Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mirrors
Mirrors
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThis document defines key terms and concepts related to plane and curved mirrors. It describes how plane mirrors produce regular reflections and how curved mirrors can be either concave or convex. Concave mirrors converge light to form real, inverted images in front of the mirror, while convex mirrors diverge light to form virtual, erect images behind the mirror. The document also defines important geometric features of mirrors like the vertex, focal point, center of curvature, focal length, and principal axis.
Original Description:
Mirrors - Science 10 notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms and concepts related to plane and curved mirrors. It describes how plane mirrors produce regular reflections and how curved mirrors can be either concave or convex. Concave mirrors converge light to form real, inverted images in front of the mirror, while convex mirrors diverge light to form virtual, erect images behind the mirror. The document also defines important geometric features of mirrors like the vertex, focal point, center of curvature, focal length, and principal axis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMirrors
Mirrors
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabagThis document defines key terms and concepts related to plane and curved mirrors. It describes how plane mirrors produce regular reflections and how curved mirrors can be either concave or convex. Concave mirrors converge light to form real, inverted images in front of the mirror, while convex mirrors diverge light to form virtual, erect images behind the mirror. The document also defines important geometric features of mirrors like the vertex, focal point, center of curvature, focal length, and principal axis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
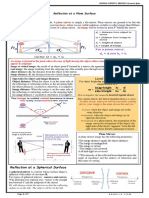
Mirror: highly polished surface Ray Diagramming: technique to
that can produce images by describe the LOST (Location,
reflection Orientation, Size, Type)
Plane Mirror: flat, smooth, reflects Principal Ray: parallel to PA,
light in a regular way passes F
Curved/Spherical: portion of a Focal Ray: passes F, hits the mirror,
sphere reflects parallel to PA
a. Concave: reflects light from Chief Ray- leaves the object and
inner surface, converging mirror passes thru c
b. Convex: reflects light from outer
surface, diverging mirror
Object: source of diverging light
rays, source of incident ray
Image: reproduction of the object
by the mirror
Real image: formed by
convergence, formed in front of
the mirror, can be projected,
always inverted
Virtual image: formed by
divergence, formed behind the
mirror, cannot be projected,
always erect
Images formed by plane mirror:
same size, same distance, erect,
has reversal effect
Images formed by curved mirrors:
differs in size, location, orientation
Vertex (v)- physical center of the
mirror
Focal point (F) or focus, midpoint
Center of Curvature (c)-
geometrical center
Focal length (f)- distance from f to
v
Principal axis (PA)- perpendicular
line to the mirror
Radius of curvature- distance
from c to v
You might also like
- Plane Mirrors: Law of Light ReflectionDocument4 pagesPlane Mirrors: Law of Light Reflectionkabuto94No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Mirror Ray DiagramDocument5 pagesActivity Sheet in Mirror Ray DiagramJanna AlindoganNo ratings yet
- Week 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1Document90 pagesWeek 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1clairearabelle iloyNo ratings yet
- MirrorsDocument3 pagesMirrorspenaroyowensthonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson 3 ScienceieuozsNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Reflection of Light 2017Document89 pages5.1 Reflection of Light 2017MOHD FARHAN BIN MOHD NA'AIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors PDFDocument9 pagesSpherical Mirrors PDFAditya SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Forliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebDocument32 pagesForliveteaching 3 220616045804 9ea2c7ebPrincess Rehanne PadiosNo ratings yet
- 6 - MirrorsDocument13 pages6 - MirrorsAstrid MinNo ratings yet
- Mirrors LectureDocument14 pagesMirrors LecturemkanwarsNo ratings yet
- Lenses and Mirrors Part1Document38 pagesLenses and Mirrors Part1Ian DibNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Reflection of LightDocument48 pagesReflection & Reflection of LightChanderKishoreJoshiNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light at Curved SurfacesDocument10 pagesReflection of Light at Curved SurfacesSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Reflection of LightDocument44 pagesMirrors and Reflection of LightJennifer Bernas BerdulNo ratings yet
- Lens andDocument17 pagesLens andRandy AugustNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument22 pagesLight Reflection and Refractionapi-246793885100% (1)
- Synchronous Encounter Notes-MirrorsDocument2 pagesSynchronous Encounter Notes-MirrorsRaven Leymi MajesticNo ratings yet
- LCH 26Document68 pagesLCH 26chethngalla2021No ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesChapter Notes Light - Reflection & Refractionroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- Blue Illustrative Understanding Characterization Education PresentationDocument28 pagesBlue Illustrative Understanding Characterization Education PresentationChikapu TrashcanNo ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument14 pages10 Lightnynaitikyadavu1No ratings yet
- Reflection of Light in Concave MirrorDocument16 pagesReflection of Light in Concave MirrorLiza Cordova RiveraNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument12 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesGiovan George MendezNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 - Light - Geometric Optics TransDocument11 pagesChapter 23 - Light - Geometric Optics TransKim HocsonNo ratings yet
- Science ReportingDocument26 pagesScience ReportingadreanneNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Optics NotesDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Optics NotesRina Marie Besin CartesianoNo ratings yet
- Parallel Beam Convergent Beam Divergent BeamDocument16 pagesParallel Beam Convergent Beam Divergent BeamNaman YadavNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotesDocument44 pagesLesson NotesZildjian Apud100% (1)
- Light ShikshaDocument13 pagesLight Shikshabratajeet.ghosh.14No ratings yet
- Light FinalDocument8 pagesLight Finalghs NambalNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesReflection of LightenricoluismendozaNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirror and LensesDocument3 pagesSpherical Mirror and LensesNins SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Image Formation in Plane and Curved MirrorsDocument8 pagesImage Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrorsemmarie llantinoNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light 1Document28 pagesReflection of Light 1Anne MalobagoNo ratings yet
- 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument43 pages10 Light Reflection and Refractiong8one2020No ratings yet
- Light Reflection NotesDocument8 pagesLight Reflection NotesSuperParthz GAMING100% (2)
- Light - Reflection & Refraction - (22-23)Document25 pagesLight - Reflection & Refraction - (22-23)Vishal dandeNo ratings yet
- Light and ReflectionDocument34 pagesLight and ReflectionAmina AlmarzooqiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Spherical Mirrors BDocument49 pagesReflection Spherical Mirrors BEros James JameroNo ratings yet
- Mirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Document24 pagesMirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Donna100% (1)
- Ray DiagramDocument47 pagesRay Diagramjimmy cocoNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrorDocument13 pages5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrormariamNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFDocument7 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- G10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesDocument98 pagesG10 U2L2 - Reflection and Mirrors Refraction and LensesErika Mae Cordero100% (1)
- Geometric Optics: Mirrors, Lenses, Light, and Image FormationDocument62 pagesGeometric Optics: Mirrors, Lenses, Light, and Image FormationRonald Abrasaldo SatoNo ratings yet
- Light Class XDocument109 pagesLight Class XLekshmipriya PNo ratings yet
- RRB NTPC - Physics - LightDocument5 pagesRRB NTPC - Physics - LightAkella LokeshNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrorDocument13 pages5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrorMastura MohamadNo ratings yet
- Physics Mirror ReportDocument14 pagesPhysics Mirror ReportSKSNo ratings yet
- Eve Ross - 10.3a - Note - Images in Concave MirrorsDocument8 pagesEve Ross - 10.3a - Note - Images in Concave MirrorsEve RossNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and Refractiondjshlok359No ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 - Jan 11 2024Document2 pagesSCIENCE10 - Jan 11 2024Ryuusei TetsurouNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionAnant WatsNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesLight-Reflection and RefractionANJALI RANANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument42 pagesChapter - 10: Light: Reflection and RefractionGarvit Khare75% (4)
- Differences Between Specular and Diffused ReflectionDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Specular and Diffused ReflectionTHANMAYA GARIMELLA 9 TH JEE SECTIONNo ratings yet
- Photographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignFrom EverandPhotographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Axonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandAxonometric Projection: Exploring Depth Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet