Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U3b Higher Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser
AQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U3b Higher Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
gundavannessa270 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pages1) Chemical reactions conserve mass, so the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products. However, if a gas is involved, the mass may increase from oxygen being added or decrease if a gas is released.
2) The relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses (Ar) of the atoms in its chemical formula. The percentage composition of an element in a compound can be calculated from the Ar and Mr.
3) A limiting reactant is the first reactant to be completely used up in a chemical reaction, which determines how much product can be produced. If the amount of a limiting reactant is decreased, the amount of product decreases proportionally
Original Description:
Its for oundation tier
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Chemical reactions conserve mass, so the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products. However, if a gas is involved, the mass may increase from oxygen being added or decrease if a gas is released.
2) The relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses (Ar) of the atoms in its chemical formula. The percentage composition of an element in a compound can be calculated from the Ar and Mr.
3) A limiting reactant is the first reactant to be completely used up in a chemical reaction, which determines how much product can be produced. If the amount of a limiting reactant is decreased, the amount of product decreases proportionally
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesAQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U3b Higher Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser
AQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U3b Higher Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
gundavannessa271) Chemical reactions conserve mass, so the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products. However, if a gas is involved, the mass may increase from oxygen being added or decrease if a gas is released.
2) The relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses (Ar) of the atoms in its chemical formula. The percentage composition of an element in a compound can be calculated from the Ar and Mr.
3) A limiting reactant is the first reactant to be completely used up in a chemical reaction, which determines how much product can be produced. If the amount of a limiting reactant is decreased, the amount of product decreases proportionally
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
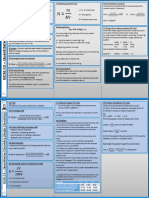
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Combined Science) Unit 5.
3: Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser - Higher
Conservation of Mass Relative Formula Mass Calculating Percentage Mass of an Element During a reaction the mass can change. If one of the
No atoms can be created or made during The relative formula mass in a Compound reactants is a gas, the mass can go up.
a chemical reaction, so the mass of the (Mr) is the sum of all the percentage mass of an element in a E.g.
reactants will equal the mass of the relative atomic masses (Ar) of compound = magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide
product. the atoms in the formula.
Examples: Ar × number of atoms of that element Oxygen from the air is added to the magnesium
Mr of the compound
Reactions can be shown as a word or HCl (making the product) which will be heavier in mass.
symbol equation. Ar of H = 1 Find the percentage mass of oxygen in
magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide Ar of Cl = 35.5 magnesium oxide.
Mg + O MgO Mr of HCI =1 + 35.5 = 36.5
Ar of magnesium = 24 Ar of oxygen = 16
Symbol equations should also be
balanced; they should have the same H2SO4 Mr of MgO = 24 + 16
number of atoms on each side. Ar of H = 1 = 40
Ar of S = 32 Ar 16
Ar of O = 16 % mass = M = 40 = 0.4 0.4 × 100 = 40%
2Mg + O2 2MgO r
If one of the products is a gas, the mass can go
Mr of H₂SO₄ = (1 × 2) + 32 + down.
(16 × 4)
E.g.
Mr of H₂SO₄ = 2 + 32 + 64
sodium carbonate sodium oxide + carbon dioxide
Mr of H₂SO₄ = 98
Conservation of Mass
Show that mass is conserved in a reaction. When sodium carbonate is thermally decomposed,
carbon dioxide gas is produced and released into the
Concentration of Solutions 2Mg + O2 2MgO atmosphere.
Concentration is the amount of a substance in a specific volume
(2 × 24) + (2 × 16) 2(24 + 16)
of a solution. The more substance that is dissolved, then the more
concentrated the solution is. 48 + 32 2 × 40
80 80
It is possible to calculate the concentration of a solution with the Total Mr on the left-hand side of the equation
following equation: is the same as the Mr on the right-hand side.
concentration (g/dm3) = mass (g) ÷ volume of solvent (dm3)
Calculate the mass of the product.
The equation can be rearranged to find the mass of the dissolved 6g of magnesium reacts with 4g of oxygen:
substance: 6 + 4 = 10g of magnesium oxide
mass (g) = concentration (g/dm3) × volume (dm3)
Page 1 of 2 visit twinkl.com
AQA GCSE Chemistry (Combined Science) Unit 5.3: Quantitative Chemistry Knowledge Organiser - Higher
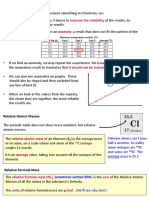
The Mole Limiting Reactions
The Avogadro constant, 6.02 × 10²³, is the number of molecules of a If one reactant gets used up in a reaction before the other, then the
substance that make up one mole of that substance. reaction will stop. The reactant that has been used up is limiting.
Iron has an Ar of 56, so 1 mole of iron has a mass of 56g.
Oxygen (O₂) gas has an Mr of 32, so 1 mole of oxygen has a mass of 32g. If you halve the amount of reactant then the amount of product will
Ammonia (NH₃) has an Mr of 17, so 1 mole of ammonia has a mass of also be halved.
17g.
number of moles = mass in g (of an element or compound )
Mr (of the element or compound)
Moles and Equations
Write a balanced symbol equation for the reaction in which 5.6g of iron
reacts with 10.65g of chlorine to form iron chloride.
Work out the Mr of all the substances.
Ar of Fe = 56 and Ar of Cl = 35.5
Divide the mass of each substance by its Mr to calculate how many moles
of each substance reacted or produced.
moles Fe = 5.6/56 = 0.1
moles Cl = 10.65/35.5 = 0.3
Divide by the smallest number of moles
Fe = 0.1 =1 Cl = 0.3 =3
0.1 0.1
Write down the balanced symbol equation.
Fe + 3Cl
Chlorine exists as Cl₂ so the whole thing must be multiplied by 2.
2Fe + 3Cl₂ 2FeCl₃
Page 2 of 2 visit twinkl.com
You might also like
- 八大題型全攻略Document32 pages八大題型全攻略Jeff Suck100% (1)
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Lab Write Up Electrolysis Copper II Sulphate Active & Inert ElectrodesDocument4 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Lab Write Up Electrolysis Copper II Sulphate Active & Inert ElectrodesDhauniel Richards100% (2)
- Equation of State of Ideal Gases With Cobra 4Document10 pagesEquation of State of Ideal Gases With Cobra 4DanielLugoNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 2024Document11 pagesStoichiometry 2024Kef7No ratings yet
- Mass Volume RelationshipDocument4 pagesMass Volume RelationshipThanni AkanbiNo ratings yet
- Chemical CalculationDocument10 pagesChemical Calculationazeen.zanzoonNo ratings yet
- Hein Chem12 Ch2 AnsDocument9 pagesHein Chem12 Ch2 AnsPyNo ratings yet
- Booklet - Mole CalculationsDocument12 pagesBooklet - Mole CalculationsydislikeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MaterialDocument30 pagesChemistry MaterialHari Haran SNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassDocument5 pagesRevision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassDocument9 pagesRevision Checklist:4.3 Quantitative Chemistry: Relative Formula MassPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes: Main IdeaDocument4 pagesChemical Changes: Main IdeaJude MetanteNo ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- AR and MRDocument3 pagesAR and MRmagnumspprtsNo ratings yet
- Calculating Atomic and Molecular MassesDocument30 pagesCalculating Atomic and Molecular MassesBright MindsNo ratings yet
- c4 Chemical CalculationsDocument4 pagesc4 Chemical CalculationsNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Moles PowerPointDocument11 pagesMoles PowerPointiffat.bibiNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMDocument12 pages2.1.3 Amount of Substance: Molar Gas Volume (Gas Volume Per Mole, Units DMAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Calculations Calculat PDFAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- Stoicchiomentry and Redox Reactiions TheoryDocument22 pagesStoicchiomentry and Redox Reactiions TheoryVenkycommercial 23No ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Basic Concepts of Chemistry and ChemicalDocument5 pagesChapter-1-Basic Concepts of Chemistry and ChemicalvenusrinivassNo ratings yet
- C3 Quantitative ChemistryDocument2 pagesC3 Quantitative ChemistrydeltaNo ratings yet
- Moles and Mole CalculationsDocument14 pagesMoles and Mole CalculationsAhmadElgindyNo ratings yet
- Moles and Empirical FormulaDocument11 pagesMoles and Empirical FormulaZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry - Chemical CalculationsDocument81 pagesStoichiometry - Chemical CalculationsZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Moles DADocument2 pagesMoles DAagentdog175No ratings yet
- 1E Chemical Formulae, Equations and CalculationsDocument68 pages1E Chemical Formulae, Equations and Calculationsjustme.azma.meNo ratings yet
- Int Chem Chap 3Document70 pagesInt Chem Chap 3Toh Kee LeongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDocument7 pagesChemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 5 CalculationDocument35 pagesUnit 1 Part 5 CalculationI LOVE JAKENo ratings yet
- Percentage CompositionDocument5 pagesPercentage CompositionMusa Bin AsimNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry EM Book Back QuestionsDocument58 pages11th Chemistry EM Book Back Questionsvanithavelaiya82No ratings yet
- Mole Concept - 2 - VMathDocument68 pagesMole Concept - 2 - VMathkolasanjay26893No ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument13 pagesRelative Atomic MassAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- What Is A Chemical Equation (Stoichiometry)Document15 pagesWhat Is A Chemical Equation (Stoichiometry)brenda.mofokeng06No ratings yet
- DT Reaksi Kimia and HK Dasar XDDocument3 pagesDT Reaksi Kimia and HK Dasar XDmamamia69420lovepizzaNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument3 pagesMole Conceptjuswalim300No ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument39 pagesChemical ReactionAsteraceae ChrysanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document49 pagesChapter 4Jr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic 3Document4 pagesChemistry Topic 3husna.k0907No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryTilak K C100% (1)
- Maths For As ChemistryDocument4 pagesMaths For As ChemistryonaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Amount of SubstanceDocument12 pages2.1.3 Amount of SubstanceSara KarimNo ratings yet
- Quick Notes: Relative Atomic MassDocument20 pagesQuick Notes: Relative Atomic Massanwar9602020No ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Plus One Che 1. Some Basic Concepts Q&ADocument9 pagesHSSRPTR - Plus One Che 1. Some Basic Concepts Q&Adxkmyffqv7No ratings yet
- 5 Reacting Masses and Chemical EquationsDocument35 pages5 Reacting Masses and Chemical Equationsbushraa162024No ratings yet
- Stochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thDocument8 pagesStochiometry Grade 9th Short Note For Grade 12thWesNo ratings yet
- CH 1. SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY Chapter 1Document8 pagesCH 1. SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY Chapter 1Arvindhkandhavel RNo ratings yet
- Class 9 ScienceChapter 8Document9 pagesClass 9 ScienceChapter 8Lr VarteNo ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Moles NotesDocument104 pagesForm 3 Moles Notesogangayvonne91No ratings yet
- 1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance Iedxcel TDocument25 pages1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance Iedxcel TBest ProgressNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry CalculationsDocument27 pagesIGCSE Chemistry CalculationsMartin MulengaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.3Document29 pagesChapter 4.38997g4k2qrNo ratings yet
- Mass Volume RelationshipDocument9 pagesMass Volume Relationshiprabiumuhsin7No ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Arike Wayanad ChemistryDocument34 pagesHsslive Xi Arike Wayanad Chemistry16739No ratings yet
- 6CH04 01 Que 20160614Document17 pages6CH04 01 Que 20160614snoopyNo ratings yet
- Prac2 AnswersDocument8 pagesPrac2 AnswersAnna SellaNo ratings yet
- 2 1 3 Amount of SubstanceDocument8 pages2 1 3 Amount of SubstanceAik WeiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-1. Some Basic Concepts Q & ADocument9 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Ch-1. Some Basic Concepts Q & Anavaneethmp9No ratings yet
- Calculation of Air-Fuel RatioDocument16 pagesCalculation of Air-Fuel RatiorajeshNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy: Submitted by Reenu - Thankachan First Semester, M Pharm Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocument38 pagesMass Spectroscopy: Submitted by Reenu - Thankachan First Semester, M Pharm Pharmaceutical AnalysisReenu ThankachanNo ratings yet
- BRHS Chap3 Hydrogen Ignition Version 0 9 0Document17 pagesBRHS Chap3 Hydrogen Ignition Version 0 9 0Adel SukerNo ratings yet
- Erosion CorrosionDocument26 pagesErosion CorrosionElma MhjNo ratings yet
- New Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionDocument46 pagesNew Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionkarinhyhoNo ratings yet
- Tabla de CompresoresDocument9 pagesTabla de CompresoresLuisNo ratings yet
- Steady State Approximation: Supplementary Notes For The Course "Chemistry For Physicists"Document5 pagesSteady State Approximation: Supplementary Notes For The Course "Chemistry For Physicists"Rishav DugarNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Solved Chemistry 2006Document9 pagesIIT-JEE Solved Chemistry 2006Abhinav93% (15)
- Pearlstick For Footwear Sole Bonding Solution Data Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesPearlstick For Footwear Sole Bonding Solution Data Sheet PDFAndrei LazoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Week 18, MCQS, RevisionDocument27 pages2023 Week 18, MCQS, RevisionNicole El-hazhaliNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Determination of Fluid Saturations: by Dr-Eissa Shokir PE 363Document12 pagesLaboratory Determination of Fluid Saturations: by Dr-Eissa Shokir PE 363José TimanáNo ratings yet
- Plasma Physics HomeworkDocument4 pagesPlasma Physics Homeworkafnadyebqjzazl100% (1)
- Dpps ElectroDocument14 pagesDpps ElectroVanshika MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Polyurethane Foam ApplicationDocument5 pagesPolyurethane Foam ApplicationMichelle EvelynNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualDocument16 pagesThin Film Experiment Labrotary ManualSishir JanaNo ratings yet
- Paddington Academy: Topic 1 Test Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesPaddington Academy: Topic 1 Test Mark Schemehamna rizwanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Operating Guide DOWFROSTDocument44 pagesEngineering Operating Guide DOWFROSTcarlone07No ratings yet
- E3 13 08ggDocument9 pagesE3 13 08ggAgent 47No ratings yet
- And Lue ISBN Test BankDocument59 pagesAnd Lue ISBN Test Bankrobert100% (27)
- Icse Class X Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesIcse Class X Chemical BondingKush kankariya KankariyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 14Document6 pagesChemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 14Abdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Winmostar tutorial: Gromacs Vapor Pressure・Surface TensionDocument12 pagesWinmostar tutorial: Gromacs Vapor Pressure・Surface TensionEliasSMonteiroFilhoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - Sanfoundryagyemangamankwah5No ratings yet
- Gas DiffusionDocument10 pagesGas DiffusionFunsho OlorunyomiNo ratings yet
- Prep.2 - Science Final Revision First Term - 2018Document21 pagesPrep.2 - Science Final Revision First Term - 2018Zeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Ach 4150 Chemistry 1 Cat 2 (Take Away)Document2 pagesAch 4150 Chemistry 1 Cat 2 (Take Away)JpricarioNo ratings yet
- Group 4 ProjectDocument1 pageGroup 4 ProjectEleeistNo ratings yet
- H S S X S S HDocument4 pagesH S S X S S HahmadskhanNo ratings yet