Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Structure and Function Answer Key
Animal Structure and Function Answer Key
Uploaded by
kpenales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document provides an answer key for animal structure and function and animal nutrition questions. It defines the four animal tissues and their functions, and lists the accessory organs involved in digestion as the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. It then describes the seven stages of the digestive process from mouth to rectum, including the roles of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an answer key for animal structure and function and animal nutrition questions. It defines the four animal tissues and their functions, and lists the accessory organs involved in digestion as the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. It then describes the seven stages of the digestive process from mouth to rectum, including the roles of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesAnimal Structure and Function Answer Key
Animal Structure and Function Answer Key
Uploaded by
kpenalesThe document provides an answer key for animal structure and function and animal nutrition questions. It defines the four animal tissues and their functions, and lists the accessory organs involved in digestion as the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. It then describes the seven stages of the digestive process from mouth to rectum, including the roles of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
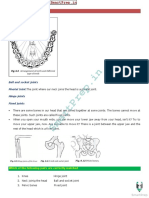
ANSWER KEY FOR ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND ANSWER KEY FOR ANIMAL NUTRITION
FUNCTION 1. Enumerate the Accessory Organs involved in digestion.
1. Enumerate the four animal tissues and their functions. a) Liver – largest gland in the body, secrete bile which is a greenish-yellow
a. Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces and lines body cavities. liquid that contains bile salts & bile pigments which help to speed up
Functions include lining, protecting, and forming glands. digestion of fats by emulsifying fats into small fat molecules
b. Connective tissue serves many purposes in the body: binding, b) gall bladder is the temporary storage area for bile, connected and release bile
supporting, protecting, forming blood, storing fats and filling space to duodenum via bile duct
c. Muscle tissue facilitates movement of the animal by contraction of c) pancreas is connected to the duodenum by pancreatic duct, produces
individual muscle cells (referred to as muscle fibers) pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes along with the hormones
d. Nervous tissue functions in the integration of stimulus and control of insulin and glucagon
response to that stimulus. Nerve cells are called neurons. Each neuron 2. Describe the Digestive Process.
has a cell body, an axon, and many dendrites.
a. Mouth. Food starts to move through your GI tract when you eat. When you
2. What do you call a group of closely associated, similar cells that carry out specific swallow, your tongue pushes the food into your throat. A small flap of tissue,
functions? Tissue called the epiglottis, folds over your windpipe to prevent choking and the food
3. What are the Three Types of Epithelial Tissues According to Shape? passes into your esophagus.
a. Squamous epithelial cells
b. Cuboidal epithelial cells b. Esophagus. Once you begin swallowing, the process becomes automatic. Your
brain signals the muscles of the esophagus and peristalsis begins.
c. Columnar epithelial cells
4. What are the 3 Types of Muscle Tissues in Vertebrates? c. Lower esophageal sphincter. When food reaches the end of your esophagus,
a. Skeletal muscle a ringlike muscle—called the lower esophageal sphincter —relaxes and lets food
b. Cardiac muscle pass into your stomach. This sphincter usually stays closed to keep what’s in your
stomach from flowing back into your esophagus.
c. Smooth muscle
5. What do you call cells that are especially active in developing tissue and are d. Stomach. After food enters your stomach, the stomach muscles mix the food
important in healing wounds? Fibroblasts and liquid with digestive juices. The stomach slowly empties its contents,
6. What is formed when tissues associate? Organs called chyme, into your small intestine.
7. What is formed by groups of tissues and organs of a complex organism? Organ
systems e. Small intestine. The muscles of the small intestine mix food with digestive
juices from the pancreas, liver, and intestine, and push the mixture forward for
8. What is present when cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems work together to further digestion. The walls of the small intestine absorb water and the digested
maintain a relatively constant internal environment? Homeostasis nutrients into your bloodstream. As peristalsis continues, the waste products of
9. Differentiate Tendons and Ligaments. Tendons are cords that connect muscles the digestive process move into the large intestine.
to bone. Ligaments are cables that connect bones to one another.
f. Large intestine. Waste products from the digestive process include undigested
10. What does a muscle fiber contain?
parts of food, fluid, and older cells from the lining of your GI tract. The large
myofibrils, proteins, myosin, and actin intestine absorbs water and changes the waste from liquid into stool. Peristalsis
helps move the stool into your rectum.
g. Rectum. The lower end of your large intestine, the rectum, stores stool until it
pushes stool out of your anus during a bowel movement.
You might also like
- Nutrition & You - Chapter 3Document30 pagesNutrition & You - Chapter 3Bridget KathleenNo ratings yet
- K.R. Shivanna, Rajesh Tandon (Auth.) - Reproductive Ecology of Flowering Plants - A Manual-Springer India (2014)Document178 pagesK.R. Shivanna, Rajesh Tandon (Auth.) - Reproductive Ecology of Flowering Plants - A Manual-Springer India (2014)Elisabeth Tölke100% (1)
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Cris Tolentino100% (1)
- AN01200.PDF PigDocument4 pagesAN01200.PDF PigGabu FiguracionNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System M.I.Document10 pagesThe Digestive System M.I.May KimNo ratings yet
- Digestive Tract of The PigDocument3 pagesDigestive Tract of The Pigmihai2242No ratings yet
- Digestive Tract of The PigDocument3 pagesDigestive Tract of The Pigmihai2242No ratings yet
- Wardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1St Edition Byrd Bredbenner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesWardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition A Functional Approach 1St Edition Byrd Bredbenner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcharles.osborne574100% (11)
- 8.4.4 Digestive SystemDocument22 pages8.4.4 Digestive SystemVaasviNo ratings yet
- Caballero DigestiveDocument5 pagesCaballero DigestiveClairyssa Myn D CaballeroNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument1 pageDigestiveadasdsadsafNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEMDocument43 pagesUnit-6 PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEMAmrita RanaNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec 2Document2 pagesNCM 105 Lec 2Rizaga, Carlos BenedictNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science8Document60 pagesQ4 Science8AILEEN LUZON100% (1)
- CLASS New SIX Science Subject 25-02 - 2024docxDocument14 pagesCLASS New SIX Science Subject 25-02 - 2024docxSaman AkramNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemGenesis SarengoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ContinuationDocument38 pagesDigestive System ContinuationLocal ClownNo ratings yet
- How Animals Survive (Science PT) - 2019Document5 pagesHow Animals Survive (Science PT) - 2019Sanyatha VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaDocument9 pagesLab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaEricka ElloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument2 pagesNutrition in AnimalsManivannan RamanNo ratings yet
- Science8 Lasq4 Week-1Document11 pagesScience8 Lasq4 Week-1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemChloe Gabrielle LlamasNo ratings yet
- Biology Material For - GroupsDocument94 pagesBiology Material For - GroupsaravindambatiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of DigestionDocument14 pagesPhysiology of DigestionMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument33 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsMari FeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesDigestive SystemHerry HermawanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- 6 - Body Human SystemDocument19 pages6 - Body Human SystemANDREA PAOLA DIAZ ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Name - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsDocument5 pagesName - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsRJ CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Module Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesModule Digestive SystemVynz Morales Cosep100% (1)
- Science 8 Q4 Revised Module 1 2Document24 pagesScience 8 Q4 Revised Module 1 2Rai0% (1)
- AnaPhy Reporting ScriptDocument5 pagesAnaPhy Reporting ScriptAlliah Angela Soldevilla BasadreNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument444 pagesHuman PhysiologyAnas AhmedhNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Standard Five Term - ScienceDocument40 pagesStandard Five Term - ScienceJigna PatelNo ratings yet
- Science q4 ModuleDocument40 pagesScience q4 ModuleKesh LisabaNo ratings yet
- Biological Processes in The Human BodyDocument26 pagesBiological Processes in The Human BodyAsela JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- Content in Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesContent in Demo TeachingAgustines, Marie Char C.No ratings yet
- CH 18: Nutrients & Digestion: What You Should Read! Chapter 18 Pages 523 - 529Document13 pagesCH 18: Nutrients & Digestion: What You Should Read! Chapter 18 Pages 523 - 529richteremsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Cardiovascular SystermDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Cardiovascular SystermFrancesca TejadaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Digestive SystemDocument25 pages2.1 Digestive SystemmegattaliffNo ratings yet
- 5th STD Term I Science EM - FTB - V22Document40 pages5th STD Term I Science EM - FTB - V22Dr. Naresh GohelNo ratings yet
- ScebdDocument16 pagesScebdabiiibenitez13No ratings yet
- BIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Document6 pagesBIO 1133 Exercise 9 (Digestive Sytem of The Frog)Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1Document1 pageEnhanced Science 8 Q4 Week 1chl03b4y09No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson in Science For Grade 8: ObjectivesDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson in Science For Grade 8: ObjectivesKatherine Canisguin AlvarecoNo ratings yet
- Science 8: Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1Document4 pagesScience 8: Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1abadloraine0331No ratings yet
- The Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12Document4 pagesThe Digestive System Handouts GENBIO2 STEM12April Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Digestion Flowchart Telegram ISHITA 4 UDocument7 pagesDigestion Flowchart Telegram ISHITA 4 UGautam AryaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q4 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver10-1Document41 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q4 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver10-1EFREN REYESNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 OrganisationDocument31 pagesTopic 2 OrganisationMeriNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Human AnatomyDocument42 pagesDigestive System: Human Anatomycristobal melegritoNo ratings yet
- Homoestatic Mechanisms Regulate An Animal's Internal Environment. TheDocument19 pagesHomoestatic Mechanisms Regulate An Animal's Internal Environment. TheGabbie CruzNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument10 pagesStudy Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE. 8 Q4 Week-1 7Document39 pagesSCIENCE. 8 Q4 Week-1 7Javier AugustNo ratings yet
- 7th Biology L-2 Q & A'sDocument3 pages7th Biology L-2 Q & A'sRicky 's PremiumNo ratings yet
- Circulatory+Digestive System 2Document20 pagesCirculatory+Digestive System 2madeleine.gaudissartNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Guided Reading Chapter 41: Adapted From L. Miriello by S. SharpDocument6 pagesAP Biology Guided Reading Chapter 41: Adapted From L. Miriello by S. SharpPerla Villarreal100% (2)
- A Joosr Guide to... Gut by Giulia Enders: The Inside Story of Our Body’s Most Underrated OrganFrom EverandA Joosr Guide to... Gut by Giulia Enders: The Inside Story of Our Body’s Most Underrated OrganRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Uji Daya Hambat Ekstrak Daun Bunga Tanjung (Mimusops: Elengi L.) TERHADAP PERTUMBUHAN Candida AlbicansDocument8 pagesUji Daya Hambat Ekstrak Daun Bunga Tanjung (Mimusops: Elengi L.) TERHADAP PERTUMBUHAN Candida AlbicansRendi Permana100% (1)
- Splanchnopleure vs. Somatopleure: I) DefinitionsDocument1 pageSplanchnopleure vs. Somatopleure: I) DefinitionsYoga WitularNo ratings yet
- HL - PH - 001Document2 pagesHL - PH - 001stepuptoblockNo ratings yet
- Histo SupDocument8 pagesHisto SupAbdoulhaleem MoNo ratings yet
- The Major Pathways of Complement ActivationDocument2 pagesThe Major Pathways of Complement ActivationAsish GeiorgeNo ratings yet
- Altschul The Genus Anadenanthera in Amerindian Cultures - 2 PDFDocument99 pagesAltschul The Genus Anadenanthera in Amerindian Cultures - 2 PDFAlex Moore-MinottNo ratings yet
- Immuno GlowDocument11 pagesImmuno GlowNoly ClaveringNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Main Branches of AnthropologyDocument9 pages1.3 Main Branches of AnthropologyRohanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal: Isolasi Khamir Dari Batang Tanaman Tebu Dan Identifikasinya Berdasarkan Sekuens InternalDocument14 pagesJurnal: Isolasi Khamir Dari Batang Tanaman Tebu Dan Identifikasinya Berdasarkan Sekuens InternalAndi endang AdininsiNo ratings yet
- VocabularyDocument2 pagesVocabularyapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Anticancer Plant-Derivatives: Deciphering Their Oncopreventive and Therapeutic Potential in Molecular TermsDocument30 pagesAnticancer Plant-Derivatives: Deciphering Their Oncopreventive and Therapeutic Potential in Molecular Termsbmounika 206No ratings yet
- Sorghum Root and Stalk RotsDocument288 pagesSorghum Root and Stalk RotsFindi DiansariNo ratings yet
- Science (9 Curie) - Rep 1Document15 pagesScience (9 Curie) - Rep 1mary eugene carmeli arantonNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis Adenomyosis Dr-IrabonDocument67 pagesEndometriosis Adenomyosis Dr-IrabonAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet
- CSE4019 Image - Processing ETH 1 AC41Document13 pagesCSE4019 Image - Processing ETH 1 AC41jyotismitaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems Regents ReviewDocument10 pagesEcosystems Regents Reviewapi-303120399No ratings yet
- Informatics in Medicine Unlocked: Joseph Malinzi, Kevin Bosire Basita, Sara Padidar, Henry Ademola AdeolaDocument15 pagesInformatics in Medicine Unlocked: Joseph Malinzi, Kevin Bosire Basita, Sara Padidar, Henry Ademola Adeolalevi trianaNo ratings yet
- G12 Q3 W5 M5 General-Biology-2 Pilario PDFDocument27 pagesG12 Q3 W5 M5 General-Biology-2 Pilario PDFJohn Michael Romarez100% (1)
- RA 9162 IRR Traditional VarietyDocument13 pagesRA 9162 IRR Traditional VarietyJerry SerapionNo ratings yet
- A Review of Root Resorption in Orthodontics PDFDocument5 pagesA Review of Root Resorption in Orthodontics PDFRahulLife'sNo ratings yet
- Genetics IntroductionDocument17 pagesGenetics IntroductionWayne FangNo ratings yet
- Potencial Evocado Auditivo de Media Latencia: M.M. Báez-Martín, I. Cabrera-AbreuDocument8 pagesPotencial Evocado Auditivo de Media Latencia: M.M. Báez-Martín, I. Cabrera-AbreuDaniela Berndt PonceNo ratings yet
- Mendel's Law of SegregationDocument6 pagesMendel's Law of Segregationhanfa zamanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Transport JOHN W. BAYNES, MAREK H. DOMINICZAK - Medical Biochemistry-Elsevier Inc. (2019)Document15 pagesOxygen Transport JOHN W. BAYNES, MAREK H. DOMINICZAK - Medical Biochemistry-Elsevier Inc. (2019)Malika MohNo ratings yet
- Von WillebrandDocument11 pagesVon WillebrandRAHUL SUTHARNo ratings yet
- Tran 2021Document12 pagesTran 2021Tzeto Han CongNo ratings yet
- Malaria/Hms: Dr. Muhammad Hamza (MB, BS, FMCP) Department of Medicine Akth/Buk KanoDocument47 pagesMalaria/Hms: Dr. Muhammad Hamza (MB, BS, FMCP) Department of Medicine Akth/Buk Kanoadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Covert and Overt RulesDocument6 pagesCovert and Overt Rulesapi-390048149No ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab ReportJavier Fuentes100% (2)