Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Viruses
Viruses
Uploaded by
eveleenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Viruses
Viruses
Uploaded by
eveleenCopyright:
Available Formats
Viruses
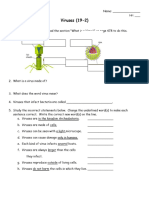
What is a virus?
Core of nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) surrounded by a _____________________
Dead or alive
Do not display the characteristics of any living things
Outside a host cell they are considered non living chemicals, however inside the host cell
they can replicate making them alive
_______________________________
Typical structure of a virus (bacteriophage) Remember this is a typical
structure, there are lots of
other shapes
Difference between a bacterial cell and a virus
Bacteria has: Virus doesn’t have these, look at the
virus above
1. _____________________________
2. _____________________________
3. _____________________________
Virus replication
1. Attachment: The virus attaches to a ________________
2. Entry: The virus forms a hole in the ______________________________________________
of the host. The nucleic acid of the virus enters the host cell.
3. Synthesis: The virus’ nucleic acid is used to make new
_________________________________________________________ for the new viruses being
produced. (The host cells’ DNA becomes deactivated)
4. Assembly: _____________________________________________________ inside the host
cell.
5. Release: The host ________________________ to release the new viruses. The bursting is
called ___________________
Disadvantages of Viruses
Viruses cause numerous human diseases; flu, measles, rubella, smallpox, HIV, chickenpox,
herpes virus (cold sores), human papillomavirus (warts, cervical cancer) (learn one or two)
Viruses also cause diseases in plants which will destroy the plants and have economic
disadvantages e.g. the Tobacco mosaic virus
Advantages of Viruses
_________________________________
Control of infections
Biological control (important example is Myxoma Virus (Myxomatosis) used to
control the rabbit population)
You might also like
- Terms and Conditions of Use For Amoeba Sisters Answer KeysDocument3 pagesTerms and Conditions of Use For Amoeba Sisters Answer KeysAlannaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis-Webquest Answer KeyDocument4 pagesMeiosis-Webquest Answer KeyAshwin Raghuraman0% (1)
- Cells Immune System Click Learn WorksheetDocument3 pagesCells Immune System Click Learn WorksheetAngie Gabriela Rivera RamosNo ratings yet
- Snurfle Meiosis Another WSDocument2 pagesSnurfle Meiosis Another WSAdriana IzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cellseric wyatt33% (3)
- Learning Guide CHP 3Document9 pagesLearning Guide CHP 3wworldwide7No ratings yet
- 2015 Viruses CN NotesDocument2 pages2015 Viruses CN NotesLeonie ManafaNo ratings yet
- Biology 21.1 Guided NotesDocument5 pagesBiology 21.1 Guided Notesericaoh0709No ratings yet
- Virus Web Quest12Document4 pagesVirus Web Quest12api-433033266No ratings yet
- 2.1 A Microscopic Look at Life's Organization 2.2 Comparing Bacteria and Archaea-Student WorksheetDocument5 pages2.1 A Microscopic Look at Life's Organization 2.2 Comparing Bacteria and Archaea-Student Worksheeteshaaljamal27No ratings yet
- Virus Ly Tic Cycles eDocument5 pagesVirus Ly Tic Cycles eElleNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument34 pagesVirusdieu.ltm.64nttsNo ratings yet
- And Physiology/ Immune System Chapter 12-Objectives:: AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnd Physiology/ Immune System Chapter 12-Objectives:: AnatomyJustine May Balinggan DelmasNo ratings yet
- Pathogens and Disease Worksheets Science HouseDocument4 pagesPathogens and Disease Worksheets Science HouserileysandersjakeNo ratings yet
- Viruses SGDocument4 pagesViruses SGansh09febNo ratings yet
- Virus Worksheet 2Document2 pagesVirus Worksheet 2Ale Trigueros100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Virus Lytic CycleDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Virus Lytic CycleBryce Mattox100% (1)
- Imported FileDocument3 pagesImported FilemaotianjiamattymNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 3 Combined With BlanksDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Module 3 Combined With Blanksapi-331588274No ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureDocument34 pages1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureJustin Dave ManantanNo ratings yet
- Name: - GR & Sec: - A. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesName: - GR & Sec: - A. Answer The Following QuestionsLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- Formative activity 5Document2 pagesFormative activity 5邱珊珊No ratings yet
- 10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionDocument6 pages10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionJJNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Transmission of HIVDocument15 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus: Transmission of HIVdlneisha61No ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument21 pagesReproductionSahrulRashidNo ratings yet
- Biology Review Assignment (48556)Document8 pagesBiology Review Assignment (48556)Rebecca tejadaNo ratings yet
- VirusworksheetDocument2 pagesVirusworksheetOentoeng JahjaNo ratings yet
- SC Form 1Document4 pagesSC Form 1Nurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1sarah jane lomaNo ratings yet
- BACTERIA Virus and Bacteria WorksheetDocument2 pagesBACTERIA Virus and Bacteria WorksheetSuha AlgharazNo ratings yet
- A1.2 NotesDocument16 pagesA1.2 NotesteddyenNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity BookletDocument7 pagesAQA Immunity Bookletsu966No ratings yet
- Understanding Viruses Video SheetDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Viruses Video Sheetapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Science No.24 PDFDocument9 pagesScience No.24 PDFPanida Mhew SukkasemNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity BookletDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Bookletnchauhan212No ratings yet
- Cell Membranes Practice QuestionDocument1 pageCell Membranes Practice QuestionUyenNo ratings yet
- Biology Review 1Document4 pagesBiology Review 1Mehakpreet GillNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Science Chapter 2 Viruses and BacteriaDocument42 pages6th Grade Science Chapter 2 Viruses and Bacteriagurdeep singhNo ratings yet
- Parts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesParts of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsRose Yan JiNo ratings yet
- Unit Standard Number Unit Standard Title Demonstrate Knowledge of Biotechnology. Element Range PC 1.1 PC 1.2Document8 pagesUnit Standard Number Unit Standard Title Demonstrate Knowledge of Biotechnology. Element Range PC 1.1 PC 1.2api-3826124No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Science Chapter 2 Viruses and BacteriaDocument42 pages6th Grade Science Chapter 2 Viruses and BacteriaAshley BrookensNo ratings yet
- Taller Grado Quinto - Semana 6 Al 10 de MayoDocument3 pagesTaller Grado Quinto - Semana 6 Al 10 de MayoMelinaNo ratings yet
- Cells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetDocument3 pagesCells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetEmiliano Arvizu Franco Jr100% (2)
- L07 - Fillable Cell CycleDocument2 pagesL07 - Fillable Cell Cyclejesselyn.tubayasNo ratings yet
- Vaccine WEBDocument3 pagesVaccine WEBHeidi KwonNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesLymphatic SystemJamaica LunaNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureDocument34 pages1) Introduction To Microbiology - Cell StructureJustin Dave ManantanNo ratings yet
- Ameba Sisters WorksheetDocument2 pagesAmeba Sisters WorksheetVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- CH - 10 Dragonfly Mitosis Final EditDocument36 pagesCH - 10 Dragonfly Mitosis Final Edit639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Recombinant DnaDocument2 pagesWorksheet Recombinant DnaSånśkār Sıñģh RåńåNo ratings yet
- SOL Review Answer SheetDocument15 pagesSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7No ratings yet
- Bacterial Cells Activity 2Document1 pageBacterial Cells Activity 2RACHEL DAMALERIONo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science Genetic EngineeringDocument65 pages7th Grade Science Genetic EngineeringSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Quiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesQuiz About Cell & Cell OrganellesJune Emerson ManalangNo ratings yet
- LE Bare Essentials Word BankDocument51 pagesLE Bare Essentials Word BankhiNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemJustine May Balinggan Delmas100% (1)
- Finding The Mystery Pathogen: Bacteria Virus FungusDocument3 pagesFinding The Mystery Pathogen: Bacteria Virus Fungusapi-350126589No ratings yet
- A2.2 Cell Structure NotesDocument23 pagesA2.2 Cell Structure NotesteddyenNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Blanks. Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Example True Nucleus DNA Cell Division SizeDocument3 pagesFill in The Blanks. Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Example True Nucleus DNA Cell Division SizeblonnamNo ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet