Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
Uploaded by
Rhasher YbañezThis document discusses the extensive and intensive properties of matter. It defines extensive properties like mass and volume that depend on the amount of matter, and intensive properties like density and temperature that do not. The document also covers the three states of matter, physical and chemical properties, and types of chemical reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- PS Lesson 3Document2 pagesPS Lesson 3euginNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument29 pagesMatterJeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document21 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1mariayvankaNo ratings yet
- Science SA#2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience SA#2 ReviewerJulia Ricel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- Pop Sheet 3Document4 pagesPop Sheet 3pang batzNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYwella wellaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept MapMar YaNo ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1Document3 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1jjjangchunNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic ChemistryAngelou HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesChemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesMary Roselen MonayaNo ratings yet
- Handout On Matter (2018)Document9 pagesHandout On Matter (2018)scientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesMy Chemistry Notess2023100462No ratings yet
- SHS-General Chemistry 1Document32 pagesSHS-General Chemistry 1JC PerezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Is The Study of Matter, Its Composition, Its Structure, Its Properties, The Processes ThatDocument5 pagesChemistry Is The Study of Matter, Its Composition, Its Structure, Its Properties, The Processes ThatDiane DimaalaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocument26 pagesChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1yoonsjwlNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesMatter and Its Properties Properties of MattermiahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Article Theory of MatterDocument19 pagesChemistry: Article Theory of MatterLizzy XeryuuNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesC15 Notes CH1 IntroductionArnieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Park JeydsskiiNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChemistryDocument17 pages1 - ChemistryJOANA ESTINOCONo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesChemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Liezel Brillantes100% (1)
- Reviewer Firstsem GenchemDocument7 pagesReviewer Firstsem GenchemChricellFNo ratings yet
- Chem F1 U2 NoteDocument3 pagesChem F1 U2 NoteumaymaupdirahmanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryGIAN CARLONo ratings yet
- (Module 1) Introduction To Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument25 pages(Module 1) Introduction To Chemistry and Measurementsstipen dwaytNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec: Basic Concepts About MatterDocument12 pagesChemistry Lec: Basic Concepts About MatterJanna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- Properties of The Matter and Chemical StructureDocument22 pagesProperties of The Matter and Chemical StructureCholo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Document40 pagesLesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Evelyn Battuac de AustriaNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument3 pagesMatterCUIZON, GEORDETTE DIVINENo ratings yet
- Prelim ChemDocument6 pagesPrelim ChemMim MimNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterBilledo ClarkNo ratings yet
- Matter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleDocument8 pagesMatter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleMichael S LeysonNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Chemistry 3rd QuarterDocument18 pagesScience 8 Chemistry 3rd QuarterOrowa, Barbie Jane R.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- CHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Document4 pagesCHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Alexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Compilation Report in Science: Submitted byDocument24 pagesCompilation Report in Science: Submitted byHan ONo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Fernandez, Nadine Kate T.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document7 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Matter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingDocument26 pagesMatter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingBiruk BtNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document6 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Fu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Document58 pagesFu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument3 pagesMATTERkatherine regioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry First SemDocument8 pagesChemistry First SemceeNo ratings yet
- Review of Chemistry ConceptsDocument15 pagesReview of Chemistry ConceptsAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of MatterRampotz Ü EchizenNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral ChemistryBon AshleeNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Unit eDocument20 pagesUnit eVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTprexa indiaNo ratings yet
- 6728286Document12 pages6728286johan hicoruNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper-1Document3 pagesChemistry Model Paper-1sivarajeshwarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument1 pageChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Q. Computacional Computational Chemistry Reviews Vol 9 (Leszczynski)Document258 pagesQ. Computacional Computational Chemistry Reviews Vol 9 (Leszczynski)paolo giovanni zucchini cuevasNo ratings yet
- Dissociation Energies of Diatomic MoleculesDocument2 pagesDissociation Energies of Diatomic MoleculesNyau NyauNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding - AnswerDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding - Answer6brk8sjszqNo ratings yet
- Outline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesOutline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Tos & TQDocument7 pagesTos & TQglenn floresNo ratings yet
- 09 EvaporationDocument4 pages09 EvaporationDelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Spectroscopy: Online Learning CenterDocument8 pagesChapter 13: Spectroscopy: Online Learning CenterShailendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnswer KeyAra CaturanNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide For GCSE Science ChemistryDocument9 pagesRevision Guide For GCSE Science Chemistryjenny10040% (1)
- Chapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsDocument11 pagesChapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsswatkoolNo ratings yet
- 2 Modul 1 SoalanDocument23 pages2 Modul 1 SoalanSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadDocument23 pagesTopic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadSamihah YaacobNo ratings yet
- David A. Rubenstein, ... Mary D. Frame, In, 2015: Biofluid Mechanics (Second Edition)Document2 pagesDavid A. Rubenstein, ... Mary D. Frame, In, 2015: Biofluid Mechanics (Second Edition)Maria Graça RochaNo ratings yet
- Anthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (001-031)Document31 pagesAnthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (001-031)HARDY EDDISONNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Fuel Cycle Coursera Calculations HandoutDocument11 pages1.6 Fuel Cycle Coursera Calculations HandoutJon WeaverNo ratings yet
- Nature of MagnetismDocument284 pagesNature of MagnetismKatelyn GreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical CompoundsDocument49 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Compoundssomrat azamNo ratings yet
- Natural PolymersDocument28 pagesNatural PolymersSHRUTI VERMANo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument7 pagesChapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistrySridhar MarellaNo ratings yet
- Arihant Chemistry HandBookDocument574 pagesArihant Chemistry HandBookKRISHNA MODALANo ratings yet
- Sample Question - UG - Updated From Summer 2023 - 6 Mar 23Document5 pagesSample Question - UG - Updated From Summer 2023 - 6 Mar 23Fattah Rahman MahiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Overview: Prof. Ronald Jefferson A. NarcedaDocument50 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Overview: Prof. Ronald Jefferson A. NarcedapolajanaNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLDocument46 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Topic 03 MolesDocument3 pagesTopic 03 Moleszafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Thermodynamics and Soft MatterDocument1 pageExercises in Thermodynamics and Soft MattermzmohamedarifNo ratings yet
3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
Uploaded by
Rhasher Ybañez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThis document discusses the extensive and intensive properties of matter. It defines extensive properties like mass and volume that depend on the amount of matter, and intensive properties like density and temperature that do not. The document also covers the three states of matter, physical and chemical properties, and types of chemical reactions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the extensive and intensive properties of matter. It defines extensive properties like mass and volume that depend on the amount of matter, and intensive properties like density and temperature that do not. The document also covers the three states of matter, physical and chemical properties, and types of chemical reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pages3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1
Uploaded by
Rhasher YbañezThis document discusses the extensive and intensive properties of matter. It defines extensive properties like mass and volume that depend on the amount of matter, and intensive properties like density and temperature that do not. The document also covers the three states of matter, physical and chemical properties, and types of chemical reactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
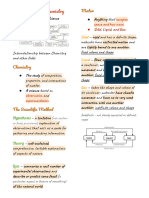
3rd MASTERY [CHEM 1: GENCHEM] INTENSIVE AND EXTENSIVE PROPERTIES OF
MATTER
Extensive properties including mass and
CHEMISTRY
volume are proportional to the amount of
branch of natural science that deals principally matter being weighed. Density and color, for
with the properties of substances, the changes example, are not affected by the amount of
they undergo, and the natural laws that matter present.
describe these changes.
1. INTENSIVE PROPERTY – independent of the
MATTER amount of matter present.
EX: pressure and temperature, color, boiling
Matter is any substance that has mass and point, density
takes up space by having volume.
2. EXTENSIVE PROPERTY – dependent on the
Matter is described as something that has mass amount of matter in a sample.
and occupies space. All physical structures are
made up of matter, and the state or process of EX: mass and volume, size, shape, length,
matter is an easily observed property of matter. mass, height
STATES OF MATTER CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER - measured
or observed as matter transforms into a
SOLID - hold its own shape and is hard to particular type of matter.
compress (squash). The molecules in a solid are
closely packed together – they have a 1. REACTIVITY – tendency of matter to
high density. combine chemically with other
substances
LIQUID - molecules have the ability to move 2. FLAMMABILITY – tendency of matter to
around and slide past each other. A liquid will burn
take on the shape of the container it is being 3. TOXICITY – extent to which a chemical
held in. Easier to compress than a solid. element or a combination of chemicals
GAS - atoms are much more spread out than in may harm an organism.
solids or liquids, and the 4. ACIDITY – ability to react with an acid is
atoms collide randomly with one another. A a chemical property.
gas will fill any container, but if the container is Chemical properties are extremely helpful
not sealed, the gas will escape. Compressed when it comes to distinguishing compounds.
much more easily than a liquid or solid. Chemical properties, on the other hand, can
PLASMA - very similar to gas, a gas that can only be detected when a material is in the
carry an electrical charge. Form of matter that process of being changed into another
exists when atoms are in an excited state. substance.
BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATE (BEC) CHANGES OF MATTER
PROPERTIES OF MATTER PHYSICAL CHANGE - changes in which no
bonds are broken or formed. The same types
- Matter is made up of atoms of compounds or elements that were there at
- Properties are the characteristics that the beginning of the change are there at the
enable us to differentiate one material end of the change (such as color, boiling
from another. point, etc.).
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER - attribute of - Physical changes involve moving
matter that is independent of its chemical molecules around, but not changing
composition. them.
- Density, color, hardness, melting and Some types of physical changes include:
boiling points, and electrical
conductivity are all examples of • Changes of state (changes from a solid
physical properties. to a liquid or a gas and vice versa).
Any characteristic that can be measured, such • Separation of a mixture.
as an object’s density, color, mass, volume, • Physical deformation (cutting, denting,
length, malleability, melting point, hardness, stretching).
odor, temperature, and more, are considered
properties of matter.
• Making solutions (special kinds of CLASSES OF MATTER w/respect to
mixtures). COMPOSITION
Physical changes can further be classified as Matter can be classified into two broad
reversible or irreversible. categories:
Other changes of state PURE SUBSTANCE - form of matter that has a
constant composition (meaning that it is the
vaporization (liquid to gas)
same everywhere) and properties that are
freezing (liquid to solid) constant throughout the sample (meaning that
there is only one set of properties such as
condensation (gas to liquid) melting point, color, boiling point, etc.
CHEMICAL CHANGE - occur when bonds are throughout the matter).
broken and/or formed between molecules or - ELEMENT - substance that cannot be
atoms. One substance with a certain set of broken down into chemically simpler
properties (such as melting point, color, taste, components.
etc.) is turned into a different substance with - COMPOUND - substance that can be
different properties. broken down into chemically simpler
- Chemical changes are frequently components (because it has more than
harder to reverse than physical one element)
changes. MIXTURE - material composed of two or more
Observations that help to indicate chemical substances. Elements and compounds are
change include: both examples of pure substances.
• Temperature changes - HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURE - the
composition is uniform throughout the
• Light given off. mixture.
• Unexpected color changes - HETEROGENEOUS MIXTURE - the
composition is not uniform throughout
• Different smell or taste the mixture.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
1. COMBINATION – two or more
substances combined to form single
new product (synthesis reaction)
[A+B→AB]
2. DECOMPOSITION - opposite of
combination, single substance will break
into two different element/ simpler
substance
[AB→A+B]
3. SINGLE REPLACEMENT – one element will
replace another element in the
compound
[AB+C→AC+B]
(look for the product to determine if it is
positively or negatively charged)
4. DOUBLE REPLACEMENT – two compound
exchange bonds to form different
compounds.
[AB+CD→AD+CB]
You might also like
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- PS Lesson 3Document2 pagesPS Lesson 3euginNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument29 pagesMatterJeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document21 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1mariayvankaNo ratings yet
- Science SA#2 ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience SA#2 ReviewerJulia Ricel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- Pop Sheet 3Document4 pagesPop Sheet 3pang batzNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYwella wellaNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept MapMar YaNo ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1Document3 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1jjjangchunNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesBasic ChemistryAngelou HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesChemistry 11: Lesson 1 - Matter and Its PropertiesMary Roselen MonayaNo ratings yet
- Handout On Matter (2018)Document9 pagesHandout On Matter (2018)scientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesMy Chemistry Notess2023100462No ratings yet
- SHS-General Chemistry 1Document32 pagesSHS-General Chemistry 1JC PerezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Is The Study of Matter, Its Composition, Its Structure, Its Properties, The Processes ThatDocument5 pagesChemistry Is The Study of Matter, Its Composition, Its Structure, Its Properties, The Processes ThatDiane DimaalaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocument26 pagesChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1yoonsjwlNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties Properties of MatterDocument4 pagesMatter and Its Properties Properties of MattermiahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Article Theory of MatterDocument19 pagesChemistry: Article Theory of MatterLizzy XeryuuNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesC15 Notes CH1 IntroductionArnieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Park JeydsskiiNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- 1 - ChemistryDocument17 pages1 - ChemistryJOANA ESTINOCONo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesChemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Liezel Brillantes100% (1)
- Reviewer Firstsem GenchemDocument7 pagesReviewer Firstsem GenchemChricellFNo ratings yet
- Chem F1 U2 NoteDocument3 pagesChem F1 U2 NoteumaymaupdirahmanmohamedNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryGIAN CARLONo ratings yet
- (Module 1) Introduction To Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument25 pages(Module 1) Introduction To Chemistry and Measurementsstipen dwaytNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lec: Basic Concepts About MatterDocument12 pagesChemistry Lec: Basic Concepts About MatterJanna EchavezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- Properties of The Matter and Chemical StructureDocument22 pagesProperties of The Matter and Chemical StructureCholo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Document40 pagesLesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Evelyn Battuac de AustriaNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument3 pagesMatterCUIZON, GEORDETTE DIVINENo ratings yet
- Prelim ChemDocument6 pagesPrelim ChemMim MimNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterBilledo ClarkNo ratings yet
- Matter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleDocument8 pagesMatter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleMichael S LeysonNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Chemistry 3rd QuarterDocument18 pagesScience 8 Chemistry 3rd QuarterOrowa, Barbie Jane R.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classification of MatterDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Classification of MatterPatrice Francisco100% (1)
- CHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Document4 pagesCHEM HANDOUT W1 and W2Alexander DolinNo ratings yet
- Compilation Report in Science: Submitted byDocument24 pagesCompilation Report in Science: Submitted byHan ONo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 - Lesson 1Fernandez, Nadine Kate T.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document7 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Matter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingDocument26 pagesMatter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingBiruk BtNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document6 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Fu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Document58 pagesFu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- MATTERDocument3 pagesMATTERkatherine regioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry First SemDocument8 pagesChemistry First SemceeNo ratings yet
- Review of Chemistry ConceptsDocument15 pagesReview of Chemistry ConceptsAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument6 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of MatterRampotz Ü EchizenNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral ChemistryBon AshleeNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Unit eDocument20 pagesUnit eVenkateswara Rao DoodalaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding SPECIAL ASSIGNMENTprexa indiaNo ratings yet
- 6728286Document12 pages6728286johan hicoruNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper-1Document3 pagesChemistry Model Paper-1sivarajeshwarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument1 pageChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- Q. Computacional Computational Chemistry Reviews Vol 9 (Leszczynski)Document258 pagesQ. Computacional Computational Chemistry Reviews Vol 9 (Leszczynski)paolo giovanni zucchini cuevasNo ratings yet
- Dissociation Energies of Diatomic MoleculesDocument2 pagesDissociation Energies of Diatomic MoleculesNyau NyauNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding - AnswerDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding - Answer6brk8sjszqNo ratings yet
- Outline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesOutline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Tos & TQDocument7 pagesTos & TQglenn floresNo ratings yet
- 09 EvaporationDocument4 pages09 EvaporationDelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Spectroscopy: Online Learning CenterDocument8 pagesChapter 13: Spectroscopy: Online Learning CenterShailendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnswer KeyAra CaturanNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide For GCSE Science ChemistryDocument9 pagesRevision Guide For GCSE Science Chemistryjenny10040% (1)
- Chapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsDocument11 pagesChapter 5: Probability, Combinations & PermutationsswatkoolNo ratings yet
- 2 Modul 1 SoalanDocument23 pages2 Modul 1 SoalanSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadDocument23 pagesTopic 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds: Najmiyatul Fadilah MohamadSamihah YaacobNo ratings yet
- David A. Rubenstein, ... Mary D. Frame, In, 2015: Biofluid Mechanics (Second Edition)Document2 pagesDavid A. Rubenstein, ... Mary D. Frame, In, 2015: Biofluid Mechanics (Second Edition)Maria Graça RochaNo ratings yet
- Anthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (001-031)Document31 pagesAnthony M. Wachinski - Environmental Ion Exchange - Principles and Design-Taylor & Francis, Chapman and Hall - CRC (2016) (1) (001-031)HARDY EDDISONNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Fuel Cycle Coursera Calculations HandoutDocument11 pages1.6 Fuel Cycle Coursera Calculations HandoutJon WeaverNo ratings yet
- Nature of MagnetismDocument284 pagesNature of MagnetismKatelyn GreenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical CompoundsDocument49 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Compoundssomrat azamNo ratings yet
- Natural PolymersDocument28 pagesNatural PolymersSHRUTI VERMANo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument7 pagesChapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistrySridhar MarellaNo ratings yet
- Arihant Chemistry HandBookDocument574 pagesArihant Chemistry HandBookKRISHNA MODALANo ratings yet
- Sample Question - UG - Updated From Summer 2023 - 6 Mar 23Document5 pagesSample Question - UG - Updated From Summer 2023 - 6 Mar 23Fattah Rahman MahiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Overview: Prof. Ronald Jefferson A. NarcedaDocument50 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Overview: Prof. Ronald Jefferson A. NarcedapolajanaNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLDocument46 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Topic 03 MolesDocument3 pagesTopic 03 Moleszafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Thermodynamics and Soft MatterDocument1 pageExercises in Thermodynamics and Soft MattermzmohamedarifNo ratings yet