Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
Uploaded by
Christine Jade TanThis document provides information about carbohydrates including their structure, function, and classification. Carbohydrates are the most abundant bioorganic molecules and are produced through photosynthesis, storing chemical energy. They are classified based on their products after acid hydrolysis into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down, while disaccharides contain two bonded monosaccharide units and polysaccharides contain thousands of bonded units serving structural functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Unit 8 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 8 Study Guidegavin100% (1)
- Guidelines For Triage of Obstetric PatientsDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Triage of Obstetric Patientsastroirma0% (2)
- (CN 112) 1st Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages(CN 112) 1st Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Bio ChemDocument14 pagesBio Chemmary balansagNo ratings yet
- 1BIOMOLECULESDocument85 pages1BIOMOLECULESShoto TodorokiNo ratings yet
- Group 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinDocument17 pagesGroup 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinSyndy BisonayaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and GlycobiologyDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates and GlycobiologyjaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument82 pagesCarbohydratesfa2008294No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pagesBiochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellsDocument2 pages4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellscarlNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- SMB1102Document164 pagesSMB1102supremesiddharth0No ratings yet
- Chapter2 Carbohydrates 1Document66 pagesChapter2 Carbohydrates 1Alice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Introductory ArticleDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates: Introductory ArticleMauricio VidalNo ratings yet
- Science BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesScience BiomoleculesJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Module 3-CarbohydratesDocument14 pagesModule 3-Carbohydratesjanmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesLecture 10 CarbohydratesMohammedNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument27 pagesBiomoleculesStarsNo ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument15 pagesFood and NutritionAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFladywhite820No ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument15 pagesFood and Nutritionandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- of CarbohydrateDocument19 pagesof CarbohydrateshraddhagosNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Disaccharides - A Carbohydrate ThatDocument6 pagesBiochemistry: Disaccharides - A Carbohydrate ThatMary LimlinganNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd SemDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd Semorangeshibuya99No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates Biochemsaythename.smmaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument51 pagesCarbohydratesJabez CabahugNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules BiomoleculesDocument22 pagesBiomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules BiomoleculesAbhay RaghavNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec PPT 1Document7 pagesBiochem Lec PPT 1Jessi SalazarNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Module - 7Document26 pagesBiomolecules: Module - 7TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATEDocument14 pagesCARBOHYDRATEAbhay PatelNo ratings yet
- AULA 3 LipidiosDocument50 pagesAULA 3 LipidiosFernanda AvenaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesnbcNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SLG4Document16 pagesPhysical Science SLG4RALPH ABAQUITANo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY FinalDocument21 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY FinalJoliem Phya E. IdongNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesHsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Biochem CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesBiochem CarbohydratesKyle Andrei QuilaquilNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Chemistry BiomoleculesDocument22 pagesNCERT Class 12 Chemistry BiomoleculesAnant MalhotraNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratesJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesThe Chemistry of CarbohydratesANGELA DENISSE AMAT100% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesAkib AbidNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument105 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYVai SanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biomolecule Study NotesDocument317 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biomolecule Study NotesDharaneesh S.k.No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrates NotesBHAGYASHREE HIREMATHNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument5 pagesGenetics and Evolutionmahreen akramNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate WsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate WsJakie UbinaNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Document12 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Chris Francis Cia100% (1)
- Chapter-Iii:Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter-Iii:Biomolecules: Carbohydratesbereket gashuNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Seminar - CarbohydratesDocument25 pages1st Sem Seminar - CarbohydratesshararohitNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument48 pagesBiomoleculesalikhantech786No ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesMilena De CresentNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument54 pagesCARBOHYDRATESWanivwa NalweyaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Research - JaurigueDocument7 pagesBiochem Research - JauriguePauline Yvonne JaurigueNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson-1Document18 pagesBiochemistry Lesson-1Priyadarshini LenkaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates in Food Science: Carbohydrates Are Sugar andDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates in Food Science: Carbohydrates Are Sugar andCaryl Alvarado Silang0% (1)
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Aldehyde (R-CHO)Document41 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Aldehyde (R-CHO)John Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument14 pagesBiochemistryAstuti GendaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument13 pagesENGLISHChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Document1 pageEnvironmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tintin's 1ST Lab Act BioDocument2 pagesTintin's 1ST Lab Act BioChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Transes 20231108 211459 0000Document1 pageBiochemistry Transes 20231108 211459 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Brochure Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesBrochure Skeletal SystemChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument3 pagesTan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- AortaDocument6 pagesAortaChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument5 pagesTan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System QuizDocument2 pagesMuscular System QuizChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Pathogens: Fungal Pathogens of Maize Gaining Free Passage Along The Silk RoadDocument16 pagesPathogens: Fungal Pathogens of Maize Gaining Free Passage Along The Silk RoadNyemaigbani VictoryNo ratings yet
- EFM Microscope For MitosisDocument4 pagesEFM Microscope For MitosisAjit ChambalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Cognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 3rd Edition e Bruce Goldstein PDF Full ChapterDocument34 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Cognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 3rd Edition e Bruce Goldstein PDF Full Chaptercadie.tutressrwwsn100% (21)
- SeanWilliamsonThesisFinal PDFDocument248 pagesSeanWilliamsonThesisFinal PDFLê Thị Ngọc ĐiệpNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2BRDocument14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2BRImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- LRD DIV SPE FM 001a RITM Lab Test Request Form - Clinical Lab 1Document1 pageLRD DIV SPE FM 001a RITM Lab Test Request Form - Clinical Lab 1Megen PLCNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 TestDocument3 pagesGrade 5 TestDr-Hani Elsayed Sharaf EldinNo ratings yet
- Crossing Over 1Document5 pagesCrossing Over 1Malik HamzaNo ratings yet
- Herbaceous Plant - WikipediaDocument2 pagesHerbaceous Plant - WikipediaKabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Revision Term 1 - 2021Document27 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Revision Term 1 - 2021RyanNo ratings yet
- L8 Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument15 pagesL8 Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationNaomi AceroNo ratings yet
- ERQ EvolutionDocument6 pagesERQ EvolutionmayaNo ratings yet
- Roja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT IiDocument37 pagesRoja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT Iideepuphysio100% (3)
- Dieta Baja en CarbohidratosDocument19 pagesDieta Baja en CarbohidratosESTUARDO ENRIQUE JO ORELLANANo ratings yet
- On Anger Albert RothenbergDocument7 pagesOn Anger Albert RothenbergelenojofeministaNo ratings yet
- Landscape ArchitectureDocument2 pagesLandscape ArchitectureJoy CadornaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology ExpDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology Expbestmadeeasy100% (3)
- High Hydrostatic Processing Pressure in CheeseDocument18 pagesHigh Hydrostatic Processing Pressure in CheesePuspaNo ratings yet
- Blue Copper ProteinDocument13 pagesBlue Copper ProteinKundan OjhaNo ratings yet
- Contoh UAS XI MADocument4 pagesContoh UAS XI MAChubbaydillahNo ratings yet
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder The Neurobiological Impact of Psychological TraumaDocument17 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder The Neurobiological Impact of Psychological TraumaMariana VilcaNo ratings yet
- Tala Zeer - Meisosi Revision Worksheet Copy 2Document2 pagesTala Zeer - Meisosi Revision Worksheet Copy 2Tala ZeerNo ratings yet
- MDthesis PDFDocument174 pagesMDthesis PDFFifi RohmatinNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Body Movements Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 6 Body Movements Worksheet PDFsifat mongaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAkashNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Document20 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Jerald De La CruzNo ratings yet
- 0711 Performer ManualDocument15 pages0711 Performer ManualTake OtaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Biology EDUNCLEDocument54 pagesInheritance Biology EDUNCLEEvita Almeida100% (1)
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
Uploaded by
Christine Jade Tan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageThis document provides information about carbohydrates including their structure, function, and classification. Carbohydrates are the most abundant bioorganic molecules and are produced through photosynthesis, storing chemical energy. They are classified based on their products after acid hydrolysis into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down, while disaccharides contain two bonded monosaccharide units and polysaccharides contain thousands of bonded units serving structural functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Copy of BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES_20231108_211654_0000
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about carbohydrates including their structure, function, and classification. Carbohydrates are the most abundant bioorganic molecules and are produced through photosynthesis, storing chemical energy. They are classified based on their products after acid hydrolysis into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down, while disaccharides contain two bonded monosaccharide units and polysaccharides contain thousands of bonded units serving structural functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211654 - 0000
Uploaded by
Christine Jade TanThis document provides information about carbohydrates including their structure, function, and classification. Carbohydrates are the most abundant bioorganic molecules and are produced through photosynthesis, storing chemical energy. They are classified based on their products after acid hydrolysis into monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that cannot be further broken down, while disaccharides contain two bonded monosaccharide units and polysaccharides contain thousands of bonded units serving structural functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
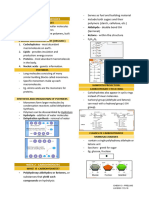
BIOCHEMISTRY
BSN CARBOHYDRATES
COLLEGE OF HEALTH AND
SCIENCES EDUCATION
CARBOHYDRATES - STRUCTURE CLASSIFICATION BASED ON
AND FUNCTION PRODUCTS OF ACID HYDROLYSIS:
CARBOHYDRATES MONOSACCHARIDES
the most abundant class of bioorganic the simple sugars.
molecules on earth. contain a single polyhydroxy aldehyde or
produced by the photosynthetic activity of the polyhydroxy ketone unit.
green plants. cannot be degraded into simpler products by
also referred to as saccharides because of hydrolysisreactions.
the sweet taste of many carbohydrates pure monosaccharides are water- soluble,
(latin, saccharum, meaning sugar) white, crystalline solids.
storehouse of chemical energy (glucose, DISACCHARIDES
starch,glycogen) contains 2 monosaccharide units covalently
a gram of digested carbohydrate gives bonded to each other.
about 4 kcal ofenergy. –crystalline and water soluble substances
complex carbohydrates are best for diet. upon hydrolysis they produce
supportive structural components in plants monosaccharides.
and some animals (cellulose, chitin).
CARBONYL GROUP
form part of the structural framework of DNA carbonyl group is a chemically organic
& RNA. functional group composed of a carbon atom
carbohydrate “markers” on cell surfaces play double-bonded to an oxygen atom --> [C=O]
key roles in cell-cell recognition processes. the simplest carbonyl groups are
CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHY- aldehydes and ketones usually attached to
DRATES another carbon compound.
simpler formula:
OLIGOSACCHARIDES
CnH2nOn or Cn(H2O)n (hydrates of C)
n = number of atmos contains 3-10 monosaccharide units -
polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy covalently bonded.
ketones or compounds that producesuch disaccharides are the most common type.
substances uponhydrolysis. trisaccharides (raffinose)
tetrasaccharides (stachyose)
free oligosaccharides, other than
disaccharides, are less common in nature.
usually found associated with proteins and
lipids in complex molecules that serve
structural and regulatory functions.
POLYSACCHARIDES
consist of tens of thousands of
monosaccharide units covalently bonded.
homopolysacchrides – polymers of a single
monosaccharide (glycogen, cellulose,starch)
9.
You might also like
- Unit 8 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 8 Study Guidegavin100% (1)
- Guidelines For Triage of Obstetric PatientsDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Triage of Obstetric Patientsastroirma0% (2)
- (CN 112) 1st Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages(CN 112) 1st Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Bio ChemDocument14 pagesBio Chemmary balansagNo ratings yet
- 1BIOMOLECULESDocument85 pages1BIOMOLECULESShoto TodorokiNo ratings yet
- Group 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinDocument17 pagesGroup 7: Bisonaya Capillo FallurinSyndy BisonayaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and GlycobiologyDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates and GlycobiologyjaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument82 pagesCarbohydratesfa2008294No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pagesBiochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellsDocument2 pages4.1.1. - Macromolecules and Composition of CellscarlNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 pagesCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- SMB1102Document164 pagesSMB1102supremesiddharth0No ratings yet
- Chapter2 Carbohydrates 1Document66 pagesChapter2 Carbohydrates 1Alice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Introductory ArticleDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates: Introductory ArticleMauricio VidalNo ratings yet
- Science BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesScience BiomoleculesJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Module 3-CarbohydratesDocument14 pagesModule 3-Carbohydratesjanmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesLecture 10 CarbohydratesMohammedNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument27 pagesBiomoleculesStarsNo ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument15 pagesFood and NutritionAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFladywhite820No ratings yet
- Food and NutritionDocument15 pagesFood and Nutritionandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- of CarbohydrateDocument19 pagesof CarbohydrateshraddhagosNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Disaccharides - A Carbohydrate ThatDocument6 pagesBiochemistry: Disaccharides - A Carbohydrate ThatMary LimlinganNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd SemDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd Semorangeshibuya99No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates Biochemsaythename.smmaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument51 pagesCarbohydratesJabez CabahugNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules BiomoleculesDocument22 pagesBiomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules Biomolecules BiomoleculesAbhay RaghavNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec PPT 1Document7 pagesBiochem Lec PPT 1Jessi SalazarNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Module - 7Document26 pagesBiomolecules: Module - 7TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATEDocument14 pagesCARBOHYDRATEAbhay PatelNo ratings yet
- AULA 3 LipidiosDocument50 pagesAULA 3 LipidiosFernanda AvenaNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesnbcNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SLG4Document16 pagesPhysical Science SLG4RALPH ABAQUITANo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY FinalDocument21 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY FinalJoliem Phya E. IdongNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesHsslive XII 2 Chemistry BiomoleculesRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Biochem CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesBiochem CarbohydratesKyle Andrei QuilaquilNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 12 Chemistry BiomoleculesDocument22 pagesNCERT Class 12 Chemistry BiomoleculesAnant MalhotraNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratesJobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesThe Chemistry of CarbohydratesANGELA DENISSE AMAT100% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesAkib AbidNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument105 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYVai SanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biomolecule Study NotesDocument317 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biomolecule Study NotesDharaneesh S.k.No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrates NotesBHAGYASHREE HIREMATHNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument5 pagesGenetics and Evolutionmahreen akramNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate WsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate WsJakie UbinaNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Document12 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Chris Francis Cia100% (1)
- Chapter-Iii:Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter-Iii:Biomolecules: Carbohydratesbereket gashuNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Seminar - CarbohydratesDocument25 pages1st Sem Seminar - CarbohydratesshararohitNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument48 pagesBiomoleculesalikhantech786No ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesMilena De CresentNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument54 pagesCARBOHYDRATESWanivwa NalweyaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Research - JaurigueDocument7 pagesBiochem Research - JauriguePauline Yvonne JaurigueNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson-1Document18 pagesBiochemistry Lesson-1Priyadarshini LenkaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates in Food Science: Carbohydrates Are Sugar andDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates in Food Science: Carbohydrates Are Sugar andCaryl Alvarado Silang0% (1)
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Aldehyde (R-CHO)Document41 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Aldehyde (R-CHO)John Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument14 pagesBiochemistryAstuti GendaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument13 pagesENGLISHChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Document1 pageEnvironmental Science Transes - 20231111 - 202740 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tintin's 1ST Lab Act BioDocument2 pagesTintin's 1ST Lab Act BioChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Transes 20231108 211459 0000Document1 pageBiochemistry Transes 20231108 211459 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211520 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211407 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Document1 pageBIOCHEMISTRY TRANSES - 20231108 - 211609 - 0000Christine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Brochure Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesBrochure Skeletal SystemChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument3 pagesTan - Lesson 1 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- AortaDocument6 pagesAortaChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Tan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningDocument5 pagesTan - Lesson 2 - Purposive Communication With Interactive LearningChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Muscular System QuizDocument2 pagesMuscular System QuizChristine Jade TanNo ratings yet
- Pathogens: Fungal Pathogens of Maize Gaining Free Passage Along The Silk RoadDocument16 pagesPathogens: Fungal Pathogens of Maize Gaining Free Passage Along The Silk RoadNyemaigbani VictoryNo ratings yet
- EFM Microscope For MitosisDocument4 pagesEFM Microscope For MitosisAjit ChambalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Cognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 3rd Edition e Bruce Goldstein PDF Full ChapterDocument34 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Cognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 3rd Edition e Bruce Goldstein PDF Full Chaptercadie.tutressrwwsn100% (21)
- SeanWilliamsonThesisFinal PDFDocument248 pagesSeanWilliamsonThesisFinal PDFLê Thị Ngọc ĐiệpNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2BRDocument14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI0) Paper 2BRImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- LRD DIV SPE FM 001a RITM Lab Test Request Form - Clinical Lab 1Document1 pageLRD DIV SPE FM 001a RITM Lab Test Request Form - Clinical Lab 1Megen PLCNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 TestDocument3 pagesGrade 5 TestDr-Hani Elsayed Sharaf EldinNo ratings yet
- Crossing Over 1Document5 pagesCrossing Over 1Malik HamzaNo ratings yet
- Herbaceous Plant - WikipediaDocument2 pagesHerbaceous Plant - WikipediaKabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Revision Term 1 - 2021Document27 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Revision Term 1 - 2021RyanNo ratings yet
- L8 Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument15 pagesL8 Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationNaomi AceroNo ratings yet
- ERQ EvolutionDocument6 pagesERQ EvolutionmayaNo ratings yet
- Roja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT IiDocument37 pagesRoja Ramani Vasamshetty MPT Iideepuphysio100% (3)
- Dieta Baja en CarbohidratosDocument19 pagesDieta Baja en CarbohidratosESTUARDO ENRIQUE JO ORELLANANo ratings yet
- On Anger Albert RothenbergDocument7 pagesOn Anger Albert RothenbergelenojofeministaNo ratings yet
- Landscape ArchitectureDocument2 pagesLandscape ArchitectureJoy CadornaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & Physiology ExpDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology Expbestmadeeasy100% (3)
- High Hydrostatic Processing Pressure in CheeseDocument18 pagesHigh Hydrostatic Processing Pressure in CheesePuspaNo ratings yet
- Blue Copper ProteinDocument13 pagesBlue Copper ProteinKundan OjhaNo ratings yet
- Contoh UAS XI MADocument4 pagesContoh UAS XI MAChubbaydillahNo ratings yet
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder The Neurobiological Impact of Psychological TraumaDocument17 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder The Neurobiological Impact of Psychological TraumaMariana VilcaNo ratings yet
- Tala Zeer - Meisosi Revision Worksheet Copy 2Document2 pagesTala Zeer - Meisosi Revision Worksheet Copy 2Tala ZeerNo ratings yet
- MDthesis PDFDocument174 pagesMDthesis PDFFifi RohmatinNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Body Movements Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 6 Body Movements Worksheet PDFsifat mongaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAkashNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Document20 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Jerald De La CruzNo ratings yet
- 0711 Performer ManualDocument15 pages0711 Performer ManualTake OtaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Biology EDUNCLEDocument54 pagesInheritance Biology EDUNCLEEvita Almeida100% (1)