Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arlan Neutralization Worksheet
Arlan Neutralization Worksheet
Uploaded by
HEY ERL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document provides information about neutralization reactions between acids and bases, including common polyatomic ions, general neutralization equations, and examples of specific acid-base reactions that produce salts and gases. Tables are included that show example reactions between acids (nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid) and bases (sodium carbonate, potassium oxide, copper hydroxide, calcium hydroxide) and the resulting salts. Word equations and balanced chemical equations are given for additional acid-base reactions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about neutralization reactions between acids and bases, including common polyatomic ions, general neutralization equations, and examples of specific acid-base reactions that produce salts and gases. Tables are included that show example reactions between acids (nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid) and bases (sodium carbonate, potassium oxide, copper hydroxide, calcium hydroxide) and the resulting salts. Word equations and balanced chemical equations are given for additional acid-base reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesArlan Neutralization Worksheet
Arlan Neutralization Worksheet
Uploaded by
HEY ERLThis document provides information about neutralization reactions between acids and bases, including common polyatomic ions, general neutralization equations, and examples of specific acid-base reactions that produce salts and gases. Tables are included that show example reactions between acids (nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid) and bases (sodium carbonate, potassium oxide, copper hydroxide, calcium hydroxide) and the resulting salts. Word equations and balanced chemical equations are given for additional acid-base reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Neutralisation Worksheet
Some common polyatomic ions:
You will need a periodic table to determine the charges on some of the ions to answer
questions.
1. Complete the following general equations for neutralization reactions:
a. Metal oxide + acid → salt and water
b. Metal hydroxide + acid → salt and water
c. Metal carbonate + acid →carbon dioxide, water and salt
2. Complete the following table to identify the salt produced by the acids and bases:
Nitric acid Hydrochloric acid Sulfuric acid
(HNO3) (HCl) (H2SO4)
Sodium carbonate sodium nitrate + sodium Sodium
- Na2CO3 water + carbon chloride+Water+ sulfate+water+ca
dioxide carbon dioxide rbon dioxide
NaNO3 NaCl Na2SO4
Potassium oxide - potassium Potassium Potassium
K2O nitrate+water chloride+water+ca sulfate+water
KNO3 rbon dioxide K2SO4
KCl
Copper hydroxide copper Copper copper
- Cu(OH)2 nitrate+water chloride+Water sulfate+water
Cu(NO3)2 CuCl2 CuSO4
3. Complete the following word equations:
Neutralisation Worksheet
a. Hydrochloric acid + copper carbonate → Copper chloride+water+Carbon
dioxide
HCl + CuCO3 → CuCl2 + H2O + CO2
b. Iron hydroxide + sulfuric acid → Iron sulfate+water
Fe(OH)2 + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2O
c. Nitric acid + calcium oxide → Calcium nitrate+water
CaO + HNO3 = Ca(NO3)2 + HO
Note: Acids react with reactive metals in the following neutralization reaction:
H2SO4 + Na2SO3 → Na2SO4 + H2O + SO2
d. sodium + sulfuric acid →sodium sulfate
e. magnesium + nitric acid→ magnesium nitrate + hydrogen
f. hydrochloric acid + potassium oxide → potassium chloride + water
g. Calcium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water
4. Write balanced equations for the word equations in question 3.
6. Complete the following sentences.
A. Litmus turns blue in basic solutions, and red in acidic solutions.
B. A soluble base is called an alkali
C. Solutions may be acidic, basic or neutral
D. To be sure that a solution is acidic you must observe a change in the color of an
indicator.
7. Use the information in the table below to answer these questions.
Neutralisation Worksheet
a. What acid is present in:
• sour milk? Lactic
• oil of wintergreen? Salicylic
• ants? Formic
b. Where would you find:
• citric acid? Citrus fruits, eg oranges and lemons
• tartaric acid? Grape juice
c. Apart from its value as vitamin C, why else is ascorbic acid added to fruit juices?
Food preservative
d. If oxalic acid is a poison, why is it possible to eat rhubarb and spinach?
There’s a significant difference in the levels of oxalic acid in the leaves of rhubarb compared
to the stalks
You might also like
- Difference Between AFBC and CFBCDocument3 pagesDifference Between AFBC and CFBCAamirMalik86% (7)
- Chemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsDocument2 pagesChemical Changes Mastery Part 4: AcidsJoeNo ratings yet
- Acids + CarbonatesDocument13 pagesAcids + CarbonatesVithuNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 4 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesYear 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 4 ANSWERSsports.kingdomNo ratings yet
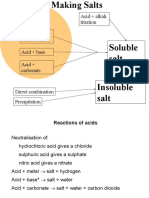
- Lesson Element Making Salts: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDocument17 pagesLesson Element Making Salts: Instructions and Answers For TeachersGracey- Ann JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- Science 1.5 Answers Worksheet Five Acids: Acid + Base Salt + WaterDocument2 pagesScience 1.5 Answers Worksheet Five Acids: Acid + Base Salt + Watermintesinot esayasNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 4Document5 pagesYear 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 4sports.kingdomNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases SummaryDocument8 pagesAcid Bases Summaryibraheemgamer786No ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument6 pagesAcid Base and SaltRajnish kumarNo ratings yet
- NeutralizationDocument13 pagesNeutralizationbarakahmuluziNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts ADocument7 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts AYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)Document6 pages2 - Acids, Bases and Salts (1)HONEY YOYONo ratings yet
- Reactions of AcidsDocument27 pagesReactions of AcidsLawrenceNo ratings yet
- Preparing Common Salts G8Document20 pagesPreparing Common Salts G8diamehta1512No ratings yet
- Quiz ChemDocument4 pagesQuiz ChemCherryNo ratings yet
- Lab 21Document3 pagesLab 21KeenanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 - Acid, Base and Salt Making PDFDocument4 pagesChapter - 17 - Acid, Base and Salt Making PDFMir Tahsanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Acid, Base and SaltDocument8 pages4 Acid, Base and Saltjosephmartinsogbu30No ratings yet
- CH 10 Salts & Its PreparationDocument25 pagesCH 10 Salts & Its Preparationapi-3774259100% (7)
- Equations Worksheet 1Document2 pagesEquations Worksheet 1jaikovskyNo ratings yet
- Salts FormationDocument19 pagesSalts FormationUrwa Abdul MannanNo ratings yet
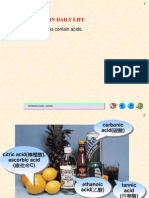
- Acids: Common Acids in Daily LifeDocument47 pagesAcids: Common Acids in Daily LifeElanIe InspiritNo ratings yet
- Class X Acids BasesDocument6 pagesClass X Acids BasesvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- 07 Acids Bases and SaltsDocument7 pages07 Acids Bases and Saltsrudi_zNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 5Document4 pagesChemistry Worksheet 5Deandra AliciaNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideDocument5 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Hydrogen ChlorideYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Solution 805196Document4 pagesSolution 805196scNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class X Science Chap 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts - BasicsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class X Science Chap 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts - BasicsMd RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsDocument7 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsView TubeNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Document3 pages8.2 Formulae Equations and Amount Edexcel 15 17Stephan MinhNo ratings yet
- 8A Salts - AnswerDocument14 pages8A Salts - AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- CBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)Document14 pagesCBSE-X Science - Chap-2 (Acids, Bases and Salts)aanwidivNo ratings yet
- PP Acid ReactionsDocument14 pagesPP Acid Reactionsapi-3696266No ratings yet
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- 3c ANSWERS More Equations (2017)Document2 pages3c ANSWERS More Equations (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equation ExerciseDocument2 pagesChemical Equation ExerciseMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument22 pagesSaltssaanvi katyalNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes: ChemistryDocument20 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes: ChemistryLavanya Priya SathyanNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Gas:: Other Endothermic ReactionsDocument7 pagesEvolution of Gas:: Other Endothermic Reactionssara parkNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Part 4 Acids and BasesDocument87 pagesPart 4 Acids and BasesnsjsNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsDocument4 pagesAcids, Bases & Salts: IndicatorsView TubeNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument73 pagesAcids and Basesapi-305909325100% (4)
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Acids RecallDocument4 pagesAcids RecallAssumpta McguckinNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science:: Worksheet On The Reactions of AcidsDocument7 pagesYear 10 Science:: Worksheet On The Reactions of AcidsLachlanNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document12 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4api-292313678No ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Reactions of Acids and Bases: Danielle AkinlaluDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1 Reactions of Acids and Bases: Danielle AkinlaludanielleNo ratings yet
- 10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must DoDocument63 pages10th SCIENCE (English Medium) Must Doanshu26stNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document2 pagesNitric Acid (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Acids - 2Document2 pagesAcids - 2Anushka ShendageNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases SummaryDocument2 pagesAcids and Bases SummaryTan Yong KhaiNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts BDocument8 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts BYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acids, BAses and SAltsDocument4 pagesAcids, BAses and SAltsRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument48 pagesReactions in Aqueous SolutionDavid MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Important QuestionsMX GamingNo ratings yet
- U4 - Waves - Characteristics & TypesDocument1 pageU4 - Waves - Characteristics & TypesHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Grade 8. Globalization and Culture Summative (A)Document8 pagesGrade 8. Globalization and Culture Summative (A)HEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionsDocument6 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionsHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- DC Review For Unit 3Document5 pagesDC Review For Unit 3HEY ERLNo ratings yet
- ArtistsDocument3 pagesArtistsHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument1 pageAnswersHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Aiya&Arlan Criterion D User ManualDocument6 pagesAiya&Arlan Criterion D User ManualHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- A Visit To A GrandmotherDocument3 pagesA Visit To A GrandmotherHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Arlan G8 Rate of Reaction Criteria B & CDocument8 pagesArlan G8 Rate of Reaction Criteria B & CHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Arlan Criterion BDocument8 pagesArlan Criterion BHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Process JournalDocument5 pagesProcess JournalHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- SponsorDocument7 pagesSponsorHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Arlan G8 Summative Plan For Health & FitnessDocument7 pagesArlan G8 Summative Plan For Health & FitnessHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Charles MansonDocument1 pageCharles MansonHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- SponsorDocument8 pagesSponsorHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- MonologuesDocument34 pagesMonologuesHEY ERLNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Titration: Presented By: Dr. Bambang Yudono, M.SCDocument36 pagesComplexometric Titration: Presented By: Dr. Bambang Yudono, M.SCFikri AndrianNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering NotesDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Notessanjay kumar mittalNo ratings yet
- Steel Pipes Dimensions - ANSI Schedule 40Document4 pagesSteel Pipes Dimensions - ANSI Schedule 40ciblixNo ratings yet
- COE-110.10, Methodology of Laboratory Failure AnalysisDocument57 pagesCOE-110.10, Methodology of Laboratory Failure AnalysisNacer Kisy100% (1)
- EPF4802 - Chapter 5 (Part 1) Utilities and Energy Efficient Design - Video - NotesDocument14 pagesEPF4802 - Chapter 5 (Part 1) Utilities and Energy Efficient Design - Video - NoteshidayantiemNo ratings yet
- Sds Titanvene Hdpe Hd5301aaDocument4 pagesSds Titanvene Hdpe Hd5301aaAndika PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chivacure 169Document2 pagesChivacure 169pekena_fer2059No ratings yet
- NDT On Concrete Pull Off Test: by Subhodeep Neogi Sai Prakash VaddiDocument12 pagesNDT On Concrete Pull Off Test: by Subhodeep Neogi Sai Prakash VaddiManish Mittal100% (1)
- Benzene - Preheater Data SheetDocument1 pageBenzene - Preheater Data Sheetsushant_jhawerNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties 301015Document47 pagesMechanical Properties 301015Eugene Daga-angNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen 2006 01 0434Document6 pagesHydrogen 2006 01 0434Rajesh VarmaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Cement PasteDocument40 pagesPhysical Properties of Cement PasteValéria OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Jbiotec 2005 06 005 PDFDocument189 pages10 1016@j Jbiotec 2005 06 005 PDFNurismy RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Systemic Mitochondrial Disorder Due To A Dominant p.Y955H Disease Variant in DNA Polymerase GammaDocument16 pagesA Multi-Systemic Mitochondrial Disorder Due To A Dominant p.Y955H Disease Variant in DNA Polymerase GammaMihai LazarNo ratings yet
- ALTA Short Course Outline Sample Pages Copper SX EWDocument7 pagesALTA Short Course Outline Sample Pages Copper SX EWHamed PiriNo ratings yet
- Neomallermin TR Tablet 6mg DissolutionDocument8 pagesNeomallermin TR Tablet 6mg DissolutionGajananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Organic ChemistryDocument43 pagesChapter 22 Organic Chemistryapi-703497157No ratings yet
- Propoxylated EmulsifierDocument1 pagePropoxylated EmulsifierFadhli KusumaNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology: David Laureys, Maarten Aerts, Peter Vandamme, Luc de VuystDocument11 pagesFood Microbiology: David Laureys, Maarten Aerts, Peter Vandamme, Luc de VuystAngeles SuarezNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Stanbio GlukosaDocument4 pagesMSDS - Stanbio GlukosaDoni Eka PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Analysis of Tea and CoffeeDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 Analysis of Tea and CoffeeSiddhant Unde100% (1)
- Chrom I TingDocument11 pagesChrom I TingAshish RawatNo ratings yet
- Using Software Gambit 2.0 and Fluent 6.0 For Simulation of Heat Mass Transfer ProblemsDocument11 pagesUsing Software Gambit 2.0 and Fluent 6.0 For Simulation of Heat Mass Transfer ProblemsJasim Al-rubayieNo ratings yet
- Rheology ModifiersDocument35 pagesRheology Modifierssbttbs67% (3)
- Determination of Some Trace Elements in Chicken Eggs From Different SourcesDocument5 pagesDetermination of Some Trace Elements in Chicken Eggs From Different SourcesaaaayoubNo ratings yet
- Fluidized-Bed Bioreactor Applications For Biological Wastewater Treatment - A Review of Research and DevelopmentsDocument13 pagesFluidized-Bed Bioreactor Applications For Biological Wastewater Treatment - A Review of Research and DevelopmentsAgeng RizkyNo ratings yet
- Modelling: Ethanol-Water Pressure Swing Distillation in An Structured Packed Bed ColumnDocument10 pagesModelling: Ethanol-Water Pressure Swing Distillation in An Structured Packed Bed ColumnAlexCooksNo ratings yet
- Benzene E34a BDocument107 pagesBenzene E34a Baww salahNo ratings yet
- TITRATION4Document7 pagesTITRATION4jadoo0246No ratings yet