaller space.
Forces
Held by strong forces Particle held by less strong
between Less forces of attraction.
of attraction. forces.
particles
Moves freely at high speed
Particles vibrate to and
Motion of colliding with each other
fro about a fixed Free to move
particles and the walls of the
position.
container.
Motion of Gas Molecules and its Temperature and Pressure.
If a gas is heated in a closed container, its molecules gain more kinetic energy and hit the
walls of the container more frequently (The frequency of collisions increases). This causes an
increase in pressure on the walls of the container. The faster the gas molecules move, the
higher the temperature they attain. The gas container can explode if it can’t withstand the
pressure build up.
Physics Notes: KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER. leemok productions 2012©
2
Brownian Motion
Brownian motion gives us the evidence that molecules in suspension (gases) are constantly
moving. When smoke is trapped in a glass box (smoke cell) and is observed with a
microscope, the smoke particle can be seen as bright specks moving around in a random and
haphazard manner.
The smoke particles move haphazardly because they collide with gas molecules that move at
high velocities at random paths. Smoke particles are bigger compared to air particles. The
specks of light seen is where collision between smoke particles and air particles occur. This
phenomena is known as Brownian motion.
Evaporation
Evaporation is the escape of high energy molecules from the surface of a liquid. Evaporation
results in a drop in the temperature of the liquid from which the molecules escaped. This is
because the molecules that escape acquire energy to do so from those which remain in the
liquid. Evaporation only takes place at the surface of the liquid and occurs at any
temperature.
Factors That Affect Evaporation
A number of factors affect the rate of evaporation. These are;
Wind speed (drought).An increase in wind speed causes an increase in rate of
evaporation
Surface area. The larger the surface area the higher the rate of evaporation.
Temperature. The higher the temperature the higher the rate of evaporation.
Humidity. The higher the humidity the lower the rate of evaporation.
Applications of evaporation
Ether is used in fridges to cool their interiors
Water sacks are put under the shade and moistened with water so that the water inside
cools as the molecules outside evaporate.
Organisms cool themselves by evaporation using different ways,
. Dogs = Panting
Elephants= Flap their ears
Humans= Perspiration
Plants=Evaporation from leaves
Physics Notes: KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER. leemok productions 2012©
You might also like
- Module 15 - Fluid Properties PDFDocument3 pagesModule 15 - Fluid Properties PDFClark Sibi67% (3)
- Measurement: DEE10013 DevicesDocument17 pagesMeasurement: DEE10013 DevicesAmir EqwanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic SusceptibilityDocument19 pagesMagnetic SusceptibilityPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 09Document16 pagesCapitulo 09Tamires MarianeNo ratings yet
- TP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1Document2 pagesTP1 - Kinetic Theory of Matter 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)Document41 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings ( Prashant Kirad ) (1)nidhimathapati123No ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10Document10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of Matter 2023 Year 10sarah awadNo ratings yet
- Third Form Packet WorkDocument19 pagesThird Form Packet WorkLizbeth Chi100% (1)
- States of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Solids Liquids and GasesMatipa DembureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument4 pagesMATTERRajiv BiswasNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Notes - Matter in Our Surroundings - ExpDocument6 pagesNotes - Matter in Our Surroundings - Expdeborah hildaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Document1 pageKinetic Molecular Theory Sept.17Clint ArranchadoNo ratings yet
- 2-Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pages2-Thermal PhysicsSamah Hafez100% (1)
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademyDocument14 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- Notes - Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument7 pagesNotes - Kinetic Theory of MatterAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- Key Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesDocument3 pagesKey Terms Definitions Particle Theory: Properties Properties PropertiesShimaa ElsharnobyNo ratings yet
- 6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346Document5 pages6463 Topper 21 101 1 2 18 1122 States of Matter Up201701031203 1483425218 7346avantikajethani20No ratings yet
- Resource 1Document13 pagesResource 1eeren41789No ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterDocument10 pagesCh. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterهندNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingDocument28 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingPrabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Transfer IDocument6 pagesThermal Transfer Iashane dwightNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- Revision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryDocument14 pagesRevision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryFarah LangrialNo ratings yet
- C1 Chapter 1Document1 pageC1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) Notes MatterDocument9 pagesChapter-1 (Matter in Our Surroundings) Notes MatterAtharva VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Particulate Nature of MatterDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - Particulate Nature of MatterPhillipe WalkerNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundingslogabi3459No ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheorykimNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry HO 01Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry HO 01AINo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSNo ratings yet
- The States of Matter CWDocument3 pagesThe States of Matter CWPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Y9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesDocument10 pagesY9 CH 1 & CH 2 NotesTeck TieNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document11 pagesiGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document58 pagesChem 1Heba HebaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic TheoryDocument4 pagesThe Kinetic TheoryMystica InnissNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsRusher SigueNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesLesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesおっぱいNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1Document37 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1AbdullaahNo ratings yet
- CH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Document13 pagesCH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics FlashcardsDocument18 pagesThermal Physics FlashcardsKhushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- 3 1Document90 pages3 1Joy MercadoNo ratings yet
- Matters in Our SurroundingDocument48 pagesMatters in Our SurroundingXm PiratesNo ratings yet
- P.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamDocument2 pagesP.E.N.School Class: Vi, Vii VisakhapatnamAnonymous IqtpuNEF0No ratings yet
- Phyw 2Document42 pagesPhyw 2Sajjad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowDocument8 pagesSolids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowAmelia AuclairNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument8 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1rida ikramNo ratings yet
- Given: (2) Find: (3) Formula: (4) Solution: (5) Final AnswerDocument5 pagesGiven: (2) Find: (3) Formula: (4) Solution: (5) Final AnswerEmpz CasesNo ratings yet
- Damper Resistor For LV MotorDocument14 pagesDamper Resistor For LV MotorsaravananNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT#3Document5 pagesEXPERIMENT#3Carlo EguieronNo ratings yet
- Physics - DDPS1713 - Chapter 4-Work, Energy, Momentum and PowerDocument26 pagesPhysics - DDPS1713 - Chapter 4-Work, Energy, Momentum and Powerjimmi_ramliNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Impact Factors of Tire Wear PDFDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Impact Factors of Tire Wear PDFAbil RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics - Unit - 5Document31 pagesApplied Physics - Unit - 5Koppula veerendra nadhNo ratings yet
- Electric Capacitance IRODOVDocument38 pagesElectric Capacitance IRODOVKillerpkNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 TZ2 SL-3Document28 pagesPhysics Paper 2 TZ2 SL-3martinNo ratings yet
- Vapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Document10 pagesVapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Nitin KurupNo ratings yet
- Sound Intensity Booklet A4 2021Document24 pagesSound Intensity Booklet A4 2021eduardo paivaNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current - QuestionDocument7 pagesAlternating Current - Questionbest badmintonNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Physical Science Q2Document2 pagesWeek 2 - Physical Science Q2Gemma Quiocho-CardenasNo ratings yet
- 04 - Design of PS-33Document5 pages04 - Design of PS-33karthiNo ratings yet
- NAME: - GRADE&SECTION:: I. Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesNAME: - GRADE&SECTION:: I. Multiple ChoiceRaymund June Tinga-Enderes AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Determining Short Circuit Valuecss in Secondary Electrical Distribution Efsystes PDFDocument24 pagesProcedure For Determining Short Circuit Valuecss in Secondary Electrical Distribution Efsystes PDFgirish19No ratings yet
- Undamped Free Vibration - RahulDocument47 pagesUndamped Free Vibration - Rahulrs100788No ratings yet
- HW8 B SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW8 B Solutionsmmsingh91100% (1)
- G7 - 3rd Quarterly ExamDocument4 pagesG7 - 3rd Quarterly ExamKarina Manalo100% (1)
- Question 1: What Pressure Will Be Exerted by 20.16 G Hydrogen Gas in A 7.5 L Cylinder atDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: What Pressure Will Be Exerted by 20.16 G Hydrogen Gas in A 7.5 L Cylinder atJoela Faith Ming GongNo ratings yet
- Energy and The First Law of Thermodynamics: Prepared By: EFREN A. DELA CRUZ E-Mail Address: Eadelacruz@clsu - Edu.phDocument7 pagesEnergy and The First Law of Thermodynamics: Prepared By: EFREN A. DELA CRUZ E-Mail Address: Eadelacruz@clsu - Edu.phBilly Jake CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Charles and Gay ProblemsDocument4 pagesCharles and Gay ProblemsJennyFloresNicolasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14: Transfer Functions of DC Motors: ET 438a Automatic Control Systems TechnologyDocument28 pagesLesson 14: Transfer Functions of DC Motors: ET 438a Automatic Control Systems TechnologyHeart hea7No ratings yet
- Potentio MetreDocument7 pagesPotentio MetreRufusyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics For Engineers 1st Edition by Chin ISBN Solution ManualDocument56 pagesFluid Mechanics For Engineers 1st Edition by Chin ISBN Solution Manualsteve100% (35)
- SUVAT Equations: Key Words & Definitions What Do I Need To KnowDocument1 pageSUVAT Equations: Key Words & Definitions What Do I Need To KnowAlex GoldsmithNo ratings yet
- M ERIAMDocument51 pagesM ERIAMsauravkr2027No ratings yet