Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radiation
Radiation
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageThis document discusses different types of radiation including electromagnetic radiation, particles like electrons and protons, and waves like light and sound. It describes ionizing radiation as radiation that can create electrically charged ions by breaking molecules and atoms, potentially causing DNA damage or genetic mutations. Examples of natural sources include radon gas from uranium in the soil and cosmic radiation from outer space, while man-made sources include nuclear power plants, medical procedures, and some consumer products. The effects of radiation exposure can range from short-term sickness to long-term health issues like cancer, and depend on factors like the radiation dose and exposure duration.
Original Description:
Radiation - Science 10 notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of radiation including electromagnetic radiation, particles like electrons and protons, and waves like light and sound. It describes ionizing radiation as radiation that can create electrically charged ions by breaking molecules and atoms, potentially causing DNA damage or genetic mutations. Examples of natural sources include radon gas from uranium in the soil and cosmic radiation from outer space, while man-made sources include nuclear power plants, medical procedures, and some consumer products. The effects of radiation exposure can range from short-term sickness to long-term health issues like cancer, and depend on factors like the radiation dose and exposure duration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageRadiation
Radiation
Uploaded by
gwenstefanabagThis document discusses different types of radiation including electromagnetic radiation, particles like electrons and protons, and waves like light and sound. It describes ionizing radiation as radiation that can create electrically charged ions by breaking molecules and atoms, potentially causing DNA damage or genetic mutations. Examples of natural sources include radon gas from uranium in the soil and cosmic radiation from outer space, while man-made sources include nuclear power plants, medical procedures, and some consumer products. The effects of radiation exposure can range from short-term sickness to long-term health issues like cancer, and depend on factors like the radiation dose and exposure duration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
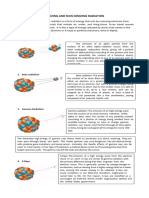
Radiant energy- energy produced X-rays and Gamma rays: high
by nuclear reactions - sun. Also energy parts of EM spec
known as Electromagnetic Alpha particles: 2 protons 2
radiation. neutrons
Beta particles: fast moving
Less energy = less effects electrons
Longer exposure = more effects Cosmic Radiation: from the outer
space
Particles: atoms, electrons, ions, Neutrons: from nuclear power
protons, neutrons plants
Wave: sound, light
Sources of Ionizing radiation
Radiation can be man made or - human activities
natural. - nuclear power plant
- natural sources
Radon is a radioactive gas from - medical procedures
uranium found in soil. Can also be
found in water, food, earth’s crust. Effects of radiation: cataracts,
Etc. It is an example of natural or skin cancer or glaucoma, sickness,
background radiation or death
Examples of manmade radiation Stochastic effects: possibility of
are nuclear medicine, tv, tobacco, effect is based on the dose. Ex.
etc. skin cancer, genetic mutation
Radiation is created when the Non stochastic effects: severity of
state of an atom changes effect based on the dose. Ex.
cataracts, skin burns
Radioactive decay is when an
unstable atom changes to be a
more stable one.
Half life is the time it takes for half
of the atom to decay
Ionizing Radiation can create
electrically charged ions. It breaks
molecules and atoms which can
cause DNA damage or genetic
mutations
Forms of Ionizing radiation
You might also like
- RadiationDocument31 pagesRadiationS RahmnNo ratings yet
- Radiation Cueto NajitoDocument89 pagesRadiation Cueto NajitoCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Name: Christina Eleanor Martin Subject: Hygiene Group: 3 Course: 4 Year 1 SemDocument21 pagesName: Christina Eleanor Martin Subject: Hygiene Group: 3 Course: 4 Year 1 SemSuthan KaveriNo ratings yet
- Radiation HazardsDocument40 pagesRadiation HazardsMunish Dogra100% (1)
- Nuclear Radioactivity and Ionizing RadiationDocument6 pagesNuclear Radioactivity and Ionizing RadiationMohamed TarekNo ratings yet
- Ind Hygiene 005 Alpha Beta Gamma RadiationDocument48 pagesInd Hygiene 005 Alpha Beta Gamma RadiationB B MandalNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Physics Chapter 12 Revision NotesGAMING IN MOODNo ratings yet
- Radbi Kelompok 2Document36 pagesRadbi Kelompok 2Try MutaqienNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity Revision NotesDocument4 pagesRadioactivity Revision NotesJohnNo ratings yet
- Radioactive PollutionDocument24 pagesRadioactive PollutionPuja SolankiNo ratings yet
- English Activity - Factores de RiesgoDocument3 pagesEnglish Activity - Factores de RiesgoMarcos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Science FolioDocument14 pagesScience FolioJunn KyleNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Radiation AlertDocument13 pagesScience 10 Radiation AlertAaron InutanNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Radiation:: Nuclear Chemistry Teacher NotesDocument3 pagesVocabulary Radiation:: Nuclear Chemistry Teacher NotesAlexia AguilarNo ratings yet
- The Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentDocument30 pagesThe Effects of EM Radiations On Living Things and EnvironmentJhunner Buan100% (1)
- Ionizing and Nonionizing RadiationDocument9 pagesIonizing and Nonionizing RadiationAshwin ShajithNo ratings yet
- IONIZING AND NON Hand OutDocument3 pagesIONIZING AND NON Hand OutJiely PacatangNo ratings yet
- Natural and Induced Radioactivity: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Hasanein Gaber Professor of BiophysicsDocument51 pagesNatural and Induced Radioactivity: Prof - Dr. Mohamed Hasanein Gaber Professor of BiophysicsAhmedAmer1No ratings yet
- Radiation Pollution 2Document17 pagesRadiation Pollution 2niteshdiscord1No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Introduction To RadiationDocument36 pagesChapter 3 Introduction To Radiationhailemicael mesfinNo ratings yet
- Subject Instructor: Subject:Industrial Safety Health &environmentDocument13 pagesSubject Instructor: Subject:Industrial Safety Health &environmentShyam TannaNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument4 pagesRadioactivityDiego BuesiNo ratings yet
- Radiation and You Brochure WEBDocument2 pagesRadiation and You Brochure WEBRiyoNo ratings yet
- 1-The Physics and Chemistry of Radiation AbsorptionDocument38 pages1-The Physics and Chemistry of Radiation AbsorptionliskatriNo ratings yet
- 2 CH 28 Nuclear Chemistry (Def Radioactivity)Document58 pages2 CH 28 Nuclear Chemistry (Def Radioactivity)Fatin IziantiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Decay (Alpha, Beta and Gamma)Document17 pagesNuclear Decay (Alpha, Beta and Gamma)Parahat.TajovNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument17 pagesRadioactivityNurasfiqah AKNo ratings yet
- Radiation PollutionDocument6 pagesRadiation PollutionFaith MainaNo ratings yet
- الإشعاع - WikipediaDocument80 pagesالإشعاع - WikipediaA.M.B M.B.M.ENo ratings yet
- Edical and Industrial RadiographyDocument3 pagesEdical and Industrial RadiographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Doe Ionizing Radiation Dose Ranges Jan 2018Document8 pagesDoe Ionizing Radiation Dose Ranges Jan 2018Fabiane GarbimNo ratings yet
- Health AND Safety in Biomedical EngineeringDocument7 pagesHealth AND Safety in Biomedical EngineeringxutemNo ratings yet
- NT Radioactive PollutionDocument12 pagesNT Radioactive PollutionJunior Kathalan100% (2)
- Alpertb Rad 8 9Document30 pagesAlpertb Rad 8 9Dylan DanovNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Radiation (Physics)Document13 pagesBiological Effects of Radiation (Physics)Josiah Dave CalumpangNo ratings yet
- Radiation: For Other Uses, SeeDocument8 pagesRadiation: For Other Uses, SeeDivakaran_Kali_4527No ratings yet
- NuclearEnergyInEverydayLife BookletDocument16 pagesNuclearEnergyInEverydayLife BookletsmashakeniNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity: Alpha Decay: During Alpha Decay, The Nucleus of An Atom Emits An Alpha Particle, WhichDocument2 pagesRadioactivity: Alpha Decay: During Alpha Decay, The Nucleus of An Atom Emits An Alpha Particle, WhichEhtasham EhtashamNo ratings yet
- Be - 3Document43 pagesBe - 3rohit adhikaryNo ratings yet
- Atomic & Nuclear PhysicsDocument9 pagesAtomic & Nuclear PhysicsPyay Lin ThantNo ratings yet
- Bone LandmarkDocument3 pagesBone LandmarkDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Hiro 1Document6 pagesHiro 1Aron JaroNo ratings yet
- Biological Effects of Radiation & Safety ConsiderationDocument21 pagesBiological Effects of Radiation & Safety ConsiderationTareq AzizNo ratings yet
- Radiation Hazards VDocument39 pagesRadiation Hazards VSWATINo ratings yet
- Cancer CausesDocument36 pagesCancer Causessufian abdo jiloNo ratings yet
- Physics Edexcel Unit 3 - Radioactivity and AstronomyDocument44 pagesPhysics Edexcel Unit 3 - Radioactivity and Astronomyshivensolanki31No ratings yet
- Integrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiDocument49 pagesIntegrantes:: Laura María Baquero Cuéllar Joan Camilo Caicedo Daniela Delmar Vásquez Ingrid Jhoana Sánchez CharrupiFabricio Echeverri LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Ai CP 01Document6 pagesAi CP 01Random gmailNo ratings yet
- Ionizing Radiation: ReferenceDocument1 pageIonizing Radiation: ReferenceEmmanuelFrancoNo ratings yet
- Do You Think Electromagnetic Waves Are BeneficialDocument2 pagesDo You Think Electromagnetic Waves Are Beneficialdenverlian18No ratings yet
- Radiation in PlantsDocument1 pageRadiation in PlantsJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- SCEICNEDocument6 pagesSCEICNESaren, Emil G.No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJahleel TroupeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PollutionDocument21 pagesNuclear PollutionEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Radiation FundamentalsDocument46 pagesRadiation FundamentalsRichard mwanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cover Sheet: Department of Zoology Mid Term AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignment Cover Sheet: Department of Zoology Mid Term Assignmenthafsa yaqoobNo ratings yet
- Nuclear HazardsDocument4 pagesNuclear Hazardsbiprajitroy481No ratings yet
- 1.01 Background Fundamentals For Diagnostic RadiologyDocument4 pages1.01 Background Fundamentals For Diagnostic RadiologyJason MirasolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationDocument9 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Diagnostic Imaging and X-Ray FormationElah TapangNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet