Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsAnatomy Lec-2
Anatomy Lec-2
Uploaded by
aminqasm111This document provides an overview of the major tissue types found in the human body, including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the classification, structure and function of each tissue type in 3-4 sentences per slide. The focus is on epithelial and connective tissues, with brief descriptions of muscle and nervous tissue. Key points covered include the four types of epithelial cells and three types of connective tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- POLYGRAPHYDocument12 pagesPOLYGRAPHYKhimber Claire Lala MaduyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- HistologyDocument64 pagesHistologyZuko JamangileNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - TissuesDocument22 pagesChap 2 - TissuesDr. Wesam Al. MagharbehNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- DR Kapama 2Document54 pagesDR Kapama 2schorastica2008No ratings yet
- Physiology - 4th SemDocument76 pagesPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument55 pagesAnimal TissuesFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Haroen RasyidDocument41 pagesAnimal Tissue: Haroen Rasyidenkidani100% (1)
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 3 TissuesDocument42 pagesAnaPhy 3 TissuesFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 pagesUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- 1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissueDocument8 pages1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissuekawiNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument47 pagesAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument22 pagesAnimal TissuesNiketNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NiketDocument22 pagesAnimal Tissues NiketNiketNo ratings yet
- Tissues and HomeostasisDocument42 pagesTissues and Homeostasissubeyr963No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- 45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pages45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Basic Tissues of Human BodyDocument34 pagesBasic Tissues of Human Bodyhifzaaijaz366No ratings yet
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTDocument48 pagesWeek 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTwarrenjames0217No ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument29 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study NotesDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study Noteschedza FordNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemDocument22 pagesCell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Family: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Document49 pagesFamily: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Zay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of TissuesDocument58 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Tissuesflex gyNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDDocument82 pagesAnimal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure N FunctionDocument113 pagesCell Structure N FunctionTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueAhmad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Diff Types of Animal TissueDocument31 pagesDiff Types of Animal TissueJames Patrick Milan100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - HistologyDocument90 pagesCHAPTER 3 - HistologyObsan AbdiiNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGDocument54 pagesBody Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Eptihelial NLDocument30 pagesEptihelial NLSalon LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - TissuesDocument41 pagesWeek 4 - TissuesJuvy CambeNo ratings yet
- Zoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedDocument85 pagesZoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedyannolerouxNo ratings yet
- 3.tissue DmaDocument111 pages3.tissue DmaFaisal Mohamad100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Based On The Number of Layers:: Simple SquamousDocument2 pagesBased On The Number of Layers:: Simple SquamousYma FeelNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues (Anatomy) PDFDocument17 pagesBody Tissues (Anatomy) PDFNixonr RamsaranNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Sectioning: Paraffin Section CuttingDocument12 pagesSectioning: Paraffin Section Cuttingaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1.2A Pictures of Glassware and EquipmentDocument2 pages1.2A Pictures of Glassware and Equipmentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument23 pagesDocumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab InustrumentDocument7 pagesLab Inustrumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab 3 HistologyDocument10 pagesLab 3 Histologyaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 Mainaminqasm111No ratings yet
- ADocument6 pagesAaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830Document15 pages242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Proteins-Ppt From Search 3Document6 pagesProteins-Ppt From Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffDocument21 pages43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.7.Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.7.aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Introduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3Document6 pagesIntroduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFDocument17 pages3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Lec-1Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Lec-1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Computer Essentials - Chapter1Document38 pagesComputer Essentials - Chapter1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024Document8 pages1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024aminqasm111No ratings yet
- CamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41Document13 pagesCamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Mastering Biology Chapter 15 HomeworkDocument8 pagesMastering Biology Chapter 15 Homeworkerjxhjxe100% (1)
- Graduate Student Handbook: Master of Science in Computational Biology & Quantitative GeneticsDocument13 pagesGraduate Student Handbook: Master of Science in Computational Biology & Quantitative GeneticsSeptian Adi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Systems Biology of Cell Signaling Recurring Themes and Quantitative Models 1St Edition James E Ferrell Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Systems Biology of Cell Signaling Recurring Themes and Quantitative Models 1St Edition James E Ferrell Online PDF All Chaptercarrie.hughes920100% (8)
- Alexander Oparin: BiographyDocument3 pagesAlexander Oparin: BiographyMyriam CastroNo ratings yet
- LichensDocument18 pagesLichens314 Bhagyalakshmi SNo ratings yet
- Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 180 (2019) 430-438Document9 pagesEcotoxicology and Environmental Safety 180 (2019) 430-438Edilberto Murrieta LunaNo ratings yet
- Sword Art Online 9 - Alicization BeginningDocument376 pagesSword Art Online 9 - Alicization BeginningAgo Philosophi95% (169)
- Emotional Intelligence2 0 Bradberry Greaves EbsDocument10 pagesEmotional Intelligence2 0 Bradberry Greaves EbsLife Time LineNo ratings yet
- Building DNA Student ExplorationDocument5 pagesBuilding DNA Student Explorationaakeelah37No ratings yet
- Scientific Paper MJBLDocument10 pagesScientific Paper MJBLMarie Joy LunaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ActivityDocument1 pageNervous System ActivityMark Owen BaldoNo ratings yet
- Division Classification Thesis ExamplesDocument4 pagesDivision Classification Thesis Examplesmichelleadamserie100% (2)
- 12 Principles of Memory HandoutDocument3 pages12 Principles of Memory HandoutvisionNo ratings yet
- Language Is A System of CommunicationDocument8 pagesLanguage Is A System of CommunicationVanessa Ives™No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Meyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDocument40 pagesMeyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDNav14No ratings yet
- General Physiology, Nerve Muscle - MCQDocument9 pagesGeneral Physiology, Nerve Muscle - MCQadhamNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary RelationshipsDocument36 pagesEvolutionary RelationshipsBeverly Anne GaranNo ratings yet
- Destruction of Red Blood CellsDocument2 pagesDestruction of Red Blood CellsakosibusayNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Mechanotransduction Cell Signaling To Cell Response Paul A Sundaram All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Mechanotransduction Cell Signaling To Cell Response Paul A Sundaram All Chapter PDFchristopher.davis772100% (7)
- CHECKLISTDocument1 pageCHECKLISTEriq BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/52omarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bapi Ghosh Assistant Professor Department of Botany (Dodl)Document45 pagesDr. Bapi Ghosh Assistant Professor Department of Botany (Dodl)Project ICTNo ratings yet
- Module 2 UcspDocument16 pagesModule 2 UcspBenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesPost Lab QuestionsSyafiqah AzirahNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments On The Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana PipiensDocument15 pagesEffects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments On The Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana PipiensAbir Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Bio Informatics: Assignment No 03Document3 pagesBio Informatics: Assignment No 03rafiullahNo ratings yet
- The Change of Coral Cover in Ujong Pancu Waters Peukan Bada Sub District Aceh BesarDocument8 pagesThe Change of Coral Cover in Ujong Pancu Waters Peukan Bada Sub District Aceh BesarrizfaNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma Wardani100% (1)
Anatomy Lec-2
Anatomy Lec-2
Uploaded by
aminqasm1110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesThis document provides an overview of the major tissue types found in the human body, including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the classification, structure and function of each tissue type in 3-4 sentences per slide. The focus is on epithelial and connective tissues, with brief descriptions of muscle and nervous tissue. Key points covered include the four types of epithelial cells and three types of connective tissue.
Original Description:
Original Title
anatomy lec-2-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the major tissue types found in the human body, including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the classification, structure and function of each tissue type in 3-4 sentences per slide. The focus is on epithelial and connective tissues, with brief descriptions of muscle and nervous tissue. Key points covered include the four types of epithelial cells and three types of connective tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views25 pagesAnatomy Lec-2
Anatomy Lec-2
Uploaded by
aminqasm111This document provides an overview of the major tissue types found in the human body, including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the classification, structure and function of each tissue type in 3-4 sentences per slide. The focus is on epithelial and connective tissues, with brief descriptions of muscle and nervous tissue. Key points covered include the four types of epithelial cells and three types of connective tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 25
Ministry of high education and scientific research
Erbil polytechnic university
Shaqlawa technical college
Medical laboratory technology
Anatomy & physiology
1st stage
By: M.Sc. Ali Zainal
2023-2024
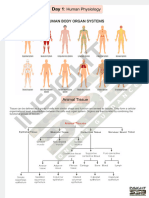
Tissue of the body
• Tissue is a group of similar cell and their
intercellular substance that have a similar
embryological origin and function together to
perform a specialized activity.
• A science that deals with the study of a tissue
is Histology.
Types of the tissue
• There are several major types of tissues. The
most common types are:
• 1-Epithelial tissue
• 2-Connective tissue
• 3-Muscle tissue
• 4-Nervous tissues
Epithelial tissue
• Epithelial tissue is tissue that covers surfaces,
lines cavities and form glands. Epithelial tissue
covers the outer surface of the body. It lines
the intestines, the lungs, and other hollow
organs.
• -Covering & lining epithelium
• - Glandular epithelium
Types of epithelial cell
• According to the arrangement of layers covering
and lining epithelium is grouped in to:
• a) Simple epithelium: it is specialized for
absorption, and filtration with minimal wear &
tear. It is a single layered
• b) Stratified epithelium, it is many layered and
found in an area with high degree of wear & tear.
• c) Pseudo-stratified, is a single layered but seem
to have many layer.
• Based on the cell shape covering and lining
epithelium is grouped in to:
• a) Squamous: - flattened & scale like
• b) Cuboidal: - cube shaped
• c) Columnar: - tall & cylindrical
• d) Transitional: - combination of cell shape
found where there is a great degree of
distention or expansion, these may be
cuboidal to columnar, cuboidal to polyhydral
and cuboidal to Squamous
Glandular Epithelium
• Their main function is secretion. A gland may
consist of one cell or a group of highly specialized
epithelial cell. Glands can be classified into
exocrine and endocrine according to where they
release their secretion.
• Exocrine: Those glands that empties their
secretion in to ducts/tubes that empty at the
surface of covering. Sweat & salivary glands are
exocrine glands.
• Endocrine: They ultimately secret their products
into the blood system, such as pancreas
Connective tissue
• Connective tissue is tissue that supports other
tissues, holds tissues together, or fills spaces.
Types of connective tissue
• There are several major types of connective
tissue (CT). These include
• 1-Connective tissue proper
• 2-Cartilage connective tissue
• 3- Osseous connective tissue (bone)
• 4-Vascular (Blood) is sometimes considered
an additional type of connective tissue
Connective tissue proper
1. -Loose (areolar) Connective tissue: It supports tissues,
organ blood vessels & nerves. It also forms
subcutaneous layer/superficial fascia/hypodermis
2. - Adipose connective tissue: around the kidney, at the
base and on the surface of the heart
3. - Dense (Collagenous) connective tissue: tendons and
ligament
4. - Elastic connective tissue: They are components of wall
of arteries, trachea, bronchial tubes & lungs
5. - Reticular connective tissue (It helps to form a delicate
supporting storma for many organs including liver,
spleen and lymph nodes. It also helps to bind together
the fibers (cells) of smooth muscle tissue.)
Cartilage connective tissue
Cartilages are classified in to hyaline, fibro & elastic
cartilage
1. Hyaline cartilage found at joints over long bones
2. Fibro cartilage found inter-vertebral discs and
knee
3. Elastic cartilage epiglottis, larynx, external part
of the ear
Osseous connective tissue (bone)
Divided in to compact and spongy bone
Muscle tissue
• There are muscle tissues and there are organs
called muscles. Muscles are made up of
muscle tissues. Muscle tissues and the
muscles they make up are specialized to
contract. Because of their ability to shorten
(contract), muscles are able to produce
motion
Types of muscle tissue
• a. Skeletal Muscle Tissue. The cells (muscle
fibers) of skeletal muscle tissue
• are long and cylindrical and have numerous
nuclei. The arrangement of the cellular
contents is very specific and results in a
striated appearance when viewed with the
microscope. This type of muscle tissue is
found mainly in the skeletal muscles
b. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
• The cells (muscle fibers) of cardiac muscle
tissue
• are short, branched, contain one nucleus, and
are striated. This tissue makes up the
myocardium (wall) of the heart.
c. Smooth Muscle Tissue
• The cells (muscle fibers) of smooth muscle
tissue
• are spindle-shaped, contain one nucleus, and
are not striated. Smooth muscle tissue is
generally found in the walls of hollow organs
such as the organs of the digestive and
respiratory systems, the blood vessels, the
ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and
reproductive ducts.
Nervous tissue
• Nervous tissue is a collection of cells that respond to
stimuli and transmit information.
• a. A neuron (figure 2-4), or nerve cell, is the cell of the
nervous tissue that actually picks up and transmits a
signal from one part of the body to another.
• b synapse (figure 2-5) is the point at which a signal
passes from one neuron to the next.
• c. The neuroglia (also known as glia) is made up of the
supporting cells of the nervous system (glial cells).
• d. The nervous tissues
You might also like
- POLYGRAPHYDocument12 pagesPOLYGRAPHYKhimber Claire Lala MaduyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- HistologyDocument64 pagesHistologyZuko JamangileNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 - TissuesDocument22 pagesChap 2 - TissuesDr. Wesam Al. MagharbehNo ratings yet
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- DR Kapama 2Document54 pagesDR Kapama 2schorastica2008No ratings yet
- Physiology - 4th SemDocument76 pagesPhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument55 pagesAnimal TissuesFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue: Haroen RasyidDocument41 pagesAnimal Tissue: Haroen Rasyidenkidani100% (1)
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 3 TissuesDocument42 pagesAnaPhy 3 TissuesFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 pagesUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- 1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissueDocument8 pages1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissuekawiNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument47 pagesAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitNo ratings yet
- Tissues NTBDocument39 pagesTissues NTBAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument75 pagesEp It HeliumSahin mollickNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument22 pagesAnimal TissuesNiketNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NiketDocument22 pagesAnimal Tissues NiketNiketNo ratings yet
- Tissues and HomeostasisDocument42 pagesTissues and Homeostasissubeyr963No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- 45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pages45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Basic Tissues of Human BodyDocument34 pagesBasic Tissues of Human Bodyhifzaaijaz366No ratings yet
- Week 2 The Tissues MembranesDocument60 pagesWeek 2 The Tissues MembranesJeqtopher RoaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTDocument48 pagesWeek 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTwarrenjames0217No ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument29 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study NotesDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study Noteschedza FordNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemDocument22 pagesCell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Family: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Document49 pagesFamily: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Zay SalazarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of TissuesDocument58 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Tissuesflex gyNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDDocument82 pagesAnimal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure N FunctionDocument113 pagesCell Structure N FunctionTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueAhmad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Diff Types of Animal TissueDocument31 pagesDiff Types of Animal TissueJames Patrick Milan100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - HistologyDocument90 pagesCHAPTER 3 - HistologyObsan AbdiiNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGDocument54 pagesBody Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Eptihelial NLDocument30 pagesEptihelial NLSalon LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - TissuesDocument41 pagesWeek 4 - TissuesJuvy CambeNo ratings yet
- Zoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedDocument85 pagesZoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedyannolerouxNo ratings yet
- 3.tissue DmaDocument111 pages3.tissue DmaFaisal Mohamad100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- Based On The Number of Layers:: Simple SquamousDocument2 pagesBased On The Number of Layers:: Simple SquamousYma FeelNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues (Anatomy) PDFDocument17 pagesBody Tissues (Anatomy) PDFNixonr RamsaranNo ratings yet
- Tissue Notes 9Document7 pagesTissue Notes 9Priyad MundadaNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Sectioning: Paraffin Section CuttingDocument12 pagesSectioning: Paraffin Section Cuttingaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1.2A Pictures of Glassware and EquipmentDocument2 pages1.2A Pictures of Glassware and Equipmentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument23 pagesDocumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab InustrumentDocument7 pagesLab Inustrumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab 3 HistologyDocument10 pagesLab 3 Histologyaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 Mainaminqasm111No ratings yet
- ADocument6 pagesAaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830Document15 pages242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Proteins-Ppt From Search 3Document6 pagesProteins-Ppt From Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffDocument21 pages43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.7.Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.7.aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Introduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3Document6 pagesIntroduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFDocument17 pages3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Lec-1Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Lec-1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Computer Essentials - Chapter1Document38 pagesComputer Essentials - Chapter1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024Document8 pages1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024aminqasm111No ratings yet
- CamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41Document13 pagesCamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Mastering Biology Chapter 15 HomeworkDocument8 pagesMastering Biology Chapter 15 Homeworkerjxhjxe100% (1)
- Graduate Student Handbook: Master of Science in Computational Biology & Quantitative GeneticsDocument13 pagesGraduate Student Handbook: Master of Science in Computational Biology & Quantitative GeneticsSeptian Adi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Systems Biology of Cell Signaling Recurring Themes and Quantitative Models 1St Edition James E Ferrell Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Systems Biology of Cell Signaling Recurring Themes and Quantitative Models 1St Edition James E Ferrell Online PDF All Chaptercarrie.hughes920100% (8)
- Alexander Oparin: BiographyDocument3 pagesAlexander Oparin: BiographyMyriam CastroNo ratings yet
- LichensDocument18 pagesLichens314 Bhagyalakshmi SNo ratings yet
- Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 180 (2019) 430-438Document9 pagesEcotoxicology and Environmental Safety 180 (2019) 430-438Edilberto Murrieta LunaNo ratings yet
- Sword Art Online 9 - Alicization BeginningDocument376 pagesSword Art Online 9 - Alicization BeginningAgo Philosophi95% (169)
- Emotional Intelligence2 0 Bradberry Greaves EbsDocument10 pagesEmotional Intelligence2 0 Bradberry Greaves EbsLife Time LineNo ratings yet
- Building DNA Student ExplorationDocument5 pagesBuilding DNA Student Explorationaakeelah37No ratings yet
- Scientific Paper MJBLDocument10 pagesScientific Paper MJBLMarie Joy LunaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ActivityDocument1 pageNervous System ActivityMark Owen BaldoNo ratings yet
- Division Classification Thesis ExamplesDocument4 pagesDivision Classification Thesis Examplesmichelleadamserie100% (2)
- 12 Principles of Memory HandoutDocument3 pages12 Principles of Memory HandoutvisionNo ratings yet
- Language Is A System of CommunicationDocument8 pagesLanguage Is A System of CommunicationVanessa Ives™No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Meyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDocument40 pagesMeyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDNav14No ratings yet
- General Physiology, Nerve Muscle - MCQDocument9 pagesGeneral Physiology, Nerve Muscle - MCQadhamNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary RelationshipsDocument36 pagesEvolutionary RelationshipsBeverly Anne GaranNo ratings yet
- Destruction of Red Blood CellsDocument2 pagesDestruction of Red Blood CellsakosibusayNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Mechanotransduction Cell Signaling To Cell Response Paul A Sundaram All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Mechanotransduction Cell Signaling To Cell Response Paul A Sundaram All Chapter PDFchristopher.davis772100% (7)
- CHECKLISTDocument1 pageCHECKLISTEriq BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/52Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/52omarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bapi Ghosh Assistant Professor Department of Botany (Dodl)Document45 pagesDr. Bapi Ghosh Assistant Professor Department of Botany (Dodl)Project ICTNo ratings yet
- Module 2 UcspDocument16 pagesModule 2 UcspBenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab QuestionsDocument2 pagesPost Lab QuestionsSyafiqah AzirahNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments On The Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana PipiensDocument15 pagesEffects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments On The Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana PipiensAbir Hasan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Bio Informatics: Assignment No 03Document3 pagesBio Informatics: Assignment No 03rafiullahNo ratings yet
- The Change of Coral Cover in Ujong Pancu Waters Peukan Bada Sub District Aceh BesarDocument8 pagesThe Change of Coral Cover in Ujong Pancu Waters Peukan Bada Sub District Aceh BesarrizfaNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma Wardani100% (1)