Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Systemic and Local Changes
Systemic and Local Changes
Uploaded by
Aristia ObeliaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- MCQs For MRCOG Part 1 A Self-Assessment Guide PDF BookDocument118 pagesMCQs For MRCOG Part 1 A Self-Assessment Guide PDF BookAhmed Abdelmonsef Albashatly86% (14)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Drug Studies (Common Drugs Used in The Delivery Room)Document6 pagesDrug Studies (Common Drugs Used in The Delivery Room)Elle100% (2)
- All About PragnancyDocument29 pagesAll About PragnancyBaalu KathirveluNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and ChildbirthDocument14 pagesPregnancy and ChildbirthNataly Aponte CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Caloy PartDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Caloy PartCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- OB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IDocument6 pagesOB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IManjulaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Agno, John Michael L. SBC-SN: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesPrepared By: Agno, John Michael L. SBC-SN: HypothalamusJohn Michael AgnoNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Newborn 1Document133 pagesMaternal & Newborn 1Philip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions 1Document14 pagesGestational Conditions 1Fatima TañedoNo ratings yet
- The Intrapartal PeriodDocument49 pagesThe Intrapartal PeriodMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Lp2 Drug Study FormsDocument3 pagesLp2 Drug Study FormsJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy-Vd RodasDocument5 pagesDrugstudy-Vd RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- RAMOS-BN Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument2 pagesRAMOS-BN Drug Study Delivery RoomLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyDocument22 pagesLESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyV.srivaniNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram 2Document2 pagesSchematic Diagram 2NICHOLE MOJELLONo ratings yet
- The Adrenal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, And: Physiologic Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesThe Adrenal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, And: Physiologic Changes During PregnancyFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationDocument5 pagesNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationCrisheila Sarah PiedadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study For OxytocinAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Fetal Responses During LaborDocument6 pagesMaternal & Fetal Responses During LaborIrish Paulene NiroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFrancis BelotindosNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument3 pagesMethergineLoue Jean GulfanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- LP KEHAMILAN NORMAL Zaii - Id.enDocument5 pagesLP KEHAMILAN NORMAL Zaii - Id.enMuhammad ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- 3F Intranatal NotesDocument5 pages3F Intranatal NotesAlyssa Claire TumulakNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Albuterol SalbutamolDocument2 pagesAlbuterol SalbutamolPePpER29No ratings yet
- Uterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsDocument5 pagesUterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- By Jear Romero: Name: Jear F. Romero, BSN 12A Clinical Instructor: Ma'am Emvie Loyd ItableDocument2 pagesBy Jear Romero: Name: Jear F. Romero, BSN 12A Clinical Instructor: Ma'am Emvie Loyd ItableJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- OB2 - Problems With The PowerDocument10 pagesOB2 - Problems With The PowerYanaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery TopicsDocument44 pagesLabor and Delivery TopicsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Parturition PDFDocument17 pagesPhysiology of Parturition PDFNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On PhysiologicalDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On PhysiologicalruchiNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery TopicsDocument44 pagesLabor and Delivery TopicsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- 7-Onset & Physiology of LaborDocument15 pages7-Onset & Physiology of LaborNlsNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument32 pagesLaborJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Case 01 - Maternal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCase 01 - Maternal PhysiologyRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsHaleNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal PeriodDocument6 pagesIntrapartal PeriodKelsey MacaraigNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCINDocument2 pagesOXYTOCINPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Dietetics:: Day CycleDocument8 pagesNutrition and Dietetics:: Day Cyclemheo2004No ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NameSittie Nashieva A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- BrerastDocument6 pagesBrerastlunamoonvaleria00No ratings yet
- Normal Labor: Ms. Mayuri Patel Sandra Shroff Rofel College of Nursing, VapiDocument48 pagesNormal Labor: Ms. Mayuri Patel Sandra Shroff Rofel College of Nursing, Vapivimmy47100% (1)
- Fisiologi Kehamilan-1Document34 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan-1Igus UlfayazeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument3 pagesDrug Study OxytocinSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- Case Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileDocument5 pagesCase Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileFatimah Sherina HussamNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument55 pagesObstetricsKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal - Theories of LaborDocument21 pagesIntrapartal - Theories of LaborJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- Map Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument1 pageMap Physiological Changes During PregnancyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 10.theories of LaborDocument18 pages10.theories of LaborJulia Ramos100% (1)
- University of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document4 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500JM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Category For PregnantDocument33 pagesDrug Category For PregnantLovelyn B. OliverosNo ratings yet
- Careplan ExampleDocument6 pagesCareplan Exampleonecharminglady100% (1)
- #2-NCM 109 - TransesDocument19 pages#2-NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour 400lDocument102 pagesNormal Labour 400lAbdullahi Suleiman MakaNo ratings yet
- Leptin Diet For Women: Easy Solution to Get More Energy and Become HealthierFrom EverandLeptin Diet For Women: Easy Solution to Get More Energy and Become HealthierRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Holistic Pregnancy Manual: Maternal Health Manuals, #1From EverandHolistic Pregnancy Manual: Maternal Health Manuals, #1No ratings yet
- Asher Harper HCG StudyDocument8 pagesAsher Harper HCG StudySusan Leonard100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Document32 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Anitha SNo ratings yet
- Bio Chemistry EQAS CMCDocument1 pageBio Chemistry EQAS CMCKomal TomarNo ratings yet
- The HCG ModifiedDocument25 pagesThe HCG ModifiedTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- HCG Lab ReportDocument3 pagesHCG Lab Reportcaramel109100% (3)
- First-Trimester Pregnancy Termination - Uterine Aspiration - UpToDate PDFDocument30 pagesFirst-Trimester Pregnancy Termination - Uterine Aspiration - UpToDate PDFGLORIA ANDREA ORJUELA FLOREZNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossDocument17 pagesMidwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossliopergonNo ratings yet
- When To Take A Pregnancy Test Options, Cost andDocument1 pageWhen To Take A Pregnancy Test Options, Cost andOyedele OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- NASC 4 Fact or BluffDocument33 pagesNASC 4 Fact or BluffJona MangabanNo ratings yet
- Antifertility DrugsDocument12 pagesAntifertility DrugsforplancessNo ratings yet
- HCG - Human Chorionic GonadotropinDocument2 pagesHCG - Human Chorionic GonadotropinOvidiu IgnatNo ratings yet
- Fabia Ms TellmeDocument2 pagesFabia Ms TellmeDavid Chege K.No ratings yet
- HY Obgyn MehlmanmedicalDocument127 pagesHY Obgyn MehlmanmedicalalmostpetergriffinNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Fertility TestingDocument57 pages3.3 Fertility Testing21 - Tuazon, AlliahNo ratings yet
- Aborsion: Spontaneou SDocument214 pagesAborsion: Spontaneou Sorkaido berisha (Addisu)No ratings yet
- A10 - Obgyn Main Handout March 2023 Clyde Joshua EcijaDocument92 pagesA10 - Obgyn Main Handout March 2023 Clyde Joshua EcijaClarissa May AvenaNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2Document18 pagesMock Exam 2Anna StacyNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument14 pagesEctopic PregnancyPrashanta PahariNo ratings yet
- A Protocol For in Vitro Maturation and Fertilization of SheepDocument6 pagesA Protocol For in Vitro Maturation and Fertilization of SheepAnamaria Blaga PetreanNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Tests: Introduction Biological Test Immunological TestsDocument2 pagesPregnancy Tests: Introduction Biological Test Immunological TestsRikatotokari TsukishimotoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Normal and Abnormal Pregnancy From 4-10 Weeks: Monique HaakDocument49 pagesAssessing Normal and Abnormal Pregnancy From 4-10 Weeks: Monique Haakjen marbunNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument7 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Psychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument42 pagesPsychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyAustine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNo ratings yet
- Hospital REPORTDocument26 pagesHospital REPORTBrownson Succex JuniorNo ratings yet
- PreganancyDocument8 pagesPreganancydhruv asatiNo ratings yet
- TETANUS 13 Lessons On PopulationDocument8 pagesTETANUS 13 Lessons On Populationzevah35No ratings yet
- CER88 Cryptorchidism FinalReport 20121207 PDFDocument324 pagesCER88 Cryptorchidism FinalReport 20121207 PDFClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
Systemic and Local Changes
Systemic and Local Changes
Uploaded by
Aristia ObeliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Systemic and Local Changes
Systemic and Local Changes
Uploaded by
Aristia ObeliaCopyright:
Available Formats
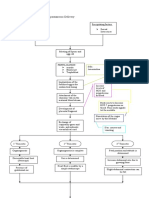
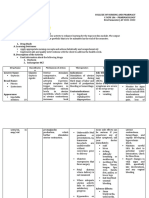
SYSTEMIC CHANGES
CIRCULATORY/CARDIOVASCULAR GASTROINTESTINAL RESPIRATORY URINARY MUSCULOSKELETAL TEMPERATUR ENDOCRINE CHANGES WEIGHT Emotional responses
CHANGES CHANGES CHANGES CHANGES E
30%-50% ↑ Urinary frequency, lordotic position (“pride of slight increase in placenta as an endocrine First trimester= gain of First trimester: the fetus is
Total cardiac volume Morning sickness Shortness of breath seen during the first pregnancy”) body temperature organ, producing large amounts 1.5 – 3 lbs an unidentified concept with
↓ Due to: increased Due to: trimester -makes ambulation easier by progesterone, but of estrogen, progesterone, HCG great future implications but
a drop in human chorionic Increased oxygen standing more straight and the body adapts and HPL 2nd trimester and 3rd without tangible evidence of
hemoglobin and hematocrit genadotropin (HCG) consumption and taller after the 4th month trimesters= gain of 10-11 reality. Some degree of
↓ acidity production of pounds per rejection, denial and
Physiologic anemia emotional factors carbon dioxide trimester disbelief, even
during the first repression.
Consequences: Management: trimester Total allowable weight
Nosebleeds Eat dry toast or crackers Increased uterine gain during entire period
Easy fatigability 30minutes before arising size causes of pregnancy is
Shortness of breath diaphragm to be 20 - 25 lbs ( = 10 – 12 kgs)
Slight hypertrophy pushed
Systolic murmurs Management: Lateral
expansion of the chest
Palpitations Heartburn Decreased renal pelvic bones Moderate enlargement of the Pattern of weight gain is Second trimester: fetus is
Management: threshold for sugar become more supple and thyroid gland due to more important than the perceived as a separate
due to: Pats of butter before ue to increased movable, wobbly gait. hyperplasia of the amount of weight entity. Fantasizes
Sympathetic nervous system meals production of glandular tissues and increased appearance of the
stimulation during first half of Avoid fried, fatty foods glucocorticoids Implication: Advise use of vascularity. baby
pregnancy Sips of milk at frequent which cause lactose low-heeled shoes after the first
Increased pressure of uterus intervals and dextrose trimester
against the diaphragm during 2nd Small, frequent meals
half of pregnancy taken slowly
Bend at the knees, not at
the waist
Poor circulation →Edema of the lower Constipation and flatulence Leg cramps are caused by: Increased size of the
extremities occurs. Management: Increased pressure of gravid parathyroids, probably to
Increase fluids uterus on lower extremities satisfy the increased need
Managements: Avoid harsh laxatives Fatigue of the fetus for calcium
Wear support hose Regular elimination time Chills
Apply elastic bandage Increase exercise Muscle tenseness
Avoid use of constricting garters Avoid enemas Low calcium high phosphorus
intake
Poor circulation in the blood vessels of Leg cramps Increased size and activity of Third trimester: has
the genitalia→varicosities of the vulva Hemorrhoids caused by: the adrenal cortex→ personal identification with
and rectum Management: Increased pressure of increasing the a real baby about to be born
Cold compress with witch gravid uterus on lower amount of circulating cortisol, and
Management: hazel extremities aldosterone and ADH, (all of realistic plans for future
Side-lying position with hips Fatigue which affect child care responsibilities.
elevated on pillows Chills carbohydrate and fat Best time to talk about
Advise modified knee-chest position Muscle tenseness metabolism) preparation of
Low calcium high layette and infant feeding
phosphorus intake method. Fear of death,
Most effective relief: Press though, is prominent
knee of the affected leg and
dorsiflex the foot
increased level of circulating fibrinogen Hyperemesis gravidarum –
excessive nausea and Gradual increase in insulin
vomiting which persists production
beyond 3 months;
↓
dehydration,
starvation and acidosis
Management:
D10 NSS 3000 ml in 24
hours
Complete bed rest
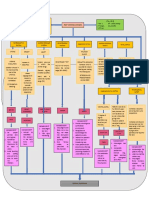
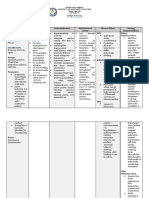
LOCAL CHANGES
Uterus Weight increase to about 1,000 grams at full term
Change in shape from pear like to avoid
Hegar’s sign, seen at about the 6th week
Mucous plugs in the cervix, called operculum, are produced to seal out bacteria
Goodell’s sign
Vagina Chadwick’s sign
Increasing amount of vaginal discharges called leukorrhea.
Management: Maintain or increase cleanliness by taking twice daily shower baths usingcoolwater.
pH of vagina changes from the normally acidic (because of the presence of the
Doderlein bacilli) to alkaline (because of increased estrogen)
*two microorganisms which love to thrive in an alkaline environment:
DISEASE SYMPTOMS TREATMENTS
Trichomoniasis. Frothy, cream-colored, irritatingly Flagyl for 10 days p.o. or vaginal
itchy, foul-smelling discharges suppositories of Trichomonicidal
compounds (e.g.,
Tricefuron, Vagisec, Devegan).
Acidic vaginal douche (1 tbsp.
white vinegar to 1 quart of water or
15
ml white vinegar in 1000 ml water)
to counteract alkaline-preferred
environment of the protozoa.
Avoid intercourse to prevent re-
infection.
Moniliasis or White, patchy, cheese-like particles Mycostatin/Nystatin p.o. or vaginal
Candidiasis. that adhere to vaginal walls. suppositories/pessaries (100,000 U)
Irritatingly itchy and twice a day
foul-smelling vaginal discharges for 15 days
Gentian violet swab to vagina (use
panty shields to prevent staining of
clothes or
underwear)
Correct diabetes
Avoid intercourse
Acidic vaginal douche
Abdominal Wall Striae gravidarum – increased uterine size results in rupture and atrophy of the
connective tissue layers, seen as pink or reddish streak
Umbilicus pushed out
Skin Linea nigra – brown line running from umbilicus to symphysis pubis
Melasma or chloasma – extra pigmentation on cheeks and across the nose due to the
increased production of melanocytes
Sweat glands unduly activated
Breasts All changes due to increased estrogen
Increase in size due to hyperplasia of mammary alveoli and fat deposits.
Feeling of fullness and tingling sensation in the breasts
Nipples more erect
Montgomery glands become bigger
Areolae become darker and diameter increase
Skin surrounding areolas turns dark
a thin, watery, high-protein fluid, called colostrums, is formed. It
is the precursor of breast milk.
Ovaries no activity
You might also like
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- MCQs For MRCOG Part 1 A Self-Assessment Guide PDF BookDocument118 pagesMCQs For MRCOG Part 1 A Self-Assessment Guide PDF BookAhmed Abdelmonsef Albashatly86% (14)
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Drug Studies (Common Drugs Used in The Delivery Room)Document6 pagesDrug Studies (Common Drugs Used in The Delivery Room)Elle100% (2)
- All About PragnancyDocument29 pagesAll About PragnancyBaalu KathirveluNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and ChildbirthDocument14 pagesPregnancy and ChildbirthNataly Aponte CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Caloy PartDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Caloy PartCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- OB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IDocument6 pagesOB1 3.1 Normal Labor and Delivery IManjulaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Agno, John Michael L. SBC-SN: HypothalamusDocument3 pagesPrepared By: Agno, John Michael L. SBC-SN: HypothalamusJohn Michael AgnoNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Newborn 1Document133 pagesMaternal & Newborn 1Philip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Gestational Conditions 1Document14 pagesGestational Conditions 1Fatima TañedoNo ratings yet
- The Intrapartal PeriodDocument49 pagesThe Intrapartal PeriodMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Lp2 Drug Study FormsDocument3 pagesLp2 Drug Study FormsJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy-Vd RodasDocument5 pagesDrugstudy-Vd RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- RAMOS-BN Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument2 pagesRAMOS-BN Drug Study Delivery RoomLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyDocument22 pagesLESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyV.srivaniNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram 2Document2 pagesSchematic Diagram 2NICHOLE MOJELLONo ratings yet
- The Adrenal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, And: Physiologic Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesThe Adrenal, Thyroid, Parathyroid, And: Physiologic Changes During PregnancyFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationDocument5 pagesNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationCrisheila Sarah PiedadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study For OxytocinAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Fetal Responses During LaborDocument6 pagesMaternal & Fetal Responses During LaborIrish Paulene NiroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFrancis BelotindosNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument3 pagesMethergineLoue Jean GulfanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- LP KEHAMILAN NORMAL Zaii - Id.enDocument5 pagesLP KEHAMILAN NORMAL Zaii - Id.enMuhammad ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- 3F Intranatal NotesDocument5 pages3F Intranatal NotesAlyssa Claire TumulakNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Albuterol SalbutamolDocument2 pagesAlbuterol SalbutamolPePpER29No ratings yet
- Uterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsDocument5 pagesUterotonic (Ecbolic) : Uterine Actions Other Actions IndicationsShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- By Jear Romero: Name: Jear F. Romero, BSN 12A Clinical Instructor: Ma'am Emvie Loyd ItableDocument2 pagesBy Jear Romero: Name: Jear F. Romero, BSN 12A Clinical Instructor: Ma'am Emvie Loyd ItableJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- OB2 - Problems With The PowerDocument10 pagesOB2 - Problems With The PowerYanaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery TopicsDocument44 pagesLabor and Delivery TopicsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Parturition PDFDocument17 pagesPhysiology of Parturition PDFNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On PhysiologicalDocument22 pagesLesson Plan On PhysiologicalruchiNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery TopicsDocument44 pagesLabor and Delivery TopicsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- 7-Onset & Physiology of LaborDocument15 pages7-Onset & Physiology of LaborNlsNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument32 pagesLaborJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Case 01 - Maternal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCase 01 - Maternal PhysiologyRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsHaleNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal PeriodDocument6 pagesIntrapartal PeriodKelsey MacaraigNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCINDocument2 pagesOXYTOCINPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Dietetics:: Day CycleDocument8 pagesNutrition and Dietetics:: Day Cyclemheo2004No ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NameSittie Nashieva A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- BrerastDocument6 pagesBrerastlunamoonvaleria00No ratings yet
- Normal Labor: Ms. Mayuri Patel Sandra Shroff Rofel College of Nursing, VapiDocument48 pagesNormal Labor: Ms. Mayuri Patel Sandra Shroff Rofel College of Nursing, Vapivimmy47100% (1)
- Fisiologi Kehamilan-1Document34 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan-1Igus UlfayazeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument3 pagesDrug Study OxytocinSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- Case Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileDocument5 pagesCase Study/Presentation: I. Patient ProfileFatimah Sherina HussamNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument55 pagesObstetricsKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Document100 pagesNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Intrapartal - Theories of LaborDocument21 pagesIntrapartal - Theories of LaborJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- Map Physiological Changes During PregnancyDocument1 pageMap Physiological Changes During PregnancyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 10.theories of LaborDocument18 pages10.theories of LaborJulia Ramos100% (1)
- University of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document4 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500JM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Drug Category For PregnantDocument33 pagesDrug Category For PregnantLovelyn B. OliverosNo ratings yet
- Careplan ExampleDocument6 pagesCareplan Exampleonecharminglady100% (1)
- #2-NCM 109 - TransesDocument19 pages#2-NCM 109 - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour 400lDocument102 pagesNormal Labour 400lAbdullahi Suleiman MakaNo ratings yet
- Leptin Diet For Women: Easy Solution to Get More Energy and Become HealthierFrom EverandLeptin Diet For Women: Easy Solution to Get More Energy and Become HealthierRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Holistic Pregnancy Manual: Maternal Health Manuals, #1From EverandHolistic Pregnancy Manual: Maternal Health Manuals, #1No ratings yet
- Asher Harper HCG StudyDocument8 pagesAsher Harper HCG StudySusan Leonard100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Document32 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Reduced Syllabus Study Material EM 220454Anitha SNo ratings yet
- Bio Chemistry EQAS CMCDocument1 pageBio Chemistry EQAS CMCKomal TomarNo ratings yet
- The HCG ModifiedDocument25 pagesThe HCG ModifiedTanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- HCG Lab ReportDocument3 pagesHCG Lab Reportcaramel109100% (3)
- First-Trimester Pregnancy Termination - Uterine Aspiration - UpToDate PDFDocument30 pagesFirst-Trimester Pregnancy Termination - Uterine Aspiration - UpToDate PDFGLORIA ANDREA ORJUELA FLOREZNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossDocument17 pagesMidwifery Management of First Trimester Bleeding and Early Pregnancy LossliopergonNo ratings yet
- When To Take A Pregnancy Test Options, Cost andDocument1 pageWhen To Take A Pregnancy Test Options, Cost andOyedele OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- NASC 4 Fact or BluffDocument33 pagesNASC 4 Fact or BluffJona MangabanNo ratings yet
- Antifertility DrugsDocument12 pagesAntifertility DrugsforplancessNo ratings yet
- HCG - Human Chorionic GonadotropinDocument2 pagesHCG - Human Chorionic GonadotropinOvidiu IgnatNo ratings yet
- Fabia Ms TellmeDocument2 pagesFabia Ms TellmeDavid Chege K.No ratings yet
- HY Obgyn MehlmanmedicalDocument127 pagesHY Obgyn MehlmanmedicalalmostpetergriffinNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Fertility TestingDocument57 pages3.3 Fertility Testing21 - Tuazon, AlliahNo ratings yet
- Aborsion: Spontaneou SDocument214 pagesAborsion: Spontaneou Sorkaido berisha (Addisu)No ratings yet
- A10 - Obgyn Main Handout March 2023 Clyde Joshua EcijaDocument92 pagesA10 - Obgyn Main Handout March 2023 Clyde Joshua EcijaClarissa May AvenaNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2Document18 pagesMock Exam 2Anna StacyNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument14 pagesEctopic PregnancyPrashanta PahariNo ratings yet
- A Protocol For in Vitro Maturation and Fertilization of SheepDocument6 pagesA Protocol For in Vitro Maturation and Fertilization of SheepAnamaria Blaga PetreanNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Tests: Introduction Biological Test Immunological TestsDocument2 pagesPregnancy Tests: Introduction Biological Test Immunological TestsRikatotokari TsukishimotoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Normal and Abnormal Pregnancy From 4-10 Weeks: Monique HaakDocument49 pagesAssessing Normal and Abnormal Pregnancy From 4-10 Weeks: Monique Haakjen marbunNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument7 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Psychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument42 pagesPsychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyAustine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNo ratings yet
- Hospital REPORTDocument26 pagesHospital REPORTBrownson Succex JuniorNo ratings yet
- PreganancyDocument8 pagesPreganancydhruv asatiNo ratings yet
- TETANUS 13 Lessons On PopulationDocument8 pagesTETANUS 13 Lessons On Populationzevah35No ratings yet
- CER88 Cryptorchidism FinalReport 20121207 PDFDocument324 pagesCER88 Cryptorchidism FinalReport 20121207 PDFClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet