Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Neurociencia 2019
Poster Neurociencia 2019
Uploaded by
Nelson Andrés Pérez UrrutiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Neurociencia 2019
Poster Neurociencia 2019
Uploaded by
Nelson Andrés Pérez UrrutiaCopyright:
Available Formats
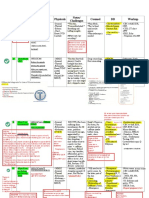
Cotinine counteracts the CS-induced morphological changes in
astrocytes and stimulates the activity of the JAK/STAT after chronic
stress in mice.
Perez-Urrutia Nelsonᵃ, Gonzalez-Rivera Mairaᵃ, Oliveros-Matus Patriciaᵃ, Alvarez-Ricartes Nathalieᵃ, Iarkov
Alexandreᵃ, Echeverria Valentinaᵃb
ᵃ Universidad San Sebastián, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Lientur 1457, Concepción, Chile.
b Bay Pines VA Healthcare System, Research and Development, Bay Pines, FL 33744, USA
Abstract Results
Chronic stress (CS) is a public health problem worldwide, it affects all social and age
groups. Intense, repeated or uncontrolled stress has been implicated in the appearance Porsolt’s test Sucrose preference test
of multiple neuropsychiatric conditions. In the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, CS
decreases the density of astrocytes and alters their morphology and function. This type CTRL + PBS
ns
of disorder, which also causes depression, is treated with selective serotonin reuptake CS + PBS
inhibitors. CS + Cot
In our previous study, we demonstrated that oral and intranasal Cotinine (Cot) CS
administration alleviated posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms via an Cot - - +
astrocyte-related and anti-inflammatory mechanism. Cotinine, a tobacco-derived p-STAT3
alkaloid, facilitates the extinction of fear, decreases depressive and anxiety behaviors, STAT3
improves memory and restores astrocytic density in the hippocampus and frontal cortex
in mice subjected to fear conditioning or with chronic stress. Here, we investigate the
Fig 1: Effect of cotinine on depressive like behavior after chronic restraint stress. p<0.05. Fig. 2 The effects of Cotinine on the regulation of JAK/STAT3
effect of cotinine on behavior, morphology of astrocytes and the activity of the JAK/STAT activity p < 0.05.
pathway in the hippocampus of C57BL/6 male mouse subjected to chronic stress.
A B
CTRL CS + PBS CS + COTININE GFAP+ cell density / field
Methods CTRL + PBS
CS + PBS
CS + Cot
ns
CA1
ns
Animals: Mice C57BL/6 were obtained from CREAV (Universidad de Concepción, Chile) *
CA3
and maintained on a 12-h light-dark cycle with ad libitum access to food and water.
Experimental Design: This study investigated the effect of oral cotinine on depressive-
like behavior, JAK/STAT pathway, and morphological changes.
Drug Treatments: Mice received daily treatments with (1, 2) oral PBS (phosphate-
buffered saline, pH 7.4); (3) oral cotinine (10 mg/ml) dissolved in PBS. ns
Behavioral Analysis: Open field, Sucrose test preference and Porsolt’s Test. All tests
carried out with ANY-maze video tracking system.
Western Blot Analysis: Brain extracts were separated by PAGE-SDS 4-20% and
GD
**
transfered to PVDF membranes and probed with a rabbit STAT3 and p-STAT3 antibody
according our standard protocols.
Immunohistochemistry: Standard protocol were performed with rabbit GFAP antibody
on sagittal brain cryosections of 30um.
Skeleton Analyze: was performed on binary images using ImageJ. Fig 3. Effect of cotinine on GFAP expression after chronic stress in hippocampus of mice. (A) The images from the left represent GFAP+ in control (CTRL), restraint
stress (RS) and treated with Cotinine (10 mg/ml) (RS + COT); (B) Graph depicting the changes in the density of GFAP+ cells.
A B
Working Hypothesis CTRL CS + PBS CS + COTININE
nAchR
Skeleton Analyze process
Astrocyte
JAK
Activity of the JAK/STAT pathway C
CA1 CA3 GD
STAT3
Density of GFAP+ Astrocytes CS-induced morphological
STAT3
changes CTRL + PBS
STAT3 ns
ns ns CS + PBS
CS + Cot
Depressive-like behaviour ns
*
**
CBP/p300
STAT3 Smad1
STAT3 Smad4
Fig 4. Representation of the image analyze on GFAP+ cells (a); Diagrams represent the skeletonized GFAP + cells (B); . (B) Graph depicting the changes in the
Endpoints of GFAP+ skeletonized cells.
Acknowledges Conclusions
The authors were supported by the Grant Fondecyt 1150194, and the University San • Co-treatment with oral cotinine reduced depressive-like behavior.
Sebastián. • STAT3 activity in the hippocampus of CS mice is stimulated by co-treatment with oral cotinine.
• Co-treatment with oral cotinine counteracts CS-induced morphological changes
• Co-treatment with oral cotinine protect the decreasing density of CS-induced GFAP+ cell in the hippocampus
You might also like
- Belonging Essay - Missing HerDocument3 pagesBelonging Essay - Missing HerGeorgina43% (7)
- Technology and Livelihood EducationDocument6 pagesTechnology and Livelihood EducationJuliet Marie MijaresNo ratings yet
- Neville Nibbles Manifesting To The Max by Mr. Twenty Twenty and Neville GoddardDocument30 pagesNeville Nibbles Manifesting To The Max by Mr. Twenty Twenty and Neville GoddardDepechePatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Assessing For Self-ImprovementDocument12 pagesChapter 10. Assessing For Self-ImprovementJaya Cajalne100% (2)
- Study Plan OriginalDocument13 pagesStudy Plan OriginalKennedy Willson Ibobo100% (1)
- Molecules: Anti-Depressive Effectiveness of Baicalin in Vitro and in VivoDocument13 pagesMolecules: Anti-Depressive Effectiveness of Baicalin in Vitro and in VivoMylena SilvaNo ratings yet
- VPHY 143 Cushing and AddisonDocument6 pagesVPHY 143 Cushing and AddisonRegulus Fidelis SevillaNo ratings yet
- Turkey Recipe 2Document43 pagesTurkey Recipe 2Laith الكويس Omar ANo ratings yet
- Duelo 4Document9 pagesDuelo 4Omar Alejandro Orbegozo HernandezNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Stress.6Document16 pagesThe Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Stress.6Utami DewiNo ratings yet
- Ketamina e CortisoloDocument8 pagesKetamina e Cortisolovalerio.messinaNo ratings yet
- Ketamine Induced Synaptic Plasticity Operates Independently of Long-Term PotentiationDocument9 pagesKetamine Induced Synaptic Plasticity Operates Independently of Long-Term PotentiationMoo GeeNo ratings yet
- Oxitocina ExtrahipotalamicaDocument8 pagesOxitocina ExtrahipotalamicaDragan StefanNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug Study 4Document2 pagesPedia Drug Study 4Geddy SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Angstman 2016Document6 pagesAngstman 2016Nadira KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Ramirez 2015Document17 pagesRamirez 2015jarecot100% (1)
- Downloaded From - UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO, On 22 Jul 2019 at 19:08:25, Subject To The Cambridge Core Terms of Use, Available atDocument11 pagesDownloaded From - UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL AUTONOMA DE MEXICO, On 22 Jul 2019 at 19:08:25, Subject To The Cambridge Core Terms of Use, Available atMontserratNo ratings yet
- 112 HTP - HypertensionDocument4 pages112 HTP - HypertensionMae CeaesarNo ratings yet
- Hwang 2020Document8 pagesHwang 2020amandasantanalila186No ratings yet
- 100205HM-SB CRA Poster Final 3Document1 page100205HM-SB CRA Poster Final 3Osama MariaNo ratings yet
- 2010 - Rescue of Cystathionine Beta-Synthase (CBS) Mutants With Chemical ChaperonesDocument8 pages2010 - Rescue of Cystathionine Beta-Synthase (CBS) Mutants With Chemical Chaperonesdo258No ratings yet
- Tejido Adiposo Pardo 1 (7809)Document3 pagesTejido Adiposo Pardo 1 (7809)Faty GallegosNo ratings yet
- Clase 5 - Stress Related NeuroplasticityDocument12 pagesClase 5 - Stress Related NeuroplasticityClaudio Andrés ArtigasNo ratings yet
- AdaptógenosDocument46 pagesAdaptógenosPoetrielNo ratings yet
- Repeated Subcutaneous Racemic Ketamine In.5Document9 pagesRepeated Subcutaneous Racemic Ketamine In.5Ana CeciliaNo ratings yet
- KASPER La Glutamatetergic Agents PPDocument22 pagesKASPER La Glutamatetergic Agents PPAndrei VlasieNo ratings yet
- Aleksandrova2020 Article KetamineAndItsMetabolite2R6R-HDocument16 pagesAleksandrova2020 Article KetamineAndItsMetabolite2R6R-HGILBERTO UEHARANo ratings yet
- Lara Lopes TCM Sensory Training For AutismDocument1 pageLara Lopes TCM Sensory Training For AutismLaraLopesNo ratings yet
- Reyes JM RequirementsDocument6 pagesReyes JM RequirementsHolyver TabarnillaNo ratings yet
- NCP # 1 Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP # 1 Acute Painernst_bondoc50% (2)
- Things About Advanced Breast Cancer That Keep Us Up at NightDocument42 pagesThings About Advanced Breast Cancer That Keep Us Up at NightmilasMDNo ratings yet
- Early Posttraumatic Brain Injury Tranexamic Acid.8Document8 pagesEarly Posttraumatic Brain Injury Tranexamic Acid.8Ricardo VillagranaNo ratings yet
- TFCBT Training GuidelinesDocument3 pagesTFCBT Training GuidelinespolNo ratings yet
- Medications: B (Breakfast), L (Lunch), D (Dinner) Lab Values/Diagnostic Test ResultsDocument3 pagesMedications: B (Breakfast), L (Lunch), D (Dinner) Lab Values/Diagnostic Test Resultsapi-547510423No ratings yet
- The Blood-Brain Barrier and Blood - Tumour Barrier in Brain Tumours and MetastasesDocument16 pagesThe Blood-Brain Barrier and Blood - Tumour Barrier in Brain Tumours and MetastasesRoy SmithNo ratings yet
- From Lab - Bioethical Principles: Review Outline For Exam Ii Material To Review From Exam IDocument10 pagesFrom Lab - Bioethical Principles: Review Outline For Exam Ii Material To Review From Exam ImofidNo ratings yet
- Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma A Systematic ReviewDocument3 pagesAutologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma A Systematic ReviewHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Science Long Term PlanningDocument6 pagesBiomedical Science Long Term PlanningKaryn MedendorpNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3Document27 pagesPresentation 3hurricaneap60No ratings yet
- Anxiolytic - and Antidepressant-Like Effects of Bacillus Coagulans Unique IS-2 Mediate Via Reshaping of Microbiome Gut-Brain Axis in RatsDocument14 pagesAnxiolytic - and Antidepressant-Like Effects of Bacillus Coagulans Unique IS-2 Mediate Via Reshaping of Microbiome Gut-Brain Axis in RatsJulio QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Effects of A Tryptic Hydrolysate From Bovine Milk Alpha S1 ... - LactiumDocument5 pagesEffects of A Tryptic Hydrolysate From Bovine Milk Alpha S1 ... - LactiumMohamed KhedrNo ratings yet
- Sarahclarke,+5695 16641 1 CEDocument4 pagesSarahclarke,+5695 16641 1 CEjayadevanNo ratings yet
- Basic Understanding of PBPK: Principles & Connection To The Broader Scope of Systems PharmacologyDocument28 pagesBasic Understanding of PBPK: Principles & Connection To The Broader Scope of Systems PharmacologyBenni IskandarNo ratings yet
- Child-Pugh Score: Patient Name: - DateDocument3 pagesChild-Pugh Score: Patient Name: - DateGede Eka Putra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To CT BrainDocument34 pagesClinical Approach To CT BrainXiaoThoong LohNo ratings yet
- Reports - Department of BiochemistryDocument3 pagesReports - Department of Biochemistrymadimohammad005No ratings yet
- Patients From The Literature Are Summarised in This TableDocument9 pagesPatients From The Literature Are Summarised in This TableEdwardNo ratings yet
- Kaptchuk Et Al Placebos BMJ 2020Document17 pagesKaptchuk Et Al Placebos BMJ 2020Diego Salinas GámezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- Sporamin induces apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB activation in human pancreatic cancer cellsDocument9 pagesSporamin induces apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB activation in human pancreatic cancer cellsDaisy Joanna Castañeda MataNo ratings yet
- Universities And/Or Hospitals They Are Affiliated With: Title of The Research StudyDocument1 pageUniversities And/Or Hospitals They Are Affiliated With: Title of The Research StudyADISAINo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- Yoa05069 61 70Document10 pagesYoa05069 61 70Felicia JesslynNo ratings yet
- Butea Superba Sci - Butea Superba-Induced Amelioration of Cognitive and Emotional Deficits in Olfactory Bulbectomized Mice and Putative MechanismsDocument11 pagesButea Superba Sci - Butea Superba-Induced Amelioration of Cognitive and Emotional Deficits in Olfactory Bulbectomized Mice and Putative MechanismsyunusNo ratings yet
- MC2 1R 2023 Prelim Class ReqDocument7 pagesMC2 1R 2023 Prelim Class ReqDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- ADMISSION Rundown OperativesDocument16 pagesADMISSION Rundown OperativesTiffany Verzil GarciaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Rejuvenates Quiescent Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells in Old Mice Through Restoration of Cyclin D1Document27 pagesExercise Rejuvenates Quiescent Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells in Old Mice Through Restoration of Cyclin D1Alana HNo ratings yet
- Jiai Wei Xiao Yao San Paper JapanDocument15 pagesJiai Wei Xiao Yao San Paper JapanEckhart TolleNo ratings yet
- Yi 2022 Toxina em Platisma e Lifting Mandibular (Otimo)Document7 pagesYi 2022 Toxina em Platisma e Lifting Mandibular (Otimo)Ana Paula NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Troponin Past and PresentDocument20 pagesTroponin Past and PresentDaniel DrimerNo ratings yet
- Chronic Stress Changes Prepulse Inhibition After Amphetamine Challenge: The Role of The Dopaminergic SystemDocument13 pagesChronic Stress Changes Prepulse Inhibition After Amphetamine Challenge: The Role of The Dopaminergic SystemArlette CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Acute and long-term effects of intracerebroventricular administration of α-ketoisocaproic acid on oxidative stress parameters and cognitive and noncognitive behaviorsDocument12 pagesAcute and long-term effects of intracerebroventricular administration of α-ketoisocaproic acid on oxidative stress parameters and cognitive and noncognitive behaviorsMatheus PioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Klengel, T. - 2015Document15 pages2 - Klengel, T. - 2015João PedroNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Betaine Supplementation Is Less Effective Than Methionine Restriction in Correcting Phenotypes of CBS Deficient MiceDocument14 pages2016 - Betaine Supplementation Is Less Effective Than Methionine Restriction in Correcting Phenotypes of CBS Deficient Micedo258No ratings yet
- FA22 - HUM110 - Assignment 4Document3 pagesFA22 - HUM110 - Assignment 4NOOB GAM1NGNo ratings yet
- ACARA - NAPLAN Preliminary Results - Data Dictionary: OfficialDocument5 pagesACARA - NAPLAN Preliminary Results - Data Dictionary: OfficialkapolaNo ratings yet
- Writing Emails Group ExercisesDocument17 pagesWriting Emails Group ExercisesSalam AlKilaniNo ratings yet
- Case Study On TCS and InfosysDocument8 pagesCase Study On TCS and InfosysNisha HcrNo ratings yet
- SAS COR0014 Day 4Document7 pagesSAS COR0014 Day 4Reahlyn Sobreviga ErmitaNo ratings yet
- 2022 ISKCON Detroit Youth RetreatDocument57 pages2022 ISKCON Detroit Youth RetreatPrashant KashyapNo ratings yet
- Memory Politics Identity and Conflict Historical Memory As A Variable 1St Edition Zheng Wang Auth Full ChapterDocument67 pagesMemory Politics Identity and Conflict Historical Memory As A Variable 1St Edition Zheng Wang Auth Full Chapterrobert.lianes220100% (6)
- Hard and Soft SkillsDocument36 pagesHard and Soft SkillsMallik M BNo ratings yet
- Making Inferences: What Is Inference?Document12 pagesMaking Inferences: What Is Inference?VilliaNo ratings yet
- Take Back Your Marriage Sticking Together in A World That Pulls Us Apa - EBOOKOIDDocument193 pagesTake Back Your Marriage Sticking Together in A World That Pulls Us Apa - EBOOKOIDGhassan El-BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- BKlood Knowledge 000Document78 pagesBKlood Knowledge 000justinregisash9No ratings yet
- Excellence Wins Part 1Document2 pagesExcellence Wins Part 1Caron DhojuNo ratings yet
- Interpreting & Solving Word Problems-Salbino P. Fontanilla Jr.Document31 pagesInterpreting & Solving Word Problems-Salbino P. Fontanilla Jr.Ruben DublaNo ratings yet
- ZM, NZ, MVN, ZV, ZDocument3 pagesZM, NZ, MVN, ZV, ZMark Anthony RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of CommunicationDocument3 pagesNature and Scope of Communicationpratap royalNo ratings yet
- Q3-Week 1-DLP-Reading&Writing-Text As A Connected DiscourseDocument4 pagesQ3-Week 1-DLP-Reading&Writing-Text As A Connected DiscourseAIMEE JANENo ratings yet
- EssayDocument1 pageEssayEdli PillatiNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument26 pagesThesisMiralyn TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Misinformation and Biases Infect Social Media, Both Intentionally and AccidentallyDocument3 pagesMisinformation and Biases Infect Social Media, Both Intentionally and AccidentallyMaryam AsadNo ratings yet
- PR2 Sample Midterm ExamDocument1 pagePR2 Sample Midterm ExamSarah Mae AventuradoNo ratings yet
- New ThesisDocument20 pagesNew ThesisAnabel BahintingNo ratings yet
- Power and PoliticsDocument21 pagesPower and Politicssanjana sethNo ratings yet
- Assignments MergedDocument18 pagesAssignments MergedYaar 1510No ratings yet
- IDIOMSDocument6 pagesIDIOMSJum IsunNo ratings yet
- PDF RW 11 Unit 18 Writing A Position Paper 4 TopicsDocument24 pagesPDF RW 11 Unit 18 Writing A Position Paper 4 TopicsGil YuuNo ratings yet