Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton's First Law
Newton's First Law
Uploaded by
Mark ProchaskaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Newton's First Law
Newton's First Law
Uploaded by
Mark ProchaskaCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics First
Name
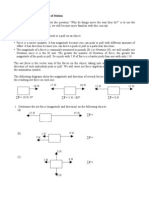
POGIL: Newtons First Law of Motion In this POGIL we will look at Newtons first law of motion. This law is useful for explaining why objects stay at rest or move at constant velocity. Newtons First Law of Motion Newtons First Law of Motion states the following: An object maintains its state of motion unless it is acted upon by a net force. By state of motion, Isaac Newton was referring to what we call velocity. The law tells us that an object at rest will stay at rest if the net force on it is zero. It also tells us that an object will move with constant velocity if the net force on it is zero. 1. The diagrams below show several people pushing on some boxes labeled A, B, and C. Assume the boxes are in free space and there is no friction. 16 N 4N 20 N A 20 N 10 N 12 N 16 N (a) Suppose all of the boxes are initially at rest. Which ones will remain at rest? Justify your answer. B 14 N 8N 20 N C
(b) Suppose all of the boxes are moving. Which ones will move in a straight line at constant speed? Justify your answer.
2. Each of the boxes below is moving to the right at 5 m/s. Draw arrows to show the direction of the force(s) needed for the box to keep moving to the right at 5 m/s. Write the magnitude of each force next to the arrow. (a) 20 N (b) 2N 14 N
Physics First
Name
(c) 6N 13 N 6N
(d) 7N 11 N
3. Can an object be moving if the net force on it is zero? Explain.
4. Can an object be at rest if there are forces exerted on it? Explain.
Problem Solving 5. Look at a book resting on a table. Suppose the book weighs 10 N. (a) What is the net force on the book?
(b) There must be a second force that acts on the book. How do we know this?
(c) What must be the magnitude and direction of this second force?
(d) What type of force is this second force?
(e) What agent exerts this second force?
Physics First
Name
6. In the picture below, a rocket moves upward at a constant velocity of 120 m/s. The gravitational force on it is 1000 N.
U S A
(a) What is the agent that exerts the gravitational force on the rocket.
(b) What is the net force on the rocket?
(c) Why must there be a second force, in addition to the gravitational force, exerted on the rocket?
(d) What must be the magnitude and direction of this second force that pushes on the rocket?
(e) What agent exerts this second force?
You might also like
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Pogil Describing MotionDocument2 pagesPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 pagesPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Torque POGIL and WebquestDocument7 pagesTorque POGIL and WebquestSamuel Jay100% (1)
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDocument3 pagesPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- WavesDocument4 pagesWavesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Impulse and MomentumDocument8 pagesImpulse and MomentumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 pagesMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Work and PowerDocument3 pagesWork and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument4 pagesSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDocument3 pagesPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzNo ratings yet
- Electric ForceDocument4 pagesElectric ForceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Pogil Theories of UniverseDocument3 pagesPogil Theories of UniverseChell Queentana FundaNo ratings yet
- 16 WEP-Work and PowerDocument6 pages16 WEP-Work and PowereltytanNo ratings yet
- Work and PowerDocument3 pagesWork and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Time DilationDocument3 pagesTime DilationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument3 pagesMass Defect and Binding EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Electric ForceDocument4 pagesElectric ForceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- POGIL: Force: Physics First NameDocument2 pagesPOGIL: Force: Physics First NameMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument4 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument3 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Forces NotesDocument13 pagesForces NotesAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- Electric ForcesDocument4 pagesElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Electric PowerDocument4 pagesElectric PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Relativistic EnergyDocument4 pagesRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument3 pagesEnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument3 pagesEm SpectrumMark Prochaska100% (1)
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocument3 pagesPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingDocument3 pagesTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Document4 pagesCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument4 pagesNewton's Second LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Second LawDocument5 pagesNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 pagesTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Universal GravitationDocument3 pagesUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 pagesVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- GB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015Document2 pagesGB Atoms Pogil 2014-2015api-261277442No ratings yet
- Vector ComponentsDocument4 pagesVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument2 pagesVectorsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument4 pagesAccelerationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocument4 pagesHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Action and ReactionDocument2 pagesAction and ReactionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Working and PowerDocument4 pagesWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesKinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument2 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument52 pagesHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAmeen ShaikNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesKinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark Prochaska50% (2)
- Ch04 Homework SolutionsDocument88 pagesCh04 Homework SolutionsOsama Maher100% (1)
- Week 15 - Gravitational Force GizmoDocument6 pagesWeek 15 - Gravitational Force GizmoCamNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Document9 pagesWorksheet No.3 in PHYSICS 1Joshua DellosaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy UnderstandingDocument12 pagesWork Energy Understandingmbs_13_1953100% (2)
- The Conservation of Energy: Conceptual ProblemsDocument22 pagesThe Conservation of Energy: Conceptual Problemsmukesh3021No ratings yet
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDocument8 pages1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- Ch06 ISMDocument67 pagesCh06 ISMThai-Son LeNo ratings yet
- Paradoxes of Newton's Third LawDocument2 pagesParadoxes of Newton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDocument5 pagesPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydNo ratings yet
- Lecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)Document14 pagesLecture Chapter 2 Physics 1 What Is Newton's First Law?: Experiment On Newtons LAW OF MOTION (Lab Activity No. 2)verboseNo ratings yet
- 5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsDocument1 page5.E Newton's Laws of Motion (Exercises) - Physics LibreTextsMuhamad AfdalNo ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesLaws of MotionJeya Plays YTNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: CausesDocument20 pagesDynamics: CausesperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 HONORS0Document25 pagesUnit 4 HONORS0Evan StarrNo ratings yet
- Relativistic EnergyDocument4 pagesRelativistic EnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 pagesVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Vector ComponentsDocument4 pagesVector ComponentsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument3 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument2 pagesVectorsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- ScaleDocument4 pagesScaleMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument3 pagesEnergyMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Electric ForcesDocument4 pagesElectric ForcesMark Prochaska100% (1)
- POGIL: Length ContractionDocument3 pagesPOGIL: Length ContractionMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Electric PowerDocument4 pagesElectric PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Working and PowerDocument4 pagesWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument2 pagesAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Newton's Second LawDocument5 pagesNewton's Second LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Temperature and HeatingDocument4 pagesTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- VelocityDocument4 pagesVelocityMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third LawDocument3 pagesNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Universal GravitationDocument3 pagesUniversal GravitationMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesKinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMark Prochaska50% (2)
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocument4 pagesHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First LawDocument4 pagesNewton's First LawMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet