Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6058 Vehicle Testing Lab
6058 Vehicle Testing Lab
Uploaded by
ashifsha930Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6058 Vehicle Testing Lab
6058 Vehicle Testing Lab
Uploaded by
ashifsha930Copyright:
Available Formats
AB MANUAL
SSM POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE, TIRUR
DEPARTMENT OF AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
LAB MANUAL
SUBJECT:
VEHICLE TESTING LAB
CODE: 6058
SEMESTER: 6 TH
REVISION: 2015
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
Vision, Mission, Objectives of the Institution
Vision:
To become an institution of international eminence in moulding Engineers capable of
addressing global challenges
Mission:
To serve the Business, Industry and Community by developing a new stream of Engineers
in whom technical competency and moral strength fused together
Mission objectives:
M-1: by imparting quality education, fostering team spirit and technology innovations
for environment friendly sustainable development.
M-2: by developing professional as well as entrepreneurial culture nurturing the ability
to adopt technological changes.
M-3: by engaging testing and consultancy for industry using state-of-the-art technology
tools.
Department Vision:
Be a centre of Excellence in Automobile field and produce quality Automobile
engineers with entrepreneurial traits and social values
Department Mission:
M1: To set up and maintain state of the art laboratories and workshops in line with
changes in technology and curriculum.
M2: To update faculty through in- house, industrial and external training.
M3: To develop continuous interaction with leading automobile industries and
Govt agencies to promote technological and entrepreneurial qualities.
M4: To enhance moral and ethical values through effective mentoring, close
parental interactions and trainings
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
Program Educational Objectives (PEO’s)
PEO1: Lead successful career in automobile industry exhibiting excellent technical and
managerial skill.
PEO2: Initiate and sustain challenges in setting up and managing own industrial units.
PEO3: Pursue higher education or continuously update professional skill and
knowledge
PEO4 : Exhibit high professional ethics, social and environmental values in all
interactions
Program Specific Outcomes
PSO 1: Apply acquired Knowledge and skill to maintain, diagnose and fix automobile
systems and units.
PSO 2: Develop and apply entrepreneurial skill to setup self- employment ventures .
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
EX NO: 1
DATE:
TWO WHEELER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
To study about dismantling and assembling of the two wheeler transmission
system.
Double end spanner, ring spanner, screw driver, hammer, combination
plier, torque wrench, circlip plier etc.
Description:
Automobile two wheeler transmission consists of primary clutch gear box and
final drive to the road wheels. Multi plate clutch is generally used in two wheelers and it
is located between the primary and transmission member. In this several friction plate and
steel plate connected to the primary driver. The outer clutch link in driven plate splined to
the transmission mounted over clutch hub. There are also some mechanisms for connect
the engine and transmission.
Gear box is used one piece clutch gear with 4, 5, 6 differential gears formed unit
and the gear tooth on this gear over lap from directly connected to the road wheels by
shafts. The gear box is sliding mesh or constant mesh. In sliding mesh transmission the
shaft force which moves the gear is controlled by shifter arm. The friction from clutch
plate is converted in to rotary motion; the shifter moves the sliding gear in to and out of
the arrangement. Gear box uses one piece clutch with four and six different gear from at
crust. This gears help to engage directly will the counter shaft gear. These gear boxes are
directly connected with chain to the road wheels.
PROCEDURE:
Dismantling:
1. First of all park the vehicle on a level ground.
2. Separate all connections into the engine and transmission.
3. Remove the function bolt of the assembly.
4. Remove the gear box from the assembly.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
5. Drain the oil from the gear box and assembly.
6. Remove the chain between the crank shaft and lay shaft.
7. Remove clutch assembly from lay shaft splines.
8. Remove all gears from main shaft with dog clutch.
9. Remove the lay shaft.
10. Check the gear ratio.
Checking, inspection and cleaning:
1. Clean all parts with kerosene and diesel.
2. Check all parts for wear and tear.
3. Replace or recondition all damaged parts.
4. Inspect gear teeth or wear and tear.
Reassembling:
1. Refit the lay shaft and main shaft with all gear in proper order.
2. Reconnect the clutch assembly on lay shaft.
3. Reconnect the chain between lay shaft and engine crank shaft.
4. After refitting all parts of gear box connect clutch and gear box to engine.
5. Fill the oil in the gear box.
Result:
Studied, dismantled, inspected and assembled the given two wheeler transmission
system.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Ex no: 2
Date:
Aim:
FRONT LIVE AXLE
Tools required:
To study about dismantling and assembling of the front live axle.
Screw driver, ball peen hammer, wheel spanner, ring spanner,
combination plier, reversible ratchet, hydraulic jack, torque wrench, sliding handle etc.
Description:
A front live axle are compared to the dead axle has the additional function of
transmitting the driving power taken from the transfer gear box to the front wheel.
Having power taken from a transfer gear box to the front wheels having a difficult
swelling mechanism. The live front axle assemblies have some difference compared to
the dead axle. The live axle has a universal joint or constant velocity joint at its both
ends. The one end is connected to the stub axle through a universal joint so that the stub
axle can turn in any steering direction. The bearing part or ball joint of universal joint are
covered with a rubber cover. The stub axle is also act as a propeller shaft. The ball
bearing in the both ends of the axle is lubricant by grease or oil of SAE90 the back plate
is connected to steering knuckle and through suspension system.
PROCEDURE:
Dismantling:
1. Park the vehicle on a level road or ground.
2. Jack up the vehicle and remove the brake fluid cable and hand brake cable
connection from the brake assembly.
3. Loosen the wheel nut and remove the wheel assembly.
4. Remove the axle nut from the stub axle.
5. Disconnect the connections of steering linkage by loosening the nuts and bolts also
by hammering it.
6. Disconnect the connection of steering knuckle from suspense on components
and also from stub axle.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
7. Remove back plate from steering
knuckle.
8. Remove the live axle with stub axle by removing the sun gear connection from
differential unit. The live axle removing by pulling outward.
9. Dismantle the line axle assembly universal joint bearing stub axle.
Checking, inspection and cleaning:
1. Clean all parts with kerosene and diesel.
2. Check all parts for wear and tear.
3. Replace or recondition all damaged parts.
Reassembling:
1. After proper working reassembling the live axle assembly.
2. Refit the live axle half shaft to sun gear of differential unit.
3. Refit the back plate to the steering knuckle.
4. Connect the stub axle to the corner plate.
5. Reconnect the suspension connection to steering knuckle and also stub axle
connection.
6. Reconnect the steering linkage connection to knuckle.
7. Refit the axle nuts to stub axle.
8. Reconnect the brake fluid cable and hand brake cable connection.
9. Remove hydraulic jack and from under the vehicle.
Result: Dismantled and assembled the constant velocity type live axle assembly.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Ex no: 3
Date:
BRAKE BLEEDING AND ADJUSTMENT
Aim
: To conduct brake bleeding and brake adjustment on the vehicle.
: Screw driver, spanner set, sliding hammer, brake fluid
Tools and apparatus required
etc.
Description:
The system requires bleeding of air when the brakes are inefficient or when air enters
into the brake system. In this time the brake pedal have a spongy effect when the
application of brake. The system must be free from air at all time. The trapped air on the
system is compressible and does not permit the pressure applied in the brake pedal to stop
the vehicle.
While brake bleeding, first bleed the longer wheel cylinder from the master
cylinder.
Brake bleeding procedure:
1. Clean all parts removed from master cylinder.
2. Remove the filter plug and fill the master cylinder with specified grade brake
fluid, its lower end of the filter neck.
3. Clean all bleeding connections of all 4-wheel cylinders.
4. Attach bleeder hose and fixture to the larger brake line wheel cylinder screw and
place end of screw the tube in a glass jar and submerge the tube with brake fluid.
5. Open the bleeds value one half to 3 quarter to a turn.
6. Departure the fork pedal allowing it to taken every pumping action. Then force
the fluid through the drain and out of the bleeder hose which carries with it away
air in the system. When bubbles connect appears at it end or the bleeds hose close
the bleed valve and remove the hose.
7. After completing the bleeding operation at wheel cylinder still the master
cylinder reservoir and replace the filter cage plug do not use the require fluid
which hose been replaced from line.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Brake adjustment:
1. Jack the wheel in a clear floor.
2. With a torque wrench loosen the lock nut for the forward brake shoe and hold it.
3. With another torque wrench the eccentric to front of the vehicle until the brake
shoe strikes the drum.
4. While turning the wheel with one hand loose eccentric until the wheel turn fully.
5. Hold the eccentric in position and taken the lock nut.
6. The operation of reverse shoe but only turn the eccentric towards the back of the
vehicle.
Res7u.lt:Do this procedure on all 4 wheels and check the fluid in the master cylinder.
Conducted the brake bleeding and adjustment.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
CYCLE: 2
EX NO: 4
DATE:
TORSION BAR
AIM:
Tools required:
Dismantle and assemble the torsion bar assembly, study and inspected the parts.
Double end spanner, torque wrench, wheel spanner, hammer, screw
driver.
Description:
Torsion bar is a simply rod acting in torsion pad taking shear only the most
amount of energy stored per unit weight of material is nearly the same as of a coil spring.
Torsion bar is often used with the independent suspension
The bar is fixed at one end of the frame while the other end is fixed to the end of
the wheel arm and supported in the bearing. The other end of the wheel arm is connected
to the wheel hub. When the wheel strikes a bump its starts to vibrate up and down, thus
exerting torque on the torsion bar which acts as a spring. Torsion bar spring is lighter as
compared to leaf spring and also it occupies less space.
PROCEDURE:
a) Dismantling:
1. Park the vehicle on a level ground.
2. Unscrew the wheel mounted nut in the wheel by wheel spanner.
3. Jack up the vehicle using hydraulic jack.
4. Release the front tire assembly.
5. Remove the wheel hub assembly and by loosening the wheel nut.
6. Remove the brake drum.
7. Disconnect the brake line from master cylinder at the fitting on the brake
shoe, from back plate by removing the retracting spring and other plate.
8. Remove the tie rod.
9. Remove the shock absorber.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
10. Remove the wheel hub spindle from upper and lower wishbone by
spanner.
11. Then unscrew the wheel arm by loosening the bolt from the torsion bar
one end.
12. Disconnect the torsion bar at the other end from the chassis cross member.
13. Place the torsion bar on the work bench.
b) Inspection and cleaning.
1. Check the torsion bar at both end for wear and tear.
2. Check the torsion bar for bending or cracking at any point.
3. Any crack is identified then replace the torsion bar.
4. Then clean the torsion bar at both ends.
C) Assembling.
1. Connect the torsion bar one end of chassis cross member.
2. Reconnect the wheel spindle arm at the upper wishbone and lower wishbone,
and then connect the shock absorber.
3. Then connect the wheel arm to the torsion bar end.
4. Reconnect the tie rod.
5. Then adjust camber, castor and toe in or toe out.
6. Reconnect the brake drum, brake shoe to the brake plate.
7. Reconnect the brake line.
8. Refit all wheel assembly.
9. Refit the tire assembly.
10. Replace the hydraulic jack.
11. Tighten the wheel mounted screw by using the torsion wrench at the
RESULT
Manufacture specification.
: dismantled and assembled the torsion bar assembly and identified the parts.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Ex no: 5
Date:
VACCUM SERVO BRAKE
Aim:
Tools required:
To dismantle and assemble the vaccum servo brakes.
Screw driver, hammer, nose plier, plier, vice grip.
Description:
When a vaccum obtained from the manifold of the engine (petrol) or a separately
driven exhaust used to assist the braking effort this system is called vaccum servo brake.
It consists of vaccum reservoir connected through a non return valve to the inlet manifold
of the engine two connections from the vaccum reservoir. One on each side of the piston
of the servo cylinder is provided. one left side the connection is through the control unit
where as right side is connected directly the piston at the servo cylinder or the brake
linkage .The control unit connect of a piston to which two valves are attached. The lower
valve controls the connection between the reservoir and left side of the servo cylinder
piston. The upper valve controls the connection between the atmospheric and the left side
of the servo cylinder piston. The other side of the piston of the control unit is actuated by
the pedal effort through a master cylinder.
Procedure:
Dismantling:
1. Park the vehicle on a level ground.
2. Disconnect the servo pushrod to the brake pedal.
3. Vaccum nose is connected to the servo unit and then disconnected by slacking the
nose dip.
4. Disconnect the servo unit from the master cylinder.
5. Servo unit is linked to the brake pedal and then disconnected if U-bolt the servo
bolt from if mounting bracket.
6. U-bolt the servo unit from it bracket on the back head and withdraw.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
7. Place the servo unit at the work bench.
8. Remove the housing by plier.
9. Remove the diaphragm or piston and springs.
Checking and inspection:
1. There is a gasket between the servo and the bulk head check whether it is worn.
2. Inspect the condition of vaccum hose; make sure that hose clip is tight.
3. There is a seat between servo and master cylinder check its condition.
4. Clean the parts of servo unit.
Assembling:
1. Reconnect the piston and other related parts and placed in the housing with tight
position.
2. Re bolts or connects the servo unit to the bracket on the bulk head with gasket.
3. Reconnect the servo unit to the master cylinder.
4. Reconnect the vaccum hose pipe to the servo unit by the correct spanner and plier.
5. Connect the servo pushrod to the brake pedal.
6. Bleed the system after re-assembling is completed.
Result: Dismantled and assembled the vehicle servo unit.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Ex no: 6
Date:
DEAD AXLE
Aim:
Dismantle the dead axle of the Maruthi 800, inspect and then assemble it.
Tools required:
Hydraulic jack, hammer, screw driver, torque wrench, wheel spanner,
and open end spanner.
Description:
Purpose of an axle shaft is to transfer driving torque from the differential assembly
to the vehicles driving wheel. A dead axle does not drive a vehicle. It supports the vehicle
load and provides a mounting place for wheels. The rear axle of a front wheel drive
vehicle is a dead axle as are the axle used on trailer. They are also shown as the stationary
axles horses down vehicle has a dead axle. They only support the rear weight of the
vehicle. They are generally used for chain drive. In case of front wheel drive car, the rear
axle is the dead axle which remains stationary with the wheels only rotating on them.
Procedure:
a) Dismantling:
1. Park the vehicle on a level ground.
2. Disconnect the –ve terminal connection of the battery.
3. Loosen the wheel nut of both rear wheels.
4. Jack up the vehicle.
5. Remove the both wheels.
6. Loosen the brake drum nut and remove the brake drum.
7. Remove the brake shoe and also hand brake connection.
8. Remove brake fluid connection and then remove the wheel cylinder.
9. Remove the nut and bolt of back plate and then remove shock absorber.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
10. Remove the u-bolt and disconnect the u-bolt steering plate and the leaf
spring shackles nut and bolts.
11. Adopt the same procedure of the other side rear.
12. Then taken out the dead axle in to the work bench.
b) Inspection :
Check for bending and wear of the dead axle. Identify or check any cracks in the dead
axle. Then clean the related parts of the dead axle.
c) Re-assembling:
1. Place the dead axle in the correct position and tighten the u- bolt with u-
plate seating bolt using the help of correct spanner.
2. Refit the leaf spring.
3. Refit the shock absorber.
4. Re-connect the back plate by tightening the mounting bolt with the help of
spanner.
5. Re-connect the wheel cylinder, brake shoe, brake drum assembly and re-
connect the brake fluid lining.
6. Tighten the brake drum nut by the help of spanner.
7. Connect the both wheels.
8. Jack down the vehicle.
9. Tighten the wheel nut of both rear wheel by the torque wrench with the
manufacture specification.
10. Re- connects the –ve terminal connection of the battery.
11. Refit the brake connection and bleed the brake system for the removal of
Result:
air particle.
To studied, dismantled and assembled the dead axle.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
EX NO: 7
DATE:
AIM: WHEEL BALANCING
TOOLS REQUIRED
To study about the wheel balancer and balance the given wheel.
MATERIALS REQUIRED:
: Weight remover, measuring scale
Wheel balancing machine, weight, and tyre
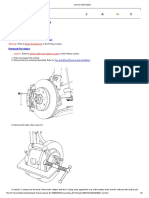
DESCRIPTION:
The system consists of main cabin, rotor assembly, electronic unit, display panel,
power panel, wheel guide standard accessories and optional accessories.
1. Main cabinet:
Main cabinet in the housing for the electronic unit, rotor, motor, display panel,
and power panel.
2. Rotor :
The rotor assembly consists of the driven pulley mounted on the shaft located in
the bearing housing mid centering device and the RPM enroller.
3. Display panel:
The unbalance values are shown on the displays panel for both inner and outer
planes using ½ seven segment LED displays the unbalance position is indicated
by rows of LED‟s. This is a soft touch key pad and following are the functions of
various key.
1) : To set dimensions and to select the function to save position
during calibration.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
2) : To increase the parameters during set dimension or to select functions.
3) : To decrease the parameters during set dimension or to select ALU
function.
4) : To stop the motor when balancing remains progress or to exit from
most of the programs.
5) : pressing the key twice within a second will start the balancing
operation.
6) : To enter the features option and special programs mode(split
weigh and optimization).
7) : To enter in to the selected feature.
8) : To toggle the units between inch and mm during the setting of
wheel dimensions. To toggle the units of unbalance between inch and ounces
during balancing.
9) : To toggle the parameters between normal and fine mode of
unbalanced display.
10) : To toggle between dynamic and static mode of balancing. To
toggle between mv and grams in raw calibration(for service personal only)
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
4. Power panel: the power panel is located at the side of main cabinet. Main power
and MCB switch are provided in the power panel.
5. Wheel guard: the wheel guard is made of high impact plastic which prevents
flying out of the weight add on the wheel rim or stone / for high particles sticking
to the tyre in any direction except towards the floor. A safety interlock switch is
provided to ensure that the wheel guard is closed during spinning of wheel. If the
wheel guard is not closed during spinning an error „EVU 1‟ will be displayed. By
closing the guard the error code will disappear and the wheel starts spinning this
feature is to ensure the safety to the operator.
Dynamic balancing (two plane balancing)
This refers to the balancing carried out on the inner and outer part of the wheel. In
this type the unbalanced readings measured by the system on both planes will be
displayed. Dynamic balancing can be carried out on both normal rims as well as alloy
rims.
Operation:
1. : Only permit qualified person to operate, maintain or repair the
balancer.
2. : Do not lift the wheel guard until the wheel is completely stop.
3. : Always ensure that the wheel are mounted properly and must be
tightened firmly before spinning the wheel.
4. : Pay attention while lifting heavy wheels. Heavy loads should not be
lifted without assistance.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
5. : Always keep the applicable accident prevention regulations.
6. : Never over load the wheel balancer.
7. : Do not hammer or hot any parts of the equipment with weight plier
tools etc.
8. : Avoid dropping of wheels heavily on the shaft while mounting
and removing which may affect the accuracy of the equipment.
9. : Do not apply brake when the motor is running.
PROCEDURE:
Preparation of wheel for balancing:
1. Check for the right size tire is mounted on the wheel.
2. Check for proper air pressure of the tire is required inflation. The tire to the
recommended pressure.
3. Remove if any foreign materials are present in the tire threads.
4. Clean the rim and tires free from the excessive dirt and stones. The central bore
and face of the rim must be thoroughly cleaned to ensure proper fitment with the
wheel mounting accessories.
5. Dismount all the existing wheel balancing weights from the rim.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Dynamic balancing sequence:
Switch on the equipment the power indicator led in the display panel will glow.
The system will perform initial checks. The software version no will be displayed for two
seconds and then the default valves of distance, width and diameter(inches) will be
displayed.
Rim dimension
Press key one the distance display will starts blinking rim distance
measured. In WB-DL-60 revolution, enter the rim distance by following any one of the
methods given below.
1. Move the distance measuring rod outwards till it touches the inner rim. Keeps the
distance measuring rods in the same position at least 3 seconds. The rim distance
will be updated on the display followed by the beep sound.
2. Move the distance measuring rod outwards till it touches the inner rim and press -
key. The rim distance will be updated.
3. Use the keys to set the rim distance value.
Rim diameter measurement:
Now press the key. The diameter display will starts blinking measure the
diameter of the rim and set the valve using keys. After setting the diameter press
key and the normal led will starts blinking.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
Rim selection
When the normal led blink, and then use keys to select the appropriate rim
type and then press key to conform the type.
Wheel balancing
1. Check and ensure that the distance measuring rod is in home position. Close
the wheel guard. Start balancing, run by pressing the key twice
within a second(double click) or by lowering the wheel guard if the auto run
mode is enable in PRG-9.
2. Now the wheel starts spinning for few seconds when the measurement is
completed the equipment will generate continues beep sound.
3. Press the brake lever until the rotation of the wheel stops. The inner and outer
unbalanced weights will be displayed.
0
4. The unbalance position will be indicated by the rows of LED‟s. The LED will
not glow if the unbalance is zero. Rotate the wheel manually to make green
LED of inner plane to blink. To retain the wheel positions apply brake by
using the brake lever. Now add indicated weights on the inner rim at 120
clock position by clipping the weight on the rim and hammering it by using
weight plier. Repeat the above steps for outer plane also.
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
5. Spin the wheel again to check whether the wheel is now balanced.
6. Normally wheels are balanced. However the wheel is unbalance is more it
may require more than one balancing run. The wheel is balance in both the
studied about the wheel balancing and balancing the given wheel.
planes; the equipment indicates it by flashing the “ok” display.
Result:
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
8. Wheel seating
9. Pressure rang
10. Power panel
11. Main power cable
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
REVISION-2015 VEHICLE TESTING LAB - 6058
SSM Polytechnic College, Tirur Department of Automobile
You might also like
- P Series ServiceDocument465 pagesP Series ServicehueyceNo ratings yet
- 0B5 7-Speed Dual ClutchDocument24 pages0B5 7-Speed Dual ClutchKeldo Gliana93% (94)
- Chevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltFrom EverandChevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- wx150 Shem Set - cgg0228400Document149 pageswx150 Shem Set - cgg0228400Николай НекрасовNo ratings yet
- Four-Stroke Engine Top-End Inspection: Study UnitDocument68 pagesFour-Stroke Engine Top-End Inspection: Study UnitnareshNo ratings yet
- 16 Engine Internals Design ReportDocument26 pages16 Engine Internals Design Reportapi-305897190No ratings yet
- Vibration DiagnosticsDocument54 pagesVibration Diagnosticsahadryk80% (5)
- U18PCAU6L1 Two Three Wheeler - LabDocument28 pagesU18PCAU6L1 Two Three Wheeler - LabKarishma GulatiNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab ManualDocument59 pagesAcs Lab ManualAanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- AU200 Maintenance ManualDocument138 pagesAU200 Maintenance ManualramiroNo ratings yet
- On Sonalika Engine AssemblyDocument19 pagesOn Sonalika Engine AssemblyAmanda Matthews67% (6)
- Pathcross 800CCDocument198 pagesPathcross 800CCgeomak2000No ratings yet
- Infiniti LPFP v1 EditDocument15 pagesInfiniti LPFP v1 EditChe MilsonNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument110 pagesManual706Saurabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Study Fabn of Clutch Final ReadyDocument109 pagesStudy Fabn of Clutch Final ReadySuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document4 pagesExperiment 10garysingh187westNo ratings yet
- A180 Service ManualDocument213 pagesA180 Service ManualramiroNo ratings yet
- 60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding RevisedDocument60 pages60 Automotive Engine Disassembling and Rebuilding Reviseddmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Peugeot 404 Owners Workshop Manual 1960-1975Document136 pagesPeugeot 404 Owners Workshop Manual 1960-1975Jonathan Bernabé González Medina100% (1)
- 1.automobile Lab ManualDocument44 pages1.automobile Lab Manualharshita gupta100% (1)
- Lesson - Rebuilding EngineDocument88 pagesLesson - Rebuilding Engineace ebradoNo ratings yet
- WheelDocument13 pagesWheelNarayanaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Scheme and Credits Credits Semester-VIIIDocument2 pagesAutomobile Engineering Scheme and Credits Credits Semester-VIIIVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Manual Transmission 18001-2 (1) - TaggedDocument93 pagesManual Transmission 18001-2 (1) - TaggedNatty NuggetNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument38 pagesLab ManualTollywood MastiNo ratings yet
- 5 Drive Unit: Service ManualDocument16 pages5 Drive Unit: Service ManualMiguel MartínezNo ratings yet
- Ice Lab 3Document7 pagesIce Lab 3aakh.med.aaliii69No ratings yet
- Four-Stroke Engine Top-End Inspection: Study UnitDocument68 pagesFour-Stroke Engine Top-End Inspection: Study UnitBochica Baganique100% (1)
- Manual General Taller Motos Keeway 50cc (Idioma Ingles)Document64 pagesManual General Taller Motos Keeway 50cc (Idioma Ingles)CordobessaNo ratings yet
- 19 Suspension Components Design ReportDocument39 pages19 Suspension Components Design Reportapi-305897190No ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Lab Manual For B E Mechanical by D S DabhadeDocument44 pagesAutomobile Engineering Lab Manual For B E Mechanical by D S DabhadeСергей ДороховNo ratings yet
- Millat Tractors Limited Final ReportDocument15 pagesMillat Tractors Limited Final ReportSaad SultanNo ratings yet
- Operating ManualDocument34 pagesOperating ManualLauraNo ratings yet
- Clutch ManualDocument16 pagesClutch ManualCO BDNo ratings yet
- Volvo Penta 3.0 GS, 4.3 GL-GS-Gi, 5.0 GL-Gi, 5.7 GS-GSi, 7.4 Gi-GSi, 8.2 GSi Sez.8-9Document35 pagesVolvo Penta 3.0 GS, 4.3 GL-GS-Gi, 5.0 GL-Gi, 5.7 GS-GSi, 7.4 Gi-GSi, 8.2 GSi Sez.8-9Luciano LiuzziNo ratings yet
- Allignment PSHDocument9 pagesAllignment PSHAfiq MuhdNo ratings yet
- Scoop Cat R1600G 2Document7 pagesScoop Cat R1600G 2Ruben Sifuentes Ç̸͜͡r̴͟ú͢͞z̴No ratings yet
- Automobile Lab ManualDocument35 pagesAutomobile Lab ManualKeshav AsopaNo ratings yet
- Steering PartsDocument9 pagesSteering PartsPankaj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Engine Repair WorkDocument8 pagesEngine Repair WorkScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Transfer Case 233 Chevrolet S10Document8 pagesTransfer Case 233 Chevrolet S10Maxi SardiNo ratings yet
- Clutch Inplant Training ReportDocument31 pagesClutch Inplant Training ReportMrityunjay Pathak100% (1)
- Ael I ManualDocument29 pagesAel I ManualNivedita kNo ratings yet
- DEC068-06 Tailift FBT15-18 Service ManualDocument314 pagesDEC068-06 Tailift FBT15-18 Service Manualrodrigo aguilarNo ratings yet
- SERVICE MANUAL 180S SpanishDocument342 pagesSERVICE MANUAL 180S SpanishScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Intership ReportDocument27 pagesIntership ReportwabdushukurNo ratings yet
- Enclave 2014 3.6L PDFDocument269 pagesEnclave 2014 3.6L PDFRulo Bolaños Plascencia100% (1)
- Lab Report 4Document6 pagesLab Report 4MALIK MUHAMMAD HAMZA FAROOQ MALIK MUHAMMAD FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Drive Axle FrontDocument23 pagesDrive Axle Frontcarloslopez85No ratings yet
- AEN Micro ProjectDocument11 pagesAEN Micro Projectvedantbakal043No ratings yet
- 6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualDocument21 pages6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualSayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument21 pagesIndustrial Training ReportSanniChChureNo ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Model Answer Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document27 pages2019 Summer Model Answer Paper (Msbte Study Resources)siddharthasawaikarNo ratings yet
- JK State Road Transport Corporation REPORTDocument17 pagesJK State Road Transport Corporation REPORTshah naumanNo ratings yet
- Lres 730Document31 pagesLres 730Inquiry XEEPLNo ratings yet
- Automobile LabDocument52 pagesAutomobile LabAboud MNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report: Field Exposure Regional Workshop Kathgodam, Nainital (Uttarakhand Transport Corporation)Document31 pagesIndustrial Training Report: Field Exposure Regional Workshop Kathgodam, Nainital (Uttarakhand Transport Corporation)Rajat VermaNo ratings yet
- DIY - Replacing Timing BeltsDocument3 pagesDIY - Replacing Timing Beltstron68bizz100% (2)
- Department of Automobile Engineering: Lab ManualDocument15 pagesDepartment of Automobile Engineering: Lab ManualAbhishek LalkiyaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - PPT On Sonalika Engine AssemblyDocument19 pagesDokumen - Tips - PPT On Sonalika Engine AssemblyPardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument17 pagesInternship ReportkannanNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Lab Manual For B E Mechanical by D S DabhadeDocument44 pagesAutomobile Engineering Lab Manual For B E Mechanical by D S DabhadeAman SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Front Brake Disc Replacement PDFDocument3 pagesFront Brake Disc Replacement PDFY. VásquezNo ratings yet
- Hybrid SeminarDocument29 pagesHybrid Seminarashifsha930No ratings yet
- Diagnostics of Transmission and Drive Line Components.Document33 pagesDiagnostics of Transmission and Drive Line Components.ashifsha930No ratings yet
- 5058 Automobile Servicing Lab IiDocument53 pages5058 Automobile Servicing Lab Iiashifsha930No ratings yet
- Vds Assignment 2Document1 pageVds Assignment 2ashifsha930No ratings yet
- White Brown Minimalist Certificate of Participation Portrait - 20231020 - 085843 - 0000Document1 pageWhite Brown Minimalist Certificate of Participation Portrait - 20231020 - 085843 - 0000ashifsha930No ratings yet
- Seminar RDocument5 pagesSeminar Rashifsha930No ratings yet
- 2&3 NewDocument20 pages2&3 Newashifsha930No ratings yet
- Gear PumpDocument12 pagesGear PumpLoru GomezNo ratings yet
- Snapper GP 21507BE Partes PDFDocument46 pagesSnapper GP 21507BE Partes PDFJavi AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- Polaris ATV Repair ManualDocument24 pagesPolaris ATV Repair ManualPool Supply SalesNo ratings yet
- Liebherr LTM 1090-4.1 Mobile Crane - 90t - InformationDocument18 pagesLiebherr LTM 1090-4.1 Mobile Crane - 90t - InformationCallumWoodward100% (2)
- Sundyne Prospekt Int Geared PDFDocument16 pagesSundyne Prospekt Int Geared PDFrohituchaniNo ratings yet
- Coronas MeritorDocument166 pagesCoronas MeritorPancho CamposNo ratings yet
- Technical Catalogue H Iec STD en Rev0 2021Document268 pagesTechnical Catalogue H Iec STD en Rev0 2021Petre IonNo ratings yet
- Spur Gear Design Some New Perspectives DDocument12 pagesSpur Gear Design Some New Perspectives DUsama GulzarNo ratings yet
- Super Seal List April-2015Document17 pagesSuper Seal List April-2015Amit Chopra AmitNo ratings yet
- 0598a17 - GBRDocument65 pages0598a17 - GBRtim kaminskyNo ratings yet
- Elems 10Document101 pagesElems 10Reynald de VeraNo ratings yet
- 473 EngineDocument119 pages473 EngineJosue SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Manual de Parte Bulldozer d8t Volumne 3Document28 pagesManual de Parte Bulldozer d8t Volumne 3henotharenasNo ratings yet
- Instruction ManualDocument52 pagesInstruction ManualEka RoksNo ratings yet
- Repair Manual - Rotary Head MotorDocument11 pagesRepair Manual - Rotary Head MotorgajendraNo ratings yet
- Verlinde EUROSTYLE GB PDFDocument8 pagesVerlinde EUROSTYLE GB PDFcandra trisilawatiNo ratings yet
- Epson Spare Parts Stock Availability Week 43Document229 pagesEpson Spare Parts Stock Availability Week 43Ion Ionut100% (1)
- BMU NEW 17sDocument60 pagesBMU NEW 17sdikdikNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalog 475 TotalDocument60 pagesParts Catalog 475 TotalIndian Empire50% (2)
- Motoredutor SIEMENS - Simogear Getriebe 2030 Op Instr 0523 en-USDocument258 pagesMotoredutor SIEMENS - Simogear Getriebe 2030 Op Instr 0523 en-USFilipe RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Trobological Audit On GearsDocument11 pagesTrobological Audit On Gearssandeep1reddy-10No ratings yet
- W4a33 ManualDocument155 pagesW4a33 ManualFranklyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- 89H303 Touareg - 4xmotionDocument62 pages89H303 Touareg - 4xmotioneduardorojas00750% (2)
- TSB SC 082aDocument18 pagesTSB SC 082apacosworldNo ratings yet
- Segway (2 Wheel Balancing Vehicle) : Project Report: in Partial Fulfilment For The Award of TheDocument31 pagesSegway (2 Wheel Balancing Vehicle) : Project Report: in Partial Fulfilment For The Award of ThemadhurNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Mathematical Modeling of Mechanical SystemsDocument93 pagesLecture 5-Mathematical Modeling of Mechanical SystemsNoor Ahmed100% (2)
- Manual de Partes Toro 0010 InstructionsDocument4 pagesManual de Partes Toro 0010 Instructionscacoman93No ratings yet