Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science - q1l1 Notes
Science - q1l1 Notes
Uploaded by
Kine HenituseCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Saturn Time Cube SimulationDocument67 pagesThe Saturn Time Cube Simulationtriple7inc100% (3)
- Courier Service AgreementDocument1 pageCourier Service AgreementSabu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Silver Refining ProcessDocument8 pagesElectrolytic Silver Refining ProcessPamo Caytano100% (1)
- Technical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentDocument7 pagesTechnical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument12 pagesSCIENCEBellaaaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesEarth Science69p6tf4mcbNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceROUENDANIELLE PLANDEZNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth: Science NotesDocument13 pagesLayers of The Earth: Science NotesFrigid GreenNo ratings yet
- The Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthDocument27 pagesThe Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthShaila SegunderaNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Sci LT #1 Term 2 G10 ReviewDocument8 pagesSci LT #1 Term 2 G10 Reviewmy3gr8kidoosNo ratings yet
- Earth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustDocument59 pagesEarth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustVJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 15 EarthinteriorDocument48 pages15 EarthinteriorJose Luric Nicolas MolobocoNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesPlate TectonicsTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- Crustal Hazards FireDocument44 pagesCrustal Hazards FireCHARLES CHIMZNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Document6 pagesScience Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- 03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMDocument84 pages03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMCarlo Bryan Ramento100% (1)
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument9 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesVictoria MashavaNo ratings yet
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document3 pagesScience Reviewer 1Leilani PelisigasNo ratings yet
- Overview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1Document36 pagesOverview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1kim968714No ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner CoreDocument3 pagesLearning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner CoreKlyde Elmarc F. GalantaNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument16 pagesEndogenic ProcessesJellah Jennifer DegamoNo ratings yet
- 2 Interior of The EarthDocument5 pages2 Interior of The EarthCHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarth Science ReviewerBenz Nicolf CasadorNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument88 pagesPlate Tectonic TheorySHWETA NATARAJANNo ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- Geology & Earth's TreasureDocument34 pagesGeology & Earth's TreasureHelaina MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Yna's EarthDocument11 pagesYna's EarthYnara VillaunuevaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Eart1Document3 pagesLayers of The Eart1HeraNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsNeal Lorenzo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - First Quarter NotesDocument6 pagesScience 10 - First Quarter NotesJulienne Nicole AmularNo ratings yet
- I. General GeologyDocument11 pagesI. General GeologyJanina Frances RuideraNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument37 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleJade QuitoNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument2 pagesLayers of The EarthCarlos MananganNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesEarth Science ReviewerSALAMANCA, AZELEI B.No ratings yet
- Earthquake Faults2ndDocument65 pagesEarthquake Faults2ndMAYETTE CHIONGNo ratings yet
- C1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsDocument2 pagesC1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsArwind RoyNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument14 pagesEndogenic Processesjulie rose degamoNo ratings yet
- Interior EarthDocument43 pagesInterior EarthSergioNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument44 pagesInterior of The EarthdrishtiNo ratings yet
- Geology NotesDocument4 pagesGeology Notesgwyneth patrice obreroNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Study PPDocument11 pagesRocks and Minerals Study PPJonet Grace JereosNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Study PPDocument11 pagesRocks and Minerals Study PPsara fekriNo ratings yet
- EARTHS INTERIOR PPT Chona Fisrt LessonDocument29 pagesEARTHS INTERIOR PPT Chona Fisrt LessonAlexis faith MalanaNo ratings yet
- KS2 MVE FormationFactsheet3Document5 pagesKS2 MVE FormationFactsheet3AndrewdKiatKiatNo ratings yet
- Whatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFDocument23 pagesWhatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFragini singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 SeismologyDocument96 pagesLecture1 SeismologyShah Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Earths Interior HeatDocument30 pagesEarths Interior HeatK-Ann AcostaNo ratings yet
- TMP 1873944701Document42 pagesTMP 1873944701Ati SukroNo ratings yet
- CloserDocument42 pagesCloserAti SukroNo ratings yet
- G10 Geosphere - Sync DiscussionDocument206 pagesG10 Geosphere - Sync Discussionhatdog dakoNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesInternal Structure of The EarthMargarette MartinNo ratings yet
- Dynamic EarthDocument30 pagesDynamic EarthKathy Claire BallegaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Earthquake EngineeringDocument41 pagesElements of Earthquake EngineeringAnjaliNo ratings yet
- Health ReportDocument21 pagesHealth ReportKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Pe Reviewer Quarter 3Document3 pagesPe Reviewer Quarter 3Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument9 pagesEnglish ReviewerKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Document6 pagesScience Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Mapeh ReviewerDocument24 pagesMapeh ReviewerKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Base Institute - Namakkal - PH: 900 37 111 66: - Mock - Ibpsguide.in - 1Document288 pagesBase Institute - Namakkal - PH: 900 37 111 66: - Mock - Ibpsguide.in - 1Kartik MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Lucent - Certkey.4a0 100.v2018!09!25.by - Amir.140qDocument62 pagesAlcatel Lucent - Certkey.4a0 100.v2018!09!25.by - Amir.140qRoshan KarnaNo ratings yet
- Dimaampao Tax NotesDocument69 pagesDimaampao Tax NotestinctNo ratings yet
- Seo Services in DelhiDocument9 pagesSeo Services in DelhiSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- (1872) Regulations For The Uniform and Dress of The Army of The United StatesDocument40 pages(1872) Regulations For The Uniform and Dress of The Army of The United StatesHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (5)
- Belt Conveyour Safetyv2Document24 pagesBelt Conveyour Safetyv2Luis MecNo ratings yet
- Europe & ThailandDocument1 pageEurope & ThailandTipitaka TripitakaNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment DCW LTDDocument2 pagesIndividual Assignment DCW LTDDurgit KumarNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Research of Acacia Mangium Glulam Integration in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesPreliminary Research of Acacia Mangium Glulam Integration in The PhilippinesHalivier Conol LegaspinaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Ch.3Document13 pagesBusiness Environment Ch.3hahahaha wahahahhaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-ITM B-School, Kharghar .: Application of Maxima & MinimaDocument12 pagesSubmitted By:-ITM B-School, Kharghar .: Application of Maxima & MinimaDeepali KunjeerNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect LINGODADocument31 pagesPresent Perfect LINGODAThayrone NeryNo ratings yet
- Fluoridi U Amb CanadaDocument122 pagesFluoridi U Amb CanadasonecuNo ratings yet
- Britain Food and DrinksDocument15 pagesBritain Food and DrinksAnny NamelessNo ratings yet
- SBCO6100 TLM - Session11 - ComLead - SVDocument43 pagesSBCO6100 TLM - Session11 - ComLead - SVNatasha McFarlaneNo ratings yet
- Ahu 01 (STD)Document5 pagesAhu 01 (STD)onspsnonsNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining (Fasteners)Document11 pagesMetal Joining (Fasteners)ganeshNo ratings yet
- EQG-How To Generate User License in S4 HANA Using SAP Audit Measurement Program (USMM) v2.00Document9 pagesEQG-How To Generate User License in S4 HANA Using SAP Audit Measurement Program (USMM) v2.00tanudyNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On RingwormDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Ringwormissyeasif100% (1)
- DDP Prithla 2021 Exp NoteDocument22 pagesDDP Prithla 2021 Exp Notelalit singhNo ratings yet
- Heresite Corrosion ProtectionDocument2 pagesHeresite Corrosion ProtectionDANIEL PEREZNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Document31 pagesSec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Abdullah100% (1)
- OISD ChecklistDocument3 pagesOISD ChecklistLoganathan DharmarNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules and Tips in Group DiscussionsDocument2 pagesBasic Rules and Tips in Group Discussionssudarsanamma89% (9)
- PS-MM IntegrationDocument2 pagesPS-MM IntegrationmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Meter Reading Details: Assam Power Distribution Company LimitedDocument1 pageMeter Reading Details: Assam Power Distribution Company LimitedPadum PatowaryNo ratings yet
Science - q1l1 Notes
Science - q1l1 Notes
Uploaded by
Kine HenituseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science - q1l1 Notes
Science - q1l1 Notes
Uploaded by
Kine HenituseCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 1: PLATE TECTONICS
Science
10-ENDURANCE | SIR RK | 1ST QTR 2022
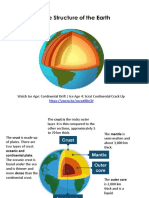
● It is a very hot surface at about
900°C.
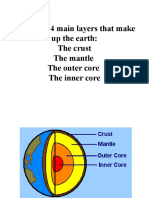
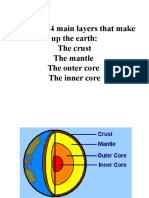
INTERNAL STRUCTURE AND
COMPOSITION OF THE EARTH ● This layer is composed of very hot
dense rock (ferro-magnesium
silicate rocks) that flows like
asphalt under a heavy weight.
CONVECTION CURRENTS
The hot material (magma) in the mantle
rises to the top of the mantle, cools,
then sinks, reheats, and rises again.
The convection currents cause
changes in the earth’s surface.
THE CRUST THE CORE
● The layer we live on, the crust is ● The core is the densest layer of
the thinnest and least dense layer the internal structure of the earth.
of the solid earth. ● About 3,500 thick from the center.
● Made up of light rock material that ● Made up of heavy metals like iron
range from 2 miles to 75 miles + oxygen, silicon, and nickel
deep. alloy.
● Usually contains silicon, aluminum,
and calcium. THE OUTER CORE
● The two types of crust are oceanic The outer core is the only layer of the
crust and continental crust. earth that is liquid. Located below the
● Composed of plates on which the mantle and is about 1,400 miles thick. It is
continents and oceans rest. composed of the melted metals nickel
● The crust of the earth is broken and iron.
into many pieces called plates.
THE INNER CORE
The inner core is the solid center of the
OCEANIC CRUST
planet. It is composed mostly of iron. The
Oceanic crust is the crust in the ocean’s inner core of the earth has temperatures
floor. and pressures so great that the metals are
squeezed together and are not able to
move about like a liquid, but are forced to
CONTINENTAL CRUST vibrate in place like a solid.
Continental crust is the crust that makes
up the continent. BOUNDARIES BETWEEN THE
LAYERS OF THE EARTH
THE MANTLE ● Lithosphere - the solid outer
section of the earth. It is made up
● The largest and thickest layer of
of the crust as well as the upper
the earth.
layer of the mantle.
● Consists of about 80% of the
earth’s mass.
LESSON 1: PLATE TECTONICS
Science
10-ENDURANCE | SIR RK | 1ST QTR 2022
● Asthenosphere - a part of the ● Travels only on the surface of the
uppermantle that flows like hot earth.
asphalt under heavy weight. ● Moves slower than body waves.
Lithospheric plates float and move ● Can cause serious damage.
around here.
● Mohorovicic Discontinuity - also LOVE WAVES
known as moho, it is the interface - Named after Augustus Edward H.
between crust and mantle. Love
● Gutenberg Discontinuity - marks - Fastest type of surface wave
the boundary between the mantle - Moves from side to side
and the outer core. - Can cause the real damage to
structures during an earthquake
RAYLEIGH WAVES
- Named after John William Strutt,
SEISMIC WAVES
also known as Lord Rayleigh.
● Waves of energy caused by the - Waves roll in circular motion
sudden breaking of rock within the - Responsible for an even greater
earth. devastation during an earthquake
● Measured using seismometers
and recorded using
seismographs. CONTINENTAL DRIFT
● There are two types of seismic Alfred Wegener proposed this theory
waves: body waves and surface that explains how continents split apart
waves. and shifted position on earth’s
surface.
BODY WAVES *not included in the pointers to review but still
keep in mind just in case
● Body waves travel through the
layers of the planet.
PRIMARY WAVES OR P-WAVES
- Fastest moving waves
- Compressional waves
- Can travel through solids and
liquids
- Pushes and pulls the rock it
moves through
SECONDARY WAVES OR S-WAVES
- The second wave you feel in an
earthquake
- Moves slower than P-waves
- Can only travel through solids
- Moves up and down or side-to-side
SURFACE WAVES
You might also like
- The Saturn Time Cube SimulationDocument67 pagesThe Saturn Time Cube Simulationtriple7inc100% (3)
- Courier Service AgreementDocument1 pageCourier Service AgreementSabu ThomasNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Silver Refining ProcessDocument8 pagesElectrolytic Silver Refining ProcessPamo Caytano100% (1)
- Technical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentDocument7 pagesTechnical Note Guidance On Corrosion Assessment of Ex EquipmentParthiban NagarajanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument12 pagesSCIENCEBellaaaNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument10 pagesEarth Science69p6tf4mcbNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceROUENDANIELLE PLANDEZNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth: Science NotesDocument13 pagesLayers of The Earth: Science NotesFrigid GreenNo ratings yet
- The Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthDocument27 pagesThe Geosphere: Our Dynamic EarthShaila SegunderaNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Sci LT #1 Term 2 G10 ReviewDocument8 pagesSci LT #1 Term 2 G10 Reviewmy3gr8kidoosNo ratings yet
- Earth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustDocument59 pagesEarth, Internal Structure of The Earth and Deformation of The CrustVJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 15 EarthinteriorDocument48 pages15 EarthinteriorJose Luric Nicolas MolobocoNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument15 pagesPlate TectonicsTomato PotatoNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- Crustal Hazards FireDocument44 pagesCrustal Hazards FireCHARLES CHIMZNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Document6 pagesScience Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- 03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMDocument84 pages03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMCarlo Bryan Ramento100% (1)
- Earth StudyDocument28 pagesEarth Studyrewardfulgueras9No ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument9 pagesEarthquakes and VolcanoesVictoria MashavaNo ratings yet
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document3 pagesScience Reviewer 1Leilani PelisigasNo ratings yet
- Overview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1Document36 pagesOverview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1kim968714No ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner CoreDocument3 pagesLearning Outcomes:: Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner CoreKlyde Elmarc F. GalantaNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument16 pagesEndogenic ProcessesJellah Jennifer DegamoNo ratings yet
- 2 Interior of The EarthDocument5 pages2 Interior of The EarthCHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarth Science ReviewerBenz Nicolf CasadorNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument88 pagesPlate Tectonic TheorySHWETA NATARAJANNo ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- Geology & Earth's TreasureDocument34 pagesGeology & Earth's TreasureHelaina MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Yna's EarthDocument11 pagesYna's EarthYnara VillaunuevaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Eart1Document3 pagesLayers of The Eart1HeraNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument44 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsNeal Lorenzo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - First Quarter NotesDocument6 pagesScience 10 - First Quarter NotesJulienne Nicole AmularNo ratings yet
- I. General GeologyDocument11 pagesI. General GeologyJanina Frances RuideraNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument37 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleJade QuitoNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument2 pagesLayers of The EarthCarlos MananganNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesEarth Science ReviewerSALAMANCA, AZELEI B.No ratings yet
- Earthquake Faults2ndDocument65 pagesEarthquake Faults2ndMAYETTE CHIONGNo ratings yet
- C1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsDocument2 pagesC1b Earth - Rocks and CeramicsArwind RoyNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument14 pagesEndogenic Processesjulie rose degamoNo ratings yet
- Interior EarthDocument43 pagesInterior EarthSergioNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument44 pagesInterior of The EarthdrishtiNo ratings yet
- Geology NotesDocument4 pagesGeology Notesgwyneth patrice obreroNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Study PPDocument11 pagesRocks and Minerals Study PPJonet Grace JereosNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Study PPDocument11 pagesRocks and Minerals Study PPsara fekriNo ratings yet
- EARTHS INTERIOR PPT Chona Fisrt LessonDocument29 pagesEARTHS INTERIOR PPT Chona Fisrt LessonAlexis faith MalanaNo ratings yet
- KS2 MVE FormationFactsheet3Document5 pagesKS2 MVE FormationFactsheet3AndrewdKiatKiatNo ratings yet
- Whatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFDocument23 pagesWhatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFragini singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 SeismologyDocument96 pagesLecture1 SeismologyShah Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Earths Interior HeatDocument30 pagesEarths Interior HeatK-Ann AcostaNo ratings yet
- TMP 1873944701Document42 pagesTMP 1873944701Ati SukroNo ratings yet
- CloserDocument42 pagesCloserAti SukroNo ratings yet
- G10 Geosphere - Sync DiscussionDocument206 pagesG10 Geosphere - Sync Discussionhatdog dakoNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesInternal Structure of The EarthMargarette MartinNo ratings yet
- Dynamic EarthDocument30 pagesDynamic EarthKathy Claire BallegaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Earthquake EngineeringDocument41 pagesElements of Earthquake EngineeringAnjaliNo ratings yet
- Health ReportDocument21 pagesHealth ReportKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Pe Reviewer Quarter 3Document3 pagesPe Reviewer Quarter 3Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument9 pagesEnglish ReviewerKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Document6 pagesScience Reviewer Quarter 1 Grade 10Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Mapeh ReviewerDocument24 pagesMapeh ReviewerKine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Base Institute - Namakkal - PH: 900 37 111 66: - Mock - Ibpsguide.in - 1Document288 pagesBase Institute - Namakkal - PH: 900 37 111 66: - Mock - Ibpsguide.in - 1Kartik MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Lucent - Certkey.4a0 100.v2018!09!25.by - Amir.140qDocument62 pagesAlcatel Lucent - Certkey.4a0 100.v2018!09!25.by - Amir.140qRoshan KarnaNo ratings yet
- Dimaampao Tax NotesDocument69 pagesDimaampao Tax NotestinctNo ratings yet
- Seo Services in DelhiDocument9 pagesSeo Services in DelhiSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- (1872) Regulations For The Uniform and Dress of The Army of The United StatesDocument40 pages(1872) Regulations For The Uniform and Dress of The Army of The United StatesHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (5)
- Belt Conveyour Safetyv2Document24 pagesBelt Conveyour Safetyv2Luis MecNo ratings yet
- Europe & ThailandDocument1 pageEurope & ThailandTipitaka TripitakaNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment DCW LTDDocument2 pagesIndividual Assignment DCW LTDDurgit KumarNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Research of Acacia Mangium Glulam Integration in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesPreliminary Research of Acacia Mangium Glulam Integration in The PhilippinesHalivier Conol LegaspinaNo ratings yet
- Business Environment Ch.3Document13 pagesBusiness Environment Ch.3hahahaha wahahahhaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-ITM B-School, Kharghar .: Application of Maxima & MinimaDocument12 pagesSubmitted By:-ITM B-School, Kharghar .: Application of Maxima & MinimaDeepali KunjeerNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect LINGODADocument31 pagesPresent Perfect LINGODAThayrone NeryNo ratings yet
- Fluoridi U Amb CanadaDocument122 pagesFluoridi U Amb CanadasonecuNo ratings yet
- Britain Food and DrinksDocument15 pagesBritain Food and DrinksAnny NamelessNo ratings yet
- SBCO6100 TLM - Session11 - ComLead - SVDocument43 pagesSBCO6100 TLM - Session11 - ComLead - SVNatasha McFarlaneNo ratings yet
- Ahu 01 (STD)Document5 pagesAhu 01 (STD)onspsnonsNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining (Fasteners)Document11 pagesMetal Joining (Fasteners)ganeshNo ratings yet
- EQG-How To Generate User License in S4 HANA Using SAP Audit Measurement Program (USMM) v2.00Document9 pagesEQG-How To Generate User License in S4 HANA Using SAP Audit Measurement Program (USMM) v2.00tanudyNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On RingwormDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Ringwormissyeasif100% (1)
- DDP Prithla 2021 Exp NoteDocument22 pagesDDP Prithla 2021 Exp Notelalit singhNo ratings yet
- Heresite Corrosion ProtectionDocument2 pagesHeresite Corrosion ProtectionDANIEL PEREZNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Document31 pagesSec 3 Welding Imperfections (Defects)Abdullah100% (1)
- OISD ChecklistDocument3 pagesOISD ChecklistLoganathan DharmarNo ratings yet
- Basic Rules and Tips in Group DiscussionsDocument2 pagesBasic Rules and Tips in Group Discussionssudarsanamma89% (9)
- PS-MM IntegrationDocument2 pagesPS-MM IntegrationmohammedraulmadridNo ratings yet
- Meter Reading Details: Assam Power Distribution Company LimitedDocument1 pageMeter Reading Details: Assam Power Distribution Company LimitedPadum PatowaryNo ratings yet