Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre Calculus
Pre Calculus
Uploaded by
kiellaus61270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document provides an introduction to conic sections, including parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles. It defines each conic section based on the intersection of a plane with a double-napped cone. Key parts of each conic section are identified, such as the vertex, focus, directrix, and axis of symmetry for parabolas. Standard equations for circles and general equations for parabolas and circles are also presented.
Original Description:
Pre-Calculus STEM 11 1st Quarter
Original Title
Pre-Calculus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to conic sections, including parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles. It defines each conic section based on the intersection of a plane with a double-napped cone. Key parts of each conic section are identified, such as the vertex, focus, directrix, and axis of symmetry for parabolas. Standard equations for circles and general equations for parabolas and circles are also presented.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePre Calculus
Pre Calculus
Uploaded by
kiellaus6127This document provides an introduction to conic sections, including parabolas, ellipses, hyperbolas, and circles. It defines each conic section based on the intersection of a plane with a double-napped cone. Key parts of each conic section are identified, such as the vertex, focus, directrix, and axis of symmetry for parabolas. Standard equations for circles and general equations for parabolas and circles are also presented.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Pre-Calculus
INTRODUCTION TO CONIC SECTIONS 2
● h & k = opposite signs, r2 = 𝑟
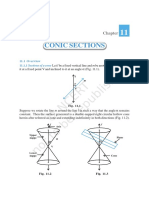
● Conic sections are obtained from
● r2 = 0 - no circle just point
the intersection between a
● r2 < 0 - no circle since there is no
double-napped cone and a plane.
negative distance
Parabolas
● Parabolas are formed when the
THE GENERAL EQUATION OF THE CIRCLE
plane is parallel to the generating
Ax2 + By2 + Cx + Dy + E = 0
line of one cone.
where: A, B, C, D, and E are real numbers
Ellipses
and A=B and are not equal to zero.
● Ellipses are formed when the plane
Step 1: regroup the given
intersects the one cone at an angle
Step 2: complete terms
other than 90°.
Step 3: simplify
Hyperbolas
e.g.
● Hyperbolas are formed when the
x2 + y2 - 6x - 8y + 7 = 0 (GE)
plane is parallel to the axis of
regroup:
revolution or the 𝑦-axis.
(x2 - 6x) + (y2 - 8y) = -7
Circles
complete terms:
● Circles are formed when the
(x2 - 6 + 9) + (y2 - 8y + 16) = -7 + 9 + 16
intersection of the plane is
! divide by two and square 2nd term to get third term.
perpendicular to the axis of
simplify:
revolution.
(x - 3)2 + (y - 4)2 = 18
● must be parallel to the base
c = (3,4)
COMMON PARTS OF THE CONIC r=3 2
SECTIONS PARABOLA
Vertex ● is a locus of points which are
● an extreme point on a parabola, equidistant from a fixed point
hyperbola, and ellipse. F(called focus) and fixed line
Focus and Directrix D(called directrix)
● the point and the line on a conic
section are used to define and PARTS OF A PARABOLA
construct the curve, respectively. Focus
Center ● Fixed point of parabola.
● It is the midpoint between the two Directrix
foci of an ellipse and hyperbola. ● Fixed line of parabola
● For circles, the center is the point Vertex (h,k)
equidistant from any point on the ● Point of intersection of the axis of
surface. symmetry and the parabola.
Axis of Symmetry
THE STANDARD EQUATION OF THE ● Line x=h; goes through the focus
CIRCLE Latus Rectum
● with center at origin (0,0) and ● Is the chord through focus parallel
radius r>0 is x2 + y2 = r2 to the directrix
● with center at c(h,k) and radius r>0
is (x-h)2 + (y-k)2 = r2 GENERAL EQUATION OF PARABOLA
Ax2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 / By2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
You might also like
- ANALYTIC GEOMETRY For DEMODocument16 pagesANALYTIC GEOMETRY For DEMOnikkoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus and KPDocument12 pagesPre-Calculus and KPFrancine MontemayorNo ratings yet
- 06 CH.6 Conic SectionsDocument21 pages06 CH.6 Conic SectionsAfrazia UmerNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesA Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsPat ChuNo ratings yet
- Maths - Parabola UnacadDocument72 pagesMaths - Parabola UnacadKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- MOD 2 - Conic SectionsDocument42 pagesMOD 2 - Conic SectionsVirender DassNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 CircleDocument23 pagesLesson 1.1 CircleSTEM 8 PRODUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- q1 Precal Notes (In Progress)Document20 pagesq1 Precal Notes (In Progress)saturosjuliaclarisseNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Maths Notes 2024 CH 6 Ex 6 1 and 6 3Document34 pages12th Class Maths Notes 2024 CH 6 Ex 6 1 and 6 3mresamtamarbbNo ratings yet
- Conics SectionDocument54 pagesConics Sectionjamaira haridNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Analytic Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument49 pagesWeek 1: Analytic Geometry and Conic SectionsPerfect BeanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2-CIRCLE PDFDocument23 pagesLesson 2.2-CIRCLE PDFChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- Slope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Document3 pagesSlope-Intercept Form: (A and B Cannot Both Be 0)Femie SurNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document14 pagesGroup 4alethuaNo ratings yet
- MathDocument7 pagesMathner sevillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Conic Sections PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Conic Sections PDFceca.mizuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Description:: Knowledge ActivationDocument18 pagesLesson Description:: Knowledge ActivationeL LeahNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics UNIT-4,5Document62 pagesComputer Graphics UNIT-4,5Technical Kamal RajputNo ratings yet
- Calculus Iii: CHAPTER 2: Curves and SurfacesDocument47 pagesCalculus Iii: CHAPTER 2: Curves and SurfacesRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Group 2 (Parabola)Document33 pagesGroup 2 (Parabola)krisgil ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Circles: Chapter HighlightsDocument55 pagesCircles: Chapter HighlightsAditya WanwadeNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument40 pagesConic SectionsMariel Milan100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - CircleDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - CircleBlaireNo ratings yet
- Circle (Theory)Document29 pagesCircle (Theory)Rohan GubbaNo ratings yet
- Curvature Functions On A One-Sheeted Hyperboloid: Boris OdehnalDocument17 pagesCurvature Functions On A One-Sheeted Hyperboloid: Boris OdehnallucasNo ratings yet
- Inps Circle Study MaterialDocument35 pagesInps Circle Study MaterialKulbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections and CirclesJanexx DioNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Class 12Document76 pagesStraight Lines Class 12technical swaroopNo ratings yet
- Conic Section NcertDocument22 pagesConic Section NcertRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summaries - Pure Maths 1Document13 pagesChapter Summaries - Pure Maths 1Aariz KhanNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument48 pagesConic SectionsMarione Angeli D. CanonizadoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument6 pagesMathematics ReviewerJared AlexanderNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION SET Math IIIDocument4 pagesSOLUTION SET Math IIIMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument27 pagesConic SectionsMARY ANNNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola Week 5: Content StandardsDocument12 pagesHyperbola Week 5: Content StandardsJackylyn FalejoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 21Document77 pagesAnalytic Geometry 21DANIEL DAGARAGNo ratings yet
- Circle - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2024Document4 pagesCircle - Mind Maps - Prayas JEE 2024Shubham SarkarNo ratings yet
- (Eduwaves360) CONIC 12th (2018C) EDocument101 pages(Eduwaves360) CONIC 12th (2018C) EAlbertNo ratings yet
- PreCal 1 NotesDocument20 pagesPreCal 1 NotesMark JimenezNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document4 pagesExercise 2ANo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Prepared By: Roqui Mabugay GonzagaDocument30 pagesConic Sections: Prepared By: Roqui Mabugay GonzagaRoqui M. GonzagaNo ratings yet
- 5 EllipseDocument39 pages5 EllipseCL CabonceNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument4 pagesConic Sectionsumirmalhotra06No ratings yet
- Conics: ParabolasDocument13 pagesConics: ParabolasJJ MosesNo ratings yet
- Conic Section PDFDocument22 pagesConic Section PDFishad satyen100% (2)
- Pre Cal Module1Document12 pagesPre Cal Module1Azhy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Section ConicDocument22 pagesSection ConicRishab Kumar100% (1)
- 10.3: Hyperbolas: I. DefinitionsDocument2 pages10.3: Hyperbolas: I. Definitionsmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- PC Reviewer Q1Document4 pagesPC Reviewer Q1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument12 pagesConic Sectiondivyanshivikramsingh2007No ratings yet
- Conic Section - SummaryDocument16 pagesConic Section - Summarymehakgarg2k5No ratings yet
- 1705808131Document134 pages1705808131Study EasyNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola NotesDocument2 pagesHyperbola NotesKunj DalalNo ratings yet
- Major Sub in STEM ReviewerSTEM C 1Document11 pagesMajor Sub in STEM ReviewerSTEM C 1Mary Rose Imperial ParagoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas ReviewDocument9 pagesGeometry Formulas Reviewleslybacallao305No ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 ParabolaDocument12 pagesWorksheet-1 ParabolaChetanNo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument32 pagesEllipsepotpotcabantog30No ratings yet
- ParabolasDocument32 pagesParabolasSun NiNo ratings yet
- Precal Notes MidtermsDocument21 pagesPrecal Notes MidtermsJudge Angelo De La Cruz100% (1)
- Weekly Exam 3Document22 pagesWeekly Exam 3TEN SAMARITANo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipseWanderlust WengNo ratings yet
- 11 Parabola Revision Notes QuizrrDocument66 pages11 Parabola Revision Notes QuizrrJainil ModiNo ratings yet
- Conics: ParabolasDocument13 pagesConics: ParabolasJJ MosesNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola Quiz - 1Document4 pagesHyperbola Quiz - 1SOHAM CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument78 pagesAnalytical GeometryChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument12 pagesConic SectionsgogoagoneNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Conic-Section. V526110765Document26 pagesDisha Publication Conic-Section. V526110765Ashish KumarNo ratings yet
- Corso - Perego (Complex Algebraic Surface Note)Document208 pagesCorso - Perego (Complex Algebraic Surface Note)kehao chengNo ratings yet
- Model Paper-1: Maths-2BDocument10 pagesModel Paper-1: Maths-2BAdilNo ratings yet
- Stable CurvesDocument8 pagesStable CurvesTabes BridgesNo ratings yet
- Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 11.7. Conic Sections in Polar CoordinatesDocument5 pagesParametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 11.7. Conic Sections in Polar Coordinatessujit kcNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Part 4 of 8Document24 pagesConic Section Part 4 of 8majji satishNo ratings yet
- Udaan Class XI Maths Part 2 PDFDocument428 pagesUdaan Class XI Maths Part 2 PDFDatta WakdeNo ratings yet
- Ellipse-04 - Exercise LevelDocument17 pagesEllipse-04 - Exercise LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 06Document13 pagesLecture Notes 06Richards Ðånte WisdomNo ratings yet
- Precalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M9 13Document3 pagesPrecalculus - ANSWERSHEET Q1 M9 13JERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- L-4 Ellipse and Hyperbola Short NotesDocument16 pagesL-4 Ellipse and Hyperbola Short NotesShresth AnandNo ratings yet
- Main & Advanced: MathematicsDocument94 pagesMain & Advanced: MathematicsDevesh SonarNo ratings yet
- PRE CALCULUS - MODULE Week 5Document8 pagesPRE CALCULUS - MODULE Week 5Azur LaneNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument18 pagesParabolaanniaAx ఌNo ratings yet
- Ltlyiiw Innoyitiont: Vertices FociDocument4 pagesLtlyiiw Innoyitiont: Vertices FociGladwin BuquironNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Practice Test02Document9 pagesConic Sections Practice Test02Shalynnie Peñuela LievanoNo ratings yet
- Unit UNIT - 1 (A) 1 (A) Unit UNIT - 1 (A) 1 (A) : Conic Sections Conic SectionsDocument39 pagesUnit UNIT - 1 (A) 1 (A) Unit UNIT - 1 (A) 1 (A) : Conic Sections Conic SectionsArun Pravin APNo ratings yet
- Identify Parts of A Circle WorksheetDocument1 pageIdentify Parts of A Circle WorksheetRiesta tarianiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1: Conic Sections Module OverviewDocument37 pagesMODULE 1: Conic Sections Module OverviewJerald EroyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Circles Parabolas and Ellipses PracticeDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Circles Parabolas and Ellipses PracticeKaviraj SinghNo ratings yet