Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIDTERM-EXAM Utilities
MIDTERM-EXAM Utilities
Uploaded by
cristineangeljasmin04Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIDTERM-EXAM Utilities
MIDTERM-EXAM Utilities
Uploaded by
cristineangeljasmin04Copyright:
Available Formats
CE 213-18 (ENGINEERING UTILITIES 1)
2CE-3 DAY : Wednesday Time : 1:00 - 4:00 pm
NAME : Cristine Angel A. Jasmin Year : 2ND Year
MIDTERM EXAMINATION
I DEFINITION OF TERMS
1. ENERGY - Energy is defined as the amount of work that can be done using force or
the ability to do work. Furthermore, energy is power that has been assimilated over time.
2. WORK - Work is the application of force, f to move an item or object over a distance,
d in the direction of the applied force. Work is performed when a force causes motion.
3. POWER - Power is the rate at which work or energy is done or conveyed.
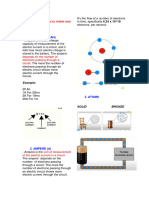
4. VOLTAGE - the electric potential difference between two points. How far the electricity
wishes to travel from one location to another. Volts are used to measure voltage.
5. ELECTRIC CURRENT - Electric current is the flow of electricity in an electrical circuit
as well as the amount of electricity flowing through a circuit. It's measured in amperes (A).
The higher the figure in amperes, the more electricity flows through the circuit.
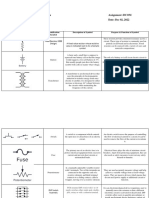
II DRAW OR SKETCH THE SYMBOLS OF THE FOLLOWING ELECTRICAL DEVICES
.
NO. ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS USAGE
DEVICES
A circuit breaker is a type
of electrical switch that
protects an electrical
circuit from damage
caused by overcurrent/overload
1. CIRCUIT or short circuit. Its primary
BREAKER function is to stop current flow
when protective relays
detect a problem.
The primary purpose of an
electric fuse is to protect
electrical equipment from
excessive current and to avoid
short circuits or mismatched
loads. Electrical fuses act as small
2. FUSE Circuit breakers.
Aside from protecting
equipment, they are also
utilized as safety precautions to
keep humans safe.
battery is a collection of cells that
converts chemical energy into
3.
BATTERY electrical energy.
A voltmeter is an electronic device
VOLTMETER used to measure the electrical voltage
4. in an electronic circuit.
The function of switch in an electric
circuit is to either make or break the
SWITCH electric circuit. A switch is used to
5. turn current to an electrical appliance
either on or off.
A push button switch is a mechanical
device used to control an electrical
circuit in which the operator
6. PUSH BUTTON manually presses a button to actuate
an internal switching mechanism
A capacitor is an electrical device
that stores and releases electrical
energy into a circuit. It actually
7.
CAPACITOR transmits alternating current into the
circuit rather than direct current.
Fixed resistors serve numerous
functions, the most important of
which is to limit the amount of
current passing through a circuit.
Excess current is dissipated as heat
8. FIXED RESISTOR energy, and each fixed resistor has a
power rating that must not be
exceeded in order to avoid failure
and probable circuit failure.
Variable resistors are extensively
used in electric circuits to modify the
value of current or voltage since their
resistance may be set to a specific
value. Variable resistors allow you to
9. VARIABLE change the voltage value by adjusting
RESISTOR the resistance while keeping the
current constant.
In an electric circuit, a cell is the
active source or elements. Its primary
10. CELL role is to provide power to the closed
circuit or to control the flow of
current through the circuit.
Antennas are energy converters that
convert electrical energy to
electromagnetic energy. Antennas
11. ANTENNA have the ability to function as both
transmitters and receivers.
An ammeter is used in series with the
part of the circuit to measure the
12. AMMETER passing current to measure direct or
alternating electric current.
A wattmeter is an instrument used
to measure and estimate electrical
power. It is typically used to
determine the amount of power
WATTMETER flowing through a circuit and can be
13.
used to estimate the electrical load of
a system.
A galvanometer is used to determine
GALVANOMETER and measure the intensity and direction
14.
of electrical current.
SPEAKER Speakers work by converting electrical
15. energy into mechanical energy
(motion).
Instructor : ENGR. BENJAMIN V. RAMOS
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Checklist Audit ISO 22000Document18 pagesChecklist Audit ISO 22000Abhishek Kumar Singh95% (20)
- 70 Ebook Photography Download FreeDocument3 pages70 Ebook Photography Download Free-roger Ron Taylor-100% (3)
- Eu 1 Turo Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesEu 1 Turo Midterm Examjulian.cuyaNo ratings yet
- Module 2&3Document2 pagesModule 2&3aguilar.anthony05122021No ratings yet
- Utilities Assignment 1Document3 pagesUtilities Assignment 1Ernest VincentNo ratings yet
- Ass 1Document3 pagesAss 1Rodney MacansantosNo ratings yet
- Symbols Industrial MotorDocument6 pagesSymbols Industrial MotorRODLAN DIPONNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument4 pagesResearch PaperMahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- Ass 1 FEEDocument3 pagesAss 1 FEE21-04126No ratings yet
- Utilities Assignment 1 1Document5 pagesUtilities Assignment 1 1Ernest VincentNo ratings yet
- Study of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical EngineeringDocument7 pagesStudy of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical Engineeringnational printersNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document2 pagesExercise 3mike ocayNo ratings yet
- Familar Ization PDFDocument2 pagesFamilar Ization PDFrere rareNo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument6 pagesGlossaryiriamiguelgarcia139No ratings yet
- Meralco Safety TipsDocument8 pagesMeralco Safety TipsKim SantosNo ratings yet
- Task Performanc E IN T.L.E.: Balmores, Jose Pascual P. Gr. 8 - OLHTDocument4 pagesTask Performanc E IN T.L.E.: Balmores, Jose Pascual P. Gr. 8 - OLHTErika BalmoresNo ratings yet
- GLOSSARY ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS Fátima ChaterDocument3 pagesGLOSSARY ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS Fátima ChaterfatimazahraechaterNo ratings yet
- BU2 - Electrical Terms, Signs and SymbolsDocument30 pagesBU2 - Electrical Terms, Signs and SymbolsAdrielle LadazzaNo ratings yet
- Team6 Ind05c P2 Ua2Document5 pagesTeam6 Ind05c P2 Ua2SERGIO--HDZNo ratings yet
- Project Report Chapter 3Document7 pagesProject Report Chapter 3ibrar82No ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electrical DevicesDocument14 pagesFamiliarization of Electrical DevicesJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- hatdogss-WPS OfficeDocument2 pageshatdogss-WPS Officejeda mae añesNo ratings yet
- Equipment Used in SubstationDocument3 pagesEquipment Used in Substationpritam PawarNo ratings yet
- Name Symbol Function Sample ApplicationDocument3 pagesName Symbol Function Sample ApplicationrheyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - Quick GuideDocument53 pagesPower Electronics - Quick Guideblessedgeraldie78No ratings yet
- ECE Workshop Exp No. 1Document6 pagesECE Workshop Exp No. 1Jai JohnNo ratings yet
- Eet02 - Module Midterm 1.1Document9 pagesEet02 - Module Midterm 1.1Mika LavadoNo ratings yet
- Amali Report 1Document7 pagesAmali Report 1Hatsune MikuNo ratings yet
- EECT Lab ManualDocument4 pagesEECT Lab ManualBlaze fireNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayDocument6 pagesOp-Amp Based Static Over Current RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical and Electronic Circuit Symbolsjuanchito39No ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument5 pagesPhysics RevisionzNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No 1 - Electrical Symbols SALVILLADocument8 pagesLearning Activity No 1 - Electrical Symbols SALVILLAShiela SalvillaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4: Lesson:7 Testing Electronics ComponentsDocument15 pagesQuarter 4: Lesson:7 Testing Electronics Componentsjohnmel indananNo ratings yet
- Switchyard 151103200304 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument26 pagesSwitchyard 151103200304 Lva1 App6891 PDFanjum duttaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Lab Sheet 1Document9 pagesGroup 4 Lab Sheet 1Gorin GorinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledCarlo EguieronNo ratings yet
- Cabt 10Document15 pagesCabt 10محمد خالدNo ratings yet
- Celda - Ee137 - Home Act 1Document7 pagesCelda - Ee137 - Home Act 1John Patrick CeldaNo ratings yet
- EE137Document7 pagesEE137John Patrick CeldaNo ratings yet
- Proper Storing of Hand Tools and Instruments: SjkhsDocument43 pagesProper Storing of Hand Tools and Instruments: SjkhsFrancess Mae BunaganNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical SystemsDocument102 pages1 Electrical SystemsElla Las PiñasNo ratings yet
- Simulab Activity 1.1. Electrical Components, Devices, Instruments and SymbolsDocument7 pagesSimulab Activity 1.1. Electrical Components, Devices, Instruments and SymbolsMissy Anne EspirituNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Technology Department Ms. Jen AndadorDocument12 pagesElectrical Engineering Technology Department Ms. Jen Andadorpeter vanderNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE m15Document2 pagesSCIENCE m15vidal.keith011006No ratings yet
- Reviewer 2Document14 pagesReviewer 2Crystel Kate Flores GarciaNo ratings yet
- PDU Lab 89Document10 pagesPDU Lab 89Yassir ButtNo ratings yet
- G1 5 ReviewerDocument68 pagesG1 5 Reviewerangelyn violaNo ratings yet
- Motor Control CenterDocument8 pagesMotor Control CenterdinoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Physics For ComputingDocument4 pagesActivity 2 - Physics For ComputingLano AmoniaNo ratings yet
- Handout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonDocument6 pagesHandout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonSRIREKHANo ratings yet
- BackgroundDocument21 pagesBackgroundMaxwellNo ratings yet
- Classification of Relays: Construction: General FunctionDocument30 pagesClassification of Relays: Construction: General FunctionMortuzaNo ratings yet
- Resistor: V Iri VRDocument2 pagesResistor: V Iri VRDany AlfiyandiNo ratings yet
- Relay: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document7 pagesRelay: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12ariyaNo ratings yet
- Rivera (BAS LT 1B) Assignment#3Document2 pagesRivera (BAS LT 1B) Assignment#3Jillian Mae RiveraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - ProtectionDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 5 - ProtectionHollow IchigoNo ratings yet
- Group 12 ProjectDocument15 pagesGroup 12 ProjectDele OdezNo ratings yet
- What Is Power Electronics?: I Nigo Mart Inez de Alegr Ia, Edorta IbarraDocument7 pagesWhat Is Power Electronics?: I Nigo Mart Inez de Alegr Ia, Edorta IbarraMiguel Esteban MartinezNo ratings yet
- Empowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearFrom EverandEmpowering Networks: A Comprehensive Guide to Medium Voltage SwitchgearNo ratings yet
- TechNote CableModellingDocument12 pagesTechNote CableModellingLeonardo LeonNo ratings yet
- General Twin Seal 06Document24 pagesGeneral Twin Seal 06Gk GaneshNo ratings yet
- English FinalDocument71 pagesEnglish FinalKhadeeja MarjanNo ratings yet
- RFIDDocument18 pagesRFIDKulavardan ThalapulaNo ratings yet
- Linear Wave ShapingDocument71 pagesLinear Wave ShapingArun Kumar DhupamNo ratings yet
- Travel Tourism in Bangladesh: A Study On Regent Tours & TravelDocument72 pagesTravel Tourism in Bangladesh: A Study On Regent Tours & TravelNahidNo ratings yet
- Nabcep AppendixesDocument32 pagesNabcep AppendixeshockpinNo ratings yet
- Auto Immune Disease - Brett HawesDocument39 pagesAuto Immune Disease - Brett HawesMelissaNo ratings yet
- Tabel EmisivitasDocument16 pagesTabel EmisivitasImam Bukhori100% (1)
- Script For FNBDocument5 pagesScript For FNBRaven Grace D. De MesaNo ratings yet
- Cub Cadet Parts Manual For Model 7232 TractorDocument20 pagesCub Cadet Parts Manual For Model 7232 Tractorjohn100% (51)
- M20 LatticeDocument30 pagesM20 LatticeKerwin Cley UgaleNo ratings yet
- Abstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZDocument6 pagesAbstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZbendel_boyNo ratings yet
- Individual Development WorkoutDocument3 pagesIndividual Development WorkoutmichelleNo ratings yet
- PVC Pressure Pipes and Fittings Catalogue (Pannon Pipe)Document8 pagesPVC Pressure Pipes and Fittings Catalogue (Pannon Pipe)vuthy prakNo ratings yet
- BLOBITECTUREDocument23 pagesBLOBITECTURESonal TarkasbandNo ratings yet
- Geography & Resources of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesGeography & Resources of The PhilippinesPaulAliboghaNo ratings yet
- Wise Sayings of Holy Prophet SAWWSDocument5 pagesWise Sayings of Holy Prophet SAWWSShireen Zahra Khan100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument48 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFrakib hasanNo ratings yet
- The Seven Spiritual Laws of Success BIZDocument7 pagesThe Seven Spiritual Laws of Success BIZDeac Roxana100% (2)
- Stalking & Dreaming PDFDocument4 pagesStalking & Dreaming PDFJoannaAllen100% (2)
- Color TheoryDocument4 pagesColor TheoryJoshua OdonioNo ratings yet
- Test Report CMI, 200 Amp 35kV Class "Tuf-Ex-Well II" Bushing WellDocument8 pagesTest Report CMI, 200 Amp 35kV Class "Tuf-Ex-Well II" Bushing WellCristobal BohorquezNo ratings yet
- 06.clutch SystemDocument24 pages06.clutch SystemTony D'AngeloNo ratings yet
- Artikel Review BiodegradasiDocument6 pagesArtikel Review BiodegradasiEka Ayu NingtyasNo ratings yet
- Caudal Duplication Syndrome-Report of A CaseDocument4 pagesCaudal Duplication Syndrome-Report of A Casekhumaira1982No ratings yet
- ENGG 10 PreCalculus For EngineersDocument11 pagesENGG 10 PreCalculus For EngineersMariel Erica RootNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Column Interaction DiagramDocument8 pagesWeek 4 - Column Interaction DiagramMAYHAY, ADRIAN PAULNo ratings yet