Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsGeological Hazards
Geological Hazards
Uploaded by
aiahGeological hazards include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. Earthquakes cause ground shaking, surface faulting, and tsunamis as seismic waves move through the Earth's crust. Volcanic eruptions can produce pyroclastic flows of hot gases and ash and lahars, or mudflows of volcanic debris and water. Landslides occur on steep slopes and hills, often induced by rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, or other human activities that weaken the soil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ncm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Document27 pagesNcm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Camille RoqueroNo ratings yet
- DRRMChapt-4 1Document31 pagesDRRMChapt-4 1lester villarealNo ratings yet
- Lavender GDocument1 pageLavender GMelford LapnawanNo ratings yet
- Jonaif Page 2Document1 pageJonaif Page 2Jonaif HadjieGafor CosainNo ratings yet
- AyokonatamanaDocument2 pagesAyokonatamanaPaolo MalabananNo ratings yet
- Els Group 1Document1 pageEls Group 1jg4sfskrmgNo ratings yet
- Effects of EarthquakeDocument4 pagesEffects of EarthquakeRichard PascoNo ratings yet
- DRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedDocument38 pagesDRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedKaterina TagleNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson NotesDocument5 pagesGeography Lesson NotesDavid NdumbaNo ratings yet
- Module4 EarthquakeDocument9 pagesModule4 EarthquakeShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- DRR - 2 Reviewer: Geologic HazardDocument2 pagesDRR - 2 Reviewer: Geologic HazardJhames HarveyNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240313 - 194702 - 0000Document1 pageGeologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240313 - 194702 - 0000mikechesterdelacruz23No ratings yet
- Geological HazardsDocument29 pagesGeological Hazardsangelica petronaNo ratings yet
- Geology MikeeDocument105 pagesGeology MikeeAngelo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardDocument24 pagesEarthquake HazardreymundmaximoalbinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document45 pagesChapter 3Duane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Earthquak e Hazards: Prepared by Mariel Manansala / GAS2Document11 pagesEarthquak e Hazards: Prepared by Mariel Manansala / GAS2Ronelyn EsmeraldaNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 2Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 2Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument21 pagesVolcanoTrizia Marie ChanNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument16 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesPitchaiahTelagathotiNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards ScienceDocument3 pagesGeologic Hazards ScienceKrystalNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards-Mitigation and AdaptationDocument9 pagesNatural Hazards-Mitigation and AdaptationGuilljamin Neo Casas -HUMSS106- MALALA YOUSAFZAINo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 3Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 3Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- HazardsDocument22 pagesHazardsGLADYS OLIVEROS100% (1)
- Aayojan School of ArchitectureDocument6 pagesAayojan School of ArchitectureAnkit Kashmiri GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13: Hazards: Geologic Processes: How Do Geological Processes Occur?Document11 pagesLesson 13: Hazards: Geologic Processes: How Do Geological Processes Occur?Margarita EcaldreNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument24 pagesEarthquake HazardsHershey Nicole Nazareno ReginioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240114 - 200907 - 0000Document2 pagesGeologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240114 - 200907 - 0000Lance PiajoNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters.Document30 pagesNatural Disasters.judith idiosoloNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument6 pagesEarthquakeKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- DRR ReviewerDocument7 pagesDRR ReviewerRimar Jhon ParasNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument6 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- AtarNotes Work UploadDocument57 pagesAtarNotes Work UploadKaira JogNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument3 pagesDRRRernalelishajeanNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument17 pagesDRRRRaeniel TimbangNo ratings yet
- Earth Science REVIEWERDocument5 pagesEarth Science REVIEWERPobar, Elaiza Viel V. G9-PONCENo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument11 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster: (A) Concept of DisasterDocument9 pagesNatural Disaster: (A) Concept of DisasterVikram DasNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument4 pagesDRRRreneetinonga27No ratings yet
- Red Purple School Supplies About Me Education Presentation 1Document43 pagesRed Purple School Supplies About Me Education Presentation 1Jasmin Caryle SamarNo ratings yet
- Mitigation and AdaptationDocument9 pagesMitigation and AdaptationCindy Claire PilapilNo ratings yet
- DRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Document7 pagesDRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Ralph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Vivin N VNo ratings yet
- Geography Note Grade 8Document7 pagesGeography Note Grade 8hasanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: TsunamiDocument2 pagesEarthquake Hazards: TsunamiNica HuangNo ratings yet
- Eals ReviewerDocument16 pagesEals ReviewerJames Patrick CampoNo ratings yet
- Endogenous Processes:: Formation of MountainsDocument4 pagesEndogenous Processes:: Formation of MountainsAnonymous Xe7tYZK0IrNo ratings yet
- Pablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas City WWW - Batstate-U.edu - PH Tel. No. (043) 425-0139 Loc. 118Document8 pagesPablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas City WWW - Batstate-U.edu - PH Tel. No. (043) 425-0139 Loc. 118Sana NgaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Document15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Ar Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Opportunities and RisksDocument15 pagesOpportunities and Risks葉凌曦No ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Disaster and Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesEarthquakes: Disaster and Risk Assessmentlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument3 pagesEarthquakeRichard V. LomboyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 1 Pengantar Bencana GeologiDocument15 pagesKuliah 1 Pengantar Bencana GeologiGILANG ABIMANYUNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards and DisastersDocument14 pagesNatural Hazards and DisastersUsama MajidNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument61 pagesEARTHQUAKEkenshin copradaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: GroundshakingDocument3 pagesEarthquake Hazards: GroundshakingHannah Andrea LaparanNo ratings yet
- Eartquake Volcanic Eruption: LanslideDocument1 pageEartquake Volcanic Eruption: LanslideYesa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 Hazards Mitigation AdaptationDocument8 pagesHandout 4 Hazards Mitigation Adaptationwana grazeNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters, What & Why? : 1st Grade Geography Series: First Grade BooksFrom EverandNatural Disasters, What & Why? : 1st Grade Geography Series: First Grade BooksNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 4Document12 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 4aiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Tectonic Forces and ProcessesDocument2 pagesActivity 6 Tectonic Forces and ProcessesaiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesaiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3aiahNo ratings yet
- Session Guide in Earth and Life ScienceDocument31 pagesSession Guide in Earth and Life ScienceaiahNo ratings yet
Geological Hazards
Geological Hazards
Uploaded by
aiah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageGeological hazards include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. Earthquakes cause ground shaking, surface faulting, and tsunamis as seismic waves move through the Earth's crust. Volcanic eruptions can produce pyroclastic flows of hot gases and ash and lahars, or mudflows of volcanic debris and water. Landslides occur on steep slopes and hills, often induced by rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, or other human activities that weaken the soil.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGeological hazards include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. Earthquakes cause ground shaking, surface faulting, and tsunamis as seismic waves move through the Earth's crust. Volcanic eruptions can produce pyroclastic flows of hot gases and ash and lahars, or mudflows of volcanic debris and water. Landslides occur on steep slopes and hills, often induced by rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, or other human activities that weaken the soil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 pageGeological Hazards
Geological Hazards
Uploaded by
aiahGeological hazards include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. Earthquakes cause ground shaking, surface faulting, and tsunamis as seismic waves move through the Earth's crust. Volcanic eruptions can produce pyroclastic flows of hot gases and ash and lahars, or mudflows of volcanic debris and water. Landslides occur on steep slopes and hills, often induced by rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, or other human activities that weaken the soil.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
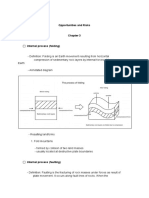
Geological Hazards
Classification of geological hazards
Earthquake
An earthquake is caused by the sudden release of slowly accumulating strain energy along a fault within the Earth’s
crust. Areas of surface or underground fracturing can experience earthquakes are known as earthquake fault zones.
Geologic hazard caused by earthquakes:
a. Ground shaking
b. Surface faulting
c. Tsunami
a. Ground shaking
Ground shaking or ground motion, a principal cause of the total collapse of structures, is the vibration of the ground
caused by seismic waves during an earthquake.
b. Surface faulting
Surface faulting is the tearing or fracturing of the ground surface by differential movement along a fault during an
earthquake.
c. Tsunami
A tsunami is a very high, large waves or seismic sea waves caused by the sudden movement of the ocean floor due to
earthquake or volcanic eruption.
Volcanic eruption
The location of the Philippines in the Pacific Ring of Fire is near the subduction zone of the Pacific Plate. Subduction
zone is the sinking region of a convergent plate boundary. Thus, it is prone to volcanic eruption.
Lahar- or mudflow is a flowing slurry of volcanic debris and water that originates on a volcano.
Pyroclastic flows- is consist of hot gases infused with incandescent ash and larger lava fragments. Also referred to as
nuée ardentes (glowing avalanches), these fiery flows are capable of racing down steep volcano.
landslides
Occur in a slope, steep hill or mountain. Usually, if the soil is not compact and devoid of vegetation, gravity can drive
soil and rocks to slide.
a. Rainfall-induced landslide
In sloping areas, the gravitational descent of loosened soil makes it possible for landslides to occur. This is a common
phenomenon in places with tropical climates after very intense and long rains during wet season.
b. Earthquake-induced landslide
This type of landside happens during or after an earthquake when a piece of weakened land slides off primarily due to
gravity.
The development of frail rock or soil foundation may be due to the natural makeup of soil consisting of soft layers;
man-made activities that induce erosion, such as deforestation, excavation, mining and other vibrations from natural
ground activities.
You might also like
- Ncm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Document27 pagesNcm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Camille RoqueroNo ratings yet
- DRRMChapt-4 1Document31 pagesDRRMChapt-4 1lester villarealNo ratings yet
- Lavender GDocument1 pageLavender GMelford LapnawanNo ratings yet
- Jonaif Page 2Document1 pageJonaif Page 2Jonaif HadjieGafor CosainNo ratings yet
- AyokonatamanaDocument2 pagesAyokonatamanaPaolo MalabananNo ratings yet
- Els Group 1Document1 pageEls Group 1jg4sfskrmgNo ratings yet
- Effects of EarthquakeDocument4 pagesEffects of EarthquakeRichard PascoNo ratings yet
- DRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedDocument38 pagesDRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedKaterina TagleNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson NotesDocument5 pagesGeography Lesson NotesDavid NdumbaNo ratings yet
- Module4 EarthquakeDocument9 pagesModule4 EarthquakeShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- DRR - 2 Reviewer: Geologic HazardDocument2 pagesDRR - 2 Reviewer: Geologic HazardJhames HarveyNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240313 - 194702 - 0000Document1 pageGeologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240313 - 194702 - 0000mikechesterdelacruz23No ratings yet
- Geological HazardsDocument29 pagesGeological Hazardsangelica petronaNo ratings yet
- Geology MikeeDocument105 pagesGeology MikeeAngelo AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardDocument24 pagesEarthquake HazardreymundmaximoalbinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document45 pagesChapter 3Duane AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Earthquak e Hazards: Prepared by Mariel Manansala / GAS2Document11 pagesEarthquak e Hazards: Prepared by Mariel Manansala / GAS2Ronelyn EsmeraldaNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 2Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 2Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument21 pagesVolcanoTrizia Marie ChanNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument16 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesPitchaiahTelagathotiNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards ScienceDocument3 pagesGeologic Hazards ScienceKrystalNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards-Mitigation and AdaptationDocument9 pagesNatural Hazards-Mitigation and AdaptationGuilljamin Neo Casas -HUMSS106- MALALA YOUSAFZAINo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 3Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 3Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- HazardsDocument22 pagesHazardsGLADYS OLIVEROS100% (1)
- Aayojan School of ArchitectureDocument6 pagesAayojan School of ArchitectureAnkit Kashmiri GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13: Hazards: Geologic Processes: How Do Geological Processes Occur?Document11 pagesLesson 13: Hazards: Geologic Processes: How Do Geological Processes Occur?Margarita EcaldreNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument24 pagesEarthquake HazardsHershey Nicole Nazareno ReginioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Geologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240114 - 200907 - 0000Document2 pagesGeologic Hazards Educational Infographic in Blue and YellowLine Drawing ST - 20240114 - 200907 - 0000Lance PiajoNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters.Document30 pagesNatural Disasters.judith idiosoloNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument6 pagesEarthquakeKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- DRR ReviewerDocument7 pagesDRR ReviewerRimar Jhon ParasNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument6 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- AtarNotes Work UploadDocument57 pagesAtarNotes Work UploadKaira JogNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument3 pagesDRRRernalelishajeanNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument17 pagesDRRRRaeniel TimbangNo ratings yet
- Earth Science REVIEWERDocument5 pagesEarth Science REVIEWERPobar, Elaiza Viel V. G9-PONCENo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument11 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster: (A) Concept of DisasterDocument9 pagesNatural Disaster: (A) Concept of DisasterVikram DasNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument4 pagesDRRRreneetinonga27No ratings yet
- Red Purple School Supplies About Me Education Presentation 1Document43 pagesRed Purple School Supplies About Me Education Presentation 1Jasmin Caryle SamarNo ratings yet
- Mitigation and AdaptationDocument9 pagesMitigation and AdaptationCindy Claire PilapilNo ratings yet
- DRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Document7 pagesDRRR 11 Reviewer Q2Ralph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Vivin N VNo ratings yet
- Geography Note Grade 8Document7 pagesGeography Note Grade 8hasanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: TsunamiDocument2 pagesEarthquake Hazards: TsunamiNica HuangNo ratings yet
- Eals ReviewerDocument16 pagesEals ReviewerJames Patrick CampoNo ratings yet
- Endogenous Processes:: Formation of MountainsDocument4 pagesEndogenous Processes:: Formation of MountainsAnonymous Xe7tYZK0IrNo ratings yet
- Pablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas City WWW - Batstate-U.edu - PH Tel. No. (043) 425-0139 Loc. 118Document8 pagesPablo Borbon Main II, Alangilan Batangas City WWW - Batstate-U.edu - PH Tel. No. (043) 425-0139 Loc. 118Sana NgaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Document15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Architecture: Presented by Naveen Minj 19122035 P.B.V. Laxman 19122043Ar Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Opportunities and RisksDocument15 pagesOpportunities and Risks葉凌曦No ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Disaster and Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesEarthquakes: Disaster and Risk Assessmentlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument3 pagesEarthquakeRichard V. LomboyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 1 Pengantar Bencana GeologiDocument15 pagesKuliah 1 Pengantar Bencana GeologiGILANG ABIMANYUNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards and DisastersDocument14 pagesNatural Hazards and DisastersUsama MajidNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument61 pagesEARTHQUAKEkenshin copradaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: GroundshakingDocument3 pagesEarthquake Hazards: GroundshakingHannah Andrea LaparanNo ratings yet
- Eartquake Volcanic Eruption: LanslideDocument1 pageEartquake Volcanic Eruption: LanslideYesa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 Hazards Mitigation AdaptationDocument8 pagesHandout 4 Hazards Mitigation Adaptationwana grazeNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters, What & Why? : 1st Grade Geography Series: First Grade BooksFrom EverandNatural Disasters, What & Why? : 1st Grade Geography Series: First Grade BooksNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 4Document12 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 1 Week 4aiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Tectonic Forces and ProcessesDocument2 pagesActivity 6 Tectonic Forces and ProcessesaiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Tectonic Plate BoundariesaiahNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3aiahNo ratings yet
- Session Guide in Earth and Life ScienceDocument31 pagesSession Guide in Earth and Life ScienceaiahNo ratings yet