Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsEntrepreneurship Finals
Entrepreneurship Finals
Uploaded by
JOHN PAULO I LICUPThis document discusses various concepts related to entrepreneurship including entrepreneurial opportunities, actions, thinking, resources, strategies for new market entry, and methods for generating new ideas. Key points covered include assessing uncertainty, using existing resources in new ways, forming opportunity beliefs through creative thinking, possessing rare and difficult to imitate resources, and addressing demand uncertainty through strategies like franchising that focus on imitation to reduce risk. The document also outlines different techniques entrepreneurs can use to stimulate reflection on situations, including comprehension questions, reflection tasks, and connection tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Set It and Forget It Small by Eric HoDocument36 pagesSet It and Forget It Small by Eric HoAditya Sharma50% (4)
- Grow From Within (PB): Mastering Corporate Entrepreneurship and InnovationFrom EverandGrow From Within (PB): Mastering Corporate Entrepreneurship and InnovationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Comprehensive M&a Due Diligence Checklist For BuyersDocument30 pagesComprehensive M&a Due Diligence Checklist For BuyersSimon Tseung100% (2)
- Prospeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahDocument5 pagesProspeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahOto ErwinNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting EntrepreneurshipAriana AriolaNo ratings yet
- Hatdog Ewan Ko DitoDocument6 pagesHatdog Ewan Ko DitominnieNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Competencies Why Is It Important? According To Man and ChanDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial Competencies Why Is It Important? According To Man and ChanDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Entrep (Mod12 4) ReviewerDocument12 pagesEntrep (Mod12 4) ReviewerBobby Ken Alfonso MorataNo ratings yet
- q1 Reviewer (Entrep)Document9 pagesq1 Reviewer (Entrep)kris krossNo ratings yet
- Techno ReviewerDocument4 pagesTechno ReviewerNathan ash ClintonNo ratings yet
- Nature and Relevance of EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesNature and Relevance of Entrepreneurshipvictorianomarielle03No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Chapter 1: The Entrepreneurial MindsetDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurship: Chapter 1: The Entrepreneurial Mindsetayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Prospeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahDocument5 pagesProspeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahabutholaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerSOLIS, John Ernest S.No ratings yet
- ENTREP REVIEWERDocument7 pagesENTREP REVIEWERNathalie Nichole I. Inductivo Pesta�oNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument2 pages3rd Quarter Exam ReviewerJheriko Mallari100% (2)
- Entrep ReviewerDocument20 pagesEntrep ReviewerBianca MalinabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Defining EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Defining EntrepreneurshipAndrea CaparosoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerBianca De Castro VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Prelims ReviewerDocument1 pagePrelims Reviewerlyka deguzmanNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurshipTricia Baltazar0% (1)
- MGMT3004 Wk1 230711Document45 pagesMGMT3004 Wk1 230711LeeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Reviewer 2 NDDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship Reviewer 2 NDIrish ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter NotesDocument12 pages3rd Quarter NotesMary Grace BuenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-03 (Entraprenurship Process)Document3 pagesLecture-03 (Entraprenurship Process)Shanewaz Mahmood SohelNo ratings yet
- MidtermsDocument6 pagesMidtermsnirichdaitttNo ratings yet
- Entrep 12Document10 pagesEntrep 12Yhana jamille CalixterioNo ratings yet
- Entrep - ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrep - Reviewerjcmansanadis8126qcNo ratings yet
- Entrep Lesson 1Document1 pageEntrep Lesson 1Christian BaldoviaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerChristian BelanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2andiNo ratings yet
- 1 Entrepreneurship Examination ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Entrepreneurship Examination ReviewerJam Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerAj GoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial ReviewerDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurial ReviewerVeronique EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Entrep ReviewerDocument7 pagesEntrep ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Midterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerPrince LitchNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chapter1Document43 pagesEntrepreneurship Chapter1Altaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship Reviewerauhsojgab07No ratings yet
- Reviewer Entrep QuizDocument3 pagesReviewer Entrep Quizgrace bruanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerChristian BelanoNo ratings yet
- Importance of EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesImportance of EntrepreneurshipSteven Duane PradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Entrepreneurial Skills and CompetenciesDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - Entrepreneurial Skills and CompetenciesLance Richard FlaminianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveDocument31 pagesChapter 1 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveJamilet RivasNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurshipAj GoNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 - EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesWeek 1-2 - EntrepreneurshipGelli GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Entrep11Document3 pagesReviewer in Entrep11yannie isanan100% (3)
- Reviewer TechnoDocument2 pagesReviewer TechnoJennifer LigayaNo ratings yet
- GR 12 - EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesGR 12 - Entrepreneurshipdot comNo ratings yet
- Entrep ModuleDocument6 pagesEntrep Modulekaye maleNo ratings yet
- Entrep MidtermsDocument4 pagesEntrep Midtermskc.jarobillaNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship pt1Document4 pagesTechnopreneurship pt1aremtiii101No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument15 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerMika VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning Week 3 6Document20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning Week 3 6zyra.position1seoNo ratings yet
- Ge Elec 3 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGe Elec 3 ReviewerJoy-Joy Fernandez AgotNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurshipJ-ira LariosaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam (Final)Document5 pages1st Quarter Exam (Final)Honie Jane D. AmerilaNo ratings yet
- App004 ReviewerDocument5 pagesApp004 ReviewerCatherine Sanchez RosarioNo ratings yet
- What Makes Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurial?: Saras D. SarasvathyDocument10 pagesWhat Makes Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurial?: Saras D. SarasvathyAshokNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesEntrep Q1 ReviewerCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Chapter 3Document3 pagesEntrep Chapter 3Carl Jacob LandichoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Trends in Entrepreneurship ResearchDocument5 pages21st Century Trends in Entrepreneurship ResearchkimashleymandronNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 SolvedDocument10 pagesAssignment-1 SolvedMd. Shahriar Kabir RishatNo ratings yet
- C-Pcbu2 Case StudyDocument7 pagesC-Pcbu2 Case StudyJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- CONTENTDocument12 pagesCONTENTJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- Baroque Architecture.1Document52 pagesBaroque Architecture.1JOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways of Looking at Morality-7-20Document14 pages5 Ways of Looking at Morality-7-20JOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drawings of A BungalowDocument1 pageArchitectural Drawings of A BungalowJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
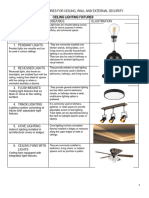
- FRAUD Upon The Court Motion - BOA V Julme-FL Case#CACE09-21933-051 - 2010-09-29 PDFDocument30 pagesFRAUD Upon The Court Motion - BOA V Julme-FL Case#CACE09-21933-051 - 2010-09-29 PDFStar Gazon100% (2)
- MC 006 2019 - PRRDDocument6 pagesMC 006 2019 - PRRDmarjNo ratings yet
- Perceived Financial KnowledgeDocument36 pagesPerceived Financial KnowledgeAnkh64No ratings yet
- Ramos Vs Bpi Family Savings BankDocument3 pagesRamos Vs Bpi Family Savings BankLorenzo Marvin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Check List For Audit Irregularities Ba MangaluruDocument15 pagesCheck List For Audit Irregularities Ba MangaluruKislayNikharNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On LoanDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Loanafeavbrpd100% (1)
- B.inggris N Kel.2Document34 pagesB.inggris N Kel.2Putra RakhmadaniNo ratings yet
- Press Release Saksoft Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Document5 pagesPress Release Saksoft Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Sandy SanNo ratings yet
- I. Pledge and Mortgage Essential Requisites Promise To DeliverDocument4 pagesI. Pledge and Mortgage Essential Requisites Promise To DeliverZaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- FR Ind As 20Document28 pagesFR Ind As 20Dheeraj TurpunatiNo ratings yet
- Activity Chapter 4: Ans. 2,320 SolutionDocument2 pagesActivity Chapter 4: Ans. 2,320 SolutionRandelle James FiestaNo ratings yet
- METROPOLITAN BANK & TRUST COMPANY Vs ASB HOLDINGS, INC. CASE DIGESTDocument2 pagesMETROPOLITAN BANK & TRUST COMPANY Vs ASB HOLDINGS, INC. CASE DIGESTNullus cumunisNo ratings yet
- Mint Discussion On FreshstartDocument3 pagesMint Discussion On FreshstartVinod ChanrasekharanNo ratings yet
- HSC Past Paper Questions 2u Maths - Time Payments 1Document1 pageHSC Past Paper Questions 2u Maths - Time Payments 1greycouncilNo ratings yet
- Jamuna Bank Presentation 1Document49 pagesJamuna Bank Presentation 1Md ShahnewazNo ratings yet
- Form-Business Assessment QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesForm-Business Assessment QuestionnaireOveine SmallNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Civil Service (Conduct) Rules 1966 (Eng)Document27 pagesKarnataka Civil Service (Conduct) Rules 1966 (Eng)Alissa BarnesNo ratings yet
- AB0520New PDFDocument78 pagesAB0520New PDFWilfrid FokaNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument26 pagesMoney MarketPigeons LoftNo ratings yet
- Informal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateDocument7 pagesInformal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateAkingbesote VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Weekly PDF January 2020 1st Week (1-7) by AffairsCloud PDFDocument23 pagesCurrent Affairs Weekly PDF January 2020 1st Week (1-7) by AffairsCloud PDFSailen GopeNo ratings yet
- Purchase and Sale AgreementDocument9 pagesPurchase and Sale Agreementapi-26011493No ratings yet
- Commodatum DigestsDocument10 pagesCommodatum DigestsCharlie PeinNo ratings yet
- Cash Management Challenges of Small Businesses in A Developing CommunityDocument11 pagesCash Management Challenges of Small Businesses in A Developing CommunitySuoi HoaNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Prospects of Interest Free Banking ServicesDocument6 pagesChallenges and Prospects of Interest Free Banking ServicesBiruk TadessaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Consultants: Sample Form of Evaluation ReportDocument35 pagesSelection of Consultants: Sample Form of Evaluation Reportkyawzaywin2No ratings yet
- Financial Modeling of Automobile Industry (Maruti Suzuki)Document26 pagesFinancial Modeling of Automobile Industry (Maruti Suzuki)Harshit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Practical Law US - Representations Warranties Covenants Rights and ConditionsDocument20 pagesPractical Law US - Representations Warranties Covenants Rights and ConditionsTinn ApNo ratings yet
Entrepreneurship Finals
Entrepreneurship Finals
Uploaded by
JOHN PAULO I LICUP0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views7 pagesThis document discusses various concepts related to entrepreneurship including entrepreneurial opportunities, actions, thinking, resources, strategies for new market entry, and methods for generating new ideas. Key points covered include assessing uncertainty, using existing resources in new ways, forming opportunity beliefs through creative thinking, possessing rare and difficult to imitate resources, and addressing demand uncertainty through strategies like franchising that focus on imitation to reduce risk. The document also outlines different techniques entrepreneurs can use to stimulate reflection on situations, including comprehension questions, reflection tasks, and connection tasks.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various concepts related to entrepreneurship including entrepreneurial opportunities, actions, thinking, resources, strategies for new market entry, and methods for generating new ideas. Key points covered include assessing uncertainty, using existing resources in new ways, forming opportunity beliefs through creative thinking, possessing rare and difficult to imitate resources, and addressing demand uncertainty through strategies like franchising that focus on imitation to reduce risk. The document also outlines different techniques entrepreneurs can use to stimulate reflection on situations, including comprehension questions, reflection tasks, and connection tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views7 pagesEntrepreneurship Finals
Entrepreneurship Finals
Uploaded by
JOHN PAULO I LICUPThis document discusses various concepts related to entrepreneurship including entrepreneurial opportunities, actions, thinking, resources, strategies for new market entry, and methods for generating new ideas. Key points covered include assessing uncertainty, using existing resources in new ways, forming opportunity beliefs through creative thinking, possessing rare and difficult to imitate resources, and addressing demand uncertainty through strategies like franchising that focus on imitation to reduce risk. The document also outlines different techniques entrepreneurs can use to stimulate reflection on situations, including comprehension questions, reflection tasks, and connection tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
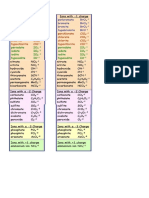
1. Entrepreneurship- ∙ The activity of 10.
Engage in Bricolage- This
setting up a business, taking on involves taking existing resources
financial risks in the hope of profit. (those at hand) and experimenting,
repackaging, and reframing them so
2. Entrepreneurship - Its actions begin
they can be used in a way for which
at the nexus of a
they were not originally designed.
lucrative opportunity and an
11. Effectuate/ Effectuation - starts with
enterprising individual.
what is available and thinking about
3. Entrepreneurial Opportunities- These
the many possible alternatives that can
represent something new. It could be
be generated.
creating a new technological product
12. Cognitive Adaptability - It describes
for an existing product.
the extent to which entrepreneurs are
4. Entrepreneurial Action - a key to
dynamic, flexible, self-regulating, and
understanding entrepreneurial action
engage in the process of generating
is being able to assess the amount of
multiple decisions.
uncertainty.
13. Comprehension questions - are
5. Entrepreneurial thinking - individuals’
designed to increase entrepreneur’s
mental processes of overcoming
understanding of the nature of
ignorance to decide whether a signal
environment before they begin to
represents an opportunity for someone.
address an entrepreneurial challenge.
6. Meta cognition- it requires us to think
14. Intentions - As a general rule, the
about thinking, which requires and
stronger the intention to engage in a
helps provide knowledge and control
behavior, the more likely should be its
over out thinking and learning activities.
performance.
7. Think Structurally- Forming opportunity
15. Intentions – capture the motivational
beliefs requires creative mental leaps.
factors that influence a behavior.
8. Superficial similarities- exist when
16. High self-efficacy - leads to
the basic elements of technology
increased initiative and persistence,
resemble (match) the basic elements
thus, improved performance
of the market.
17. Reflection tasks – are designed to
9. Structural similarities- exist when the
stimulate entrepreneurs to think about
underlying mechanisms of the
the current situation in terms of
technology resemble (match) the
similarities and differences.
underlying mechanisms of the market.
18. Sustainable Entrepreneurship - It is
focused on preserving nature, life
support, and community sustainability threats, and offer goods and services
in the pursuit of perceived that are valued by customers.
opportunities to bring future products,
25. Rare - when it is possessed by few
processes, and services into existence
potential competitors.
for gain.
26. Inimitable - when replication of this
19. Strategic tasks – are designed to
combination of resources would be
stimulate entrepreneurs to think about
difficult for competitors.
which strategies are appropriate for
solving the problem (and why) or 27. Knowledge – it resides in the mind of
pursuing the opportunity (and how). an entrepreneur and in the
20. Connection tasks – are designed to collective mind of management and
stimulate entrepreneurs to think about employees.
the current situation in terms of
28. Market knowledge – refers to the
similarities to and differences from
entrepreneur’s possession of
situations previously faced and solved.
information, technology, know-how,
and skills that provide insight into a
market and its customers.
21. New Entry – refers to offering a
29. Technological knowledge – refers to
new product to an established or new
the entrepreneur’s possession of
market, offering an established
information, technology, know-how,
product to a new market, or creating
and skills that provide insight into
a new organization.
ways to create new knowledge.
22. Entrepreneurial strategy – represents
30. An error of omission – occurs from
the set of decisions, actions, and
the decision not to act on the new
reactions that first generate and
entry opportunity, only to find out
exploit a new entry in a way that
later that the entrepreneur had
maximizes the benefits of newness
underestimated his ability to create
and minimize its costs.
customer demand and/or to protect
23. Resources - are the basic building
the technology from imitation by
blocks to a firm’s functioning and
competitors.
performance.
31. Demand uncertainty - makes it
24. Valuable - when it enables the firm to
difficult to estimate future demand,
pursue opportunities, neutralize
which has important implications for
new venture performance as 38. Brain writing - is a form of written
overestimating and underestimating. brainstorming. It differs from classical
brainstorming by giving participants
32. Demand uncertainty - also makes it
more time to think than in a
difficult to predict if the market will
brainstorming session, where the
grow.
ideas are expressed spontaneously.
33. Franchising – is an example of a new
39. Reverse brainstorming is similar to
entry that focuses on imitation to
brainstorming, except that criticism is
reduce the risk of downside loss for
allowed.
the franchisee.
40. Gordon Method is a method for
34. “Me-too strategy” - This form of
developing new ideas when the
imitation is often referred to as a
individuals are unaware of the
“me-too strategy”.
problem.
35. Managing newness - It offers some
41. Collective notebook method deals
challenges not faced by
with developing a new idea by group
entrepreneurs who manage
members regularly recording ideas.
established firms.
42. Attribute listing deals with developing
a new idea by looking at the positives
and negatives.
36. Focus groups - a moderator leads a
43. Big-dream approach deals with
group of participants through an open,
developing a new idea by thinking
in-depth interview. For a new
without constraints.
product area, the moderator focuses
the discussion of the group in either a 44. Innovation - is the key to the
directive or nondirective manner. economic development of any
company, region of a country,
37. Brainstorming - is probably the most
or country itself.
well known and most widely used for
both creative problem solving as well
as idea generation. - stimulates 45. Major Events - It can create sudden
individuals to be creative by meeting shifts in public opinion or new buying
with others and participating in an habits overnight.
organized group experience.
46. Management Contract - It is another end consumer in the form of higher
way of entering a foreign market prices.
without a large equity investment. 54. Psycho graphics - It refers to interest,
47. Monetary Policy - It refers to interest activities, opinions, and helps explain
and exchange rates which in turn what consumer value and how they
impacts inflation. make their choices.
48. Conflicts - It may target a company's 55. Licensing - An arrangement between
employees as well as creating a delay two parties, where one party has
or total block in the free flow of a proprietary rights over some
company's goods and services. information, process or technology.
49. Turnkey Project - It is a method by 56. Intellectual property - This represents
which the entrepreneur can do important assets to the entrepreneur
international business without much risk. and should be understood even before
50. Licensing - It involves an entrepreneur engaging the services of an attorney.
who is a manufacturer (licensee), 57. Trademarks - It identifies the source or
giving a foreign manufacturer (licensor) sponsorships of certain goods or
the right to use a patent, trademark, services.
technology, production process, or 58. Licensing - It has a significant value as
product in return for the payment of a a marketing strategy to holders of
royalty. patents, trademarks, or copyrights to
51. Scanning environment - It Includes grow their business in new markets.
identifying a framework to analyze the 59. Trade secret - A protection against
four factors that shape or affect others revealing or disclosing
business. information that could be damaging to
52. Regulations - It can impact advertising business.
strategies in what can be said in the 60. Patents - This is granted by the
copy, labeling, ingredients, and government in exchange for disclosure
packaging or in the support needed of the invention.
for advertising claims in different 61. Worker’s Compensation - It provides
countries. benefits to employees in case of work-
53. Trade Policy - It can act as a form of related injury.
taxation as well, especially if countries 62. Contract - A legally enforceable
impose tariffs on goods which a agreement between two or more
company may need to pass on their parties as long as certain conditions
are met.
63. Life insurance - It can also provide products or even to supply large
financial protection for survivors of a quantities of materials on consignment.
sole proprietorship. 72. Lenders - They want to review the plan
64. Bonding - It protects a company in before buying a product that may
case of employee theft of funds or require significant long-term
protects contractor if he fails to commitment.
complete a job. 73. Contingency planning - It is important
65. Lenders - They are primarily interested for the entrepreneur to be prepared for
in the ability of the new venture to pay sudden changes or disasters that can
back the debt including interest within affect the implementation of the
a designated period of time. business plan.
66. Business Plan - It is a written document 74. Plan - It will also differ in scope
prepared by the entrepreneur that depending on the type of business or
describes all the relevant external and the anticipated size of the start up
internal elements involved in starting a operation.
new venture. 75. Marketing Plan- It focuses on not just
67. Investors - It often places more marketing issues but also such decisions
emphasis on the entrepreneur's as research and development,
character than lenders do, and often operations, manufacturing, personnel,
spend much time conducting financial projections and analysis, and
background checks. future growth strategies.
68. Budget - It includes capital 76. Product- Quality of components of
expenditures, direct operating materials, style, features, brand name,
expenses, and cash expenditures. packaging, sizes, service availability,
69. Planning - It is extremely important in and warranties
the early stages of any new venture 77. Price - Prior to setting the price, the
when the entrepreneur will need to entrepreneurs need to consider three
prepare a preliminary business plan. important elements: costs, markups,
70. Market information - It is one of the and competition.
initial pieces of information needed by 78. Promotion -It is necessary for the
the entrepreneur for the product or entrepreneur to inform potential
service. customers about the product’s
71. Suppliers - They want to see a business availability or to educate the
plan before signing a contract to consumer, using advertising media,
produce either components or finished
such as print, radio, television, and land, stocks, or bonds), or the assets of
social media. the consigner of the note.
79. Intensive – selection of as many 87. Account receivables - provide a good
retailers and/or wholesalers as possible basis for a loan, especially if the
80. Selective – choose only a small number customer is well known and
of channel members based on some creditworthy.
set of criteria or requirements. 88. Inventory loans - is another of the firm’s
81. Exclusive – select only one wholesaler assets that can often be the basis for a
and/or retailer. loan, particularly when the inventory is
82. Ownership- the owner is the individual more liquid and can be easily sold.
who starts the business. He has 89. Equipment loans - Equipment can be
full responsibility for the operations. used to secure long-term financing,
83. Liability- is one of the most critical financing the purchase of new
reasons for establishing a corporation equipment, financing used equipment
rather than any other form of business. already owned by the company, or
The proprietor and general partners lease financing.
are liable for all aspects of the business. 90. Real estate loan - is frequently used in
84. Self (personal funds) - Often referred to asset-based financing. This mortgage
as blood equity, the typical sources of financing is usually obtained to finance
personal funds include savings, life a company’s land, plant, or building,
insurance, or mortgage on a house or often up to 75 percent of its value.
car. 91. Cash flow financing - The other type of
85. Family and friends - usually provide debt financing frequently provided by
smaller amounts of equity funding for commercial banks and other financial
new ventures, reflecting in part the institution.
small amount of capital needed for 92. Installment loans can also be obtained
newest ventures getting started. by a venture with a track record of
86. Commercial Banks - are the source of sales and profits.
short-term funds for the entrepreneur 93. Straight commercial loan is a hybrid of
when collateral is available. This the installment loan by which funds
collateral can be in the form of are advanced to the company for 30-
business assets (land, equipment, or 90 days.
the building of the venture), personal 94. Long-term loans are loans (usually
assets (the entrepreneur’s house, car, available only to strong, mature
companies) can make funds available
for up to 10 years.
95. Character loans must have the assets
of the entrepreneur or some other
individual pledge as collateral or else
have the loan consigned by another
individual.
You might also like
- Set It and Forget It Small by Eric HoDocument36 pagesSet It and Forget It Small by Eric HoAditya Sharma50% (4)
- Grow From Within (PB): Mastering Corporate Entrepreneurship and InnovationFrom EverandGrow From Within (PB): Mastering Corporate Entrepreneurship and InnovationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Comprehensive M&a Due Diligence Checklist For BuyersDocument30 pagesComprehensive M&a Due Diligence Checklist For BuyersSimon Tseung100% (2)
- Prospeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahDocument5 pagesProspeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahOto ErwinNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting EntrepreneurshipAriana AriolaNo ratings yet
- Hatdog Ewan Ko DitoDocument6 pagesHatdog Ewan Ko DitominnieNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Competencies Why Is It Important? According To Man and ChanDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial Competencies Why Is It Important? According To Man and ChanDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Entrep (Mod12 4) ReviewerDocument12 pagesEntrep (Mod12 4) ReviewerBobby Ken Alfonso MorataNo ratings yet
- q1 Reviewer (Entrep)Document9 pagesq1 Reviewer (Entrep)kris krossNo ratings yet
- Techno ReviewerDocument4 pagesTechno ReviewerNathan ash ClintonNo ratings yet
- Nature and Relevance of EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesNature and Relevance of Entrepreneurshipvictorianomarielle03No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Chapter 1: The Entrepreneurial MindsetDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurship: Chapter 1: The Entrepreneurial Mindsetayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Prospeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahDocument5 pagesProspeperity: Good Luck For Final Exam Prepared By: Ira - SitizafirahabutholaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerSOLIS, John Ernest S.No ratings yet
- ENTREP REVIEWERDocument7 pagesENTREP REVIEWERNathalie Nichole I. Inductivo Pesta�oNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument2 pages3rd Quarter Exam ReviewerJheriko Mallari100% (2)
- Entrep ReviewerDocument20 pagesEntrep ReviewerBianca MalinabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Defining EntrepreneurshipDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Defining EntrepreneurshipAndrea CaparosoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerBianca De Castro VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Prelims ReviewerDocument1 pagePrelims Reviewerlyka deguzmanNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurshipTricia Baltazar0% (1)
- MGMT3004 Wk1 230711Document45 pagesMGMT3004 Wk1 230711LeeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Reviewer 2 NDDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurship Reviewer 2 NDIrish ZaragosaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter NotesDocument12 pages3rd Quarter NotesMary Grace BuenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-03 (Entraprenurship Process)Document3 pagesLecture-03 (Entraprenurship Process)Shanewaz Mahmood SohelNo ratings yet
- MidtermsDocument6 pagesMidtermsnirichdaitttNo ratings yet
- Entrep 12Document10 pagesEntrep 12Yhana jamille CalixterioNo ratings yet
- Entrep - ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrep - Reviewerjcmansanadis8126qcNo ratings yet
- Entrep Lesson 1Document1 pageEntrep Lesson 1Christian BaldoviaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerChristian BelanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2andiNo ratings yet
- 1 Entrepreneurship Examination ReviewerDocument7 pages1 Entrepreneurship Examination ReviewerJam Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerAj GoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial ReviewerDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurial ReviewerVeronique EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Entrep ReviewerDocument7 pagesEntrep ReviewerJustin JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Midterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerPrince LitchNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chapter1Document43 pagesEntrepreneurship Chapter1Altaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship Reviewerauhsojgab07No ratings yet
- Reviewer Entrep QuizDocument3 pagesReviewer Entrep Quizgrace bruanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument11 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerChristian BelanoNo ratings yet
- Importance of EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesImportance of EntrepreneurshipSteven Duane PradoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Entrepreneurial Skills and CompetenciesDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - Entrepreneurial Skills and CompetenciesLance Richard FlaminianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveDocument31 pagesChapter 1 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveJamilet RivasNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurshipAj GoNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2 - EntrepreneurshipDocument12 pagesWeek 1-2 - EntrepreneurshipGelli GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Entrep11Document3 pagesReviewer in Entrep11yannie isanan100% (3)
- Reviewer TechnoDocument2 pagesReviewer TechnoJennifer LigayaNo ratings yet
- GR 12 - EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesGR 12 - Entrepreneurshipdot comNo ratings yet
- Entrep ModuleDocument6 pagesEntrep Modulekaye maleNo ratings yet
- Entrep MidtermsDocument4 pagesEntrep Midtermskc.jarobillaNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship pt1Document4 pagesTechnopreneurship pt1aremtiii101No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ReviewerDocument15 pagesEntrepreneurship ReviewerMika VillarazaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning Week 3 6Document20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning Week 3 6zyra.position1seoNo ratings yet
- Ge Elec 3 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGe Elec 3 ReviewerJoy-Joy Fernandez AgotNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurshipJ-ira LariosaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam (Final)Document5 pages1st Quarter Exam (Final)Honie Jane D. AmerilaNo ratings yet
- App004 ReviewerDocument5 pagesApp004 ReviewerCatherine Sanchez RosarioNo ratings yet
- What Makes Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurial?: Saras D. SarasvathyDocument10 pagesWhat Makes Entrepreneurs Entrepreneurial?: Saras D. SarasvathyAshokNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesEntrep Q1 ReviewerCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Chapter 3Document3 pagesEntrep Chapter 3Carl Jacob LandichoNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Trends in Entrepreneurship ResearchDocument5 pages21st Century Trends in Entrepreneurship ResearchkimashleymandronNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 SolvedDocument10 pagesAssignment-1 SolvedMd. Shahriar Kabir RishatNo ratings yet
- C-Pcbu2 Case StudyDocument7 pagesC-Pcbu2 Case StudyJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- CONTENTDocument12 pagesCONTENTJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- Baroque Architecture.1Document52 pagesBaroque Architecture.1JOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways of Looking at Morality-7-20Document14 pages5 Ways of Looking at Morality-7-20JOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drawings of A BungalowDocument1 pageArchitectural Drawings of A BungalowJOHN PAULO I LICUPNo ratings yet
- FRAUD Upon The Court Motion - BOA V Julme-FL Case#CACE09-21933-051 - 2010-09-29 PDFDocument30 pagesFRAUD Upon The Court Motion - BOA V Julme-FL Case#CACE09-21933-051 - 2010-09-29 PDFStar Gazon100% (2)
- MC 006 2019 - PRRDDocument6 pagesMC 006 2019 - PRRDmarjNo ratings yet
- Perceived Financial KnowledgeDocument36 pagesPerceived Financial KnowledgeAnkh64No ratings yet
- Ramos Vs Bpi Family Savings BankDocument3 pagesRamos Vs Bpi Family Savings BankLorenzo Marvin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Check List For Audit Irregularities Ba MangaluruDocument15 pagesCheck List For Audit Irregularities Ba MangaluruKislayNikharNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On LoanDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Loanafeavbrpd100% (1)
- B.inggris N Kel.2Document34 pagesB.inggris N Kel.2Putra RakhmadaniNo ratings yet
- Press Release Saksoft Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Document5 pagesPress Release Saksoft Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Sandy SanNo ratings yet
- I. Pledge and Mortgage Essential Requisites Promise To DeliverDocument4 pagesI. Pledge and Mortgage Essential Requisites Promise To DeliverZaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- FR Ind As 20Document28 pagesFR Ind As 20Dheeraj TurpunatiNo ratings yet
- Activity Chapter 4: Ans. 2,320 SolutionDocument2 pagesActivity Chapter 4: Ans. 2,320 SolutionRandelle James FiestaNo ratings yet
- METROPOLITAN BANK & TRUST COMPANY Vs ASB HOLDINGS, INC. CASE DIGESTDocument2 pagesMETROPOLITAN BANK & TRUST COMPANY Vs ASB HOLDINGS, INC. CASE DIGESTNullus cumunisNo ratings yet
- Mint Discussion On FreshstartDocument3 pagesMint Discussion On FreshstartVinod ChanrasekharanNo ratings yet
- HSC Past Paper Questions 2u Maths - Time Payments 1Document1 pageHSC Past Paper Questions 2u Maths - Time Payments 1greycouncilNo ratings yet
- Jamuna Bank Presentation 1Document49 pagesJamuna Bank Presentation 1Md ShahnewazNo ratings yet
- Form-Business Assessment QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesForm-Business Assessment QuestionnaireOveine SmallNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Civil Service (Conduct) Rules 1966 (Eng)Document27 pagesKarnataka Civil Service (Conduct) Rules 1966 (Eng)Alissa BarnesNo ratings yet
- AB0520New PDFDocument78 pagesAB0520New PDFWilfrid FokaNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument26 pagesMoney MarketPigeons LoftNo ratings yet
- Informal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateDocument7 pagesInformal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateAkingbesote VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Weekly PDF January 2020 1st Week (1-7) by AffairsCloud PDFDocument23 pagesCurrent Affairs Weekly PDF January 2020 1st Week (1-7) by AffairsCloud PDFSailen GopeNo ratings yet
- Purchase and Sale AgreementDocument9 pagesPurchase and Sale Agreementapi-26011493No ratings yet
- Commodatum DigestsDocument10 pagesCommodatum DigestsCharlie PeinNo ratings yet
- Cash Management Challenges of Small Businesses in A Developing CommunityDocument11 pagesCash Management Challenges of Small Businesses in A Developing CommunitySuoi HoaNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Prospects of Interest Free Banking ServicesDocument6 pagesChallenges and Prospects of Interest Free Banking ServicesBiruk TadessaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Consultants: Sample Form of Evaluation ReportDocument35 pagesSelection of Consultants: Sample Form of Evaluation Reportkyawzaywin2No ratings yet
- Financial Modeling of Automobile Industry (Maruti Suzuki)Document26 pagesFinancial Modeling of Automobile Industry (Maruti Suzuki)Harshit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Practical Law US - Representations Warranties Covenants Rights and ConditionsDocument20 pagesPractical Law US - Representations Warranties Covenants Rights and ConditionsTinn ApNo ratings yet