Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ALEA - Exercise 11 Respiration
ALEA - Exercise 11 Respiration
Uploaded by
Christine AleaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ALEA - Exercise 11 Respiration
ALEA - Exercise 11 Respiration
Uploaded by
Christine AleaCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 11
The Products of Respiration
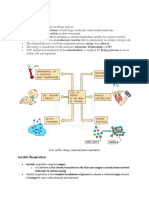
Respiration is the breakdown of glucose to simple substances CO 2 , H2O and energy in a form of
ATP. The carbon dioxide will be released into the atmosphere while the ATP will be used by the
plant cells to carry out energy-requiring reactions. The water may be released in a form of
moisture or used by the plant for several metabolic activities.
Objectives:
After the exercise, the students must be able to:
1. Explain the concept that respiration is a kind of oxidation process, hence it is an oxygen-
requiring process.
2. Discuss that respiration is a catabolic process by the type of products obtained in the
set-ups.
Materials:
Release of Carbon dioxide:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D-dWv4V4VcI
Release of heat:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZqzqFudrdeI
Procedure:
Observe a virtual laboratory procedure that depicts the release of carbon dioxide and heat as
indications that respiration occur in living organisms.
1. Release of Carbon Dioxide and Water During Respiration.
2. Release of Heat Energy During Respiration.
Temperature Readings (oC)
Live seeds Dead seeds
Initial 0 0
40 min. after n>0 0
Interpret the results and explain:
- Both the live seeds and dead seeds have the same initial temperature. After 40
minutes, there is an increase in temperature in the live seeds (germinated peas),
while there is no increase or decrease in temperature in the dead seeds. Hence, we
can conclude that respiration in live cells of seeds results in the release of heat.
Explain the changes that took place in:
1. Give the reaction involved to obtain the result to release CO2 and energy.
- Cellular respiration is the process, where oxygen and glucose are converted into energy
and carbon dioxide, which is released into the atmosphere.
2. What did you observe in the phenol red with the living seeds? Explain this result.
- The phenol red changes color from red to a yellow color, showing a positive result and
indicating the presence of carbon dioxide. This signifies that the germinated peas were still
capable of performing cellular respiration.
3. How about the phenol red with the dead seeds? Explain this result.
- The phenol red did not change to a yellow color, indicating that there was no carbon dioxide
present. This is because heat destroys the enzymes in peas, preventing them from performing
the respiration process, thus not producing carbon dioxide.
Questions:
1. What are the products of respiration observed in the experiments?
- In the first experiment, the product of respiration is carbon dioxide. It was tested, using
phenol red, the container with the germinated peas turned yellow indicating the presence
of carbon dioxide. In the second experiment, the product of respiration is heat. We can
observe that the flask containing the live seeds, rises in temperature which indicates that
the respiration in the germinated peas (live seeds) results in the release of heat.
2. What is the reason why some of the seeds used in the experiment were boiled seeds?
- This is because boiling denatures the composition of the cells that make up the seeds. Using
boiled seeds acts as the control set up for the experiment as they neither germinate nor
respire.
3. Explain why initially the seeds were soaked in water.
- The seeds were initially soaked in water to allow the seeds to germinate. Germination is
the period of growth after a period of dormancy.
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Intestinal ObstructionJOvie Rectin100% (2)
- 07-Cell Cycle Virtual Lab Handout SolutionsDocument4 pages07-Cell Cycle Virtual Lab Handout Solutionschuckly100% (2)
- 1.5 Respiration 2021 (Lesson 5)Document5 pages1.5 Respiration 2021 (Lesson 5)ruaridh.sayerNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesCellular RespirationAlessiaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesCellular Respirationjacques.duplessisNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationmandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- CH.7 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Class 9 Notes IcseDocument7 pagesCH.7 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Class 9 Notes IcseFebin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Practical Note and HeredityDocument18 pagesPractical Note and HeredityCalifornia KnightNo ratings yet
- Respiration ExperimentDocument5 pagesRespiration ExperimentAlexanderNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- 17-Respiration in PlantDocument19 pages17-Respiration in PlantqingxuguNo ratings yet
- Purwanchal Vidyamandir SESSION: 2021-2022 Class: Ix Subject: BiologyDocument8 pagesPurwanchal Vidyamandir SESSION: 2021-2022 Class: Ix Subject: BiologyKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - CO2 Is Released During RespirationDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - CO2 Is Released During RespirationSumit BissuNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 2020Document10 pagesCellular Respiration 2020Stephanie BoatengNo ratings yet
- Pringle Pop Lab Report p.2Document5 pagesPringle Pop Lab Report p.2Catherine DiscorsonNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Respiration in Plants: Many Steps) - StepDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank Respiration in Plants: Many Steps) - StepJoyabrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Lab 5Document13 pagesAP Bio Lab 5Alyona Booth100% (1)
- Worksheet (Eng)Document4 pagesWorksheet (Eng)s2322336No ratings yet
- Respiration and Breathing Edexcel 2Document34 pagesRespiration and Breathing Edexcel 2alishairabbasi69No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationGabriel R. SamsonNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Document14 pagesClass 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Dadi SindhuNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Cell RespirationDocument6 pagesActivity 4 - Cell RespirationJaneNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION TheoryDocument8 pagesRESPIRATION TheorySiddi AadiNo ratings yet
- Biology - Respiration AnswersheetDocument3 pagesBiology - Respiration AnswersheetHitakshi BhanushaliNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 7 Respiration in PlantsDocument16 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 7 Respiration in PlantsSima SinghNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationCHANCHAL AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 - External RespirationDocument32 pagesExercise 15 - External RespirationAldrin LozanoNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument7 pagesAerobic RespirationnothandoleratomNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsDocument5 pagesRespiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsEiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFDocument5 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 10Document2 pagesExercise No. 10Francis Jay MerencilloNo ratings yet
- 2 - Respiration - The Energy Releasing System-X (29-52)Document24 pages2 - Respiration - The Energy Releasing System-X (29-52)saijitesh.gNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Mursaleen KhanNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in PlantsDocument7 pages06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in PlantsAyush ShindeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.4 Respiration-SAAMDocument24 pagesUnit 1.4 Respiration-SAAMTrương Thị Phương ThùyNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaeDocument29 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaezulaikhaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kadar Co 2 DitaDocument16 pagesLaporan Kadar Co 2 DitaDita Linda YaniNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1Document7 pagesLearning Task 1Ron StephenNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Photosynthesis M1Document22 pagesUnit 3 Photosynthesis M1Kanittarin SukumpantanasarnNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Biology Aug Wrk2Document4 pagesClass 7 Biology Aug Wrk2Shriya MishraNo ratings yet
- Lab 13 PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesLab 13 PhotosynthesispreciousalabiteNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument33 pagesCellular Respirationapi-202349222100% (1)
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAnushreeNo ratings yet
- General Biology q2 Week 4Document11 pagesGeneral Biology q2 Week 4cherrylmoanamarieaemfatNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Respiration 2023Document8 pagesTopic 10 Respiration 2023nizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- Mealwormlab LabreportDocument4 pagesMealwormlab Labreportapi-257546392100% (1)
- Biodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)Document19 pagesBiodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)aekimNo ratings yet
- Plant Respiration BIOLOGY FORM 4Document34 pagesPlant Respiration BIOLOGY FORM 4sitimarziahNo ratings yet
- Physiology of RespirationDocument27 pagesPhysiology of RespirationNingshesil Ny HermantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- Ssc-Biology Text Book Must StudyDocument212 pagesSsc-Biology Text Book Must StudyShaik BajiNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Damariz CeballosDocument4 pagesLab 6 Damariz CeballosdamarizNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument7 pagesNutritionsemasingheNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Respiration 2021 (Lesson 4) TYPE INDocument9 pages1.5 Respiration 2021 (Lesson 4) TYPE INruaridh.sayerNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Released in RespirationDocument1 pageHeat Energy Released in RespirationJason Montesa50% (2)
- The Science of Brain Breathing: Part 1Document4 pagesThe Science of Brain Breathing: Part 1sssmou100% (5)
- Building ArmsDocument12 pagesBuilding Armse_sehicNo ratings yet
- Development of The Drosophila Body PlanDocument25 pagesDevelopment of The Drosophila Body PlanDaiana GroismanNo ratings yet
- PGR's in Quality Vegetable ProductionDocument3 pagesPGR's in Quality Vegetable ProductionHaripriyaNo ratings yet
- The Punin CalvariumDocument50 pagesThe Punin CalvariumTierra de Puruwaes100% (1)
- 100 Beats Per Minute. Many DifferentDocument4 pages100 Beats Per Minute. Many Differentjovan teopizNo ratings yet
- 8 Steps Krebs+ETCDocument3 pages8 Steps Krebs+ETCRhianne Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesHealth Psychology 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualJosephMartinezwgrin100% (15)
- Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument35 pagesRespiratory System PhysiologySherwan R Shal100% (2)
- Inergetix 6 Software and Hardware Installation Jan 2013Document116 pagesInergetix 6 Software and Hardware Installation Jan 2013kisgallcsaba100% (1)
- Biol 110 Test 1 Study GuideDocument2 pagesBiol 110 Test 1 Study Guideapi-281761748No ratings yet
- Blood Supply Face and Scalp NNDocument14 pagesBlood Supply Face and Scalp NNCyrus ChanNo ratings yet
- Psychology TheoriesDocument35 pagesPsychology TheoriessokkanlingamNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocument43 pagesIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsMadeline SibuloNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Micropropagation of Trichopus Zeylanicus Gaetn.Document5 pagesIn Vitro Micropropagation of Trichopus Zeylanicus Gaetn.bravohr98No ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and PhysiologyJackson JastariNo ratings yet
- 15-Sensory OrgansDocument23 pages15-Sensory OrgansMilad HabibiNo ratings yet
- Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument29 pagesStanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyElena AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Neurologic FunctionDocument49 pagesAssessment of The Neurologic FunctionNor Jeannah PolaoNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument34 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiaAmir MuhrizNo ratings yet
- The Resonance Theory of ConsciousnessDocument1 pageThe Resonance Theory of Consciousnessty7ur4e3No ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Serous Membranes of The Abdominal CavityDocument3 pagesChapter 8. Serous Membranes of The Abdominal Cavityleafyislucky 91No ratings yet
- Zoology Practical Exam Tips 2024Document62 pagesZoology Practical Exam Tips 2024sureshsooraj426No ratings yet
- Week 2 Chemical Examination of UrineDocument44 pagesWeek 2 Chemical Examination of UrineDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument47 pagesAcid-Base BalanceEmmanuel RocksonNo ratings yet
- Adrenal DiseasesDocument66 pagesAdrenal DiseasesNebiyu NegaNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Approach For Management of Liver Parenchymal Disease Acase Study 2161 069X 1000554Document3 pagesAyurvedic Approach For Management of Liver Parenchymal Disease Acase Study 2161 069X 1000554aman tiwariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearancemishyjayNo ratings yet