Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsIjaerv13n10 56-16
Ijaerv13n10 56-16
Uploaded by
nazasraf2012This document provides definitions and guidelines for hazard identification and risk assessment. It defines key terms like hazard, risk, risk assessment, and risk management. It also provides tables to rate exposure, severity, probability, and overall risk level. The purpose is to provide a systematic approach to identifying hazards and assessing their associated risks to implement control measures and ensure workplace safety. Risk is defined as the likelihood and severity of an event, while risk assessment evaluates safety and health risks from hazards. The employer's duties include identifying hazards and controlling risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Case Study On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument8 pagesCase Study On Diabetes Mellitus Type IITuTitNo ratings yet
- HSE-BMS-006 Risk Assessment & JSADocument39 pagesHSE-BMS-006 Risk Assessment & JSAShahid Alam0% (1)
- Wellness RevolutionDocument4 pagesWellness RevolutionWaqar GhoryNo ratings yet
- COSH Report 4Document60 pagesCOSH Report 4Maricca U. HagitanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)Document24 pagesRisk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)ardesh abdille100% (1)
- Lecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk ManagementDocument25 pagesLecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk Managementeladio30No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment 1Document13 pagesRisk Assesment 1Dian Kristina RusmanaNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Applicant PreviousDocument4 pagesSection 3 Applicant PreviousAkhilNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Reviewer MidtermDocument10 pagesRisk Management Reviewer MidtermFrancois MarcialNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Control Module 1Document39 pagesRisk Assessment & Control Module 1Marvin ReggieNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveDocument25 pagesRisk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveParth RavalNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TrainingDocument32 pagesRisk Assessment TrainingAmodhya vikumshanNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and HealthDocument15 pagesOccupational Safety and Healthagus purwantoNo ratings yet
- RM PrelimDocument14 pagesRM PrelimJazper InocNo ratings yet
- QAS 7-Hazard Identification and Risk AssesmentDocument8 pagesQAS 7-Hazard Identification and Risk AssesmentTariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Hazard List CreationDocument14 pagesHazard List CreationChalak TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Training On 09Dec09-ECEDocument36 pagesRisk Assessment Training On 09Dec09-ECENasr EldeepNo ratings yet
- HirarcDocument9 pagesHirarcMohammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Risk ManagementDocument17 pagesNotes On Risk Managementdwimukh360No ratings yet
- ЛЕК 3 РИЗИК - en-USDocument41 pagesЛЕК 3 РИЗИК - en-USsva1.1nbNo ratings yet
- OSHJ-CoP-01 Risk Management and Control Version 1 EnglishDocument15 pagesOSHJ-CoP-01 Risk Management and Control Version 1 EnglishsajinNo ratings yet
- Hazard, Hazid, Hazan and Hazop - Part of Safety and Risk Management - IspatGuru PDFDocument9 pagesHazard, Hazid, Hazan and Hazop - Part of Safety and Risk Management - IspatGuru PDFnaren_013100% (1)
- 101.09 Risk AssessmentDocument11 pages101.09 Risk AssessmentnihadNo ratings yet
- Implementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015Document7 pagesImplementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015faizNo ratings yet
- Note Osha Chapter 5Document5 pagesNote Osha Chapter 5FrancisNo ratings yet
- 6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixDocument7 pages6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixWelma JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument12 pages1 PBMohd Agung Al-HuseinNo ratings yet
- Expert Risk AssessmentDocument37 pagesExpert Risk Assessmentmohamed elhawaryNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash Personal Protective Equipment Applying Risk Management Principles - IIDocument7 pagesArc Flash Personal Protective Equipment Applying Risk Management Principles - IIRajuNo ratings yet
- Guide For Major Hazard Facilities: Safety AssessmentDocument48 pagesGuide For Major Hazard Facilities: Safety AssessmentKhaled SaadnehNo ratings yet
- Safety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveDocument5 pagesSafety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety PlanDocument20 pagesHealth and Safety PlanAbu Muhammed KhwajaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - RMDocument3 pagesPart 1 - RMDexie Marie JumadasNo ratings yet
- Risk ManaGementDocument4 pagesRisk ManaGementBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Training: by Faculty of Engineering, Safety UnitDocument36 pagesRisk Assessment Training: by Faculty of Engineering, Safety Unitabhijeet sawantNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentMosfer Al kerdemNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentShadeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Riskmgt NotesDocument14 pagesRiskmgt Notesapi-3733731No ratings yet
- Introduct Ion To Risk Managem ENT: Jessica Lile - 18042044Document32 pagesIntroduct Ion To Risk Managem ENT: Jessica Lile - 18042044Jessica LileNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument28 pagesRisk Assesmentyaseen100% (1)
- T R ITP G: HE ISK Ractitioner UideDocument1 pageT R ITP G: HE ISK Ractitioner Uidelouis kNo ratings yet
- Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and SanitationDocument10 pagesRisk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and Sanitationladyharmony117No ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument18 pagesApplicationgreenzone686No ratings yet
- Application 1Document21 pagesApplication 1greenzone686No ratings yet
- Assingment OSHADocument23 pagesAssingment OSHAFikri HaziqNo ratings yet
- 04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFDocument84 pages04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFFitNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment at Sea Training CourseDocument32 pagesRisk Assessment at Sea Training CourseNikkolai Kirril Gementiza UguisNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci & Eng'g. Learning Material-Topic 5Document27 pagesEnvi Sci & Eng'g. Learning Material-Topic 5Janice C. PusposNo ratings yet
- Ijaerv13n10 56-17Document1 pageIjaerv13n10 56-17nazasraf2012No ratings yet
- Standard Procedure - Risk and Opportunities ManagementDocument25 pagesStandard Procedure - Risk and Opportunities ManagementShahzad Khan100% (2)
- Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment - BroadleafDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment and Risk Treatment - BroadleafpriyankaNo ratings yet
- Xvi Paper 28Document14 pagesXvi Paper 28a.h.saberbaghban001No ratings yet
- Environmental Risk Assessment: Abir Goldar Development Studies Discipline Khulna UniversityDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Risk Assessment: Abir Goldar Development Studies Discipline Khulna UniversityNina AzizNo ratings yet
- Risk Management POUDocument37 pagesRisk Management POUGeena boengai100% (2)
- 4.4 Relevant Definitions in The Risk Management Process: Risk Severity X Probability (X Detectability)Document4 pages4.4 Relevant Definitions in The Risk Management Process: Risk Severity X Probability (X Detectability)Jolly SushmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment HiracsDocument29 pagesAssignment HiracsIntanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Sheet Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageQuick Revision Sheet Risk AssessmentHaseebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment Risk Control (HIRARC)Document39 pagesChapter 4 - Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment Risk Control (HIRARC)eyqinleeNo ratings yet
- IN-SITE: Keys to an Effective Site Safety and Security ProgramFrom EverandIN-SITE: Keys to an Effective Site Safety and Security ProgramNo ratings yet
- The Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsFrom EverandThe Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsNo ratings yet
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Collins - Grammar For IELTSDocument36 pagesCollins - Grammar For IELTSBao HoaNo ratings yet
- CHW Pipe Installation, Insulation & Cladding - JSA - Risk AssessmentDocument13 pagesCHW Pipe Installation, Insulation & Cladding - JSA - Risk Assessmentlike saddamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan BiomoleculesQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae, TriasDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae, TriasRamadani RuriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Management SystemDocument4 pagesPharmacy Management SystemTaniya FernandoNo ratings yet
- IWR 2014 FullReport PDFDocument363 pagesIWR 2014 FullReport PDFFranco DegiuseppeNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Ascariasis Levels of PrevDocument2 pagesAscariasis Levels of PrevLeslie Noelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mswe 001Document48 pagesMswe 001AhammedKabeerNo ratings yet
- Goboy - Risk For Infection NCPDocument3 pagesGoboy - Risk For Infection NCPLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns Part 2Document30 pagesHealth Trends, Issues, and Concerns Part 2D AngelaNo ratings yet
- 903 1829 1 SMDocument11 pages903 1829 1 SMKane ElishaNo ratings yet
- ReDocument4 pagesReIsabel Mamani RamirezNo ratings yet
- E1. EpidemiologyDocument108 pagesE1. EpidemiologyEshetu WondimuNo ratings yet
- BRAC Myanmar 2020Document34 pagesBRAC Myanmar 2020Hein Nay SoeNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Clinical Guidelinesv2 PDFDocument15 pagesPain Management Clinical Guidelinesv2 PDFErwin Novia Rachmawati100% (1)
- Bexinfo Therapeutic IndexDocument426 pagesBexinfo Therapeutic Indexmdgayas70100% (1)
- Risk Register Peralatan Medik 2022Document8 pagesRisk Register Peralatan Medik 2022maintenance anmedNo ratings yet
- Nur 097 Health Assessment Reviewer Term 1Document7 pagesNur 097 Health Assessment Reviewer Term 1Nathalie Karina Liwanag CaberoNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life 1Document10 pagesQuality of Life 1Anjuka100% (1)
- Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Duration Position Statement October 2021 v1Document3 pagesSurgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Duration Position Statement October 2021 v1debby twonabilaNo ratings yet
- Report ThreeDocument37 pagesReport Threehariprasad boddepalliNo ratings yet
- Overview of PHNDocument14 pagesOverview of PHNariel camusNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching: On A Modern ApproachDocument11 pagesClinical Teaching: On A Modern ApproachMay JuneNo ratings yet
- HSE Plan ConstructionDocument99 pagesHSE Plan ConstructionYashod Doobary100% (1)
- Research Paper Topics Athletic TrainingDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Topics Athletic Traininggz7vxzyz100% (1)
- I. Topic: Pertussis II. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesI. Topic: Pertussis II. ObjectivesKaren PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To Occupational Health and SafetyDocument31 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To Occupational Health and SafetysekinNo ratings yet
Ijaerv13n10 56-16
Ijaerv13n10 56-16
Uploaded by
nazasraf20120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document provides definitions and guidelines for hazard identification and risk assessment. It defines key terms like hazard, risk, risk assessment, and risk management. It also provides tables to rate exposure, severity, probability, and overall risk level. The purpose is to provide a systematic approach to identifying hazards and assessing their associated risks to implement control measures and ensure workplace safety. Risk is defined as the likelihood and severity of an event, while risk assessment evaluates safety and health risks from hazards. The employer's duties include identifying hazards and controlling risks.
Original Description:
Original Title
ijaerv13n10_56-16
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides definitions and guidelines for hazard identification and risk assessment. It defines key terms like hazard, risk, risk assessment, and risk management. It also provides tables to rate exposure, severity, probability, and overall risk level. The purpose is to provide a systematic approach to identifying hazards and assessing their associated risks to implement control measures and ensure workplace safety. Risk is defined as the likelihood and severity of an event, while risk assessment evaluates safety and health risks from hazards. The employer's duties include identifying hazards and controlling risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageIjaerv13n10 56-16
Ijaerv13n10 56-16
Uploaded by
nazasraf2012This document provides definitions and guidelines for hazard identification and risk assessment. It defines key terms like hazard, risk, risk assessment, and risk management. It also provides tables to rate exposure, severity, probability, and overall risk level. The purpose is to provide a systematic approach to identifying hazards and assessing their associated risks to implement control measures and ensure workplace safety. Risk is defined as the likelihood and severity of an event, while risk assessment evaluates safety and health risks from hazards. The employer's duties include identifying hazards and controlling risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 13, Number 10 (2018) pp.
7639-7667
© Research India Publications. http://www.ripublication.com
2 Sometimes (12 times per year)
3 Now and then (one per week)
6 Frequently (daily)
10 Continuous (more than two times per day)
Severity Rating
The apparent effect indicates the seriousness of the arising situation
Factor Description
1 Minor (injury without time / work restriction FAC)
4 Major (injury with time /work restriction MTC/RWC)
7 Serious (irreversible effect handicap LWC)
15 Critical (single fatality immediately or afterwards)
40 Disaster (multiple fatality immediately or afterwards)
Probability Rating
Factor Description
0.2 Virtually impossible (>20 years, one in a life time, only theoretical case)
0.5 Conceivable but improbable (once in a career (1/20 years)
1 Improbable / borderline case, (1/10 years)
3 Unusual (one can think of a (unusual ) scenario (1/3 years)
6 Possible (once every 6 months)
10 To be expected (one per week)
Risk Rating
Risk = Exposure x Severity x Probability
Risk
Score Priority INTERPRETATION
>20 4 Very limited risk – acceptable
20-69 3 Take additional measure to mitigate the risk level close to priority 4
70-199 2 Immediate measures required
>=200 1 Stop work until measures are taken
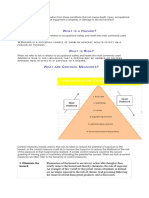
HAZARD IDENTIFICATION AND RISK damage to the environment or a combination of these.
ASSESSMENT
Hazard control means the process of implementing measures
The purpose of this guideline is to provide a systematic and to reduce the risk associate with a hazard.
objective approach to assessing hazards and their associated
Hierarchy of control means the established priority order for
risks that will provide an objective measure of an identified
the types of measures to be used to control risks.
hazard as well as provide a method to control the risk. It is
one of the general duties as prescribed under the Occupational Hazard identification means the identification of undesired
Safety and Health Act 1994 (Act 514) for the employer to events that lead to the materialization of the hazard and the
provide a safe workplaces to their employees and other related mechanism by which those undesired events could occur.
person.
Risk means a combination of the likelihood of an occurrence
of a hazardous event with specified period or in specified
circumstances and the severity of injury or damage to the
TERM AND DEFINITIONS:
health of people, property, environment or any combination of
The purpose of this guideline is to provide a systematic and these caused by the event.
objective approach to assessing hazards and their associated
Risk assessment means the process of evaluating the risks to
risks that will provide an objective measure of an identified
safety and health arising from hazards at work.
hazard as well as provide a method to control the risk. It is
one of the general duties as prescribed under the Occupational Risk management means the total procedure associated with
Safety and Health Act 1994 (Act 514) for the employer to identifying a hazard, assessing the risk, putting in place
provide a safe workplaces to their employees and other related control measures, and reviewing the outcomes.
person.
Hazard-means a source or a situation with a potential for harm
in terms of human injury or ill health, damage to property,
7654
You might also like
- Case Study On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument8 pagesCase Study On Diabetes Mellitus Type IITuTitNo ratings yet
- HSE-BMS-006 Risk Assessment & JSADocument39 pagesHSE-BMS-006 Risk Assessment & JSAShahid Alam0% (1)
- Wellness RevolutionDocument4 pagesWellness RevolutionWaqar GhoryNo ratings yet
- COSH Report 4Document60 pagesCOSH Report 4Maricca U. HagitanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)Document24 pagesRisk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)ardesh abdille100% (1)
- Lecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk ManagementDocument25 pagesLecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk Managementeladio30No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment 1Document13 pagesRisk Assesment 1Dian Kristina RusmanaNo ratings yet
- Section 3 Applicant PreviousDocument4 pagesSection 3 Applicant PreviousAkhilNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Reviewer MidtermDocument10 pagesRisk Management Reviewer MidtermFrancois MarcialNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Control Module 1Document39 pagesRisk Assessment & Control Module 1Marvin ReggieNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveDocument25 pagesRisk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveParth RavalNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TrainingDocument32 pagesRisk Assessment TrainingAmodhya vikumshanNo ratings yet
- Occupational Safety and HealthDocument15 pagesOccupational Safety and Healthagus purwantoNo ratings yet
- RM PrelimDocument14 pagesRM PrelimJazper InocNo ratings yet
- QAS 7-Hazard Identification and Risk AssesmentDocument8 pagesQAS 7-Hazard Identification and Risk AssesmentTariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Hazard List CreationDocument14 pagesHazard List CreationChalak TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Training On 09Dec09-ECEDocument36 pagesRisk Assessment Training On 09Dec09-ECENasr EldeepNo ratings yet
- HirarcDocument9 pagesHirarcMohammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Risk ManagementDocument17 pagesNotes On Risk Managementdwimukh360No ratings yet
- ЛЕК 3 РИЗИК - en-USDocument41 pagesЛЕК 3 РИЗИК - en-USsva1.1nbNo ratings yet
- OSHJ-CoP-01 Risk Management and Control Version 1 EnglishDocument15 pagesOSHJ-CoP-01 Risk Management and Control Version 1 EnglishsajinNo ratings yet
- Hazard, Hazid, Hazan and Hazop - Part of Safety and Risk Management - IspatGuru PDFDocument9 pagesHazard, Hazid, Hazan and Hazop - Part of Safety and Risk Management - IspatGuru PDFnaren_013100% (1)
- 101.09 Risk AssessmentDocument11 pages101.09 Risk AssessmentnihadNo ratings yet
- Implementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015Document7 pagesImplementation of HIRARC in A Small Sized Organization: September 2015faizNo ratings yet
- Note Osha Chapter 5Document5 pagesNote Osha Chapter 5FrancisNo ratings yet
- 6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixDocument7 pages6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixWelma JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument12 pages1 PBMohd Agung Al-HuseinNo ratings yet
- Expert Risk AssessmentDocument37 pagesExpert Risk Assessmentmohamed elhawaryNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash Personal Protective Equipment Applying Risk Management Principles - IIDocument7 pagesArc Flash Personal Protective Equipment Applying Risk Management Principles - IIRajuNo ratings yet
- Guide For Major Hazard Facilities: Safety AssessmentDocument48 pagesGuide For Major Hazard Facilities: Safety AssessmentKhaled SaadnehNo ratings yet
- Safety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveDocument5 pagesSafety Security Biosafety Laboratory Biosecurity PerspectiveZabdiel Ann SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety PlanDocument20 pagesHealth and Safety PlanAbu Muhammed KhwajaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - RMDocument3 pagesPart 1 - RMDexie Marie JumadasNo ratings yet
- Risk ManaGementDocument4 pagesRisk ManaGementBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Training: by Faculty of Engineering, Safety UnitDocument36 pagesRisk Assessment Training: by Faculty of Engineering, Safety Unitabhijeet sawantNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentMosfer Al kerdemNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentShadeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Riskmgt NotesDocument14 pagesRiskmgt Notesapi-3733731No ratings yet
- Introduct Ion To Risk Managem ENT: Jessica Lile - 18042044Document32 pagesIntroduct Ion To Risk Managem ENT: Jessica Lile - 18042044Jessica LileNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument28 pagesRisk Assesmentyaseen100% (1)
- T R ITP G: HE ISK Ractitioner UideDocument1 pageT R ITP G: HE ISK Ractitioner Uidelouis kNo ratings yet
- Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and SanitationDocument10 pagesRisk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and Sanitationladyharmony117No ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument18 pagesApplicationgreenzone686No ratings yet
- Application 1Document21 pagesApplication 1greenzone686No ratings yet
- Assingment OSHADocument23 pagesAssingment OSHAFikri HaziqNo ratings yet
- 04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFDocument84 pages04 Identifikasi Bahaya Dan Hirarki Kontrol PDFFitNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment at Sea Training CourseDocument32 pagesRisk Assessment at Sea Training CourseNikkolai Kirril Gementiza UguisNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci & Eng'g. Learning Material-Topic 5Document27 pagesEnvi Sci & Eng'g. Learning Material-Topic 5Janice C. PusposNo ratings yet
- Ijaerv13n10 56-17Document1 pageIjaerv13n10 56-17nazasraf2012No ratings yet
- Standard Procedure - Risk and Opportunities ManagementDocument25 pagesStandard Procedure - Risk and Opportunities ManagementShahzad Khan100% (2)
- Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment - BroadleafDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment and Risk Treatment - BroadleafpriyankaNo ratings yet
- Xvi Paper 28Document14 pagesXvi Paper 28a.h.saberbaghban001No ratings yet
- Environmental Risk Assessment: Abir Goldar Development Studies Discipline Khulna UniversityDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Risk Assessment: Abir Goldar Development Studies Discipline Khulna UniversityNina AzizNo ratings yet
- Risk Management POUDocument37 pagesRisk Management POUGeena boengai100% (2)
- 4.4 Relevant Definitions in The Risk Management Process: Risk Severity X Probability (X Detectability)Document4 pages4.4 Relevant Definitions in The Risk Management Process: Risk Severity X Probability (X Detectability)Jolly SushmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment HiracsDocument29 pagesAssignment HiracsIntanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Sheet Risk AssessmentDocument1 pageQuick Revision Sheet Risk AssessmentHaseebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment Risk Control (HIRARC)Document39 pagesChapter 4 - Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment Risk Control (HIRARC)eyqinleeNo ratings yet
- IN-SITE: Keys to an Effective Site Safety and Security ProgramFrom EverandIN-SITE: Keys to an Effective Site Safety and Security ProgramNo ratings yet
- The Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsFrom EverandThe Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsNo ratings yet
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Collins - Grammar For IELTSDocument36 pagesCollins - Grammar For IELTSBao HoaNo ratings yet
- CHW Pipe Installation, Insulation & Cladding - JSA - Risk AssessmentDocument13 pagesCHW Pipe Installation, Insulation & Cladding - JSA - Risk Assessmentlike saddamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan BiomoleculesQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae, TriasDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae, TriasRamadani RuriNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Management SystemDocument4 pagesPharmacy Management SystemTaniya FernandoNo ratings yet
- IWR 2014 FullReport PDFDocument363 pagesIWR 2014 FullReport PDFFranco DegiuseppeNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Ascariasis Levels of PrevDocument2 pagesAscariasis Levels of PrevLeslie Noelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mswe 001Document48 pagesMswe 001AhammedKabeerNo ratings yet
- Goboy - Risk For Infection NCPDocument3 pagesGoboy - Risk For Infection NCPLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Health Trends, Issues, and Concerns Part 2Document30 pagesHealth Trends, Issues, and Concerns Part 2D AngelaNo ratings yet
- 903 1829 1 SMDocument11 pages903 1829 1 SMKane ElishaNo ratings yet
- ReDocument4 pagesReIsabel Mamani RamirezNo ratings yet
- E1. EpidemiologyDocument108 pagesE1. EpidemiologyEshetu WondimuNo ratings yet
- BRAC Myanmar 2020Document34 pagesBRAC Myanmar 2020Hein Nay SoeNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Clinical Guidelinesv2 PDFDocument15 pagesPain Management Clinical Guidelinesv2 PDFErwin Novia Rachmawati100% (1)
- Bexinfo Therapeutic IndexDocument426 pagesBexinfo Therapeutic Indexmdgayas70100% (1)
- Risk Register Peralatan Medik 2022Document8 pagesRisk Register Peralatan Medik 2022maintenance anmedNo ratings yet
- Nur 097 Health Assessment Reviewer Term 1Document7 pagesNur 097 Health Assessment Reviewer Term 1Nathalie Karina Liwanag CaberoNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life 1Document10 pagesQuality of Life 1Anjuka100% (1)
- Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Duration Position Statement October 2021 v1Document3 pagesSurgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Duration Position Statement October 2021 v1debby twonabilaNo ratings yet
- Report ThreeDocument37 pagesReport Threehariprasad boddepalliNo ratings yet
- Overview of PHNDocument14 pagesOverview of PHNariel camusNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching: On A Modern ApproachDocument11 pagesClinical Teaching: On A Modern ApproachMay JuneNo ratings yet
- HSE Plan ConstructionDocument99 pagesHSE Plan ConstructionYashod Doobary100% (1)
- Research Paper Topics Athletic TrainingDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Topics Athletic Traininggz7vxzyz100% (1)
- I. Topic: Pertussis II. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesI. Topic: Pertussis II. ObjectivesKaren PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction To Occupational Health and SafetyDocument31 pagesUnit-1 Introduction To Occupational Health and SafetysekinNo ratings yet