Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsFsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Fsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Uploaded by
K59 LE NGUYEN HA ANHThis document summarizes accounting for intangible assets. It discusses:
1) How intangible assets are initially recorded depending on whether they are acquired or developed internally. Acquired assets are recorded at fair value while developed costs may be expensed or capitalized depending on the stage of development.
2) Requirements for subsequent capitalization of costs and disclosure of information about intangible assets in financial statements. Costs must be capitalized if they provide future benefits, and disclosures include carrying amounts, amortization, and impairments.
3) Accounting for impairment losses and revaluations of intangible assets to fair value under IFRS. Impairments result in writing down
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Wall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesWall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat Sheetxandar198No ratings yet
- Module - 1 & 2Document330 pagesModule - 1 & 2Swatantra KumarNo ratings yet
- Ias 16 - Property, Plant and Equipment: Compiled By: Murtaza QuaidDocument8 pagesIas 16 - Property, Plant and Equipment: Compiled By: Murtaza QuaidFalak FaizNo ratings yet
- Summary of IFRSDocument32 pagesSummary of IFRSFarwa Samreen67% (3)
- Module 1 - FA at FVDocument5 pagesModule 1 - FA at FVNorfaidah Didato GogoNo ratings yet
- Long Lived Assets (Peserta)Document23 pagesLong Lived Assets (Peserta)bush0275No ratings yet
- Intangible AssetsDocument3 pagesIntangible Assetsgreat angelNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Costs PDFDocument15 pagesBorrowing Costs PDFAbhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document18 pagesChapter 05Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Modes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsDocument4 pagesModes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Andp Fiepreciation4p: $ Non-Current AssetsDocument5 pagesAndp Fiepreciation4p: $ Non-Current AssetsShahid MahmudNo ratings yet
- 03 DCF Valuation M&ADocument47 pages03 DCF Valuation M&AI DNo ratings yet
- Intangible Assets - Mary and AllyDocument4 pagesIntangible Assets - Mary and AllyMary Ann B. GabucanNo ratings yet
- PAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureDocument3 pagesPAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Investment Accounts: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument47 pagesInvestment Accounts: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Finance NotesDocument23 pagesFinance NoteschamilasNo ratings yet
- Nas 16Document33 pagesNas 16bhattag283No ratings yet
- Notes Payable With Debt RestructuringDocument3 pagesNotes Payable With Debt RestructuringZehra LeeNo ratings yet
- 1 - IAS 36 SummaryDocument1 page1 - IAS 36 Summaryhuzaifa.sami96No ratings yet
- SBR笔记总结分享Document33 pagesSBR笔记总结分享Suet CheeNo ratings yet
- CFAS NotesDocument6 pagesCFAS NotesAngelNo ratings yet
- Coop 8Document2 pagesCoop 8hoxhiiNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument3 pagesE-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsKaye NaranjoNo ratings yet
- SFM PDFDocument22 pagesSFM PDFZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- KCBL DD and Val Scope 221222Document13 pagesKCBL DD and Val Scope 221222mamur.mustaphaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management: A Capsule For Quick RevisionDocument22 pagesStrategic Financial Management: A Capsule For Quick RevisionدهانوجﻛﻮﻣﺎﺭNo ratings yet
- TTS - Merger Model PrimerDocument4 pagesTTS - Merger Model PrimerKrystleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26-Smes Assets (Inventories, Basic Chapter 27 - Smes Assets (Ppe, GovernmentDocument2 pagesChapter 26-Smes Assets (Inventories, Basic Chapter 27 - Smes Assets (Ppe, GovernmentRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.No ratings yet
- EV and VNB MethodologyDocument2 pagesEV and VNB MethodologySaravanan BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Afar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFDocument5 pagesAfar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFCyrille Keith FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Far 17 Investment PropertyDocument12 pagesFar 17 Investment PropertyTeresaNo ratings yet
- Financial Assets at Fair ValueDocument2 pagesFinancial Assets at Fair ValueNicole Allyson AguantaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Chapter 4Document45 pagesWeek 5 - Chapter 4AJNo ratings yet
- 74697bos60485 Inter p1 cp5 U3Document35 pages74697bos60485 Inter p1 cp5 U3aryanharsh2004No ratings yet
- DcfvalDocument198 pagesDcfvalHemant bhanawatNo ratings yet
- Cost Vs Equity MethodDocument10 pagesCost Vs Equity Methodalam_gir76100% (1)
- Zrive IB 1Q23 Intro To Valuation Methods Up2Document9 pagesZrive IB 1Q23 Intro To Valuation Methods Up2Luis Soldevilla MorenoNo ratings yet
- Aziacdixon FinanceDocument2 pagesAziacdixon Financegoitsemodimoj31No ratings yet
- Accounting 2Document7 pagesAccounting 2Valentina SerratoreNo ratings yet
- Oacc - Pp&e P 1 - P3Document23 pagesOacc - Pp&e P 1 - P3Trixie Divine SantosNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of IOCL 158Document1 pageAnnual Report of IOCL 158Nikunj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Long-Lived Assets: Revsine/Collins/Johnson/Mittelstaedt: Chapter 10Document18 pagesLong-Lived Assets: Revsine/Collins/Johnson/Mittelstaedt: Chapter 10NileshAgarwalNo ratings yet
- IFRS 9 Part 2Document24 pagesIFRS 9 Part 2ErslanNo ratings yet
- As 16: Borrowing Cost: OverviewDocument7 pagesAs 16: Borrowing Cost: OverviewShree Tisai100% (1)
- Referencer For Strategic Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesReferencer For Strategic Financial ManagementgauravNo ratings yet
- Fa Assignment 2Document3 pagesFa Assignment 2AmnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Depreciation Accounting PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Depreciation Accounting PDFravibhartia197888% (8)
- S.No Particulars Description 1. Company Hascol Petroleum Limited Company ProfileDocument3 pagesS.No Particulars Description 1. Company Hascol Petroleum Limited Company ProfileAmnaNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Accounting PDFDocument42 pagesDepreciation Accounting PDFASIFNo ratings yet
- IND AS 109 v12 050516Document70 pagesIND AS 109 v12 050516Ashish.kaklotar7No ratings yet
- Long Lived Assets L1Document37 pagesLong Lived Assets L1heisenbergNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4wasilqureshi2004No ratings yet
- 5.07 Analysis of Long-Term Assets - AnswersDocument36 pages5.07 Analysis of Long-Term Assets - Answersgustavo eichholzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document6 pagesLesson 12Jamaica bunielNo ratings yet
- FAR 007 Summary Notes - Intangible AssetsDocument5 pagesFAR 007 Summary Notes - Intangible AssetsMarynelle Labrador SevillaNo ratings yet
- ValuationDocument69 pagesValuationSivasankariNo ratings yet
- Reading 23 - Long-Lived AssetsDocument7 pagesReading 23 - Long-Lived AssetsLuis Henrique N. SpínolaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets Management PDFDocument20 pagesFixed Assets Management PDFDnukumNo ratings yet
- Accounting PPT - Intangible AssetDocument58 pagesAccounting PPT - Intangible AssetGokul RamNo ratings yet
- SOX OverviewDocument7 pagesSOX Overview2010 mujtaba qureshiNo ratings yet
- As 4Document21 pagesAs 4Chutmaarika GoteNo ratings yet
- HFAC130 1 JanJun2024 FA1 GC V.2 07022024Document9 pagesHFAC130 1 JanJun2024 FA1 GC V.2 07022024ICT ASSIGNMENTS MZANSINo ratings yet
- XML BS PL - ISCPL Consolidated IND AS 2021.xmlDocument156 pagesXML BS PL - ISCPL Consolidated IND AS 2021.xmlBhagwan BachaiNo ratings yet
- FORM 20K) For Other Countries: Annual Report Is Not A Substitute For This. SemiannuallyDocument2 pagesFORM 20K) For Other Countries: Annual Report Is Not A Substitute For This. SemiannuallyNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting FundamentalsDocument36 pagesAccounting FundamentalsJoenell CabungcalNo ratings yet
- FAA Unit IDocument95 pagesFAA Unit ISayalee GomaseNo ratings yet
- Pony Up Case - RSM323Document6 pagesPony Up Case - RSM323Dheeman ShahriNo ratings yet
- Report On The Financial Statements: StandaloneDocument9 pagesReport On The Financial Statements: StandaloneAbdul aNo ratings yet
- Audit Services RFPDocument2 pagesAudit Services RFPadi_skNo ratings yet
- Jonaxx Trading Corporation 1ST PageDocument1 pageJonaxx Trading Corporation 1ST PageRona Karylle Pamaran DeCastroNo ratings yet
- Team ProjectDocument2 pagesTeam ProjectkeremNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 6-QuesDocument7 pagesQUIZ 6-QuesPhán Tiêu TiềnNo ratings yet
- Cheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerDocument13 pagesCheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerAlec AndersenNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance - Mock Test Paper - Questions - Oct 2022 - CA Inter (New)Document9 pagesAuditing and Assurance - Mock Test Paper - Questions - Oct 2022 - CA Inter (New)KM ASSOCIATESNo ratings yet
- 08 Audit Khidmat Pengesahan, Insuran Dan Tanggungjawab Selepas AuditDocument45 pages08 Audit Khidmat Pengesahan, Insuran Dan Tanggungjawab Selepas Auditathirah jamaludinNo ratings yet
- BazetoDocument13 pagesBazetonigussieabagazNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledRima WahyuNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Nonprofit Organizations:: A Case Study of British Red CrossDocument69 pagesAccounting For Nonprofit Organizations:: A Case Study of British Red CrossArchitecture ArtNo ratings yet
- Bus ComDocument61 pagesBus ComMisganaw DebasNo ratings yet
- SMEs - Module-04-Statement of Financial PositionDocument27 pagesSMEs - Module-04-Statement of Financial PositionChris Iero-WayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Adjusting EntriesDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Adjusting EntriesBLANKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Afar Part 2Document20 pagesChapter 23 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Afar Part 2Kathrina RoxasNo ratings yet
- 33 9804Document36 pages33 9804IH InanNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisDocument37 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisStudent Sokha Chanchesda100% (1)
- HI5020Document13 pagesHI5020takeshiru000No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument13 pagesModule 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsShruthi PNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument12 pagesNotesIsha Manzano LacuestaNo ratings yet
- Gelua Accounting - PlatoDocument57 pagesGelua Accounting - PlatoJerome NatividadNo ratings yet
Fsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Fsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Uploaded by
K59 LE NGUYEN HA ANH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis document summarizes accounting for intangible assets. It discusses:
1) How intangible assets are initially recorded depending on whether they are acquired or developed internally. Acquired assets are recorded at fair value while developed costs may be expensed or capitalized depending on the stage of development.
2) Requirements for subsequent capitalization of costs and disclosure of information about intangible assets in financial statements. Costs must be capitalized if they provide future benefits, and disclosures include carrying amounts, amortization, and impairments.
3) Accounting for impairment losses and revaluations of intangible assets to fair value under IFRS. Impairments result in writing down
Original Description:
Original Title
Fsa c2_balance Sheet_long-lived Asset Analysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes accounting for intangible assets. It discusses:
1) How intangible assets are initially recorded depending on whether they are acquired or developed internally. Acquired assets are recorded at fair value while developed costs may be expensed or capitalized depending on the stage of development.
2) Requirements for subsequent capitalization of costs and disclosure of information about intangible assets in financial statements. Costs must be capitalized if they provide future benefits, and disclosures include carrying amounts, amortization, and impairments.
3) Accounting for impairment losses and revaluations of intangible assets to fair value under IFRS. Impairments result in writing down
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesFsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Fsa c2 - Balance Sheet - Long-Lived Asset Analysis
Uploaded by
K59 LE NGUYEN HA ANHThis document summarizes accounting for intangible assets. It discusses:
1) How intangible assets are initially recorded depending on whether they are acquired or developed internally. Acquired assets are recorded at fair value while developed costs may be expensed or capitalized depending on the stage of development.
2) Requirements for subsequent capitalization of costs and disclosure of information about intangible assets in financial statements. Costs must be capitalized if they provide future benefits, and disclosures include carrying amounts, amortization, and impairments.
3) Accounting for impairment losses and revaluations of intangible assets to fair value under IFRS. Impairments result in writing down
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
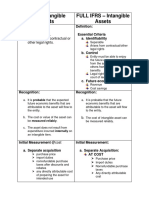
Acquired in a
Purchasing Price is recorded at fair value; business combination INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Any remaining amount of the Purchasing Price is Accounting for Intangible Asset
recorded as Goodwill (capitalized on BS) depends on how it is acquired Subsequent costs are capitalized if they are expected to
provide benefit beyond one year => Go to Balance Sheet as PPE
e.g.: purchasing price, freight and insurance, delivery, Go to Cash Flow Statement as Cash Flow from Investing
Recorded at fair value at acquisition. installation and testing, reinforcing floor, rebuilding, etc.
Purchased
1. CAPITALIZATION Otherwise they are expensed => Go to Income Statement as Expenses, Depreciation
Under IFRS: Research costs are expensed & vs. EXPENSING e.g.: staff training, painting, repair and maintenance Go to Cash Flow Statement as Cash Flow from Operating
Development costs are capitalized.
Under GAAP: Both are expensed
Interest costs incurred during the construction of an asset can be capitalized as part of the
Development costs for a software for sale to others: asset cost:
IFRS: are expensed until technological feasibility Developed internally If no construction : Still use rate on borrowing related to construction to capitalize the
has been established; Subsequent costs should be interest cost.
capitalized. Capitalized interest NOT reported as Interest Expense on IS BUT part of the asset's cost
GAAP: capitalized all development costs. CAPITALIZATION OF and depreciated or amortized over its useful life.
INTEREST COSTS IFRS: Interest on short-term lending OFFSETs capitalized costs (not allowed in GAAP)
Firms are require to disclose: Effects:
+) Carrying value for each asset During the period of capitalization : Higher Net Income, EBIT (as Interest costs are being
+) Accumulated depreciation & amortization spread over the asset's useful life) -> greater Interest Coverage Ratios
+) Title restrictions and assets pledged as 4. FIXED ASSET DISCLOSURE Subsequent periods: Higher Asset Values and Depreciation (depreciation/ amortization
collateral expense in subsequent periods will be higher because it is based on the increased asset value) ->
+) For impaired assets: loss amount and Lower Net Income, EBIT and Interest Coverage.
reasons under loss
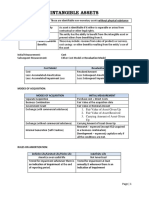
Straight-line method: Depreciation is the same amount each
+) For valued assets: the revaluation date,
year over asset's useful life
fair value and carrying value
[FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS] 2. DEPRECIATION & AMORTIZATION DEPRECIATION
CHAP 2: BALANCE SHEET
(3) LONG-LIVED ASSET ANALYSIS Carrying amount ("Net book value"; reported on BS) = Accelerated methods: More depreciation expense is
e.g., Historical cost (Gross) - Accumulated depreciation recognized in early years & less in later years of asset's life.
Only permitted under IFRS
An asset is carried at depreciated cost, but at each revaluation date, the
carrying amounts is adjusted to fair value.
REVALUATION Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized
over useful lives.
First Revaluation Date : Same methods as Depreciations Units-of-production methods : Depreciation is based on usage
+) Fair value < Carrying value -> Record Loss in IS Infinite life: Trademark (have a specific expiration rather than time
+) Fair value > Carrying value -> Record Revaluation surplus in Equity
date, but can be renewed at minimum cost); AMORTIZATION
.
Franchise agreement; Goodwill
Subsequent Revaluation Dates:
+) Fair value < Carrying value -> Difference reduces RS and then the
remaining (in difference, if any) is recorded as Loss in IS
+) Fair value > Carrying value -> The gain reverses any previous Loss Effects of
and the remaining (in gain, if any) is recorded in RS in Equity. Salvage (residual/ disposal) value
Depreciation Methods
3. IMPAIRMENT & REVALUATION
e.g.,
Reflect an unanticipated decline in the value of an asset. (e.g., adverse
change in market conditions, technological/ legal changes) Useful Lives
Both IFRS and GAAP require companies to write down the carrying
amount of impaired assets. IMPAIRMENT
Impairment reversals are permitted only under IFRS Indefinite lives -> NOT amortized but are tested for
Under IFRS: Impaired when Carrying value > Recoverable amount -> impairment at lease annually (Trademark*, Goodwill,
Written down to Recoverable Amount (on BS) -> Impairment Loss (in Franchise Agreement)
IS) Intangible Assets Impairment loss is recognized when Carrying Amount > Fair
Value
IMPAIRMENT LOSS = Carrying Amount - Recoverable Amount
Recoverable Amount = Max(Fair value - Cost to sell; Value in use)
Value in use = PV of Asset's future cash flow
You might also like
- Wall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesWall Street Mastermind S Investment Banking Technical Interview Cheat Sheetxandar198No ratings yet
- Module - 1 & 2Document330 pagesModule - 1 & 2Swatantra KumarNo ratings yet
- Ias 16 - Property, Plant and Equipment: Compiled By: Murtaza QuaidDocument8 pagesIas 16 - Property, Plant and Equipment: Compiled By: Murtaza QuaidFalak FaizNo ratings yet
- Summary of IFRSDocument32 pagesSummary of IFRSFarwa Samreen67% (3)
- Module 1 - FA at FVDocument5 pagesModule 1 - FA at FVNorfaidah Didato GogoNo ratings yet
- Long Lived Assets (Peserta)Document23 pagesLong Lived Assets (Peserta)bush0275No ratings yet
- Intangible AssetsDocument3 pagesIntangible Assetsgreat angelNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Costs PDFDocument15 pagesBorrowing Costs PDFAbhishek JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document18 pagesChapter 05Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Modes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsDocument4 pagesModes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Andp Fiepreciation4p: $ Non-Current AssetsDocument5 pagesAndp Fiepreciation4p: $ Non-Current AssetsShahid MahmudNo ratings yet
- 03 DCF Valuation M&ADocument47 pages03 DCF Valuation M&AI DNo ratings yet
- Intangible Assets - Mary and AllyDocument4 pagesIntangible Assets - Mary and AllyMary Ann B. GabucanNo ratings yet
- PAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureDocument3 pagesPAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Investment Accounts: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument47 pagesInvestment Accounts: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Finance NotesDocument23 pagesFinance NoteschamilasNo ratings yet
- Nas 16Document33 pagesNas 16bhattag283No ratings yet
- Notes Payable With Debt RestructuringDocument3 pagesNotes Payable With Debt RestructuringZehra LeeNo ratings yet
- 1 - IAS 36 SummaryDocument1 page1 - IAS 36 Summaryhuzaifa.sami96No ratings yet
- SBR笔记总结分享Document33 pagesSBR笔记总结分享Suet CheeNo ratings yet
- CFAS NotesDocument6 pagesCFAS NotesAngelNo ratings yet
- Coop 8Document2 pagesCoop 8hoxhiiNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument3 pagesE-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsKaye NaranjoNo ratings yet
- SFM PDFDocument22 pagesSFM PDFZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- KCBL DD and Val Scope 221222Document13 pagesKCBL DD and Val Scope 221222mamur.mustaphaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management: A Capsule For Quick RevisionDocument22 pagesStrategic Financial Management: A Capsule For Quick RevisionدهانوجﻛﻮﻣﺎﺭNo ratings yet
- TTS - Merger Model PrimerDocument4 pagesTTS - Merger Model PrimerKrystleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26-Smes Assets (Inventories, Basic Chapter 27 - Smes Assets (Ppe, GovernmentDocument2 pagesChapter 26-Smes Assets (Inventories, Basic Chapter 27 - Smes Assets (Ppe, GovernmentRichard Rhamil Carganillo Garcia Jr.No ratings yet
- EV and VNB MethodologyDocument2 pagesEV and VNB MethodologySaravanan BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Afar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFDocument5 pagesAfar.2905 Business Combination Mergers PDFCyrille Keith FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Far 17 Investment PropertyDocument12 pagesFar 17 Investment PropertyTeresaNo ratings yet
- Financial Assets at Fair ValueDocument2 pagesFinancial Assets at Fair ValueNicole Allyson AguantaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Chapter 4Document45 pagesWeek 5 - Chapter 4AJNo ratings yet
- 74697bos60485 Inter p1 cp5 U3Document35 pages74697bos60485 Inter p1 cp5 U3aryanharsh2004No ratings yet
- DcfvalDocument198 pagesDcfvalHemant bhanawatNo ratings yet
- Cost Vs Equity MethodDocument10 pagesCost Vs Equity Methodalam_gir76100% (1)
- Zrive IB 1Q23 Intro To Valuation Methods Up2Document9 pagesZrive IB 1Q23 Intro To Valuation Methods Up2Luis Soldevilla MorenoNo ratings yet
- Aziacdixon FinanceDocument2 pagesAziacdixon Financegoitsemodimoj31No ratings yet
- Accounting 2Document7 pagesAccounting 2Valentina SerratoreNo ratings yet
- Oacc - Pp&e P 1 - P3Document23 pagesOacc - Pp&e P 1 - P3Trixie Divine SantosNo ratings yet
- Annual Report of IOCL 158Document1 pageAnnual Report of IOCL 158Nikunj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Long-Lived Assets: Revsine/Collins/Johnson/Mittelstaedt: Chapter 10Document18 pagesLong-Lived Assets: Revsine/Collins/Johnson/Mittelstaedt: Chapter 10NileshAgarwalNo ratings yet
- IFRS 9 Part 2Document24 pagesIFRS 9 Part 2ErslanNo ratings yet
- As 16: Borrowing Cost: OverviewDocument7 pagesAs 16: Borrowing Cost: OverviewShree Tisai100% (1)
- Referencer For Strategic Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesReferencer For Strategic Financial ManagementgauravNo ratings yet
- Fa Assignment 2Document3 pagesFa Assignment 2AmnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Depreciation Accounting PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 5 Depreciation Accounting PDFravibhartia197888% (8)
- S.No Particulars Description 1. Company Hascol Petroleum Limited Company ProfileDocument3 pagesS.No Particulars Description 1. Company Hascol Petroleum Limited Company ProfileAmnaNo ratings yet
- Depreciation Accounting PDFDocument42 pagesDepreciation Accounting PDFASIFNo ratings yet
- IND AS 109 v12 050516Document70 pagesIND AS 109 v12 050516Ashish.kaklotar7No ratings yet
- Long Lived Assets L1Document37 pagesLong Lived Assets L1heisenbergNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4wasilqureshi2004No ratings yet
- 5.07 Analysis of Long-Term Assets - AnswersDocument36 pages5.07 Analysis of Long-Term Assets - Answersgustavo eichholzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document6 pagesLesson 12Jamaica bunielNo ratings yet
- FAR 007 Summary Notes - Intangible AssetsDocument5 pagesFAR 007 Summary Notes - Intangible AssetsMarynelle Labrador SevillaNo ratings yet
- ValuationDocument69 pagesValuationSivasankariNo ratings yet
- Reading 23 - Long-Lived AssetsDocument7 pagesReading 23 - Long-Lived AssetsLuis Henrique N. SpínolaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets Management PDFDocument20 pagesFixed Assets Management PDFDnukumNo ratings yet
- Accounting PPT - Intangible AssetDocument58 pagesAccounting PPT - Intangible AssetGokul RamNo ratings yet
- SOX OverviewDocument7 pagesSOX Overview2010 mujtaba qureshiNo ratings yet
- As 4Document21 pagesAs 4Chutmaarika GoteNo ratings yet
- HFAC130 1 JanJun2024 FA1 GC V.2 07022024Document9 pagesHFAC130 1 JanJun2024 FA1 GC V.2 07022024ICT ASSIGNMENTS MZANSINo ratings yet
- XML BS PL - ISCPL Consolidated IND AS 2021.xmlDocument156 pagesXML BS PL - ISCPL Consolidated IND AS 2021.xmlBhagwan BachaiNo ratings yet
- FORM 20K) For Other Countries: Annual Report Is Not A Substitute For This. SemiannuallyDocument2 pagesFORM 20K) For Other Countries: Annual Report Is Not A Substitute For This. SemiannuallyNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting FundamentalsDocument36 pagesAccounting FundamentalsJoenell CabungcalNo ratings yet
- FAA Unit IDocument95 pagesFAA Unit ISayalee GomaseNo ratings yet
- Pony Up Case - RSM323Document6 pagesPony Up Case - RSM323Dheeman ShahriNo ratings yet
- Report On The Financial Statements: StandaloneDocument9 pagesReport On The Financial Statements: StandaloneAbdul aNo ratings yet
- Audit Services RFPDocument2 pagesAudit Services RFPadi_skNo ratings yet
- Jonaxx Trading Corporation 1ST PageDocument1 pageJonaxx Trading Corporation 1ST PageRona Karylle Pamaran DeCastroNo ratings yet
- Team ProjectDocument2 pagesTeam ProjectkeremNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 6-QuesDocument7 pagesQUIZ 6-QuesPhán Tiêu TiềnNo ratings yet
- Cheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerDocument13 pagesCheaptry Cheaptry: Question & AnswerAlec AndersenNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance - Mock Test Paper - Questions - Oct 2022 - CA Inter (New)Document9 pagesAuditing and Assurance - Mock Test Paper - Questions - Oct 2022 - CA Inter (New)KM ASSOCIATESNo ratings yet
- 08 Audit Khidmat Pengesahan, Insuran Dan Tanggungjawab Selepas AuditDocument45 pages08 Audit Khidmat Pengesahan, Insuran Dan Tanggungjawab Selepas Auditathirah jamaludinNo ratings yet
- BazetoDocument13 pagesBazetonigussieabagazNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledRima WahyuNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Nonprofit Organizations:: A Case Study of British Red CrossDocument69 pagesAccounting For Nonprofit Organizations:: A Case Study of British Red CrossArchitecture ArtNo ratings yet
- Bus ComDocument61 pagesBus ComMisganaw DebasNo ratings yet
- SMEs - Module-04-Statement of Financial PositionDocument27 pagesSMEs - Module-04-Statement of Financial PositionChris Iero-WayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Adjusting EntriesDocument11 pagesChapter 8 Adjusting EntriesBLANKNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Afar Part 2Document20 pagesChapter 23 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Afar Part 2Kathrina RoxasNo ratings yet
- 33 9804Document36 pages33 9804IH InanNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisDocument37 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Financial AnalysisStudent Sokha Chanchesda100% (1)
- HI5020Document13 pagesHI5020takeshiru000No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument13 pagesModule 3 - Analysis of Financial StatementsShruthi PNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument12 pagesNotesIsha Manzano LacuestaNo ratings yet
- Gelua Accounting - PlatoDocument57 pagesGelua Accounting - PlatoJerome NatividadNo ratings yet