Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bar Graph - Chart That Plots Numerical Data
Bar Graph - Chart That Plots Numerical Data
Uploaded by
nikki bel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pages.
...
....
...
Original Title
...
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document.
...
....
...
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesBar Graph - Chart That Plots Numerical Data
Bar Graph - Chart That Plots Numerical Data
Uploaded by
nikki bel.
...
....
...
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
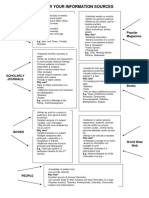
Primary sources – sources that are written by - Indexes
someone who’s present at the event - Almanac
- A first hand or contemporary account of - Directories
an event or topic - Abstracts
- Does not been subjected to evaluation - Indices
or assessment - Databases
Examples are: - History
- Diaries
- Poems Characteristics of good information
- Interviews 1. Accuracy – info must be reliable, useful,
- Letters free from errors, and high quality
- Autobiography 2. Completeness – info must provide all
- Court hearing the needed details. It should be able to
- SONA answers the W and how questions
- An article about the Philippine economy 3. Timeliness – info should be up to date,
- Ancient oil lamps recent or new
- Speeches 4. Consistency – info must be consistent
- Video recordings for it to be considered accurate and
- Government records useful
- Communication 5. Relevance – info should suit the
- News papers and magazines that demand, needs and interest of the
portray info for eye witnesses readers
6. Uniqueness – info must be distinct,
Secondary Sources – sources that are written by clear and definite
someone who’s not present at the event
- Anything that describes interprets, Textual Aids
evaluate, and analyze the info from Educational tools that SIMPLIFY comprehension
primary sources of texts that use graphical outlines or images to
Examples are: give general idea or a topic.
- Book review
- Movie review Bar Graph – chart that plots numerical data
- Commentary using bar or columns
- Critiques Pictograph – present data using images
- An article critiquing a painting Cause and Effect Diagram – emphasizes the
connection between the different concepts and
Tertiary Sources – collection of primary and is sometimes called as a beneficial organizers
secondary sources since it can be applied to all subject areas
- Index, summary, compilation - Known as the ISHIKAWA DIAGRAM
Examples are: - This were introduce by Kaoru Ishikawa
- Bibliography in 1968
- Dictionary - Used to diagnosis of product
- Encyclopedia malfunctions
- Almanac Flow Diagram / Chart – a sequence chart that
- Glossary shows series of events in order
Venn Diagram – used to identify , classify,
categorize similarities and differences of two or
more subjects
- Most common used textual aids
Graphic Organizer / Concept Map – graphic
organizers are visual displays that have key
content info.
- Provide learners with structure for
abstract concepts
Linear Text – a traditional type of text that is
read from beginning to end
- Educational texts
- Short Stories
- Novels
- Letters
Non-Linear Text – is not required to be read
from beginning to end since it is non sequential
Transcoding Linear to Non-linear
1. Read the text and get the main idea
2. Extract necessary info
3. Used keywords and phrases only
4. Classify info into categories
5. Used correct non-linear text to present
the info
Characters – a person that portrays a specific
role
- Protagonist and antagonist
Plot – arrangements or sequence of events
1. Exposition – introduces the story’s
setting, mood, characters, and time
2. Conflict -
You might also like
- 2 Present Simple Lesson PlanDocument3 pages2 Present Simple Lesson Planapi-279690289100% (1)
- Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesExcerpt PDFJatin PathakNo ratings yet
- Ethnography ResearchDocument29 pagesEthnography ResearchSam Mak100% (1)
- Gathering InfoDocument5 pagesGathering InfoAldrich Jayden FloresNo ratings yet
- R226151BDocument6 pagesR226151Bsixo sihlanguNo ratings yet
- English 10-Quarter 1Document4 pagesEnglish 10-Quarter 1Prestela Leona DeatrasNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing ReviewerDocument5 pagesReading and Writing ReviewerDion Alexander VillagarciaNo ratings yet
- Erlinda L. GarciaDocument43 pagesErlinda L. Garciaerlinda garciaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document9 pagesModule 1Cash AmpangNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument5 pagesEapp ReviewerAnne BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - Educational MediaDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy - Educational MediaitsjullianeyoNo ratings yet
- Know Your Information Sources: Newspapers Popular MagazinesDocument1 pageKnow Your Information Sources: Newspapers Popular MagazinesKNo ratings yet
- Info Lit ReviewDocument31 pagesInfo Lit ReviewCharmander LynNo ratings yet
- Eapp Q2 RebyuwerDocument5 pagesEapp Q2 RebyuwerBea ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument14 pagesEapp ReviewerHeaven Krysthel Bless R. SacsacNo ratings yet
- Enfocad RebyuwerDocument7 pagesEnfocad RebyuwerSheila Ann Mae GabayNo ratings yet
- Digital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Female Protagonist Name: Emily Del Rosario Content Area: English and Language Arts Grade Level: 11Document3 pagesDigital Unit Plan Template Unit Title: Female Protagonist Name: Emily Del Rosario Content Area: English and Language Arts Grade Level: 11api-361470814No ratings yet
- English7 q2 l3 Information SourcesDocument20 pagesEnglish7 q2 l3 Information SourcesShana Audrey GaboNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument5 pagesEnglish ReviewerAlthea Loisse ArturoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Information SourcesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - Information SourcesJake Angelo Trinidad100% (2)
- Research Project ReviewerDocument3 pagesResearch Project ReviewervaleriepamaxNo ratings yet
- W14 - Library ResearchDocument14 pagesW14 - Library Research2023477148No ratings yet
- EAPP Q2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesEAPP Q2 Reviewerjulialynsantos008No ratings yet
- ARTICLESDocument3 pagesARTICLESNNMNo ratings yet
- Intertextuality and Hypertext: 3 Things in Preparing A Book ReviewDocument6 pagesIntertextuality and Hypertext: 3 Things in Preparing A Book ReviewChristine Mae MadriaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument21 pagesEnglishRaica Hazel GuioguioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in EappDocument5 pagesReviewer in EappJenny ChinNo ratings yet
- PR 1Document3 pagesPR 1Arvín BuendíaNo ratings yet
- English Reviewers: Expository WritingDocument13 pagesEnglish Reviewers: Expository WritingJOHAYNIENo ratings yet
- Research Lecture 5Document31 pagesResearch Lecture 5Shosha BangtanNo ratings yet
- MIL - L11 - Text Information Media PDFDocument5 pagesMIL - L11 - Text Information Media PDFclainNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SourcesDocument12 pagesTypes of Information SourcesReynald Legarda Jr.No ratings yet
- Topic - Media and Information SourcesDocument6 pagesTopic - Media and Information SourcesrgnnbkdNo ratings yet
- ENG02 Draft (Reading)Document16 pagesENG02 Draft (Reading)Hannah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- CNF 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerDocument4 pagesCNF 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerCourtney BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Literature Review, Citations and References: SurveyingDocument48 pagesLiterature Review, Citations and References: SurveyingIfa AsratNo ratings yet
- Creative Nonfiction Reading and Writing Creative Nonfiction: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesCreative Nonfiction Reading and Writing Creative Nonfiction: ObjectivesNathaniel RectoNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument4 pagesENGLISHALLISONNo ratings yet
- EAPPDocument6 pagesEAPPRussel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesLiterature ReviewhannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HistoryDocument18 pagesChapter 2 HistoryKim HyunaNo ratings yet
- Information Literacy Types of Information 1. ScholarlyDocument7 pagesInformation Literacy Types of Information 1. Scholarlyback upNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER TWO - Lecture 6 &7Document43 pagesCHAPTER TWO - Lecture 6 &7Evans DrumkNo ratings yet
- Critical Approaches To LiteratureDocument4 pagesCritical Approaches To LiteratureZia Ricci DiazNo ratings yet
- Information Literacy SkillsDocument131 pagesInformation Literacy Skillssemuty92No ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument14 pagesReading and WritingAquisha Dawn EvalinNo ratings yet
- FPL ReviewerDocument6 pagesFPL Reviewerjerian uyNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step in ResearchDocument9 pagesA Step by Step in ResearchissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Media and Information LiteracyDocument9 pages1st Quarter Media and Information LiteracyitsjullianeyoNo ratings yet
- EAAP ReviewerDocument6 pagesEAAP ReviewerAtasha FilipinaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Scholarly Journal?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Scholarly Journal?Aaron BowenNo ratings yet
- 2 Sent Dec. 16 English 10 SHJ Sources of Info.Document8 pages2 Sent Dec. 16 English 10 SHJ Sources of Info.echevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Mil-Handout 5Document10 pagesMil-Handout 5cedrik mahilumNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in English 6 DAY 3 and DAY 4Document3 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in English 6 DAY 3 and DAY 4BENJ AMIN100% (1)
- English Q1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Q1 Reviewercarlosjhon.No ratings yet
- Writing of Research ReportDocument23 pagesWriting of Research ReportSonu KulhariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 ResearchDocument7 pagesLecture 1 ResearchCharles Wesley YapNo ratings yet
- Literature Review - Notes PDFDocument4 pagesLiterature Review - Notes PDFbhakti salunkeNo ratings yet
- E7 Q2 M3 (A) - Source InformationDocument29 pagesE7 Q2 M3 (A) - Source InformationVictoria Angela CastroNo ratings yet
- English Full ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Full ReviewerCarlieseNo ratings yet
- Las1 - Eng 7Document6 pagesLas1 - Eng 7Marjun CasasNo ratings yet
- Advantage Study Skllls: Assignment planning (Study Aid 6)From EverandAdvantage Study Skllls: Assignment planning (Study Aid 6)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Abraham Malherbe, Ancient Epistolary TheoristsDocument98 pagesAbraham Malherbe, Ancient Epistolary Theoristsrobert guimaraesNo ratings yet
- VSS Granthaparichayapariyojana. MAY23Document7 pagesVSS Granthaparichayapariyojana. MAY23Veda Prakash JoshiNo ratings yet
- NURSERY WLP Week4 PDFDocument19 pagesNURSERY WLP Week4 PDFAbdulmateenAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Ips M in 290Document36 pagesIps M in 290ali1860No ratings yet
- Aramaic Peshitta PDFDocument773 pagesAramaic Peshitta PDFVictor Hugo100% (1)
- Sure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Document316 pagesSure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Arthanari Vaidyanathan100% (1)
- Korean Language Text PracticeDocument1,012 pagesKorean Language Text PracticeCiobanu PaulNo ratings yet
- 810-1910-00 - D TM1 Firmware Command Set CustomerDocument46 pages810-1910-00 - D TM1 Firmware Command Set CustomerLuis SánchezNo ratings yet
- Going To-Future - English GrammarDocument2 pagesGoing To-Future - English GrammarRicardo Patricio Salazar JijónNo ratings yet
- Tieng Anh 5 Unit 11 ReviewDocument19 pagesTieng Anh 5 Unit 11 Review20140513- Hoàng Thị Giang - TH Bích Sơn Việt YênNo ratings yet
- PR-9F Procedure For Verification of Pi TapeDocument3 pagesPR-9F Procedure For Verification of Pi TaperaghbirNo ratings yet
- CLASS 9th CBSE COMPUTER TEST - ASSIGNMENTDocument2 pagesCLASS 9th CBSE COMPUTER TEST - ASSIGNMENTAnonymous zrAfrkPOJ7No ratings yet
- Demo Capsule Book JEENEET PhysicsDocument27 pagesDemo Capsule Book JEENEET Physicsiitvishal004No ratings yet
- Super Simple Songs One Lyrics and Actions: 1. Knock Knock Hello 3. Seven StepsDocument10 pagesSuper Simple Songs One Lyrics and Actions: 1. Knock Knock Hello 3. Seven StepsSamanta Tanakht RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Soar Like EaglesDocument2 pagesSoar Like EaglesJessa MagdaleraNo ratings yet
- Hasil Ujian To2 ASPD BK SDIT ALAM NURUL ISLAMDocument3 pagesHasil Ujian To2 ASPD BK SDIT ALAM NURUL ISLAMGinong Pratidhina Nur MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 75-82 An Analysis of Positive Politeness Strategies by Oprah Winfrey in Super Soul Sunday Talk ShowDocument8 pages75-82 An Analysis of Positive Politeness Strategies by Oprah Winfrey in Super Soul Sunday Talk ShowSimple GirlNo ratings yet
- Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Interfaces Configuration Guide, Release 7.xDocument368 pagesCisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Interfaces Configuration Guide, Release 7.xNingo GarridoNo ratings yet
- Excel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterDocument34 pagesExcel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterMariz PacilanNo ratings yet
- Upstream Beginner A1+ (Extra Activities)Document5 pagesUpstream Beginner A1+ (Extra Activities)Berende MonalisaNo ratings yet
- CM/PM/SM. La Parte Inferior Es Relates To CM/PM/SM VersionDocument80 pagesCM/PM/SM. La Parte Inferior Es Relates To CM/PM/SM Versionbasheer almetwakelNo ratings yet
- The Paragraph - Supporting Details, Closing SentenceDocument40 pagesThe Paragraph - Supporting Details, Closing SentenceAbby Guaki100% (2)
- English Correct UsageDocument2 pagesEnglish Correct Usagesyed taimoorNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 4 - Mathematics 2 (Module)Document12 pagesQuarter 4 Week 4 - Mathematics 2 (Module)Janzen Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- How To Create, Copy, and Move, Resources in The KM Repository Using KM APIDocument11 pagesHow To Create, Copy, and Move, Resources in The KM Repository Using KM APIMaximiliano MojaNo ratings yet
- See Chaitanya Charan's Talks Across The WorldDocument2 pagesSee Chaitanya Charan's Talks Across The WorldkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Taisho 1382 English TranslationDocument2 pagesTaisho 1382 English TranslationHenry HenryNo ratings yet