Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsThyroid Metabolic Hormones
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
Uploaded by
Hala RezaThe thyroid gland secretes the hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolic rate. A defect in the thyroid causes metabolic rate to decrease by 40-50% while excess thyroid hormone increases it by 60-100%. The gland traps iodine, which is essential for hormone production. Iodine is transported into follicular cells where it attaches to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, forming T3 and T4. TSH controls thyroid hormone secretion and is regulated by TRH from the hypothalamus. Conditions like Graves' disease cause hyperthyroidism by stimulating hormone production, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis and iodine deficiency can cause hypothyroidism.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Being Happy - Andrew MatthewsDocument242 pagesBeing Happy - Andrew MatthewsLioe Stanley100% (4)
- A Requiem To Mother EarthDocument5 pagesA Requiem To Mother EarthSandra SabuNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Document12 pagesThe Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Leslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesVitamins SpreadsheetB-Rock Daniels100% (1)
- CyclophosphamideDocument7 pagesCyclophosphamideFrances Ramos33% (3)
- Thyroid HormonesDocument7 pagesThyroid HormonesAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid HormonesDocument53 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Hormonesrehmanmughal87654No ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones and AntiDocument2 pagesThyroid Hormones and AntiNishaHasanNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument7 pagesHypothyroidismGkdhdhdgdgidNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic DysfunctionsDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic Dysfunctionskate_borovicNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument37 pagesThyroid GlandConfidence MorganNo ratings yet
- Thyriod PhysiologyDocument8 pagesThyriod PhysiologyNifemi BorodeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonDocument13 pagesThyroid HormonWira SentanuNo ratings yet
- 3.thyroid Hormones and DisordersDocument46 pages3.thyroid Hormones and DisorderssinayupeNo ratings yet
- Physio Essay 15Document3 pagesPhysio Essay 15Zoya LiaquatNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)Document8 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThyroidDocument9 pagesAnatomy of ThyroidStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono DjuwantonoDocument49 pagesThyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono Djuwantonoyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument52 pagesThyroid Glandhamid mohammedNo ratings yet
- Thyroid SynthesisDocument15 pagesThyroid Synthesistitin indramayaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument12 pagesThyroid GlandOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- 5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردDocument27 pages5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردRana Abdullah100% (1)
- 3 - Thyroid GlandDocument43 pages3 - Thyroid GlanddhenaharcaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument86 pagesThyroid DisordersJEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- PEPITO Case 2Document3 pagesPEPITO Case 2Thea PepitoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormoneDocument53 pagesThyroid Hormoneambrosekiplangat6No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument30 pagesThyroid GlandahmedkomranNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tyroid (PA)Document75 pagesBahan Tyroid (PA)Raja FadhilNo ratings yet
- BB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Document17 pagesBB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Gunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Axis and Its DisordersDocument33 pagesThyroid Axis and Its DisordersmaduksjaycryptoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineDocument51 pagesThe Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineYustina Wahyu NNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ThyroidDocument9 pagesPhysiology of ThyroidAbby EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTDocument55 pages3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTMathy MtenjeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiDocument17 pagesThyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiHayder HussienNo ratings yet
- West African College of Physicians: Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument21 pagesWest African College of Physicians: Physiology of The Thyroid GlandRuchi VatwaniNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument17 pagesParacetamolsohail mohammad (Style de sohail)No ratings yet
- Analysis of Vitamin C NewDocument59 pagesAnalysis of Vitamin C Newrose mariaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument53 pagesThyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- 1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)Document96 pages1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)hamidNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical PracticeDocument24 pagesDr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical Practiceamaal ramadanNo ratings yet
- 7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesDocument31 pages7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesVigneshwaran Ravishankar100% (1)
- The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument13 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PDFDEVANGI PANCHALNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida Round 2Document63 pagesOral Revalida Round 2Mercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Thyroid EssayDocument2 pagesThyroid EssayAine Graham100% (1)
- Thyroid Gland Biology ProjectDocument19 pagesThyroid Gland Biology Projectsouvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland (AutoRecovered)Document16 pagesThyroid Gland (AutoRecovered)souvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahDocument67 pagesThyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument14 pagesThyroid Glandsouvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument2 pagesHYPERTHYROIDISMHyacinth Joy Febria GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument84 pagesThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Anti Thyroid DrugsDocument25 pagesThyroid Anti Thyroid DrugsGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DrugsDocument22 pagesThyroid Drugsanon_569360085No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDuchess Ciedelle Abano ManatadNo ratings yet
- BB Aminoglycosides VI Sem. 4.04.2021Document44 pagesBB Aminoglycosides VI Sem. 4.04.2021Gunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Superior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Dipercabangkan Dari External Carotid Artery Inferior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Arises From The Thyrocervical Trunk (Which in TurnDocument9 pagesSuperior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Dipercabangkan Dari External Carotid Artery Inferior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Arises From The Thyrocervical Trunk (Which in TurnDapot SianiparNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument59 pagesHealthAngesh PokharelNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument112 pagesThyroid Glandthewickedone2001No ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2Document8 pagesEndocrine Part 2DilNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Regulation and FunctionDocument9 pagesThyroid Gland Regulation and Functionmalaknotfound19No ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid DrugsDocument60 pagesAnti-Thyroid DrugsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Coal Ash Dewatering SolutionDocument23 pagesCoal Ash Dewatering Solution류태하No ratings yet
- Practice Exam Linear Algebra PDFDocument2 pagesPractice Exam Linear Algebra PDFShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit VII Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesUnit VII Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (2)
- Environmental Science For AP Second EditionDocument61 pagesEnvironmental Science For AP Second Editionjoshua.little480100% (50)
- Perdev Module 3Document13 pagesPerdev Module 3Renelyn JacoNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2014 PDFDocument153 pagesAnnual Report 2014 PDFகோகுல் இராNo ratings yet
- 765 KV, 400 KV, 230 KV & 132 KV Grid Network (Existing, U/C & Planned)Document1 page765 KV, 400 KV, 230 KV & 132 KV Grid Network (Existing, U/C & Planned)SSDNo ratings yet
- Material Balance PDFDocument31 pagesMaterial Balance PDFApril Joy HaroNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- COMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewDocument40 pagesCOMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewLance RafaelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainAsimov RiyazNo ratings yet
- Ipc DRM 18FDocument34 pagesIpc DRM 18FThamilvaanan.sNo ratings yet
- Law of Mother Earth BoliviaDocument3 pagesLaw of Mother Earth Boliviarahul banerjeeNo ratings yet
- TPS54160 1.5-A, 60-V, Step-Down DC/DC Converter With Eco-Mode™Document57 pagesTPS54160 1.5-A, 60-V, Step-Down DC/DC Converter With Eco-Mode™sbrhomeNo ratings yet
- Yuxi CatalogueDocument16 pagesYuxi CatalogueSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, Inc. Science Weblinks GRADE 4 S.Y. 2020-2021Document3 pagesPeniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, Inc. Science Weblinks GRADE 4 S.Y. 2020-2021Jhocen Grace GanironNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENDocument1 pageData Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENJanne LaineNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalythic TheoryDocument1 pagePsychoanalythic TheorySilver BroochNo ratings yet
- Base On Solid-Works Design of Compact High EfficieDocument15 pagesBase On Solid-Works Design of Compact High EfficieGorgeNo ratings yet
- هاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيهDocument6 pagesهاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيههاشم عديNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 11 1Document5 pages10 Science TP 11 1Ananaya BansalNo ratings yet
- 130-87 InstructionsDocument7 pages130-87 InstructionsAlex GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tiny Talk 2 Teacher's BookDocument15 pagesTiny Talk 2 Teacher's BookAtena RaeisiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Document12 pagesCarbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Wayne MonneryNo ratings yet
- The Fruit Garden CAL: Columbine & AcanthusDocument7 pagesThe Fruit Garden CAL: Columbine & AcanthusMiraNo ratings yet
- MEP MyanmarDocument27 pagesMEP Myanmarempty87No ratings yet
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
Uploaded by
Hala Reza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesThe thyroid gland secretes the hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolic rate. A defect in the thyroid causes metabolic rate to decrease by 40-50% while excess thyroid hormone increases it by 60-100%. The gland traps iodine, which is essential for hormone production. Iodine is transported into follicular cells where it attaches to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, forming T3 and T4. TSH controls thyroid hormone secretion and is regulated by TRH from the hypothalamus. Conditions like Graves' disease cause hyperthyroidism by stimulating hormone production, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis and iodine deficiency can cause hypothyroidism.
Original Description:
Original Title
THYROID METABOLIC HORMONES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe thyroid gland secretes the hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolic rate. A defect in the thyroid causes metabolic rate to decrease by 40-50% while excess thyroid hormone increases it by 60-100%. The gland traps iodine, which is essential for hormone production. Iodine is transported into follicular cells where it attaches to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, forming T3 and T4. TSH controls thyroid hormone secretion and is regulated by TRH from the hypothalamus. Conditions like Graves' disease cause hyperthyroidism by stimulating hormone production, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis and iodine deficiency can cause hypothyroidism.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesThyroid Metabolic Hormones
Thyroid Metabolic Hormones
Uploaded by
Hala RezaThe thyroid gland secretes the hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolic rate. A defect in the thyroid causes metabolic rate to decrease by 40-50% while excess thyroid hormone increases it by 60-100%. The gland traps iodine, which is essential for hormone production. Iodine is transported into follicular cells where it attaches to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin, forming T3 and T4. TSH controls thyroid hormone secretion and is regulated by TRH from the hypothalamus. Conditions like Graves' disease cause hyperthyroidism by stimulating hormone production, while Hashimoto's thyroiditis and iodine deficiency can cause hypothyroidism.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
THYROID METABOLIC HORMONES
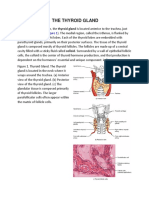
Thyroid gland secretes two hormones T3 or triiodothyronine and T4 or
tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine
Defect in thyroid gland causes the metabolic rate to fall about 40-50% below normal
and excess of thyroid hormone causes the metabolic to increase about 60-100%
above normal
Secretion mainly controlled by TSH
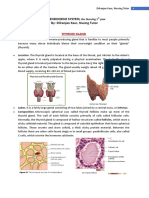
Thyroid gland is composed of many cells called follicle cells which are filled with
colloid. Colloid is lined with colloidal epithelial cells.
This gland also has parafollicular cells which secrete the hormone calcitonin
Iodine is very essential for the formation of thyroid hormones usually majority of the
iodine is excreted but around one fifth of it is absorbed by the thyroid gland from the
circulation
IODINE TRANSPORT
Iodine is transported from blood into thyroid gland with the help of a co transporter
Na. concentration of iodine in the gland is much higher than the blood.
So through active transport iodine is transported into the gland
The energy for active transport is provided by Na-K ATPase.
This way iodine is trapped in the gland and this is known as iodine trapping.
From the thyroid gland iodine is transported to the follicular cell with the help of
another transporter called pendrin where basically iodine is transported to the
follicular cell in exchange of chloride ion
T3 AND T4 FORMATION
There is protein called thyroglobulin which is synthesised in the endoplasmic
reticulum of thyroid gland and through golgi apparatus transported in to the
follicular cell
This protein is where the hormones are stored. It contains many tyrosine molecules where
the iodine comes and attaches which leads to the formation of T3 and T4
In this diagram the formation and storage of T3 AND T4 are shown
Iodine enters into the thyroid gland as explained above. As it moves from the thyroid into
−¿¿
the follicular cell there is a peroxidase enzyme which oxidizes I to I 2. This enzyme also
attaches the I2 to the tyrosine molecule on the thyroglobulin.
After the attachment of I2 to the tyrosine molecule on the thyroglobulin molecule it either
forms monoiodothyronine(MIT) or diiodothyronine(DIT).
In the next either MIT AND DIT combines to form triiodothyronine or T3 or DIT AND DIT
combines to form tetraiodothyronine or T4. Small amount reverse T3 is also formed but its
not functional in humans.
T3 AND T4 remains attached to the thyroglobulin in the follicular cell until there is signal
that tell the hormones to be secreted in the blood.
Once there is signal thyroid gland forms a pinocytic vesicle around the thyroglobulin which
has the hormone and releases proteases which cleaves the T3 and T4 from thyroglobulin and
releases it into the blood
MIT and DIT are mostly not released in the blood as they are cleaved by deiodinase enzyme
where iodine is again released in to the cell for future use
Usually thyroglobulin doesn’t leave the thyroid gland but some amount which combines
with an enzyme called megalin helps it to be transported into to the blood.
Forgot to mention – the process of combining iodine to tyrosine is called organification.
Most of the hormone that is formed is mainly T4 and very little about 7% is T3 but for
functioning T4 is converted into T3.
As the thyroid hormones are always bound to the protein their speed of action is slow
T4 has higher affinity to plasma proteins so they take around 6 days to be released and show
their actions where T3 has lesser affinity to plasma proteins so they can easily be released
and takes around 1 day
If a T4 injection given takes about 6 days for the action to occur as the latent period is long
due their attachment with plasma proteins. It reaches it max activity level in the 10 or 12
days.
PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS OF THYROID HORMONE
Thyroid hormones activate nuclear receptors.
Thyroid hormone receptors located in the nucleus or near the DNA. Thyroid hormone
receptor is attached to another receptor called retinoid X receptor. And these two attach
together to hormone response element(HRE).
This full complex translates many new proteins which bring about changes in the cell.
Thyroid
hormones
also has
many non
genomic effects like activate secondary messengers like cAMP and regulation of ion
channels.
When thyroid hormone is given to an animal the no of mitochondria and their size increases
One enzyme that is affected by this hormone is Na-K ATPase, which helps in the transport of
ions. These hormones also make the cells leaky to Na ions which causes excess of heat
production
These hormones have a great effect on growth hormone. Hypothyroidism can cause
dwarfism and in case of hyperthyroidism growth of bones happen at an early stage which
causes the children to grow taller at a young age but also this causes the epiphyses of the
bone to close at an early age which stops the growth.
Thyroid hormone also causes the growth and development of brain in fetal life.
Increase all aspects of carbohydrates metabolism. Increase glucose uptake by cells, glycolysis
and gluconeogenesis.
Increases fat mobilization. Doesn’t allow the fats to be stored in the cells. Causes high fat
content in plasma so for energy source fat can be used easily
Increased thyroid hormones cause decrease in cholesterol, triglycerides and phospholipids
One way to decrease cholesterol in plasma is to increase the receptors of LDL on liver so
they can be easily removed from there
Increase in thyroid hormones can cause vitamin deficiency
Increase also causes a decrease in the body weight
It causes the rapid utilization of oxygen which increases the metabolic rate which causes the
vasodilation of blood vessels. Vasodilation of blood vessels in skin is also increased in order
to eliminate the heat from the body. This causes the blood flow to increase. The increase in
blood flow causes the cardiac output to increase.
Increase heart rate and also heart strength. But excessive thyroid hormone causes the heart
muscles to become depressed due to excess of protein catabolism, so at times the patient
can die due to cardiac decompensation in case of hyperthyroidism.
Arterial pressure remains same but pulse pressure increases
Increases respiration rate and gastrointestinal motility
Increases the excitory effects on CNS.
Cause muscle tremor due to increased signals to the spinal cord
Due to the exhausting effect of thyroid hormone on muscles it becomes difficult to sleep in
case of hyperthyroidism
It increases the need of other hormones such as insulin and PTH
In men lack of thyroid hormone causes lack of libido. In women it causes menorrhagia
(excessive bleeding during menstrual cycles) and polymenorrheae (frequent bleeding)
Hypothyroidism in women causes oligomenorrhea (reduced bleeding)
REGULATION OF THYROID HORMONE SECRETION
Mainly controlled by TSH
All the steps mentioned above in the cycle are affected directly by TSH
TSH attaches to the receptor on thyroid gland activates adenylyl cyclase which converts ATP
to secondary messenger cAMP, which in turn causes many reactions.
TSH is controlled by TRH produced in the hypothalamus. TRH attaches to the receptor in
pituitary gland and activates phospholipase C which causes the release of TSH.
Cold temperatures in case of animals also increases TRH secretion
There is hormone in hypothalamus called leptin which also affects the secretion of TRH
Certain emotions also affect their secretion like anxiety and excitement reduces thyroid
hormones secretion
REGULATION
Has negative regulation
An increase in thyroid hormones in the blood causes the TRH to be inhibited and which in
turn inhibits the TSH
EXTRA POINTS
Thiocyanate ions inhibit iodine trapping
It acts as competitive inhibitor for iodine.
It doesn’t do anything but just reduces the iodine conc. in thyroid gland so iodine does not
bind to tyrosine molecule in thyroglobulin
Propylthiouracil blocks the formation of thyroid hormones. It blocks the enzyme
peroxidase(use told before)
Both these of drugs stops the formation of T3 AND T4 so TSH keeps increasing ( due to
negative feedback) which causes the enlargement of thyroid gland
DISEASES
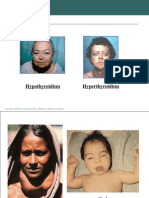
GRAVE’S DIASEASE
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism
Produces thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs) which attach to the receptor of TSH
and stimulate the secretion of thyroid hormone uncontrollably.
Increased hormones production suppresses the release of TSH.
Thyroid adenoma – tumour in thyroid gland, another cause of hyperthyroidism
People suffering from hyperthyroidism may also have exophthalmos that is protrusion of the
eyes this as well might be an autoimmune disorder.
For majority of the treatments, it is advised to remove the thyroid gland
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Lack of thyroid hormone production
Hashimoto’s disease – destroys one’s own thyroid gland
One of the main cause thyroiditis
Endemic goitres – was mainly caused in the era where there no iodized salts available
So lack of iodine caused this goitre
Since no iodine was available the hormones weren’t produced, excessive amount of TSH was
released which caused the thyroid glands to grow larger in size
Idiopathic non toxic goitre – there is no iodine deficiency in this goitre, the reason for this is
still unknown maybe caused due to thyroiditis.
This goitre blocks the pathway involved in thyroid cycle (mentioned above )
Myxedema – in patient who’s thyroid gland is completely destroyed
Bagginess under eyes, hight level of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate
Hypothyroidism causes atherosclerosis
Treatment - Oral ingestion of thyroid hormones can help to treat hypothyroidism
Cretinism – extreme case of hypothyroidism in infants and children
Cause defect in growth and mental retardation
If its due to lack of iodine it might be called endemic cretinism
A new born may seem normal without a thyroid gland in the mothers womb as the mothers
thyroid gland is supporting but after birth the child will experience growth issues and mental
retardation
You might also like
- Being Happy - Andrew MatthewsDocument242 pagesBeing Happy - Andrew MatthewsLioe Stanley100% (4)
- A Requiem To Mother EarthDocument5 pagesA Requiem To Mother EarthSandra SabuNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Document12 pagesThe Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Leslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesVitamins SpreadsheetB-Rock Daniels100% (1)
- CyclophosphamideDocument7 pagesCyclophosphamideFrances Ramos33% (3)
- Thyroid HormonesDocument7 pagesThyroid HormonesAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid HormonesDocument53 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Hormonesrehmanmughal87654No ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones and AntiDocument2 pagesThyroid Hormones and AntiNishaHasanNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument7 pagesHypothyroidismGkdhdhdgdgidNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic DysfunctionsDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic Dysfunctionskate_borovicNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument37 pagesThyroid GlandConfidence MorganNo ratings yet
- Thyriod PhysiologyDocument8 pagesThyriod PhysiologyNifemi BorodeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonDocument13 pagesThyroid HormonWira SentanuNo ratings yet
- 3.thyroid Hormones and DisordersDocument46 pages3.thyroid Hormones and DisorderssinayupeNo ratings yet
- Physio Essay 15Document3 pagesPhysio Essay 15Zoya LiaquatNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)Document8 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThyroidDocument9 pagesAnatomy of ThyroidStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono DjuwantonoDocument49 pagesThyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono Djuwantonoyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument52 pagesThyroid Glandhamid mohammedNo ratings yet
- Thyroid SynthesisDocument15 pagesThyroid Synthesistitin indramayaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument12 pagesThyroid GlandOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- 5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردDocument27 pages5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردRana Abdullah100% (1)
- 3 - Thyroid GlandDocument43 pages3 - Thyroid GlanddhenaharcaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument86 pagesThyroid DisordersJEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- PEPITO Case 2Document3 pagesPEPITO Case 2Thea PepitoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormoneDocument53 pagesThyroid Hormoneambrosekiplangat6No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument30 pagesThyroid GlandahmedkomranNo ratings yet
- Bahan Tyroid (PA)Document75 pagesBahan Tyroid (PA)Raja FadhilNo ratings yet
- BB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Document17 pagesBB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Gunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Axis and Its DisordersDocument33 pagesThyroid Axis and Its DisordersmaduksjaycryptoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineDocument51 pagesThe Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineYustina Wahyu NNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ThyroidDocument9 pagesPhysiology of ThyroidAbby EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTDocument55 pages3 Use Thyroid Gland Use TTMathy MtenjeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiDocument17 pagesThyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiHayder HussienNo ratings yet
- West African College of Physicians: Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument21 pagesWest African College of Physicians: Physiology of The Thyroid GlandRuchi VatwaniNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument17 pagesParacetamolsohail mohammad (Style de sohail)No ratings yet
- Analysis of Vitamin C NewDocument59 pagesAnalysis of Vitamin C Newrose mariaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument53 pagesThyroid Disorders: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- 1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)Document96 pages1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)hamidNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical PracticeDocument24 pagesDr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical Practiceamaal ramadanNo ratings yet
- 7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesDocument31 pages7 - Regulation and Functions of The Thyroid HormonesVigneshwaran Ravishankar100% (1)
- The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument13 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PDFDEVANGI PANCHALNo ratings yet
- Oral Revalida Round 2Document63 pagesOral Revalida Round 2Mercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Thyroid EssayDocument2 pagesThyroid EssayAine Graham100% (1)
- Thyroid Gland Biology ProjectDocument19 pagesThyroid Gland Biology Projectsouvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland (AutoRecovered)Document16 pagesThyroid Gland (AutoRecovered)souvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahDocument67 pagesThyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument14 pagesThyroid Glandsouvikrakshit2006No ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument2 pagesHYPERTHYROIDISMHyacinth Joy Febria GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument84 pagesThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Anti Thyroid DrugsDocument25 pagesThyroid Anti Thyroid DrugsGunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DrugsDocument22 pagesThyroid Drugsanon_569360085No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDuchess Ciedelle Abano ManatadNo ratings yet
- BB Aminoglycosides VI Sem. 4.04.2021Document44 pagesBB Aminoglycosides VI Sem. 4.04.2021Gunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Superior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Dipercabangkan Dari External Carotid Artery Inferior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Arises From The Thyrocervical Trunk (Which in TurnDocument9 pagesSuperior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Dipercabangkan Dari External Carotid Artery Inferior Thyroid Artery (Right and Left) Arises From The Thyrocervical Trunk (Which in TurnDapot SianiparNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument59 pagesHealthAngesh PokharelNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument112 pagesThyroid Glandthewickedone2001No ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2Document8 pagesEndocrine Part 2DilNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Regulation and FunctionDocument9 pagesThyroid Gland Regulation and Functionmalaknotfound19No ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid DrugsDocument60 pagesAnti-Thyroid DrugsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Coal Ash Dewatering SolutionDocument23 pagesCoal Ash Dewatering Solution류태하No ratings yet
- Practice Exam Linear Algebra PDFDocument2 pagesPractice Exam Linear Algebra PDFShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit VII Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesUnit VII Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (2)
- Environmental Science For AP Second EditionDocument61 pagesEnvironmental Science For AP Second Editionjoshua.little480100% (50)
- Perdev Module 3Document13 pagesPerdev Module 3Renelyn JacoNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2014 PDFDocument153 pagesAnnual Report 2014 PDFகோகுல் இராNo ratings yet
- 765 KV, 400 KV, 230 KV & 132 KV Grid Network (Existing, U/C & Planned)Document1 page765 KV, 400 KV, 230 KV & 132 KV Grid Network (Existing, U/C & Planned)SSDNo ratings yet
- Material Balance PDFDocument31 pagesMaterial Balance PDFApril Joy HaroNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- COMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewDocument40 pagesCOMPRE - MODULE 4 (Pharmacology and Toxicology) : Attempt ReviewLance RafaelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0264127522004105 MainAsimov RiyazNo ratings yet
- Ipc DRM 18FDocument34 pagesIpc DRM 18FThamilvaanan.sNo ratings yet
- Law of Mother Earth BoliviaDocument3 pagesLaw of Mother Earth Boliviarahul banerjeeNo ratings yet
- TPS54160 1.5-A, 60-V, Step-Down DC/DC Converter With Eco-Mode™Document57 pagesTPS54160 1.5-A, 60-V, Step-Down DC/DC Converter With Eco-Mode™sbrhomeNo ratings yet
- Yuxi CatalogueDocument16 pagesYuxi CatalogueSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- Peniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, Inc. Science Weblinks GRADE 4 S.Y. 2020-2021Document3 pagesPeniel Integrated Christian Academy of Rizal, Inc. Science Weblinks GRADE 4 S.Y. 2020-2021Jhocen Grace GanironNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENDocument1 pageData Sheet USB5 II 2019 05 ENJanne LaineNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalythic TheoryDocument1 pagePsychoanalythic TheorySilver BroochNo ratings yet
- Base On Solid-Works Design of Compact High EfficieDocument15 pagesBase On Solid-Works Design of Compact High EfficieGorgeNo ratings yet
- هاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيهDocument6 pagesهاشم عدي حاتم سيارات ثاني التجربة الثانيههاشم عديNo ratings yet
- 10 Science TP 11 1Document5 pages10 Science TP 11 1Ananaya BansalNo ratings yet
- 130-87 InstructionsDocument7 pages130-87 InstructionsAlex GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tiny Talk 2 Teacher's BookDocument15 pagesTiny Talk 2 Teacher's BookAtena RaeisiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Document12 pagesCarbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Wayne MonneryNo ratings yet
- The Fruit Garden CAL: Columbine & AcanthusDocument7 pagesThe Fruit Garden CAL: Columbine & AcanthusMiraNo ratings yet
- MEP MyanmarDocument27 pagesMEP Myanmarempty87No ratings yet