Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Uploaded by
teresa tsoiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- General Chemistry 11th Edition Ebbing Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesGeneral Chemistry 11th Edition Ebbing Solutions ManualNatalieAcevedogibfk100% (36)
- January 2012 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument24 pagesJanuary 2012 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Heat of Precipitation ActivityDocument8 pagesHeat of Precipitation ActivityNorfazliyana AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Enaiposha Girls High Schoo1Document8 pagesEnaiposha Girls High Schoo1euginemwakhaNo ratings yet
- F3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617Document6 pagesF3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Structured QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Structured questions 2 - 複本Document18 pagesChapter 18 Structured questions 2 - 複本connieNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 11 EDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 11 ERaiNo ratings yet
- Water, Lead Sulphide, Hydrogen, Copper, Mercury, Carbon Dioxide'Document24 pagesWater, Lead Sulphide, Hydrogen, Copper, Mercury, Carbon Dioxide'Kai Keung ChiuNo ratings yet
- Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)Document5 pagesKiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)wslNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - 1Document3 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - 1Rehan MotiwalaNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Metal With AnswerDocument5 pagesTest 2 Metal With AnswerIsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Structured Questions BlankDocument13 pagesChapter 48 Structured Questions Blankjoyousclassroom joyousclassroomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structured QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesForm 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeeuginemwakhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansDocument13 pagesChemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansapi-38240030% (2)
- Acids, Bases - Salts 4 QPDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases - Salts 4 QPANIKA DHANIKACHALAMNo ratings yet
- Exam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS OnlineDocument5 pagesExam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS Onlinehalahossam8899No ratings yet
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- 25.5.22-10th-Chem-Ab 1-2022-23Document13 pages25.5.22-10th-Chem-Ab 1-2022-23Aadarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - 10 A Assignment 1 Date: 18-08-2020 - Answer The Following QuestionsDocument10 pagesChemistry - 10 A Assignment 1 Date: 18-08-2020 - Answer The Following QuestionsRoselyn TrixieNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument10 pagesCHEMBryan WillNo ratings yet
- Wa0020.Document3 pagesWa0020.Guddi SinghNo ratings yet
- 2021 S5 1st Exam AnswerDocument8 pages2021 S5 1st Exam Answerlala LuNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements-SignedDocument7 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements-SignedMuhammed Sadiq100% (1)
- Chemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERDocument12 pagesChemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Chem Mock Brand School Mock Exam 12 P1-QDocument19 pagesChem Mock Brand School Mock Exam 12 P1-QLiu JoeNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document6 pagesChem 2ideal writersNo ratings yet
- Class: 10 Subject: Chemistry Name - DateDocument3 pagesClass: 10 Subject: Chemistry Name - Dateansh1510No ratings yet
- P545/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Certificate of Education Page 1Document15 pagesP545/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Certificate of Education Page 1Kahuma DeoNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988048-MCQDocument13 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988048-MCQabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988039-1MARKDocument8 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988039-1MARKabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemistry F3Document3 pagesChemistry F3dembeleosman266No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Summative Assessment - I Grade-7 ChemistryDocument3 pagesMark Scheme Summative Assessment - I Grade-7 ChemistryVivek Sadasivan NairNo ratings yet
- Chem F3 Temeke Marking GuideDocument8 pagesChem F3 Temeke Marking Guidendururutseg98No ratings yet
- Part III 2019 Updated QBDocument6 pagesPart III 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesForm 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeMejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- 2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查Document4 pages2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查s202001001No ratings yet
- WS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetDocument8 pagesWS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetSiyaNo ratings yet
- Ms Class 10 Science 2022 23Document7 pagesMs Class 10 Science 2022 23methesmrtyNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988058-MCQ-PART2Document11 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988058-MCQ-PART2abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Marking Guide For Getting Ready For Zimsec - 231108 - 204409Document15 pagesMarking Guide For Getting Ready For Zimsec - 231108 - 204409tinevimbomagureNo ratings yet
- Chem 3 ADocument3 pagesChem 3 AKobe YuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Structured QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Part I 2019 Updated QBDocument7 pagesPart I 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements Q & ADocument10 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements Q & A3093 Ayoob NNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDocument9 pagesChemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDhilfa Eleyedath International Indian School - Abu DhabiNo ratings yet
- Workbk 10Document177 pagesWorkbk 10Manushree NayakNo ratings yet
- Chem PP1 MSDocument9 pagesChem PP1 MSianmutwiriNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPDocument31 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPRanjitha BanuNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 2 End Term 3Document8 pagesChem Form 2 End Term 3DenisNo ratings yet
- 10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument12 pages10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023Document7 pagesYr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023troyrodrigues36No ratings yet
- Part 3 MetalsDocument8 pagesPart 3 Metals劉曉晴No ratings yet
- Eje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Document7 pagesEje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Nassrah JumaNo ratings yet
- Xii PB Che MS 2023Document8 pagesXii PB Che MS 2023Hitesh PerniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Structured QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 13 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 6 QPDocument9 pagesRate of Reaction 6 QPmalak tahaNo ratings yet
- CISCE Gr-9 Chemistry Term2 Sample-Paper 2023-24Document9 pagesCISCE Gr-9 Chemistry Term2 Sample-Paper 2023-24abhipisharody09No ratings yet
- Question 837579Document10 pagesQuestion 837579Techno DevtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Assertion-Reason QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 Assertion-Reason Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Structured QuestionsDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Structured QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Structured QuestionsDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument24 pagesChapter 9 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Structured QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- 3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)Document8 pages3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)teresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Structured QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 1A 1B 2 - New QuestionDocument58 pagesQuestion Bank 1A 1B 2 - New Questionteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- QB 1A ch05 e QuestionsDocument12 pagesQB 1A ch05 e Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Sampling of Liquid Cast IronDocument2 pagesSampling of Liquid Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646No ratings yet
- TEPZZ - Z 78 A - T: European Patent ApplicationDocument13 pagesTEPZZ - Z 78 A - T: European Patent ApplicationDesi Rahma PrihandiniNo ratings yet
- PGM Extractive MetallurgyDocument15 pagesPGM Extractive MetallurgyAde SatriaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Procedure For HACH DR 2800Document6 pagesAmmonia Procedure For HACH DR 2800Berliana Cahya NingtiasNo ratings yet
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDocument285 pagesPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- 2004 Chemistry - James Ruse With SolutionsDocument36 pages2004 Chemistry - James Ruse With SolutionsWilliam HouNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Naming Chemical CompoundsDocument6 pagesChem Notes Naming Chemical CompoundsAbigail Ambrosio (ABI)No ratings yet
- GR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument18 pagesGR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperagangdayimaniNo ratings yet
- Astm D 511Document9 pagesAstm D 511Daniel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/21Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/21nmeghani325No ratings yet
- Lindab Round Duct and FittingDocument108 pagesLindab Round Duct and FittingNguyễn Xuân ĐiệpNo ratings yet
- Chem12015 ExamDocument16 pagesChem12015 ExamAAVANINo ratings yet
- Compounds Containing Nitorgen & Practical Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesCompounds Containing Nitorgen & Practical Organic ChemistryAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- Solubilitynotesnocomicsv4 PDFDocument29 pagesSolubilitynotesnocomicsv4 PDFterryNo ratings yet
- MCQ - WS! June 2023Document7 pagesMCQ - WS! June 2023Prakriti DhakalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure For Grade 10Document4 pagesAtomic Structure For Grade 10Aja AndersonNo ratings yet
- VALUES OF CRM UpdatedDocument137 pagesVALUES OF CRM UpdatedArijit DasGuptaNo ratings yet
- D BlockDocument17 pagesD Block145556No ratings yet
- Soylent Formula V3Document2 pagesSoylent Formula V3Ryan AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 2012 Acs Practice ExamDocument17 pages2012 Acs Practice ExamNyxas IoannisNo ratings yet
- Solution For "Introduction To Chemical Engineering" Chapter 11Document8 pagesSolution For "Introduction To Chemical Engineering" Chapter 11jiholee1117No ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemistry)Document25 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemistry)bm OUREMNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsDocument36 pagesThe Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-La3. Raw FileDocument9 pagesBiochemistry-La3. Raw Filejazzermill acobNo ratings yet
- Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiDocument23 pagesProgress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiWalid BadrNo ratings yet
- 10.thermodynamics and Chemistry Data: Cement Process Engineering Vade MecumDocument10 pages10.thermodynamics and Chemistry Data: Cement Process Engineering Vade MecumHasnaoui SamirNo ratings yet
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Uploaded by
teresa tsoiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Chapter 11 Structured Questions
Uploaded by
teresa tsoiCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
Chemistry: Chapter 11 Reactivity of metals
Combined Science (Chemistry Part): Chapter 11 Reactivity of metals
Structured questions
Section 11.1
|!|CMELF0031100001|!| |!|CSELF0031100001|!|
A student added zinc granules to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Write a chemical equation for this reaction. (1 mark)
(b) State ONE use of the gas produced in the experiment. (1 mark)
(c) Y is a more reactive metal than zinc. Compare the observations of zinc and Y
towards dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
(d) State TWO safety precautions for carrying out this experiment. (2 marks)
(e) State ONE hazardous nature of dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
##
(a) Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) 1
(b) It is used as a rocket fuel / to make hydrochloric acid / to make margarine
/ to make fertilizers. 1
(c) More colourless gas bubbles would evolve from the surface of Y than
from the zinc surface. 1
(d) Wear safety spectacles. 1
Dispose of the wastes into labelled waste bottles. 1
(e) It is irritating / corrosive. 1
___
6
##
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
238
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
|!|CMELF0031100002|!| |!|CSELF0031100002|!|
Consider the following three metals:
sodium, magnesium, copper
(a) Describe what would be observed when each of the above metals is strongly
heated. (3 marks)
(b) Write the chemical equations for each of the reactions involved in (a). (3 marks)
(c) (i) State which of the above metals react(s) with cold water. (1 mark)
(ii) Write the chemical equation(s) for the reaction(s) involved in (c)(i). (1 mark)
(d) Arrange the above metals in descending order of reactivity. (1 mark)
##
(a) Sodium would burn vigorously with a golden yellow flame and produce a
white powder. 1
Magnesium would burn with a very bright white flame and produce a
white powder. 1
Copper would not burn but its surface would turn black. 1
(b) 4Na(s) + O2(g) 2Na2O(s) 1
2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s) 1
2Cu(s) + O2(g) 2CuO(s) 1
(c) (i) Sodium 1
(ii) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) 1
(d) Sodium, magnesium, copper 1
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
239
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
___
9
##
|!|CMELF0031100003|!| |!|CSELF0031100003|!|
A student investigated the reaction of zinc with water.
(a) State any observable change when zinc granules were added to cold water.
(1 mark)
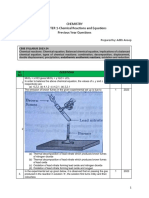
(b) The student carried out an experiment using the set-up as shown below.
zinc granules
gas X
wet sand heat
water
(i) What is the function of the wet sand in the set-up? (1 mark)
(ii) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. (1 mark)
(iii) Suggest a chemical test for gas X. (2 marks)
(c) The student repeated the experiment in (b) by using iron nails instead of zinc
granules. State and explain whether the reaction would become more vigorous or
not. (2 marks)
##
(a) Zinc granules sink in water. 1
(b) (i) The wet sand contains water. When it is heated, the water evaporates.
The steam produced would pass to react with zinc granules. 1
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
240
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
(ii) Zn(s) + H2O(g) ZnO(s) + H2(g) 1
(iii) Test the gas with a burning splint. 1
It burns with a ‘pop’ sound. 1
(c) The reaction would be less vigorous 1
because iron is lower than zinc in the metal reactivity series. 1
___
7
##
|!|CMELF0031100006|!| |!|CSELF0031100006|!|
A student learnt that both sodium and calcium are reactive metals. After studying the
properties of sodium, the student made the following predictions about calcium:
Calcium is a shiny metal. It reacts vigorously with cold water and moves
very quickly on the water surface. The resultant solution formed is alkaline.
(a) There are TWO mistakes in the student’s prediction. Suggest corrections for
them. (2 marks)
(b) Hydrogen is produced during the reaction.
(i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction of calcium with water. (1 mark)
(ii) Suggest a chemical test for hydrogen. (2 marks)
(c) Suggest a method to show that the resultant solution is alkaline. (2 marks)
(d) Filter the resultant solution. The filtrate can be used to test for the presence of
carbon dioxide.
(i) State the observable change when carbon dioxide is bubbled into the filtrate.
(1 mark)
(iii) Write a chemical equation, with state symbols, for the reaction between the
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
241
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
filtrate and carbon dioxide. (1 mark)
##
(a) Calcium is a dull metal. 1
It reacts readily with cold water and it sinks in water. 1
(b) (i) Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) 1
(ii) Test the gas with a burning splint. 1
It burns with a ‘pop’ sound. 1
(c) Any ONE:
- Test it with a red litmus paper. 1
It turns the red litmus paper blue. 1
- Test it with a pH paper. (1)
It turns the pH paper blue. (1)
- Test it with universal indicator. (1)
It turns the universal indicator blue. (1)
(Accept other reasonable answers)
(d) (i) The filtrate turns milky. 1
(ii) Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) 1
___
9
##
Section 11.2
|!|CMELF0031100004|!| |!|CSELF0031100004|!|
A student carried out an experiment to investigate the reaction between potassium and
water.
(a) State ONE safety precaution that the student should take. (1 mark)
(b) State TWO observations that the student could make. (2 marks)
(c) After the reaction, the student tested the resultant solution with a piece of red
litmus paper. What would happen to the red litmus paper? (1 mark)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
242
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
(d) Caesium is an alkali metal below potassium in the Periodic Table. Compare the
reactivity of caesium and potassium towards water. Explain your answer.(2
marks)
(e) Describe how potassium can be stored in the school laboratories. (1 mark)
##
(a) Any ONE:
- Wear safety spectacles 1
- Wear protective gloves (1)
- Use a small piece of potassium for the experiment. (1)
(b) Any TWO:
- Potassium melts to form a silvery ball. 1
- Potassium moves about quickly on the water surface. 1
- A hissing sound is heard. (1)
- Potassium burns with a lilac flame. (1)
(c) The red litmus paper turned blue. 1
(d) Caesium would react with water more vigorously than potassium. / The
reaction is explosive. 1
The reactivity of Group I metals increases down the group. 1
(e) It can be stored under paraffin oil. 1
___
7
##
Sections 11.311.7
|!|CMELH0031100005|!| |!|CSELH0031100005|!|
Chromium can be extracted by heating a mixture of chromium(III) oxide and
aluminium.
(a) Write a word equation for the reaction between chromium(III) oxide and
aluminium. (1 mark)
(b) What does this reaction tell us about the positions of chromium and aluminium in
the metal reactivity series? (1 mark)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
243
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
*(c) Outline an experiment to compare the positions of chromium and iron in the
metal reactivity series. (4 marks)
##
(a) chromium(III) oxide + aluminium chromium + aluminium oxide 1
(b) Chromium is lower than aluminium in the metal reactivity series. 1
(c) - Dip a piece of iron in a solution of chromium(III) salt. 1
- If displacement reaction occurs (as indicated by shiny deposits of
chromium), it indicates that iron is higher than chromium in the
metal reactivity series. 1
- If there is no apparent change, it indicates that iron is lower than
chromium in the metal reactivity series. 1
- Communication mark 1
___
6
##
|!|CMELF0031100007|!| |!|CSELF0031100007|!|
Barium is an alkaline earth metal.
(a) State the number of electrons in the outermost shell of a barium atom. (1 mark)
(b) Barium reacts with chlorine to give barium chloride.
(i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. (1 mark)
(ii) Draw the electron diagram for barium chloride, showing electrons in the
outermost shells only. (1 mark)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
244
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
(c) Besides by the direct combination of barium with chlorine, barium chloride can
also be prepared by the reaction of barium hydroxide solution with hydrochloric
acid. Write a chemical equation for the reaction of barium hydroxide solution
with hydrochloric acid. (Hint: Water is also produced in the reaction.) (1 mark)
(d) Predict, with explanation, whether barium or magnesium is more reactive
towards chlorine. (2 marks)
##
(a) 2 1
(b) (i) Ba(s) + Cl2(g) BaCl2(s) 1
(ii)
(c) Ba(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) BaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) 1
(d) Barium is more reactive towards chlorine. 1
The reactivity of Group II metals increases down the group. 1
___
6
##
|!|CMELF0031100008|!| |!|CSELF0031100008|!|
When a piece of aluminium is put into copper(II) nitrate solution, displacement
reaction occurs.
(a) State and explain TWO observable changes. (4 marks)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
245
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction involved. (1 mark)
(c) State and explain whether similar observations in (a) could be made when
aluminium is replaced by zinc. (2 marks)
##
(a) Any TWO:
- The blue solution becomes paler 1
because the amount of copper(II) ions decreases. 1
- Aluminium dissolves in the solution 1
because aluminium displaces copper from the solution to form
aluminium ions. 1
- Reddish brown deposits form on the aluminium surface (1)
because copper(II) ions are displaced out from the solution. (1)
(b) 2Al(s) + 3Cu2+(aq) 3Cu(s) + 2Al3+(aq) 1
(c) Similar observations could be made when aluminium is replaced by zinc 1
because zinc is also more reactive than copper. 1
___
7
##
|!|CMELH0031100009|!| |!|CSELH0031100009|!|
Manganese can be extracted from its ore pyrolusite (MnO 2) by the reaction with
carbon monoxide.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction between manganese(IV) oxide (MnO 2) and
carbon monoxide. (1 mark)
(b) Predict, with reason, whether manganese is more reactive than silver. (2 marks)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
246
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part III Metals
(c) Iron is the metal next to manganese in the Periodic Table.
(i) State how iron is extracted from its ore. (1 mark)
(ii) A student stated that iron is more reactive than manganese because iron has
a higher atomic mass. Comment on the statement. (1 mark)
(iii) Briefly describe how to compare the reactivity of manganese and iron.
(2 marks)
##
(a) MnO2(s) + 2CO(g) Mn(s) + 2CO2(g) 1
(b) Manganese is more reactive than silver. 1
Silver can be extracted easier (by heating the ore alone) from its ore. 1
(c) (i) Heating the iron ore, coke, limestone and air in a blast furnace. 1
(ii) The statement is incorrect. The reactivity of a metal depends on how
readily its atoms lose electrons, but not the atomic mass of the metal. 1
(iii) Dip a piece of manganese in a solution of iron(II) salt. 1
If displacement reaction occurs, it indicates that manganese is more
reactive than iron. 1
___
7
##
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 11
247
You might also like
- General Chemistry 11th Edition Ebbing Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesGeneral Chemistry 11th Edition Ebbing Solutions ManualNatalieAcevedogibfk100% (36)
- January 2012 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument24 pagesJanuary 2012 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Heat of Precipitation ActivityDocument8 pagesHeat of Precipitation ActivityNorfazliyana AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Enaiposha Girls High Schoo1Document8 pagesEnaiposha Girls High Schoo1euginemwakhaNo ratings yet
- F3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617Document6 pagesF3 Chemistry Final Revision - 1617jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Structured QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Structured questions 2 - 複本Document18 pagesChapter 18 Structured questions 2 - 複本connieNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 11 EDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 11 ERaiNo ratings yet
- Water, Lead Sulphide, Hydrogen, Copper, Mercury, Carbon Dioxide'Document24 pagesWater, Lead Sulphide, Hydrogen, Copper, Mercury, Carbon Dioxide'Kai Keung ChiuNo ratings yet
- Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)Document5 pagesKiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) MID-YEAR EXAMINATION (2013-2014) Form 5 Chemistry Marking Scheme: Section A: (30%)wslNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations - 1Document3 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations - 1Rehan MotiwalaNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Metal With AnswerDocument5 pagesTest 2 Metal With AnswerIsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 48 Structured Questions BlankDocument13 pagesChapter 48 Structured Questions Blankjoyousclassroom joyousclassroomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structured QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesForm 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeeuginemwakhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansDocument13 pagesChemistry 2000 Paper 1+ansapi-38240030% (2)
- Acids, Bases - Salts 4 QPDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases - Salts 4 QPANIKA DHANIKACHALAMNo ratings yet
- Exam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS OnlineDocument5 pagesExam 1A For First 6 Chapters MS Onlinehalahossam8899No ratings yet
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- 25.5.22-10th-Chem-Ab 1-2022-23Document13 pages25.5.22-10th-Chem-Ab 1-2022-23Aadarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - 10 A Assignment 1 Date: 18-08-2020 - Answer The Following QuestionsDocument10 pagesChemistry - 10 A Assignment 1 Date: 18-08-2020 - Answer The Following QuestionsRoselyn TrixieNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument10 pagesCHEMBryan WillNo ratings yet
- Wa0020.Document3 pagesWa0020.Guddi SinghNo ratings yet
- 2021 S5 1st Exam AnswerDocument8 pages2021 S5 1st Exam Answerlala LuNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements-SignedDocument7 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements-SignedMuhammed Sadiq100% (1)
- Chemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERDocument12 pagesChemistry Form2 Endterm2 OPENERBenjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Chem Mock Brand School Mock Exam 12 P1-QDocument19 pagesChem Mock Brand School Mock Exam 12 P1-QLiu JoeNo ratings yet
- Chem 2Document6 pagesChem 2ideal writersNo ratings yet
- Class: 10 Subject: Chemistry Name - DateDocument3 pagesClass: 10 Subject: Chemistry Name - Dateansh1510No ratings yet
- P545/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Certificate of Education Page 1Document15 pagesP545/2 Chemistry Paper 2: Uganda Certificate of Education Page 1Kahuma DeoNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988048-MCQDocument13 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988048-MCQabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988039-1MARKDocument8 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988039-1MARKabiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Chemistry F3Document3 pagesChemistry F3dembeleosman266No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Summative Assessment - I Grade-7 ChemistryDocument3 pagesMark Scheme Summative Assessment - I Grade-7 ChemistryVivek Sadasivan NairNo ratings yet
- Chem F3 Temeke Marking GuideDocument8 pagesChem F3 Temeke Marking Guidendururutseg98No ratings yet
- Part III 2019 Updated QBDocument6 pagesPart III 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesForm 2 - Chemistry - Marking SchemeMejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- 2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查Document4 pages2122 CHEM UT2-F4-P1B-M - 已檢查s202001001No ratings yet
- WS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetDocument8 pagesWS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetSiyaNo ratings yet
- Ms Class 10 Science 2022 23Document7 pagesMs Class 10 Science 2022 23methesmrtyNo ratings yet
- CLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988058-MCQ-PART2Document11 pagesCLASS X CHEMISTRY question-988058-MCQ-PART2abiniveshofficial4708No ratings yet
- Marking Guide For Getting Ready For Zimsec - 231108 - 204409Document15 pagesMarking Guide For Getting Ready For Zimsec - 231108 - 204409tinevimbomagureNo ratings yet
- Chem 3 ADocument3 pagesChem 3 AKobe YuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Structured QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Part I 2019 Updated QBDocument7 pagesPart I 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements Q & ADocument10 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-10. S-Block Elements Q & A3093 Ayoob NNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDocument9 pagesChemistry-Chapter 1 PyqDhilfa Eleyedath International Indian School - Abu DhabiNo ratings yet
- Workbk 10Document177 pagesWorkbk 10Manushree NayakNo ratings yet
- Chem PP1 MSDocument9 pagesChem PP1 MSianmutwiriNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPDocument31 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals QPRanjitha BanuNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 2 End Term 3Document8 pagesChem Form 2 End Term 3DenisNo ratings yet
- 10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument12 pages10th Chapter 3 DPPs - Metals and Non-MetalsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Yr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023Document7 pagesYr 11 - Chem - Term 1 Revision WS - Jan 2023troyrodrigues36No ratings yet
- Part 3 MetalsDocument8 pagesPart 3 Metals劉曉晴No ratings yet
- Eje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Document7 pagesEje Islamic f4 22 Chem 1-1Nassrah JumaNo ratings yet
- Xii PB Che MS 2023Document8 pagesXii PB Che MS 2023Hitesh PerniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Structured QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 13 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 6 QPDocument9 pagesRate of Reaction 6 QPmalak tahaNo ratings yet
- CISCE Gr-9 Chemistry Term2 Sample-Paper 2023-24Document9 pagesCISCE Gr-9 Chemistry Term2 Sample-Paper 2023-24abhipisharody09No ratings yet
- Question 837579Document10 pagesQuestion 837579Techno DevtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Assertion-Reason QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 Assertion-Reason Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Structured QuestionsDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Structured QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Structured QuestionsDocument18 pagesChapter 9 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument24 pagesChapter 9 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Structured QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Multiple-Choice Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- 3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)Document8 pages3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)teresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Structured QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 1A 1B 2 - New QuestionDocument58 pagesQuestion Bank 1A 1B 2 - New Questionteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- QB 1A ch05 e QuestionsDocument12 pagesQB 1A ch05 e Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Sampling of Liquid Cast IronDocument2 pagesSampling of Liquid Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646No ratings yet
- TEPZZ - Z 78 A - T: European Patent ApplicationDocument13 pagesTEPZZ - Z 78 A - T: European Patent ApplicationDesi Rahma PrihandiniNo ratings yet
- PGM Extractive MetallurgyDocument15 pagesPGM Extractive MetallurgyAde SatriaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Procedure For HACH DR 2800Document6 pagesAmmonia Procedure For HACH DR 2800Berliana Cahya NingtiasNo ratings yet
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDocument285 pagesPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- 2004 Chemistry - James Ruse With SolutionsDocument36 pages2004 Chemistry - James Ruse With SolutionsWilliam HouNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Naming Chemical CompoundsDocument6 pagesChem Notes Naming Chemical CompoundsAbigail Ambrosio (ABI)No ratings yet
- GR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument18 pagesGR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperagangdayimaniNo ratings yet
- Astm D 511Document9 pagesAstm D 511Daniel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/21Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/21nmeghani325No ratings yet
- Lindab Round Duct and FittingDocument108 pagesLindab Round Duct and FittingNguyễn Xuân ĐiệpNo ratings yet
- Chem12015 ExamDocument16 pagesChem12015 ExamAAVANINo ratings yet
- Compounds Containing Nitorgen & Practical Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesCompounds Containing Nitorgen & Practical Organic ChemistryAshwin BalajiNo ratings yet
- Solubilitynotesnocomicsv4 PDFDocument29 pagesSolubilitynotesnocomicsv4 PDFterryNo ratings yet
- MCQ - WS! June 2023Document7 pagesMCQ - WS! June 2023Prakriti DhakalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure For Grade 10Document4 pagesAtomic Structure For Grade 10Aja AndersonNo ratings yet
- VALUES OF CRM UpdatedDocument137 pagesVALUES OF CRM UpdatedArijit DasGuptaNo ratings yet
- D BlockDocument17 pagesD Block145556No ratings yet
- Soylent Formula V3Document2 pagesSoylent Formula V3Ryan AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 2012 Acs Practice ExamDocument17 pages2012 Acs Practice ExamNyxas IoannisNo ratings yet
- Solution For "Introduction To Chemical Engineering" Chapter 11Document8 pagesSolution For "Introduction To Chemical Engineering" Chapter 11jiholee1117No ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemistry)Document25 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemistry)bm OUREMNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsDocument36 pagesThe Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-La3. Raw FileDocument9 pagesBiochemistry-La3. Raw Filejazzermill acobNo ratings yet
- Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiDocument23 pagesProgress in Particle and Nuclear Physics: M. Salvatores, G. PalmiottiWalid BadrNo ratings yet
- 10.thermodynamics and Chemistry Data: Cement Process Engineering Vade MecumDocument10 pages10.thermodynamics and Chemistry Data: Cement Process Engineering Vade MecumHasnaoui SamirNo ratings yet