Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 2stratman
Chap 2stratman
Uploaded by
ramosolaarni00 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesThis document discusses analyzing a company's external environment. It describes seven segments that comprise the general environment, including demographic, economic, political/legal, sociocultural, technological, global, and sustainable physical factors. It also discusses the industry environment and how factors like new entrants, supplier/buyer power, substitutes, and rivalry impact competition. The document outlines tools for external analysis like scanning, monitoring, forecasting, assessing trends, and understanding strategic groups and the five forces model to evaluate competitive threats and opportunities in the industry.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses analyzing a company's external environment. It describes seven segments that comprise the general environment, including demographic, economic, political/legal, sociocultural, technological, global, and sustainable physical factors. It also discusses the industry environment and how factors like new entrants, supplier/buyer power, substitutes, and rivalry impact competition. The document outlines tools for external analysis like scanning, monitoring, forecasting, assessing trends, and understanding strategic groups and the five forces model to evaluate competitive threats and opportunities in the industry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesChap 2stratman
Chap 2stratman
Uploaded by
ramosolaarni0This document discusses analyzing a company's external environment. It describes seven segments that comprise the general environment, including demographic, economic, political/legal, sociocultural, technological, global, and sustainable physical factors. It also discusses the industry environment and how factors like new entrants, supplier/buyer power, substitutes, and rivalry impact competition. The document outlines tools for external analysis like scanning, monitoring, forecasting, assessing trends, and understanding strategic groups and the five forces model to evaluate competitive threats and opportunities in the industry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
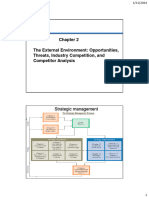
Chapter 2 StratMan External Environmental Analysis- turbulent,
complex, and global conditions that make
General Environment- composed of dimensions in
interpreting those environments difficult
the broader society that influence
Four parts:
Seven environmental segments:
1. Scanning
• Demographic 2. Monitoring
• Economic 3. Forecasting
• Political/legal 4. Assessing
• Sociocultural
• Technological Opportunity
• Global - helps a company reach strategic
• Sustainable physical competitiveness
Most companies, and certainly large ones-
continuously encounter multiple opportunities as
well as threats.
Threat- may hinder a company’s efforts to achieve
strategic competitiveness
Scanning
- entails the study of all segments in the
general environment
- to understand trends in the general
environment and to predict their implications
Monitoring- analysts observe environmental
changes to see if an important trend is emerging
Forecasting- analysts develop feasible projections
of what might happen, and how quickly
Assessing- to determine the timing and
significance of the effects of environmental
changes
Industry Environment- set of factors that directly
influences a firm and its competitive actions and 7 Segments of General Environment:
responses: 1. Demographic segment
• the threat of new entrants - concerned with a population’s size, age
• the power of suppliers structure
- commonly analyzed on a global basis
• the power of buyers
2. Economic segment- nature and direction of
• the threat of product substitutes
the economy in which a firm competes or may
• the intensity of rivalry among competing
compete
firms
3. Political/legal segment
Competitor Analysis - groups compete for attention, resources,
and a voice in overseeing the body of laws
- how the companies gather and interpret - to influence governments and how they try
information about their competitors to understand the influences
- understanding the firm’s competitor 4. Sociocultural segment- concerned with a
environment society’s attitudes and cultural values
5. Technological segment- includes the Strategic Groups
institutions and activities involved in creating
- set of firms emphasizing similar strategic
new knowledge
6. Global segment- includes relevant new global dimensions and using a similar strategy
markets, existing markets that are changing - useful for analyzing an industry’s
competitive structure
7. Sustainable physical environment segment-
potential and actual changes in the physical Competitor Analysis- focuses on each company
environment against which a firm competes directly
Industry Environment Analysis Ethical Considerations- firms must follow relevant
- companies use a rich mix of different laws and regulations as well as carefully articulated
ethical guidelines
competitive strategies to pursue above-
average returns
- has a more direct effect on the
competitive actions and responses a firm
takes to succeed
Industry- group of firms producing products that
are close substitutes
Five Forces of Competition Model
1. Threat of New Entrants- they bring
additional production capacity
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers-
increasing prices and reducing the quality of
their products
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers- buyers want
to buy products at the lowest possible price
4. Threat of Substitute Products- Substitute
products are goods or services from outside
a given industry that perform similar or the
same functions as a product that the
industry produces
5. Intensity of Rivalry among Competitors-
industry’s firms are mutually dependent,
actions taken by one company usually invite
responses
You might also like
- Importance of Leadership in Regulatory ScienceDocument14 pagesImportance of Leadership in Regulatory ScienceDr. Johanny Pestalozzi100% (2)
- 9015 - Assessment GuideDocument65 pages9015 - Assessment Guideirene hulkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Su Jiun Soon100% (3)
- Management Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesManagement Cheat Sheetnightmonkey215100% (2)
- Analyzing The External Environment of The FirmDocument4 pagesAnalyzing The External Environment of The FirmLucky Knight IINo ratings yet
- Analyzing The External Environment of The FirmDocument4 pagesAnalyzing The External Environment of The FirmLucky Knight IINo ratings yet
- 8.multinational Strategy (International Business)Document9 pages8.multinational Strategy (International Business)Asjad Jamshed100% (1)
- Summary Strategic ManagementDocument16 pagesSummary Strategic Managementasmara.savira1115No ratings yet
- Ch7 Study GuideDocument26 pagesCh7 Study Guideermias alemeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - PrelimDocument2 pagesReviewer - PrelimMary Justine GallanoNo ratings yet
- MBA Strategic Management Unit IIDocument16 pagesMBA Strategic Management Unit IImansi_veerwal0% (1)
- MGMT 1063 - Strama Module 3Document8 pagesMGMT 1063 - Strama Module 3Kay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2richard alexanderNo ratings yet
- Strategic Chapter 1,2,4 PDFDocument10 pagesStrategic Chapter 1,2,4 PDFosama muradNo ratings yet
- ADM650 CHAPTER 2 External AnalysisDocument58 pagesADM650 CHAPTER 2 External AnalysisArya zllkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 External EnvironmentDocument26 pagesUnit 3 External Environmentanon_808961301No ratings yet
- Module 2 Strategic ManagementDocument24 pagesModule 2 Strategic ManagementkpullapoyNo ratings yet
- Strama CHP 2Document8 pagesStrama CHP 2Gelliza Mae MontallaNo ratings yet
- 6 Sector Comparison WorksheetDocument6 pages6 Sector Comparison Worksheetapi-720147459No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Scanning The EnvironmentDocument17 pagesChapter 2-Scanning The EnvironmentharoldmichalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Diagnosing2 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter-5 Diagnosing2 PDFKimberly Mae StaRitaNo ratings yet
- Team5 Compilation of TopicsDocument24 pagesTeam5 Compilation of TopicsJammu JammuNo ratings yet
- Corporate StrategyDocument13 pagesCorporate StrategyWaliyullah100% (3)
- The External Environment AnalysisDocument6 pagesThe External Environment AnalysisThanh VânNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3erleen sumileNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Strategic Mgmt.Document38 pagesUnit-2 Strategic Mgmt.Arif QuadriNo ratings yet
- Monitoring The Environment and Considerations For Its Application and The Search For ValuesDocument5 pagesMonitoring The Environment and Considerations For Its Application and The Search For ValuesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- External Strategic Management Audit (Ot of SWOT)Document13 pagesExternal Strategic Management Audit (Ot of SWOT)Bethel Honey TanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document24 pagesLecture 3Shahla YasenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6Iris Jane SilvelaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportingDocument3 pagesGroup 1 ReportingErika CadagNo ratings yet
- Presentation Group 2 Bme2Document97 pagesPresentation Group 2 Bme2Ma. Lawrene T. BascoNo ratings yet
- FTU, Hanoi, Vietnam Strategic Management: Business Level Strategy Session 4: CH 4Document50 pagesFTU, Hanoi, Vietnam Strategic Management: Business Level Strategy Session 4: CH 4Anhh QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-3 Strategic ManagementDocument5 pagesChapter 2-3 Strategic ManagementMariya BhavesNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Environmental AnalysisDocument37 pagesGroup 1 Environmental AnalysisMailos JustinNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapter 01Document3 pagesNotes - Chapter 01Chad FerninNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Strategic AnalysisDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Strategic Analysisprasad guthiNo ratings yet
- BME 1 Strategy REVDocument11 pagesBME 1 Strategy REVIam IvysupanNo ratings yet
- STFM RecitationDocument7 pagesSTFM RecitationAnna Lyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management-MGT4216-BBUS-Topic 2Document38 pagesStrategic Management-MGT4216-BBUS-Topic 2Su Jiun SoonNo ratings yet
- Review of Sustainability and Sustainability ReportingDocument10 pagesReview of Sustainability and Sustainability ReportingLeah Kris DelsolorNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Marketing BehaviorDocument5 pagesReviwer Marketing BehaviorPalo, Grandhierella Candy Mhae D.No ratings yet
- W3 Industry and Internal EnvironmentDocument3 pagesW3 Industry and Internal EnvironmentColeen IbanezNo ratings yet
- 2 The External Environment AnalysisDocument14 pages2 The External Environment Analysisltquang.raitoNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - The Firm and Its EnvironmentDocument3 pagesWeek 3 - The Firm and Its EnvironmentCatherine Rivera75% (4)
- Analytical Tools in Strategic Management: Strategic AnalysisDocument61 pagesAnalytical Tools in Strategic Management: Strategic AnalysisAmogh PareekNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning Week 3 6Document20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning Week 3 6zyra.position1seoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Unit - IDocument24 pagesStrategic Management Unit - Inirthya2006No ratings yet
- PMGT 121 - Chapter 2Document31 pagesPMGT 121 - Chapter 2Kenneth Sogocio LucilaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Analyzing Competitive Environment - Spring 2022 - StudentDocument4 pages5 - Analyzing Competitive Environment - Spring 2022 - StudentwrerwerNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis - Topic 2-3Document23 pagesStrategic Analysis - Topic 2-3Raheem AzeezNo ratings yet
- Indicators of The Economics Ca FoundationDocument22 pagesIndicators of The Economics Ca Foundationoneunique.1unqNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 StrategicDocument19 pagesTopic 3 & 4 StrategicMAURICE KIOKONo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Environmental Context of ManagementDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Environmental Context of ManagementSaleena BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Strama Mod 3Document8 pagesStrama Mod 3Jaysah BaniagaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERSDocument10 pagesREVIEWERSmagdaylean87No ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic ManagementAmrita DasNo ratings yet
- NestleDocument39 pagesNestleAnaghaPuranik100% (6)
- Grading Criteria and Weightage of Each Section - Man7035Document3 pagesGrading Criteria and Weightage of Each Section - Man7035Yash BajajNo ratings yet
- Administrative Provisions For Individual Income TaxDocument20 pagesAdministrative Provisions For Individual Income Taxramosolaarni0No ratings yet
- Chap 1 LITODocument3 pagesChap 1 LITOramosolaarni0No ratings yet
- Product Management Chapter 23Document3 pagesProduct Management Chapter 23ramosolaarni0No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Inter ManDocument2 pagesTopic 3 Inter Manramosolaarni0No ratings yet
- Advanced Matplotlib in Python 1695062970Document54 pagesAdvanced Matplotlib in Python 1695062970yassine.boutakboutNo ratings yet
- Prospectus Department of Computer ScienceDocument29 pagesProspectus Department of Computer SciencevagajNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. RosalesDocument3 pagesPrepared By: Engr. Jude L. RosalesjlNo ratings yet
- Situations. Is The Employee Who Arrives Late Today Also The One Coworkers Say RegularlyDocument2 pagesSituations. Is The Employee Who Arrives Late Today Also The One Coworkers Say Regularlyshadrack nandwaNo ratings yet
- Resume of FARDUSHI FATEMADocument2 pagesResume of FARDUSHI FATEMAMahamodul Hasan ShohanNo ratings yet
- Service Learning Project Year Student Packet PART 1 INVESTIGATIONDocument13 pagesService Learning Project Year Student Packet PART 1 INVESTIGATIONFiorella MarinNo ratings yet
- Deped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Document4 pagesDeped Naga City - Schools Division: Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Quarter 1, HEALTH 8Jo DVera Gonzales IINo ratings yet
- MSI Algebra MemosDocument7 pagesMSI Algebra Memosmphodau92No ratings yet
- Price List Bahan Pt. Sari Dental MedikaDocument7 pagesPrice List Bahan Pt. Sari Dental Medika28NiMade NandaDiahPramestiNo ratings yet
- Sample 6751Document12 pagesSample 6751Atiya IftikharNo ratings yet
- CM-PR-DSG-01 Rev.02 Design ProcedureDocument10 pagesCM-PR-DSG-01 Rev.02 Design ProcedurePeter Sare WolloNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlansDocument5 pagesLesson Plansmahesh kumarNo ratings yet
- An Improved Savings Method For Vehicle Routing ProblemDocument6 pagesAn Improved Savings Method For Vehicle Routing ProblemMy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Adaptation - A Green Infrastructure Planning FramewDocument243 pagesClimate Change Adaptation - A Green Infrastructure Planning FramewMd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Webb Design Methodology PDFDocument5 pagesWebb Design Methodology PDFWilliam FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intellectual RevolutionDocument129 pagesLesson 1 Intellectual RevolutionMuttia SelgasNo ratings yet
- Social Welfare Agency AdministrationDocument22 pagesSocial Welfare Agency AdministrationMechisedec BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Extender D252 PDFDocument10 pagesExtender D252 PDFhammyNo ratings yet
- Ethics in BiotechnologyDocument42 pagesEthics in Biotechnologyronojoysengupta100% (1)
- Msme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: BatchDocument7 pagesMsme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: Batcharyan banchhorNo ratings yet
- HAP1 Review: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument37 pagesHAP1 Review: Dr. Garry Niedermayersweta paudelNo ratings yet
- Spring Bulletin 2004 Save The Redwoods LeagueDocument4 pagesSpring Bulletin 2004 Save The Redwoods LeaguemaryZbelinderNo ratings yet
- Patentable and Non Patentable InventionsDocument11 pagesPatentable and Non Patentable InventionsAniket SantraNo ratings yet
- Geneva UseDocument135 pagesGeneva UseMohit Sahu60% (5)
- The Philippines A Century HenceDocument6 pagesThe Philippines A Century HencesynovialNo ratings yet
- Abdirizak Mohamed Hassan CVDocument3 pagesAbdirizak Mohamed Hassan CVCabdirizaaq HassamNo ratings yet
- Transient Surge Filter - TSF20A240VDocument3 pagesTransient Surge Filter - TSF20A240Vvulamtd2No ratings yet
- Ampro Overcurrent: Test O-C Mcc101: 1) AbstractDocument6 pagesAmpro Overcurrent: Test O-C Mcc101: 1) AbstractMohammad TanhaNo ratings yet
- Ijcrt2004141 PDFDocument5 pagesIjcrt2004141 PDFBulbul SahuNo ratings yet