Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iprint Ugma
Iprint Ugma
Uploaded by
Leezlleeh Jenice Obeso Mondero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBone health is influenced by three main factors: heredity, nutrient intake, and estrogen levels. Genetic factors determine 25-85% of bone mass and characteristics. Inadequate intake of nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein increases risk of bone loss and osteoporosis by hindering bone formation. Estrogen promotes bone health by stimulating osteoblast activity, but dropping estrogen levels during menopause can lead to bone density loss.
Original Description:
Original Title
iprint ugma
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBone health is influenced by three main factors: heredity, nutrient intake, and estrogen levels. Genetic factors determine 25-85% of bone mass and characteristics. Inadequate intake of nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein increases risk of bone loss and osteoporosis by hindering bone formation. Estrogen promotes bone health by stimulating osteoblast activity, but dropping estrogen levels during menopause can lead to bone density loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageIprint Ugma
Iprint Ugma
Uploaded by
Leezlleeh Jenice Obeso MonderoBone health is influenced by three main factors: heredity, nutrient intake, and estrogen levels. Genetic factors determine 25-85% of bone mass and characteristics. Inadequate intake of nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein increases risk of bone loss and osteoporosis by hindering bone formation. Estrogen promotes bone health by stimulating osteoblast activity, but dropping estrogen levels during menopause can lead to bone density loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
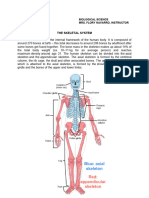
FACTORS INFLUENCING BONE HEALTH
1. HEREDITY- Genetic factors could influence skeletal growth and the amount of bone
mass attained.
A 2009 research overview explained that anywhere from 25 to 85 percent of our BMD
and other skeletal characteristics may be inherited.
2. Inadequate intake of nutrients important to bone increases the risk for bone loss and
subsequent osteoporosis. The process of bone formation requires an adequate and
constant supply of nutrients, such as calcium, protein, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamin
D, potassium, and fluoride.
3. Primary function of estrogen is development of the female secondary sex characteristics
such as ovaries, vagina and uterus.
Ovaries: Estrogen helps stimulate the growth of the egg follicle.
Vagina: In the vagina, estrogen maintains the thickness of the vaginal wall and
promotes lubrication.
Uterus: Estrogen enhances and maintains the mucous membrane that lines the
uterus.
The hormone estrogen regulates bone metabolism. It is essential to bone health
because it promotes the activity of osteoblasts, which are the cells that make new bone.
When estrogen levels drop — for example, during menopause — a person may lose
bone density.
Ribs 1–7 are classified as true ribs (vertebrosternal ribs). The
costal cartilage from each of these ribs attaches directly to the
sternum.
Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs (vertebrochondral ribs). The
costal cartilages from these ribs do not attach directly to the
sternum.
The last false ribs (11–12) are also called floating (vertebral)
ribs, because these ribs do not attach to the sternum at all.
You might also like
- BoneDocument6 pagesBoneLady CitraNo ratings yet
- English IIIDocument10 pagesEnglish IIIAyu Wulandari TrianggoNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument11 pagesProjectChristian AndersonNo ratings yet
- 18-Unit 1 Anatomy and Physiology For Health and ExerciseDocument91 pages18-Unit 1 Anatomy and Physiology For Health and ExercisesamNo ratings yet
- Normal Bone Formation and RemodelingDocument4 pagesNormal Bone Formation and RemodelingFernando AnibanNo ratings yet
- Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ, 3rd. Hip Fractures in The Elderly: A World-Wide Projection. Osteoporosis Int. 1992 2 (6) :285-289Document5 pagesCooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ, 3rd. Hip Fractures in The Elderly: A World-Wide Projection. Osteoporosis Int. 1992 2 (6) :285-289Noor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- Bones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateDocument10 pagesBones and Soft Tissue - Clinical GateAkira MasumiNo ratings yet
- Primary Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal WomenDocument5 pagesPrimary Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal WomenAzmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Task Related To Muscles and Bone ProblemDocument6 pagesTask Related To Muscles and Bone ProblemFOONG YI KUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- ASKEP OsteoporosisDocument41 pagesASKEP OsteoporosisMaya PinteNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemlorence.13911No ratings yet
- Osteoporosis and AsthakshayaDocument8 pagesOsteoporosis and AsthakshayaBala Kiran GaddamNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Processes in The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesPhysiologic Processes in The Skeletal SystemAry Romeo ShakespeareNo ratings yet
- Four Types of Cells in BoneDocument5 pagesFour Types of Cells in BoneTazrian Islam FarihaNo ratings yet
- Love HormoneDocument4 pagesLove HormoneNanda Nabilah UbayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23: Osteoporosis of The SpineDocument15 pagesChapter 23: Osteoporosis of The SpineTraian UrsuNo ratings yet
- Running Head: OSTEOPOROSIS 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: OSTEOPOROSIS 1AssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- What Is OsteologyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Osteology69722No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology AssignmentDocument12 pagesPathophysiology AssignmentBalqis HyoleeNo ratings yet
- 1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalDocument27 pages1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalAshar AbilowoNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Skeletal SystemDocument20 pagesDiseases of The Skeletal Systemlateef ramonNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Signs and SymptomsDocument9 pagesOsteoporosis: Signs and SymptomschelseachoirNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Program Studi S-1 KeperawatanDocument28 pagesOsteoporosis: Program Studi S-1 KeperawatanMhd RidwanNo ratings yet
- Arnett, T.Document10 pagesArnett, T.Alex AmorimNo ratings yet
- TGS KelipingDocument4 pagesTGS KelipingAldiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Bone Densitometru For The Medical PhysicistDocument10 pagesEssentials of Bone Densitometru For The Medical PhysicistAmanda Farias FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PhysiologyDocument17 pagesSkeletal System PhysiologyAmalia NahdaNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis For BonesDocument24 pagesOsteoporosis For BonesRoking KumarNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec 6Document2 pagesANAPHY Lec 6Mary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Other Factors Affecting Osteoporosis Risk in WomenDocument7 pagesAlcohol and Other Factors Affecting Osteoporosis Risk in WomenRo KohnNo ratings yet
- Bone Patology PDFDocument12 pagesBone Patology PDFLuis Humberto Padilla VazquezNo ratings yet
- Maxilary Sinus Graft ArunDocument181 pagesMaxilary Sinus Graft ArunJose Fernando Fragozo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Paper II-Skeleton SystemDocument4 pagesPaper II-Skeleton Systemritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Formation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteDocument13 pagesFormation: Blood Calcium Level - Calcium HydroxyapatiteClarissa IsuriñaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Sinus Bone GraftingDocument181 pagesMaxillary Sinus Bone GraftingTuấn Hành TrầnNo ratings yet
- Cell Lines and Primary Cell Cultures in The Study of Bone Cell Biology PDFDocument24 pagesCell Lines and Primary Cell Cultures in The Study of Bone Cell Biology PDFFilipa PereiraNo ratings yet
- Herbal Treatment For Osteoporosis: A Current Review: Ping Chung Leung, Wing Sum SiuDocument6 pagesHerbal Treatment For Osteoporosis: A Current Review: Ping Chung Leung, Wing Sum Siusiska khairNo ratings yet
- OsteosarcomaDocument3 pagesOsteosarcomaGeneral, Juliana Rose A.No ratings yet
- Normal Bone Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNormal Bone Anatomy and PhysiologyElsa GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Bone Structure: OsteoblastsDocument4 pagesBone Structure: OsteoblastsamlniNo ratings yet
- Factors of Bone Resorption of The Residual Ridge Ortman1962Document12 pagesFactors of Bone Resorption of The Residual Ridge Ortman1962AbdelKhalek BouararaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diseases and Bone HealthDocument11 pagesThyroid Diseases and Bone Healthmiguel saba sabaNo ratings yet
- Bone Health DiseaseDocument62 pagesBone Health Diseasejoeyjose18No ratings yet
- Nutritional Zinc Plays A Pivotal Role in Bone Health and Osteoporosis PreventionDocument14 pagesNutritional Zinc Plays A Pivotal Role in Bone Health and Osteoporosis PreventionDewi HenssaNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument6 pagesBones1NC21IS038 POLATHALA MOUNIKANo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument29 pagesChemistryIshkruti WaghmareNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesThe Human Skeletal SystemFelix AyornuNo ratings yet
- Update Osteoporosis Management (Listo)Document18 pagesUpdate Osteoporosis Management (Listo)Jossie AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Human Skeleton: Navigation SearchDocument7 pagesHuman Skeleton: Navigation SearchvinaiyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Treatment of Osteoporosis: Challenges For Clinical Practice in Older PeopleDocument15 pagesPathophysiology and Treatment of Osteoporosis: Challenges For Clinical Practice in Older PeopleDeddy ZulkarnaenNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: The Potential of Probiotics As A Therapy For OsteoporosisDocument26 pagesHHS Public Access: The Potential of Probiotics As A Therapy For OsteoporosisBagastyoNo ratings yet
- Systems of The BodyDocument144 pagesSystems of The BodyTweetie Borja DapogNo ratings yet
- 4 OsteoporosisDocument6 pages4 OsteoporosisLilianna Ireen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesOsteoporosisbiologoroger3637No ratings yet
- Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts, and Osteocytes: Unveiling Their Intimate-Associated Responses To Applied Orthodontic ForcesDocument12 pagesOsteoblasts, Osteoclasts, and Osteocytes: Unveiling Their Intimate-Associated Responses To Applied Orthodontic ForcesMariya NazimNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - mp4 - Google DriveDocument7 pagesSkeletal System - mp4 - Google Drivefaresalesa2005No ratings yet
- Answer The Following QuestionsDocument8 pagesAnswer The Following QuestionsHussain HussainNo ratings yet