Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024
Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024
Uploaded by
thakur.shrish.singhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024
Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024
Uploaded by
thakur.shrish.singhCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Organisation in Animals
A group of similar cells along with intercellular substance performing specific function is known as TISSUE.
When 2 or more organs perform a common function by the physical or chemical interaction, they
together form organ system.
Animal Tissue
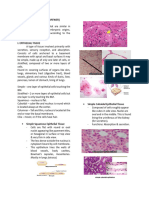
Epithelial Tissue
It has a free surface which faces body fluid or outside environment,
hence forms covering or internal lining. Cells are compactly packed with little intercellular space.
Compound
Simple • 2 or more layers of cell
• Single layer. • Protective function in skin.
• Cover dry surface of skin,
• Lining for body cavities. •Moist surface of buccal cavity,Pharynx,
• Ducts & tubes. inner lining of salivary glands & pancreatic
ducts.
Cuboidal Columnar Squamous
Cube like cells Tall,slender cells Flattened cells with
perform secretion with nuclei at base irregular boundaries
& absorption. Eg- help in secretion & form diffusion
ducts of glands, absorption. Eg. boundaries. Eg- wall
tubular part of Lining of of blood vessels, air
nephron. stomach, intestine. sac of lungs.
Glandular epithelium Ciliated Epithelium
May be UNICELLULAR-isolated glandular
• May be cuboidal/columnar.
cell(eg-goblet cell) OR MULTICELLULAR- • Helps in transportation.
cluster of cells (eg-salivary gland).
Junctions
• Present inside hollow organs like bronchioles
• fallopian duct.
May be EXOCRINE-have duct(eg-
mucus, saliva ear wax, oil, milk) OR
ENDOCRINE-ductless(eg-thyroid).
Adhering Connexis Tight Gap
junction With the help of 2 junction junction
Keeps protein cylinders. • For communication and
To stop
neighbouring substance to transfer of ions.
cells together. leak. • small molecules &
sometime big molecules.
Connective tissue
(Most abundant in body)
All cells in them(except in blood) secrete fibres of structural protein collagen & elastin, the fibres give strength,stretchability & elasticity.
Cells also secrete polysaccharide (modified) which accumulate between cells and form matrix(ground substance).
Loose Connective Dense Connective Specialised Connective
Tissue Tissue Tissue
Fibres & fibroblasts CARTILAGE- Solid, pliable,resists
Fibres loosely arranged in are compactly packed. compression. Chondrocyte cells present
semi-fluid matrix. in self made cavity. Present on nose
tip, ear pinna, b/w bones of vertebra, lips
& hands of adults.
BONE-hard, non-pliable & rich in Calcium
salts, collagen fibres. Osteocytes are
present in lacunae. Bone marrow helps in
Areolar Adipose production of RBC. Long bone have
Beneath skin,contain Beneath skin,stores fat. weight gaining function.
fibroblast(secrete Blood : Fluid Connective Tissue
fibre), macrophages,
mast cells. Support
framework for
epithelium.
Dense Irregular Dense Regular
Collagen fibre
Oriented present in rows between
differently, parallel bundles of
contain fibres. Eg-
fibroblast & Tendon (bone to
mostly muscle), Ligament
collagen. (bone to bone).
Eg- skin.
Muscular tissue
These fibres are composed of myofibrils they contract(for any stimulus) & relax in coordinated fashion
Cardiac Muscle
muscle smooth muscle
Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle
muscle
• Fusiform(taper
fusiform(taper at both ends Synectium
Syncytium
• Contractile
contractile tissue
tissue
•• Do
do not shows striations.
striations • attached
Attached to skeletal bone
bone.
• Cell
cell junction fuse plasma membrane
and
and make
make them
them stick
stick together.
together • Cell
cell junction hold them together • eg-Biceps(they
Eg-Biceps(they are arranged
(involuntary).
(involuntary) in parallel fashion held by
• Intercalated
intercalated connective
connective tissue).
tissue)
disc(communication junction) makes • Wall
wall of blood vessel, stomach,
all cell to contract at single time. intestine
intestine contain
contain these
these muscles.
muscles •• Striated/striped,
striated/striped, voluntary.
voluntary
Neural tissue
Unit of neural system are nervous which are excitable cells the neuroglial cells make up more than half the volume of neural tissue in our body which protection
& support neurons. When it is stimulated, an electrical disturbance travels along its plasma membrane.
Our heart contain all four type of tissues. The complexity in organ and organ system displays discernible trend which is called as evolutionary trend.
cockroach
Morphology
Segments in abdomen Introduction
• 34-53 mm long wings (beyond abdomen tip in male).
& respective organs • Body of cockroach = head + • May be bright yellow/red/ green coloured
in tropical regions.
thorax(prothorax,mesothorax, metathorax)+ abdomen.
IN FEMALE-7th boat shaped sterna, (7th, 8th,9th • Size-1/4 inch to 3 inch (0.6-7.6cm) they have flat
• The exoskeleton has hardened plates called sclerites extension of upper body wall that concoels head.
sterna) forms brood/genital pouch which contains
(dorsal ->tergite, ventral-> sternite) that are joined by
gonopore, spermathecal pore & collateral glands.
articular membrane (Arthrodial membrane). • They are serious pests & vectors of
IN MALE-(9th, 10th terga + 9th sterna) forms several diseases.
• Triangular head lies anteriorly at right angle to body
genital pouch/ chamber contains dorsal axis(longitudinal). Head- 6 segments, thorax- 3
anus, ventral male genital pore, gonapophysis. segments, abdomen-10 segments.
In male anal style are present.
• Mobility in all direction due to flexible neck.
IN BOTH- 10th segment bears anal cerci
• Head capsule bear compound eye.
(filamentous structure).
•Antennae (help in monitoring env.) arise from
membranous sockets lying in front of eye.
• Mouth parts = labrum(upper lip) + labium(lower lip)
+ pair of mandible & maxilla + hypopharynx(tongue).
• The head is connected to thorax by short extension
of prothorax known as neck/pronotum.
• Each thoracic segment bear a pair of walking legs.
First pair of wings(tegmina/forewings)-> mesothoracic
(opaque & dark coloured to cover hind wings), second
pair of wings (hindwings)-> metathoracic (for
flight/transparent).
ANATOMY OF COCKROACH
Blood vascular system Digestive system Respiratory system
•Open type, blood vessels (poorly developed) open • Alimentary canal • Trachea that open through 10 pairs of small holes
into Haemocoel. (foregut+midgut+hindgut) called spiracles.
• Blood is haemolymph (plasma+haemocytes). • Mouth(salivary gland)->tubular part ->crop(food) • Present on lateral side of body.
•Heart lies at mid dorsal line of thorax & abdomen. It is proventriculus( secrete gastric juice,outer • Tracheoles(subdivisions) carry oxygen from air to
differentiated into funnel shaped chambers with lined by circular muscle & inner 6 high all parts.
ostia on either side. Blood is entered through ostia chitinous plate called teeth which grind •The opening of spiracles is regulated by the sphincters
and pumped anteriorly to sinuses again. food). ->6,8 blind tubules (hepatic • Exchange of gases takes place by diffusion.
ceaceae)->100-150 yellow coloured
malphigian tubule(help in removal
of excretory waste from
haemolymph). ->hindgut(broader
than midgut)->anus.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
• Series of fused segmentally arranged ganglia joined by paired longitudinal connective on the ventral side.
• 3 ganglia in thorax & 6 ganglia in abdomen.
• Head holds a bit of nervous system and rest is situated on ventral(belly) side of body.
• If head is cut off a cockroach it will be alive for 1 week.
• Brain is represented by supra-oesophageal ganglion which supplies nerves to antennae & compound eyes.
• SENSE ORGANS-antennae,eyes,maxillary palps, labial palps and cerci.
• Compound eyes are located on dorsal surface. Each eye consist of 2000 omantidia (hexagonal) because of which Cockroach can see
several images of an object. This vision is MOSAIC vision(more sensitivity,less Resolution) {nocturnal vision}
EXCRETION
• Performed by malphigian tubules, each tubule is lined by glandular and ciliated cells.
• They convert N2 waste into uric acid.
• The fat body,nephrocytes & urecose glands also help in excretion.
REPRODUCTION SYSTEM
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
• Ovaries lie laterally in 2nd-6th abdomen.
• 1 ovary = 8 ovarian tubules/ovarioles containing a chain of
developing ova.
• Oviduct from each ovary unite to form median oviduct/vagina
which opens into genital chamber.
• Sperms are transferred through spermatophores. Their fertilised
eggs are encased in capsules called oothecae(dark reddish to MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
blackish brown capsule -3/8" (8mm) long).
• They are dropped or glued at a surface near a food source. • One testis lying on each lateral side in 4th - 6th abdominal
segments.
• Female produces 9-10 ootheceae, containing 14-16 eggs each.
• Vas deferens from each testis open into ejaculatory duct
• Development is through nymphal stage which is known as
through seminal vesicle which furthers opens into male gonopore
paurametabolus.
situated ventral to anus.
• Nymph grows by moulting 13 times to reach the adult form.
• Mushroom gland is present in between 6th-7th abdomen
• Next to last stage have wing pods but only adult cockroach segment which function as an accessory reproductive gland.
have wings.
• External genitalia are represented by male gonapophysis or
phallomere(chitinous asymmetric structure surrounding male
gonopore).
• Sperms are glued in seminal vesicle & formed into bundles
called spermatophores, which are discharged during copulation.
There is no economic use of cockroach. They are pests because spoil food & contaminate it with their smelly excreta and
by this they can transmit a variety of bacterial diseases.
You might also like
- Edtpa Task 1 - Lesson Plans For LearningDocument9 pagesEdtpa Task 1 - Lesson Plans For Learningapi-325331113No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in Animals Mind MapDocument3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals Mind MapAstha Agrawal80% (5)
- Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsJOAN KLAIRE I. LIBOTNo ratings yet
- 1 Animal OrganisationDocument29 pages1 Animal OrganisationPERTUNIA KORABINo ratings yet
- Histology ReviewerDocument11 pagesHistology ReviewerMaryell Denize LandichoNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Group 2Document39 pagesAnimal Tissues Group 2Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 22Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 22Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 pagesBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- 07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterDocument12 pages07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterexercisestartNo ratings yet
- Module 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument12 pagesModule 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationchellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDocument2 pages7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab 5 Tissues - Lab ReportbrittNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuDocument9 pagesAnimal Tissudamon salvatoreNo ratings yet
- Histology - Epithelial TissuesDocument4 pagesHistology - Epithelial TissuesKrissa OmandamNo ratings yet
- Basic HistologyDocument8 pagesBasic Histologyroy_dubouzetNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- Human Body TissuesDocument5 pagesHuman Body TissueschellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL-CELL Group 2Document35 pagesANIMAL-CELL Group 2mjecbjNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDocument16 pagesCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIANo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 pagesEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Tissues, SkinDocument11 pagesTissues, SkinkimcheeseNo ratings yet
- Mc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Document5 pagesMc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Karl Devin CorderoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument3 pagesTissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 TissuesAl-Shuaib Astami Son100% (1)
- 2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument47 pages2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsFHATIN AMIRA BINTI MUSA MoeNo ratings yet
- E1.3 Body TissuesDocument5 pagesE1.3 Body TissueshzntrpNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerNo ratings yet
- Conn. Tissue HemopoiesisDocument14 pagesConn. Tissue HemopoiesischennielafleurNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita DirgantaraDocument30 pagesAnimal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita Dirgantarahafiz amriNo ratings yet
- BSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermDocument4 pagesBSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermLynell Caraang BarayugaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument5 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesFrederick ManaigNo ratings yet
- Tissues Pre LabDocument43 pagesTissues Pre LabCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissue Q&ADocument5 pagesEpithelium Tissue Q&ANo NameNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDocument8 pagesHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsDocument10 pagesBiology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsFatima Zulqarnain100% (1)
- BIO 9 SM3 23-24pDocument11 pagesBIO 9 SM3 23-24pNandini Pritesh PatelNo ratings yet
- AM Animal TissuesDocument35 pagesAM Animal Tissuestechnicalfacts31No ratings yet
- TISSUES - Class Notes - SprintDocument40 pagesTISSUES - Class Notes - SprintMr Vinod yadavNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesStructural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Types of Tissues: Lesson 02Document33 pagesTypes of Tissues: Lesson 02DASH100% (2)
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Module3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyDocument11 pagesModule3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- Cell 4Document80 pagesCell 4jocajoldinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument31 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsVenom Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Tissue of The BodyDocument12 pagesTissue of The BodyJuliet Aira Cabero Quibilan100% (1)
- Animal Tissue L 1Document35 pagesAnimal Tissue L 1Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissues 2024-01Document45 pagesEpithelial Tissues 2024-01jcrosa137No ratings yet
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 pagesTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement For BiodieselDocument8 pagesThesis Statement For Biodieselkualxkiig100% (2)
- Gender Issues in Jekyll and Hyde, Spirits of The Dead and Bloody ChamberDocument1 pageGender Issues in Jekyll and Hyde, Spirits of The Dead and Bloody Chamberjackmartin14No ratings yet
- Tle Freezing and Defrosting MeatDocument17 pagesTle Freezing and Defrosting MeatEnna PaulaNo ratings yet
- Drainage NOTESDocument9 pagesDrainage NOTESAuraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan #5 (Diversity Lesson Plan) Lesson Objective/sDocument7 pagesLesson Plan #5 (Diversity Lesson Plan) Lesson Objective/sapi-198000409No ratings yet
- Boyd Aiw Lesson Cover PageDocument2 pagesBoyd Aiw Lesson Cover Pageapi-244827434No ratings yet
- BS ConsolidationDocument25 pagesBS ConsolidationKamukwema johnNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Strain Index Scoring Sheet: Date: Task: Company: Supervisor: Dept: EvaluatorDocument1 pageStrain Index Scoring Sheet: Date: Task: Company: Supervisor: Dept: EvaluatorAngeline Henao BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Cat 772g BRDocument28 pagesCat 772g BR111No ratings yet
- Elias M. Gutierrez JR.: Education: Seminars AttendedDocument1 pageElias M. Gutierrez JR.: Education: Seminars AttendedRachel Arañes MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bhopal Disaster: Too LongDocument5 pagesBhopal Disaster: Too LongrevathisudhaNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagram of Instrument (INS)Document8 pagesWiring Diagram of Instrument (INS)Rendy MechanicNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)Document8 pagesUnit Plan-Badminton Jenna Maceachen: Subject Area Grade Level Topic Length of Unit (Days)api-507324305No ratings yet
- CGR1 Text ModeDocument11 pagesCGR1 Text ModeRaj SuraseNo ratings yet
- Is 5 8Document218 pagesIs 5 8andispotifyaccNo ratings yet
- JavaScript - Math - Random Method Example - DiraskDocument3 pagesJavaScript - Math - Random Method Example - DiraskKelve AragaoNo ratings yet
- 42 Items Q and ADocument2 pages42 Items Q and AJoy NavalesNo ratings yet
- WS 2 FUNDAMENTALS OF PARTNERSHIP - DocxDocument5 pagesWS 2 FUNDAMENTALS OF PARTNERSHIP - DocxGeorge Chalissery RajuNo ratings yet
- Mama AnnDocument2 pagesMama AnnVon JimenezNo ratings yet
- Series: LTJ: Toe Capacity: 2.5 - 25 Ton - Head Capacity: 5 - 50 Ton - Stroke Length For Toe: 50 MMDocument1 pageSeries: LTJ: Toe Capacity: 2.5 - 25 Ton - Head Capacity: 5 - 50 Ton - Stroke Length For Toe: 50 MM220479No ratings yet
- G.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentDocument7 pagesG.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentMaria AndresNo ratings yet
- Communication and Presentation Skill 1Document229 pagesCommunication and Presentation Skill 1shanthakumargcNo ratings yet
- Price and Output Determination Under Monopolistic OnDocument13 pagesPrice and Output Determination Under Monopolistic OnShoaib Ahmed KhosoNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Intel ProcessorsDocument4 pagesEvolution of Intel Processors이고양No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving ProblemsDocument22 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving Problemsnoahzaec100% (2)
- Assignment Nicmar / Code OfficeDocument8 pagesAssignment Nicmar / Code OfficeRevanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Cinefantastique v06n04 v07n01 B (1978)Document96 pagesCinefantastique v06n04 v07n01 B (1978)Phillip Lozano100% (1)
- Why Is Omkar Called As Pranav MantraDocument6 pagesWhy Is Omkar Called As Pranav Mantraami1577No ratings yet