Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skeletal Cytology Worksheet
Skeletal Cytology Worksheet
Uploaded by
Dan Klo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesThis document contains a worksheet assessing understanding of bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It includes matching, multiple choice, fill in the blank, true/false, short answer, and conceptual questions. The worksheet covers topics like bone cell types and functions, components of the extracellular matrix, how nutrients reach chondrocytes, cartilage types and locations, ligament and tendon composition, and injuries to these tissues.
Original Description:
A worksheet on the cells of the skeletal system.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a worksheet assessing understanding of bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It includes matching, multiple choice, fill in the blank, true/false, short answer, and conceptual questions. The worksheet covers topics like bone cell types and functions, components of the extracellular matrix, how nutrients reach chondrocytes, cartilage types and locations, ligament and tendon composition, and injuries to these tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesSkeletal Cytology Worksheet
Skeletal Cytology Worksheet
Uploaded by
Dan KloThis document contains a worksheet assessing understanding of bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It includes matching, multiple choice, fill in the blank, true/false, short answer, and conceptual questions. The worksheet covers topics like bone cell types and functions, components of the extracellular matrix, how nutrients reach chondrocytes, cartilage types and locations, ligament and tendon composition, and injuries to these tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Name:
Class:
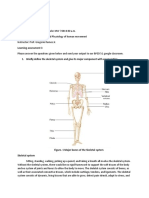
Bone:
Part A: Matching (5 minutes)
Directions: Match each bone cell type to its correct function.
Bone Cells:
1. Osteoblasts
2. Osteocytes
3. Osteoclasts
Functions:
a. Mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue.
b. Bone-building cells responsible for forming new bone.
c. Cells that break down bone, releasing calcium and phosphorus into the bloodstream.
Part B: Short Answer (5 minutes)
Directions: Write a brief answer for each of the following questions.
1. Describe the primary components of the bone's extracellular matrix.
2. Why is the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts crucial for bone health?
Part C: True or False (5 minutes)
Directions: Indicate whether each statement is true or false by circling the correct option.
1. Collagen in bones provides rigidity and resistance to compression. [True / False]
2. Hydroxyapatite crystals are made up of mainly nitrogen and hydrogen. [True / False]
3. Vitamin D helps the body absorb proteins and fats for muscle health. [True / False]
Part D: Fill in the Blanks (3 minutes)
Directions: Use the word bank provided to complete the sentences below.
Word Bank: remodelling, calcium, osteocytes, phosphate, collagen
1. Bone ___________ refers to the continuous process of bone formation and
resorption.
2. ___________ and ___________ are crucial elements that give bones their hardness.
3. The flexibility and tensile strength of bones are primarily provided by ___________.
Part E: Conceptual Drawing (2 minutes)
Directions: In the space below, draw a simple diagram of the bone remodelling process,
showing both osteoblasts and osteoclasts at work.
Cartilage:
Part A: Matching (4 minutes)
Directions: Match each term to its correct description.
Terms:
1. Chondrocytes
2. Fibrocartilage
3. Proteoglycans
4. Elastic Cartilage
5. Lacunae
Descriptions:
a. Cavities in cartilage that house specific cells.
b. Large molecules that resist compression and make cartilage resilient.
c. Cells responsible for maintaining cartilage tissue.
d. Flexible type of cartilage found in the ear and epiglottis.
e. Tough cartilage found in the knee menisci and intervertebral discs.
Part B: Multiple Choice (4 minutes)
Directions: Circle the best answer.
1. Which fibers primarily provide tensile strength to cartilage?
a) Elastic Fibers
b) Collagen Fibers
c) Keratin Fibers
2. What is a notable feature of cartilage when compared to other tissues?
a) High blood supply
b) Presence of many nerves
c) Avascular nature
Part C: Short Answer (6 minutes)
Directions: Provide a concise answer for each question.
1. Why is the avascular nature of cartilage significant in terms of injury and repair?
2. How do nutrients reach chondrocytes if cartilage lacks blood vessels?
3. Describe the primary role of chondroblasts in cartilage formation.
Part D: Concept Mapping (4 minutes)
Directions: Draw lines to connect each type of cartilage to its associated primary location or
feature.
Cartilage Types:
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Locations/Features:
Nose
Intervertebral Discs
Ear
Most abundant type
Strongest type
Highly flexible
Part E: Critical Thinking (2 minutes)
Directions: Given its composition and properties, why might cartilage serve as the tissue in
our noses and ears?
Tendons/Ligaments:
Part A: Matching (5 minutes)
Directions: Match each term to its correct description.
Terms:
1. Ligaments
2. Tendons
3. Fibroblasts
4. Collagen
5. Elastin
Descriptions: a. Provides elasticity, especially prevalent in ligaments. b. Principal cells in both
structures, responsible for producing the extracellular matrix. c. Connects muscles to bones.
d. Offers strength and flexibility, predominantly Type I in both structures. e. Connects bones
to other bones.
Part B: Fill in the Blanks (3 minutes)
Directions: Complete the sentences using the words provided.
Word Bank: Sprain, Strain, Joints, Muscle-bone junctions, Slow.
1. Ligaments stabilize _______ while tendons transmit force.
2. An injury to a ligament is called a _______.
3. Tendon injuries are referred to as _______.
4. Tendons are primarily found at _______.
5. The limited blood supply in tendons and ligaments can make healing _______.
Part C: True or False (3 minutes)
Directions: Indicate whether each statement is true or false.
1. Fibrocytes are mature fibroblasts.
2. Ground substance in tendons and ligaments is a solid material.
3. Both ligaments and tendons predominantly contain Type II collagen.
4. Ligaments and tendons both play crucial roles in movement and stability.
Part D: Short Answer (5 minutes)
Directions: Provide a brief answer to each question.
1. How does the molecular makeup of ligaments and tendons contribute to their
respective functions?
2. Why might a severe tear in a tendon or ligament require surgical intervention?
3. Based on what you've learned, hypothesize why athletes often suffer from sprains
and strains.
Part E: Conceptual Application (4 minutes)
Directions: Given their function and composition, explain why it's crucial for athletes,
especially in high-contact sports, to regularly strengthen and condition their ligaments and
tendons.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Understanding Anatomy Physiology 3rd Edition Gale Sloan ThompsonDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Understanding Anatomy Physiology 3rd Edition Gale Sloan Thompsonamydominguez09081990kze100% (23)
- Test Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition by TortoraDocument57 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15th Edition by Tortoramatthewhannajzagmqiwdt100% (23)
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy 6th Edition Kenneth SaladinDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Human Anatomy 6th Edition Kenneth Saladinjordanmeyersszkrywqfog100% (31)
- Solution Manual For Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory Manual Making Connections Cat Version 2nd Edition Catharine C WhitingDocument11 pagesSolution Manual For Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory Manual Making Connections Cat Version 2nd Edition Catharine C WhitingSamuelBrownnwoxi100% (92)
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument47 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Tortora Test Bankrandallperrykdepbtozqf100% (28)
- Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Kenneth SaladinDocument39 pagesTest Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Kenneth Saladinthomasbrownmjtbonysgk100% (21)
- The Collective Memory ReaderDocument6 pagesThe Collective Memory Readernordurljos50% (6)
- Human Anatomy 8th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual DownloadDocument14 pagesHuman Anatomy 8th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual DownloadMary Brown100% (23)
- Roscommon Newspapers Volume 2Document16 pagesRoscommon Newspapers Volume 2St. John's Parish Heritage Group.No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank DownloadDocument33 pagesIntroduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test Bank DownloadGary Harris100% (21)
- Principles of Anatomy Physiology 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument63 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy Physiology 13th Edition Tortora Test Banksociablyrunning6y4vpe100% (25)
- Introduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument33 pagesIntroduction To The Human Body 10th Edition Tortora Test Bankbrittanywilliamsonxpmzdnebgt100% (34)
- Introduction To The Human Body 10Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument54 pagesIntroduction To The Human Body 10Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFjohnvuaaefxh100% (12)
- Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues 7Th Edition Johnson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesHuman Biology Concepts and Current Issues 7Th Edition Johnson Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdavid.cordero230100% (11)
- BIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)Document11 pagesBIOLOGY WORKSHEET-ANIMAL TISSUES (Launch Pad 1)RaashiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Sample Homework QuestionsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Sample Homework QuestionsMawuli Wilson ApetiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 15Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 15Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFAndrewRobinsonixez100% (9)
- PDF Anatomy and Physiology Marieb 5Th Edition Test Bank Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument44 pagesPDF Anatomy and Physiology Marieb 5Th Edition Test Bank Online Ebook Full Chapterandrew.bandy876100% (10)
- Anatomy Learning Assessment 3Document13 pagesAnatomy Learning Assessment 3Jay Lure Gomez BaguioNo ratings yet
- C9apstudy GuideDocument37 pagesC9apstudy GuidejqtdNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 1 Muscle N Bone 20222023Document1 pageTUTORIAL 1 Muscle N Bone 20222023Dhanen DranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 AnswersDocument19 pagesChapter 8 Answersdaniell.baii2526No ratings yet
- PDF Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 4Th Edition by Marieb Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument45 pagesPDF Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 4Th Edition by Marieb Online Ebook Full Chaptercarolina.bay108100% (4)
- ICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionDocument4 pagesICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- PDF Test Bank For Anatomy Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 9Th Edition Kenneth Saladin Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument54 pagesPDF Test Bank For Anatomy Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 9Th Edition Kenneth Saladin Online Ebook Full Chapterrobert.wilkins535100% (3)
- Document (1) OkDocument8 pagesDocument (1) OkShiv Thakkar1No ratings yet
- Medical English: I. Warm Up II. Meaningful Vocabulary Iii. Functions of Skeleton IV. Types of BonesDocument2 pagesMedical English: I. Warm Up II. Meaningful Vocabulary Iii. Functions of Skeleton IV. Types of BonesMohammed Abdul AleemNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 1st by PattonDocument12 pagesSolution Manual For Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 1st by PattonDeanBucktdjx100% (41)
- Biomechanics 2015Document2 pagesBiomechanics 2015Guilherme GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- P - 7 Science Lesson NotesDocument104 pagesP - 7 Science Lesson Notesmichaelopi63No ratings yet
- Chaper 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone StructureDocument25 pagesChaper 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone StructurelolasparkleNo ratings yet
- CSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Biology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesBiology M10 Musculo-Skeletal SystemMark Nathaniel100% (2)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesThe Skeletal SystemDaryhen GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Test Bank DownloadDocument69 pagesMaders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 8th Edition Susannah Nelson Longenbaker Test Bank DownloadMelissa Resto100% (19)
- Science LPDocument2 pagesScience LPBizmates WenaNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh19Document10 pagesUnlock SGCh19Silax100% (1)
- Ch. 6 Student Packet (ANP 1)Document8 pagesCh. 6 Student Packet (ANP 1)Alex ZhangNo ratings yet
- Bone Physiology NotesDocument6 pagesBone Physiology NotesTAMMY CHARLENE HARTELNo ratings yet
- Bones and Skeletal TissueDocument10 pagesBones and Skeletal Tissuejinni0926No ratings yet
- Science CH 8Document10 pagesScience CH 8DarkNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Behavior 12th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument65 pagesPhysiology of Behavior 12th Edition Carlson Test Bankgabrielcongk6s0nc100% (28)
- Microsoft Word - The Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesMicrosoft Word - The Skeletal SystemNino Alania0% (2)
- BI 275 Exam II 2008.docx2Document8 pagesBI 275 Exam II 2008.docx2Alexandra Lauren EzellNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Behavior 11th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument46 pagesPhysiology of Behavior 11th Edition Carlson Test Bankthornyrooftreehjv100% (36)
- Packet Anatomy Week 3 Packet 3Document27 pagesPacket Anatomy Week 3 Packet 3Sevilla ErnestdonNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument22 pagesTissuesmustafathegreat02No ratings yet
- Ch6Bone StudentDocument66 pagesCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13No ratings yet
- Histology PYQ EditedDocument56 pagesHistology PYQ EditedA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Musculo-Skeletal System Q2, Week 1Document8 pagesLesson 1: Musculo-Skeletal System Q2, Week 1Grace Micah Dayucos CaisioNo ratings yet
- 19 BIOL 220 SG CH 6Document3 pages19 BIOL 220 SG CH 6Shirley PinedaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy. Lesson 6Document4 pagesAnaphy. Lesson 6Richee LunnayNo ratings yet
- PERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 4.2-Learning TaskDocument5 pagesPERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 4.2-Learning TaskEmmalyn PeridaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson DownloadDocument57 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition Gerard J Tortora Bryan H Derrickson Downloadbradleypetersonbqnsyzaegm100% (24)
- PDF Test Bank For Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 6Th Edition Frederic H Martini Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument68 pagesPDF Test Bank For Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 6Th Edition Frederic H Martini Online Ebook Full Chapterdaniel.duncan540100% (2)
- Science 6 TG q2Document112 pagesScience 6 TG q2Pinaka ShungaNo ratings yet
- Anatomyand Physiology Ratio Activity SAS 8-14Document8 pagesAnatomyand Physiology Ratio Activity SAS 8-14Clarisse Biagtan CerameNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 8Th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesHuman Anatomy 8Th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFStevenAdkinsyjmd100% (11)
- Bio Learn Lab Activities Musculoskeletal Full StudentDocument9 pagesBio Learn Lab Activities Musculoskeletal Full StudentHeydrick GuyoNo ratings yet
- (Checked) Rodriguez Maria Andrea N Skeletal System Worksheet 5Document16 pages(Checked) Rodriguez Maria Andrea N Skeletal System Worksheet 5Mira AurumtinNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument25 pagesThe Skeletal SystemEyda CartagenaNo ratings yet
- The Benchwarmers Is A Comedy-Sports Movie That Was Made inDocument10 pagesThe Benchwarmers Is A Comedy-Sports Movie That Was Made inapi-302024270No ratings yet
- BLACKBEARD: The Golden Age of Piracy: Condensed RulesDocument8 pagesBLACKBEARD: The Golden Age of Piracy: Condensed RulesT DarbNo ratings yet
- Adam and Rob: Elementary Podcast Transcript - Series 3 Episode 10Document3 pagesAdam and Rob: Elementary Podcast Transcript - Series 3 Episode 10Ridwan baritoNo ratings yet
- Summerville V CA G. R. No. 158767Document7 pagesSummerville V CA G. R. No. 158767Janine Kae UrsulumNo ratings yet
- Case Digest: Banco Filipino Savings and Mortgage Bank V. Tala Realty Services CorporationDocument2 pagesCase Digest: Banco Filipino Savings and Mortgage Bank V. Tala Realty Services CorporationRuiz Arenas AgacitaNo ratings yet
- Memorial-Prosecution-Surana Trial AdvocacyDocument137 pagesMemorial-Prosecution-Surana Trial AdvocacyNausheenNo ratings yet
- St. Paul College Quezon City, Et Al. vs. Remigio Michael A. Ancheta II and Cynthia A. Ancheta, G.R. No. 169905. September 7, 2011Document8 pagesSt. Paul College Quezon City, Et Al. vs. Remigio Michael A. Ancheta II and Cynthia A. Ancheta, G.R. No. 169905. September 7, 2011KhiarraNo ratings yet
- Request For Legal OpinionDocument8 pagesRequest For Legal OpinionJorge M. GarciaNo ratings yet
- People Vs GomezDocument1 pagePeople Vs GomezVanessa Grace TamarayNo ratings yet
- American Revolution: Discuss The Causes, Nature, and Significance of The American RevolutionDocument4 pagesAmerican Revolution: Discuss The Causes, Nature, and Significance of The American RevolutionRamita Udayashankar100% (4)
- Civ3701 201 1 23 1Document12 pagesCiv3701 201 1 23 1mphephumillicent602No ratings yet
- David McCalden - The Amazing, Rapidly Shrinking HolocaustDocument14 pagesDavid McCalden - The Amazing, Rapidly Shrinking HolocaustmadlenedNo ratings yet
- Digest CastilloDocument3 pagesDigest CastilloMaureen PátajoNo ratings yet
- Shit HappensDocument160 pagesShit HappensJehan DaruwalaNo ratings yet
- IB History HL Internal Assessment:: "To What Extend Can Germany's Declaration of War in 1914 Be Justified?"Document8 pagesIB History HL Internal Assessment:: "To What Extend Can Germany's Declaration of War in 1914 Be Justified?"Modestas ZiugzdaNo ratings yet
- Digests For Cases On AppealDocument12 pagesDigests For Cases On AppealDanJalbunaNo ratings yet
- Melting Pot LawsuitDocument75 pagesMelting Pot LawsuitSam GnerreNo ratings yet
- Handbook On The Use of Force For Private PDFDocument98 pagesHandbook On The Use of Force For Private PDFSalvador Dagoon JrNo ratings yet
- Plaintiff's Opposition To US Bank DemurrerDocument19 pagesPlaintiff's Opposition To US Bank DemurrerCameron Totten100% (4)
- Banal vs. TadeoDocument1 pageBanal vs. TadeoDeus Dulay100% (2)
- Overseas VisaDocument4 pagesOverseas VisaSatish RamananNo ratings yet
- Causes of World War I: Name - Date - PDDocument2 pagesCauses of World War I: Name - Date - PDAlexis CarranzaNo ratings yet
- BAMBIDocument3 pagesBAMBILuisito MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nawaz Sharif Second TenureDocument7 pagesNawaz Sharif Second Tenureafsheen24akramNo ratings yet
- Child Protection Policy Tumbao ESDocument16 pagesChild Protection Policy Tumbao ESlloyd vincent magdaluyo50% (2)
- Memories Currencies of CountriesDocument13 pagesMemories Currencies of CountriesQIE PSNo ratings yet
- Rahul Sharma vs. StateDocument4 pagesRahul Sharma vs. StateShaiwal SatyarthiNo ratings yet
- Article Slavery and Christianity 1st To 15th CenturiesDocument17 pagesArticle Slavery and Christianity 1st To 15th CenturiesHoscoFoodsNo ratings yet