Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Interpretation of Statutes
Interpretation of Statutes
Uploaded by
SHRAVANCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Evagrius Talking Back PDFDocument2 pagesEvagrius Talking Back PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Performance Management at Vitality Health EnterpriseDocument4 pagesPerformance Management at Vitality Health EnterpriseMymie MaandigNo ratings yet
- 2023 BallotDocument2 pages2023 Ballotisaac_maykovichNo ratings yet
- Legal ProfessionalsDocument20 pagesLegal ProfessionalsDebojyoti Koner 0022No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document1 pageChapter 3Hieu Tran Vo TamNo ratings yet
- Object Purpose and NecessityDocument5 pagesObject Purpose and NecessityQueen BeeNo ratings yet
- Structure of ICCDocument2 pagesStructure of ICCRaaghav SapraNo ratings yet
- Separation of Powers 2Document1 pageSeparation of Powers 2SimpliciusNo ratings yet
- Settlement of International DisputesDocument11 pagesSettlement of International Disputesanshumanpanda135No ratings yet
- Union and TerritoriesDocument1 pageUnion and TerritoriesAkansha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Key Provisions of DPDPADocument1 pageKey Provisions of DPDPAAy UshNo ratings yet
- CambridgeDocument5 pagesCambridgepaquete GNo ratings yet
- Deped Gen. Trias - Draft MOADocument5 pagesDeped Gen. Trias - Draft MOAJofit DayocNo ratings yet
- 8 02 Seeing All The BranchesDocument3 pages8 02 Seeing All The BranchesBrian Minh DaoNo ratings yet
- Midsem Notes GrammarDocument4 pagesMidsem Notes GrammarFarid AshaariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 24-May-2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 24-May-2024xinmiu725No ratings yet
- Polity English Compiled NotesDocument130 pagesPolity English Compiled NotesJay Vardhan SihagNo ratings yet
- Report On Human RightsDocument5 pagesReport On Human RightsQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- Miriam Tillinger CVDocument6 pagesMiriam Tillinger CVapi-222275167No ratings yet
- ICTAD Specifications For WorksDocument12 pagesICTAD Specifications For Workssanojani50% (8)
- Bappa BanerjeeDocument2 pagesBappa BanerjeeSuranjan BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- The 21st Century From The Positions of Modern Science: Intellectual, Digital and Innovative AspectsDocument705 pagesThe 21st Century From The Positions of Modern Science: Intellectual, Digital and Innovative AspectsLeiliNo ratings yet
- DUE 2016 Registration Form1Document1 pageDUE 2016 Registration Form1Mananga destaingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-V 5Document80 pagesChapter 1-V 5Heleina Alexies100% (2)
- Manager-Magazin 2006 10 48923426Document10 pagesManager-Magazin 2006 10 48923426Neel DoshiNo ratings yet
- An Analysis Model of Industrial International CompetitivenessDocument4 pagesAn Analysis Model of Industrial International CompetitivenessYasir AltafNo ratings yet
- Appendix 17 - Instructions - FAR No. 1Document2 pagesAppendix 17 - Instructions - FAR No. 1Tesa GD100% (1)
- Jamshedpur DraftDocument45 pagesJamshedpur DraftArangNo ratings yet
- Moot ProblemDocument11 pagesMoot ProblemDiganta RoyNo ratings yet
- Melting Pot or Salad Bowl? Cultural DiversityDocument9 pagesMelting Pot or Salad Bowl? Cultural DiversityRingle JobNo ratings yet
- AggressionDocument9 pagesAggressionapi-645961517No ratings yet
- Final Demo Iam Blessed 2Document5 pagesFinal Demo Iam Blessed 2Janine DizonNo ratings yet
- Catalog Top Angajatori Pentru Care Sa Lucrezi in 2023Document148 pagesCatalog Top Angajatori Pentru Care Sa Lucrezi in 2023Marinel RaduNo ratings yet
- Sch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopDocument5 pagesSch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopVan Russel Robles0% (1)
- Makalah Biography: Universitas Mahakarya Asia YogyakartaDocument9 pagesMakalah Biography: Universitas Mahakarya Asia YogyakartaKristianus A.J UleNo ratings yet
- Legal Principles in Shipping Business 2014Document3 pagesLegal Principles in Shipping Business 2014MarvinNo ratings yet
- The Break Up of AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Break Up of AnswersMuhammad MudassirNo ratings yet
- Petition For Original JurisdictionDocument28 pagesPetition For Original JurisdictionNBC MontanaNo ratings yet
- Memorandum MODDocument21 pagesMemorandum MODrajeshd006100% (2)
- AffidavitsDocument36 pagesAffidavitsKarexa Skye LeganoNo ratings yet
- Office of The Executive SecretaryDocument4 pagesOffice of The Executive SecretaryJewel AnggoyNo ratings yet
- Ohe! Vaishnava ThakuraDocument3 pagesOhe! Vaishnava ThakuraagnelwaghelaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Learn Serbian. Have FunDocument11 pagesStudy Guide: Learn Serbian. Have FunragkaraNo ratings yet
- The Interdependent Nature of BusinessDocument7 pagesThe Interdependent Nature of Businessdajiah greenNo ratings yet
- State Legislature - Article 168 - 212: Bicameral and Unicameral StatesDocument5 pagesState Legislature - Article 168 - 212: Bicameral and Unicameral StatesKirti KanaujiyaNo ratings yet
Interpretation of Statutes
Interpretation of Statutes
Uploaded by
SHRAVANOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Interpretation of Statutes
Interpretation of Statutes
Uploaded by
SHRAVANCopyright:
Available Formats
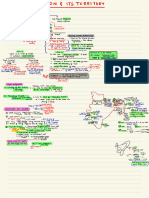
BRUSH PEN-25 % - 0 .
INTERPRETATION OF STATUTES
⑪
↳ Parliament entere understand Role of
Count the will of
Interprets Judiciary
Legislature
THE LAW
cannot
Judge
alter a law he ,
English
is not
cam
only interpret Language
make it clear an instrument
It ispassed by of mathematical
② the president when
precision
barlament is not working
GENERAL CLASSIFICATION
OF INTERPRETATION
->
LEGAL Actual role of law which binds the judge to
place a certain interpretation
->
DOCTRINAL -
Real and True
meaning of Statute
->
AUTHENTIC Interpretation derived from the legislator himself
-
GRAMMATICAL Applies ordinary rules of speech to find out the meaning
-
->
->
USUAL It comes from other source such as custome
-
->
LOGKAL -
Goes beyond the words and tries to discover the intention of the statute
O
3 INSTRUMENTS
Common PARLANCE -
formal legal document which creates
record
or confirms a
right or a fact .
FORMAL WRITING -
An agreement deed , or record
drawn up and executed in a Technical
form .
Sec-2 (in)
STAMP DOTY ACT- Instrument includes document
every is
by
right a abilitie
which
any or
ENTERPRETATION & CONSTRUCTION purports to be a
Extended recorded
0
↳
,
extinguished or .
often used interchangeably
DEEDS Us INSTRUMENT All deeds instruments
They overlap
each other
-
are
C
Though all instruments
may not be
deeds .
In India ,
be no distinction seems to
①
Finding true sense ① Drawing conclusions made between instruments and deeds .
of words used .
from the interpretations .
②
using the letter ② Using the spirit ⑤
of law ↑
of law .
IMPORTANCE Or IOS
To Find out Ineffectiveness Establish
Uniformity serves as a
bridge
True Intentions of of in
understanding by of understanding
the legislature Language Intensive use
of legal between the law
maker and its
techniques in 10s for users .
greater accuracy .
HUMAN LIMITATION 8 It is not within human powers to predict all the facts that
may
arise on future .
Hence we need Roles of Interpretation along with the tools to
Interpret .
RULES OF INTERPRETATION/construction
PRIMARY RULES
① LITERAL CONSTRUCTION
-
Also called grammatical construction .
(literal
-
First approach the words as
is to read
is clear - no need to adopt
they are
meaning)
construction
8
when
languageis other
-
any ⑧
>
whole there
ambiguity $ absurdity ,
Literal construction fails .
② REASONABLE CONSTRUCTION
Also called
golden
as rule of interpretation
-
Give a sensible
meaning give effect to the intention of the legislature
-
Inspect Proxies
and reasonable interpretation (: LI Indra vs
-
/
MOA must be read
fairly . o
A L
r . Mudaliar)
Neither too rigid nor too libral
-
③ PURPOSIVE CONSTRUCTION
-
Also called as Mischief Rule OR rule
of beneficial construction .
-
Used when there is a possibility of more than one interpretation .
-
four matters to considered : -
·
Law
Before
·
Mischief caused by it
③.
③
Remedy
·
Reason
-
Court will adopt the construction which shall suppress mischief and
advance
aemidy .
③ HARMONIOUS CONSTRUCTION
construct provisions which harmonize conflicting laws
-
-
EXCEPTION I
Statute itself makes clear by using the word "NOTWITHSTANDING" Then this rule
will not apply -
-
EXCEPTION 2
When it is impossible to avoid inconsistency/conflict blu two laws , then
latest provision is preferred over old provision .
-
A
specific rule will always override a
general rule .
"SUBJECT To
"
"NOTWITHSTANDING" "WITHOUT PREJUDICE"
Husband
says I am what work in
eg .
eg .
Notwithstanding Particular provisions will
of the house addition to the
the boss
my
husband
say , you general provisions .
subject to what have to listen to re ive Particular provisions will not
my
.
wife says · restrict the operation and generality
N ↓ of the
prceeding general provision .
subservient overriding
⑤ EJUSDEM GENERIS
-
Interpretation of general words should be
of the same "kindor species" of the
words mentioned with them along .
-
where general words are used after the specific words ,
then the general
words will take the color from the specific words .
-
EXCEPTION
where specific words are of different categories and not of the same nature .
⑥ EXCEPTIONAL CONSTRUCTION
-
where certain words would defeat real object of
the an enactment , then as an exception
such words be eliminated (Common SENSE RULES
may
.
-
The word "and" is conjuctive .
where as the word "or" is to separate .
Shall pimply Mandatory
"
Provision
words like shall moststreetly complied
-
See
,
SECONDARY RLLES
①EXPRESS MENTION OF ONE THING IMPLIES THE EXCLUSION OF ANOTHER
-
where there is a
specific section regulating a
particular artical , General provisions can be
ignored for the said article .
② CONTEMPORARY CONSTRUCTION (EFFECT of USAGE OR PRACTICE)
The best read it it would have been
way to interpret a document is to
-
as
read when it was made .
-
If an old law does not comply with today's workings or procedures ,
it needs to be amended .
CODIFIED LAN UNCODIFIED LA
↓ A
means
they've converted it is
only a tradition
law and
your custom into custom
③ NOSCITUR A SOCIs
It is known the associated by the keeps
by company It
-
or .
coupled
twomorewordswhichaCapable it lateeeee "
when
-
or are
④ STRICT AND LIBERAL CONSTRUCTION
Situation interpreted according a
Depending harta an
-
,
it has to be
- YOOLs To INTERPRETATION -
within the
INTERNAL TOOLS ACT
Itself
① LONG TTLES
the enactment
The short title
merely identifies and is chosen
merely for
-
convenience .
Long titles of the act Describes the enactment, therefore we can offer to
it to ascertain the object scope and purpose
of the act
,
.
② PREAMBLE
-
Preamble expresses the scope , object and purpose of the act .
override But of the statutes
Does not of
theplanprovisions te word gives rise
ple
~
to doubts . can be reffered e
to
order to arrive at the proper construction .
③ CHAPTER HEADINGS
Headings of the sections help to interpret
-
.
Headings cannot control override the section
-
or .
④ PROVISO
-
Provides exception to the section .
③ EXPLANATION
-
furtherance of what's given in the section for the purpose of
It is a
explaining the ,
main provision .
But the explanation SHOULD NOT be considered to widen the ambit of the section .
⑥ ILLUSTRATIONS
-
Act itself provide examples help interpretation
to .
-
-
They cannot modify the contents of the section .
⑦ SCHEDULES
and must be read
They form part of statute
together
-
~
In case of conflict ENACTMENT > SCHEDULES -
⑧ SAVINGS CLAUSE
-
It is used to preserve from destruction certain rights ,
remedies and privileges
already existing when a new law is created .
⑨ MARGINAL NOTES
-
Summaries which are often found at the side
of a section which sums up
the effect of that section .
-
NOT A PART OF ENACTMENT
-
Marginal notes related to articles of constitution are
apart of constitution ,
⑩ DEFINITIONAL SECTIONS/CLAUSES
ways of writing a definition
Three
-
when a word is defined to mean -> Exclusive ·
when a word is defined to include -> Inclusive .
when a word's defined to "mean and Include" -
outside
EXTERNAL TOOLS the
Act
CASE LAWS DICTIONARY
CONSOLIDATED STATUTES
NOMFICATIONS
OTHER LAWS PARLIAMENT PREVIOUS
INCLUDING HISTORY $ LANS
FOREIGN LAWS OLD LAWS
You might also like
- Evagrius Talking Back PDFDocument2 pagesEvagrius Talking Back PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Performance Management at Vitality Health EnterpriseDocument4 pagesPerformance Management at Vitality Health EnterpriseMymie MaandigNo ratings yet
- 2023 BallotDocument2 pages2023 Ballotisaac_maykovichNo ratings yet
- Legal ProfessionalsDocument20 pagesLegal ProfessionalsDebojyoti Koner 0022No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document1 pageChapter 3Hieu Tran Vo TamNo ratings yet
- Object Purpose and NecessityDocument5 pagesObject Purpose and NecessityQueen BeeNo ratings yet
- Structure of ICCDocument2 pagesStructure of ICCRaaghav SapraNo ratings yet
- Separation of Powers 2Document1 pageSeparation of Powers 2SimpliciusNo ratings yet
- Settlement of International DisputesDocument11 pagesSettlement of International Disputesanshumanpanda135No ratings yet
- Union and TerritoriesDocument1 pageUnion and TerritoriesAkansha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Key Provisions of DPDPADocument1 pageKey Provisions of DPDPAAy UshNo ratings yet
- CambridgeDocument5 pagesCambridgepaquete GNo ratings yet
- Deped Gen. Trias - Draft MOADocument5 pagesDeped Gen. Trias - Draft MOAJofit DayocNo ratings yet
- 8 02 Seeing All The BranchesDocument3 pages8 02 Seeing All The BranchesBrian Minh DaoNo ratings yet
- Midsem Notes GrammarDocument4 pagesMidsem Notes GrammarFarid AshaariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 24-May-2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 24-May-2024xinmiu725No ratings yet
- Polity English Compiled NotesDocument130 pagesPolity English Compiled NotesJay Vardhan SihagNo ratings yet
- Report On Human RightsDocument5 pagesReport On Human RightsQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- Miriam Tillinger CVDocument6 pagesMiriam Tillinger CVapi-222275167No ratings yet
- ICTAD Specifications For WorksDocument12 pagesICTAD Specifications For Workssanojani50% (8)
- Bappa BanerjeeDocument2 pagesBappa BanerjeeSuranjan BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- The 21st Century From The Positions of Modern Science: Intellectual, Digital and Innovative AspectsDocument705 pagesThe 21st Century From The Positions of Modern Science: Intellectual, Digital and Innovative AspectsLeiliNo ratings yet
- DUE 2016 Registration Form1Document1 pageDUE 2016 Registration Form1Mananga destaingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-V 5Document80 pagesChapter 1-V 5Heleina Alexies100% (2)
- Manager-Magazin 2006 10 48923426Document10 pagesManager-Magazin 2006 10 48923426Neel DoshiNo ratings yet
- An Analysis Model of Industrial International CompetitivenessDocument4 pagesAn Analysis Model of Industrial International CompetitivenessYasir AltafNo ratings yet
- Appendix 17 - Instructions - FAR No. 1Document2 pagesAppendix 17 - Instructions - FAR No. 1Tesa GD100% (1)
- Jamshedpur DraftDocument45 pagesJamshedpur DraftArangNo ratings yet
- Moot ProblemDocument11 pagesMoot ProblemDiganta RoyNo ratings yet
- Melting Pot or Salad Bowl? Cultural DiversityDocument9 pagesMelting Pot or Salad Bowl? Cultural DiversityRingle JobNo ratings yet
- AggressionDocument9 pagesAggressionapi-645961517No ratings yet
- Final Demo Iam Blessed 2Document5 pagesFinal Demo Iam Blessed 2Janine DizonNo ratings yet
- Catalog Top Angajatori Pentru Care Sa Lucrezi in 2023Document148 pagesCatalog Top Angajatori Pentru Care Sa Lucrezi in 2023Marinel RaduNo ratings yet
- Sch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopDocument5 pagesSch-Memo-No 44 - SLCP and Aip WorkshopVan Russel Robles0% (1)
- Makalah Biography: Universitas Mahakarya Asia YogyakartaDocument9 pagesMakalah Biography: Universitas Mahakarya Asia YogyakartaKristianus A.J UleNo ratings yet
- Legal Principles in Shipping Business 2014Document3 pagesLegal Principles in Shipping Business 2014MarvinNo ratings yet
- The Break Up of AnswersDocument3 pagesThe Break Up of AnswersMuhammad MudassirNo ratings yet
- Petition For Original JurisdictionDocument28 pagesPetition For Original JurisdictionNBC MontanaNo ratings yet
- Memorandum MODDocument21 pagesMemorandum MODrajeshd006100% (2)
- AffidavitsDocument36 pagesAffidavitsKarexa Skye LeganoNo ratings yet
- Office of The Executive SecretaryDocument4 pagesOffice of The Executive SecretaryJewel AnggoyNo ratings yet
- Ohe! Vaishnava ThakuraDocument3 pagesOhe! Vaishnava ThakuraagnelwaghelaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Learn Serbian. Have FunDocument11 pagesStudy Guide: Learn Serbian. Have FunragkaraNo ratings yet
- The Interdependent Nature of BusinessDocument7 pagesThe Interdependent Nature of Businessdajiah greenNo ratings yet
- State Legislature - Article 168 - 212: Bicameral and Unicameral StatesDocument5 pagesState Legislature - Article 168 - 212: Bicameral and Unicameral StatesKirti KanaujiyaNo ratings yet