Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus ECEN3008
Syllabus ECEN3008
Uploaded by
tiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus ECEN3008
Syllabus ECEN3008
Uploaded by
tiCopyright:
Available Formats
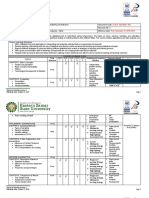
Major Programme: Bachelor of Science in Electrical and Computer Engineering
✓ CM – Compulsory Major □ CPE – Community and Peer Education □ GE – General Education □ MI – Minor
Course Type:
□ RE – Required Elective □ L&S – Languages and Skills □ FE – Free Elective
GE Area in 2017/2018 model (applicable to students admitted in academic year 2017/2018 onwards)
□ Science and Technology, FHS □ Society and Behaviour, FSS
□ Literature and Humanities, FAH □ Global Awareness, FSS
Equivalent to 2011/2012 GE model (applicable to students admitted in academic year 2016/2017 or before)
□ Area 1 – English Language □ Area 8 – World Histories and Cultures
□ Area 2 – Chinese/Foreign Language □ Area 9 – Macao, China and other Societies
□ Area 3 – Communication □ Area 10 – Values, Ethics and Meaning of life
□ Area 4 – Mathematics/Quantitative Reasoning □ Area 11 – Physical Education
□ Area 5 – Information Technology and Knowledge Society □ Area 12 – Visual and Performing Arts
□ Area 6 – Physical Science and the World □ Area 13 – University Life
□ Area 7 – Life Science, Health and the Human Condition
Course Title: Power Systems Analysis
(in English, Chinese and 電力系統分析
Portuguese) Análise de Sistemas de Potência
Credit Units:
Course code ECEN3008 3
Duration: ✓ Semester Course □ Yearly Course Suggested Year of Study: Year 3
Grading System: ✓ Letter Grade □ P/NP Pre-requisite: None
(if any)
English
Medium of Instruction:
Text Book and “Power System Analysis”, John Grainger, William Stevenson
Reference
This course provides fundamental knowledge on power system. It includes calculation on line
parameters, line models, admittance matrix calculation, load flow calculation, symmetrical
Course Description:
networks, machine model for short circuit calculation, symmetrical and asymmetrical short
circuit calculation and state estimation.
1. Introduction to Power System
2. Parameters Calculation for Transmission Line/Cable
3. Transmission Line Models
Course Content 4. Power Flow Analysis
5. Reactive Power
Compensation/Power Factor Correction
6. Fault Analysis
7. Introduction to Power System Stability
8. Introduction to Power System Protection
CILO 1: Ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering.
Course Intended CILO 2: Ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems.
Learning Outcomes CILO 3: Ability to use the techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for
(CILO): engineering practice.
CILO 4: Ability to design and conduct experiments.
Case Study
Role Playing
Student Presentation
project / paper
Individual
Group project / paper
Group discussions
Writing Assignment
Exercises & problems
Service learning
Internship
Field study
Company visits
Assessments / tests
Reading & Writing
Assessments / tests
Listening & Oral
Major Assessment
Methods:
Assignment(s) 40% ✓ ✓
Quiz 10% ✓ ✓
Final 50% ✓
You might also like
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Cultural Relativism and EthnocentrismDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Cultural Relativism and EthnocentrismDERICK REBAY86% (43)
- Data Analytics For Absolute Beginners A Deconstructed Guide To Data Literacy 1081762462 9781081762469Document133 pagesData Analytics For Absolute Beginners A Deconstructed Guide To Data Literacy 1081762462 9781081762469CristinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson ExemplarDocument5 pagesLesson ExemplarKristine ManuelNo ratings yet
- Inferno SummaryDocument4 pagesInferno SummaryAva Barrameda67% (3)
- Copy of Industry Associations Updated As On 28 Aug 17Document14 pagesCopy of Industry Associations Updated As On 28 Aug 17mahajan.gouravNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ECEN3007Document2 pagesSyllabus ECEN3007tiNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Business AdministrationDocument3 pagesBachelor of Business AdministrationWang Hon YuenNo ratings yet
- DBMS Course FileDocument193 pagesDBMS Course Fileabdul rehmanNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviDocument9 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviZeeshan DuddiandaNo ratings yet
- Ecesyllabus Scheme 18 19 PDFDocument150 pagesEcesyllabus Scheme 18 19 PDFAzharNo ratings yet
- EcschDocument9 pagesEcschDaisyQueenNo ratings yet
- 7.inplant Training 15ce67pDocument9 pages7.inplant Training 15ce67pTony SamNo ratings yet
- 6..project Work-IIDocument15 pages6..project Work-IIJagadeesh k v JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- MCT 3423Document6 pagesMCT 3423abdio89No ratings yet
- ECE1201 Engineering Lab IIDocument6 pagesECE1201 Engineering Lab IIbelkhair ahmedNo ratings yet
- CT043-3-1-IN Introduction To Networking (VD1) 20 September 2019Document2 pagesCT043-3-1-IN Introduction To Networking (VD1) 20 September 2019Jang Hang ChooNo ratings yet
- BMPJ6404Document2 pagesBMPJ6404Zoey SchullyNo ratings yet
- BMPJ6603Document3 pagesBMPJ6603Zoey SchullyNo ratings yet
- Reservoiur OperarionDocument5 pagesReservoiur OperarionEmmanuel NamkumbeNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University, Punjab: Format For Instruction Plan (For Courses With Lectures and Tutorials)Document9 pagesLovely Professional University, Punjab: Format For Instruction Plan (For Courses With Lectures and Tutorials)Shivani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ccdi g8 22-23 t3 Ip 2Document1 pageCcdi g8 22-23 t3 Ip 2api-135128257No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Power Syste, PDFDocument7 pagesSyllabus - Power Syste, PDFJhonna TrinidadNo ratings yet
- No Science Investigation Will: SPECIFIC AIM (Learning Outcome)Document3 pagesNo Science Investigation Will: SPECIFIC AIM (Learning Outcome)Cebiswa MambaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan For Direct CurrentDocument3 pagesLearning Plan For Direct CurrentMarianell S. TorinoNo ratings yet
- Table 3: Summary of Information On Each Course/ModuleDocument4 pagesTable 3: Summary of Information On Each Course/Moduleewan_0306No ratings yet
- Internship Evaluation form-DEEDocument3 pagesInternship Evaluation form-DEEAtyab razaNo ratings yet
- Tre2601 Module FormDocument5 pagesTre2601 Module Formshalona behariNo ratings yet
- BALOI Syllabus-for-Grade-7Document9 pagesBALOI Syllabus-for-Grade-7Rhy Bint AhmadNo ratings yet
- AnalyticDocument6 pagesAnalyticlinelljoieNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus 2021-25Document78 pagesUG Syllabus 2021-25Vishwas Venkatesh PaiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Eee 801Document3 pagesSyllabus For Eee 801Eze UkiweNo ratings yet
- m106 Solid GeometryDocument8 pagesm106 Solid GeometryMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Session Plan Calculus of Single Variable (Old)Document4 pagesSession Plan Calculus of Single Variable (Old)Sanjoy BrahmaNo ratings yet
- CoursePlanner 212Document3 pagesCoursePlanner 212weimin chooNo ratings yet
- RP Tip Print NewDocument6 pagesRP Tip Print NewattaullahNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms SyllabusDocument9 pagesData Structures and Algorithms SyllabusBongbong GalloNo ratings yet
- Dea 3333Document12 pagesDea 3333clairons84No ratings yet
- III and IV Sem AIML Syllabus 2023Document59 pagesIII and IV Sem AIML Syllabus 2023adobeNo ratings yet
- Im 254Document1 pageIm 254znour alyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering - I: by Muhammad Farhan AroojDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Engineering - I: by Muhammad Farhan AroojAli AbidNo ratings yet
- Design of ExperimentDocument2 pagesDesign of Experimentafnene1No ratings yet
- REQ - PM Lab Manual (CSE651P) - UpdatedDocument37 pagesREQ - PM Lab Manual (CSE651P) - UpdatedLiNuNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan For Direct Current FinalDocument2 pagesLearning Plan For Direct Current FinalMarianell S. TorinoNo ratings yet
- JMN 451 Assignment 2.1 2023Document7 pagesJMN 451 Assignment 2.1 2023Khana N MazuluNo ratings yet
- A Lecture-IntroDocument11 pagesA Lecture-IntroSachin BisenNo ratings yet
- 2017 SNU ISISyllabus For Team Teaching FormatDocument3 pages2017 SNU ISISyllabus For Team Teaching FormatLewis PattenNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control 4th ClassDocument6 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control 4th ClassZaidoon MohsinNo ratings yet
- Department of Accounting Faculty of Economics and Business Universitas Muhammadiyah YogyakartaDocument5 pagesDepartment of Accounting Faculty of Economics and Business Universitas Muhammadiyah YogyakartaSafira SilmiyaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Reservoir Simulation, Fall-2016Document3 pagesNumerical Reservoir Simulation, Fall-2016TerryNo ratings yet
- Cobe Syllabus. Math Ed 7 (Calculus 1 With Analytic Geometry)Document14 pagesCobe Syllabus. Math Ed 7 (Calculus 1 With Analytic Geometry)Damai Paguntalan-MacalandongNo ratings yet
- STAT-205 Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesSTAT-205 Probability and StatisticsMuhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Format For Faculty Academic Performance EvaluationDocument6 pagesFormat For Faculty Academic Performance EvaluationMayank GandhiNo ratings yet
- Probability and StaticticsDocument4 pagesProbability and StaticticsrodrigoNo ratings yet
- ITE2204 Course StructureDocument2 pagesITE2204 Course StructureMing Zhi EditNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument4 pagesDiscrete MathematicsSayed AliNo ratings yet
- GEN201 Course Specs 232Document5 pagesGEN201 Course Specs 232ziademadaldeNo ratings yet
- PEA306Document20 pagesPEA306Adarsh PatilNo ratings yet
- ECE 2018 Syllabus PDFDocument130 pagesECE 2018 Syllabus PDFmanjunath s.kNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Diversity Epiphytic Diatoms of Seagrass Blades in Merambong Shoal, JohorDocument9 pagesInvestigation of Diversity Epiphytic Diatoms of Seagrass Blades in Merambong Shoal, JohorjulianaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ScienceDocument8 pagesDecision Making SciencePoornima SaiNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: No. Course Learning Outcome Programme Learning Outcome(s) Addressed Assessment Methods PO1Document5 pagesCourse Outline: No. Course Learning Outcome Programme Learning Outcome(s) Addressed Assessment Methods PO1Nuradin Ibrahim XassanNo ratings yet
- Fazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaDocument132 pagesFazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaGiuseppe DecaroNo ratings yet
- Common Ailments LPDocument5 pagesCommon Ailments LPJeyxa Keizz Viernes-Apostol BalanayNo ratings yet
- Spelling Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpelling Lesson Planapi-476785297100% (1)
- The BestDocument342 pagesThe BestTrader RetailNo ratings yet
- LSMW - WSQ - GL Master TextDocument7 pagesLSMW - WSQ - GL Master Textpatankar.vaibhav08No ratings yet
- Flipkart Case StudyDocument9 pagesFlipkart Case StudyHarshini ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ward Council AgendaDocument2 pagesWard Council AgendaJosh SambonoNo ratings yet
- Ananya Agarwal - Case Study Analysis (CIA 1)Document11 pagesAnanya Agarwal - Case Study Analysis (CIA 1)ANANYA AGARWAL 20224305No ratings yet
- Parag Milk FoodsDocument32 pagesParag Milk FoodsDivya MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- International Council For Management Studies (ICMS), Chennai (Tamilnadu) Chennai, Fees, Courses, Admission Date UpdatesDocument2 pagesInternational Council For Management Studies (ICMS), Chennai (Tamilnadu) Chennai, Fees, Courses, Admission Date UpdatesAnonymous kRIjqBLkNo ratings yet
- New Public Fiscal Admin Module 1 Lesson 1Document30 pagesNew Public Fiscal Admin Module 1 Lesson 1Jöhn LöydNo ratings yet
- 12 Siochi Vs GozonDocument10 pages12 Siochi Vs GozonPaolo CruzNo ratings yet
- Vrealize Automation 70 ConfigurationDocument386 pagesVrealize Automation 70 ConfigurationsatishNo ratings yet
- Parking Standards: Parking Stall Dimensions (See Separate Handout For R-1 Single Family)Document1 pageParking Standards: Parking Stall Dimensions (See Separate Handout For R-1 Single Family)Ali HusseinNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document4 pagesSet 3Sharan SNo ratings yet
- Woody AllenDocument18 pagesWoody Allendougct100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Double Entry System: Very Short QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Double Entry System: Very Short QuestionsVipulNo ratings yet
- May 6, 2016 Strathmore TimesDocument28 pagesMay 6, 2016 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Document6 pagesTingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Ninin KepoNo ratings yet
- Jenkins, Dumez, University City, + Gravity, Rotation, QuantitativeDocument1 pageJenkins, Dumez, University City, + Gravity, Rotation, QuantitativeFuranNo ratings yet
- CE 6301 DR Hasan - Adsorption L3Document40 pagesCE 6301 DR Hasan - Adsorption L3MD. NASIF HOSSAIN IMONNo ratings yet
- Butterfly Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesButterfly Lesson Planapi-272455011No ratings yet
- November/December 2016Document72 pagesNovember/December 2016Dig DifferentNo ratings yet
- Helical Pile Behaviour Analysis in Different Soils: January 2009Document11 pagesHelical Pile Behaviour Analysis in Different Soils: January 2009mohamed magdyNo ratings yet
- Lección 7 - Who - Why-Because (WH Questions)Document3 pagesLección 7 - Who - Why-Because (WH Questions)jaime sordoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Third Quarterly ExamDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Third Quarterly ExamJohaira AcotNo ratings yet