Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsInformative Digital Poster Sample
Informative Digital Poster Sample
Uploaded by
kcx6g8dzdjThis document discusses quantitative research methods. It defines quantitative research as using numerical data and statistical analysis, and notes its strengths are objectivity and generalizability while weaknesses can include oversimplification. It provides guidelines for choosing a good quantitative research problem, including topics that are relevant, specific, researchable and have a clear research question addressing numerical data. It also outlines characteristics of variables, levels of measurement, qualities of a good research title, and different kinds of quantitative research.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJenie Espino100% (9)
- Difference Between Service and Product QualityDocument3 pagesDifference Between Service and Product Qualityferreirae100% (3)
- Yarn EvennessDocument30 pagesYarn EvennessMd Ahasan HabibNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Reviewernd555100% (12)
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Persuasive Speech On Limiting The Production and Use of PlasticDocument2 pagesA Persuasive Speech On Limiting The Production and Use of PlasticKemberly Semaña Penton100% (1)
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerMarlian ElgincolinNo ratings yet
- pr2 NotesDocument8 pagespr2 Notesjclmaeramonal23No ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerJhea May CatapiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Document4 pagesReviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Jv OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument8 pagesResearch Notestessamay0982No ratings yet
- Crim 7Document6 pagesCrim 7Al FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJenie EspinoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Lesson 1Document5 pagesPractical Research 2 - Lesson 1Chin KwonNo ratings yet
- Research Reviewer Q2Document3 pagesResearch Reviewer Q2senjiNo ratings yet
- PR2 ExamreviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ExamreviewerLeonah VelascoNo ratings yet
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research (PR 3)Document3 pagesQuantitative Research (PR 3)leibnagNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch ReviewerEliza MaeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Lesson 1Document2 pagesPractical Research Lesson 1Reinn DionisioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Quincy Joy SarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- Handouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Document3 pagesHandouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Alvin Ray GarciaNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument24 pagesResearch DesignNeza MAe Bulat-ag SalutanNo ratings yet
- Research HandoutsDocument14 pagesResearch HandoutsMichelle Manibale R.N100% (2)
- 1ST QT Research ReviewerDocument12 pages1ST QT Research ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Q1 PR2 Notes 2Document14 pagesQ1 PR2 Notes 2ericka khimNo ratings yet
- NCMB315 MidtermDocument19 pagesNCMB315 Midterm2 - GUEVARRA, KYLE JOSHUA M.No ratings yet
- RESEARCH ReviewerDocument4 pagesRESEARCH ReviewerCARDO SegumaNo ratings yet
- Eda - Module 1Document4 pagesEda - Module 1Zane TitaniumNo ratings yet
- Qualitative-Research IntroductionDocument7 pagesQualitative-Research Introductionmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- PR For PTDocument3 pagesPR For PTAbbyjane MadlangsakayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument8 pagesPractical Researchsrd9g6jj58No ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch ReviewerZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Research Approaches and DesignsDocument5 pagesResearch Approaches and Designsmahmoudmustapha93No ratings yet
- Practical Research II Grade 12 (1st Quarter)Document5 pagesPractical Research II Grade 12 (1st Quarter)gallegos.elijahjerome.belenNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument6 pagesResearch ReviewerChristyl Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Overview of Research Process in EducationDocument27 pagesOverview of Research Process in Educationkkeng9570No ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument69 pagesResearch MethodologyEa ShaNo ratings yet
- Research 1ST QuarterDocument3 pagesResearch 1ST QuarterSandara MarieNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument29 pagesNotesB12. Lacorte, Daniel Ross R.No ratings yet
- Research Intervention, Planning Data Analysis and Research Methodology (W2) Quarter 2Document2 pagesResearch Intervention, Planning Data Analysis and Research Methodology (W2) Quarter 2Blaise CañonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document4 pagesPractical Research 2Vinluan, Kaye Andrei P.No ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerRyan GañaNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-11Document15 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-11030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- Study Guide First QuarterDocument3 pagesStudy Guide First QuarterValNo ratings yet
- PR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Document7 pagesPR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Jasmin MasaNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument11 pagesStatsAkirha SoNo ratings yet
- NRES Review201Document223 pagesNRES Review201Jenny BalocatingNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-4Document5 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-4030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- ResprojDocument11 pagesResprojlovelykat728No ratings yet
- Respondent (Random) Respondent (Nonrandom) : Systematically Collect DataDocument3 pagesRespondent (Random) Respondent (Nonrandom) : Systematically Collect DataJasmine Joy LopezNo ratings yet
- Research MethodDocument20 pagesResearch MethodMarchelino Devan WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Practical Research 2Document3 pagesReviewer in Practical Research 2Elmo Vincent Bernardo MurosNo ratings yet
- PracRes - 1st Quarter Notes-MinDocument10 pagesPracRes - 1st Quarter Notes-Minlalla.lilli026No ratings yet
- ECD415 Project Preliminary SyllabusDocument7 pagesECD415 Project Preliminary Syllabuslakshmivs23No ratings yet
- How To Write A Thesis StatementDocument8 pagesHow To Write A Thesis StatementNgọc Quân TrươngNo ratings yet
- About The Job Smelter Operation ReadinessDocument4 pagesAbout The Job Smelter Operation Readinessmuhammad ridwanNo ratings yet
- Proc No 548 Multimodal TransportDocument19 pagesProc No 548 Multimodal TransportasdfNo ratings yet
- TD13 enDocument12 pagesTD13 enkiyong namNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing PartsDocument14 pagesEssay Writing PartsPAK JANNo ratings yet
- Material Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)Document4 pagesMaterial Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)krishanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflDocument7 pagesNumerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflvinodNo ratings yet
- Conclusion PolymersDocument1 pageConclusion Polymershuong louNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Resorcinol in Presence of PhenolDocument2 pagesQuantitative Determination of Resorcinol in Presence of Phenolראול אפונטהNo ratings yet
- Riding The Waves of CultureDocument3 pagesRiding The Waves of CultureWaqar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- EPP E2 Activity 2Document2 pagesEPP E2 Activity 2Hannah Nore TalingtingNo ratings yet
- HSE Calendar 2023 - 221230 - 112723Document13 pagesHSE Calendar 2023 - 221230 - 112723Mkd OfficialNo ratings yet
- Bioethics-UNIT 2Document81 pagesBioethics-UNIT 2Bea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Matlab Sheet 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesMatlab Sheet 1 SolutionLonardo WajihNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 109Document3 pagesProf Ed 109Nadnad DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsGerald BaculnaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Different Heights and Angles of EnerDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Different Heights and Angles of EnersaiNo ratings yet
- The Awesome Classroom Design CommitteeDocument3 pagesThe Awesome Classroom Design CommitteeVatamanu ValeriaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CalculationsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry CalculationsasyaroesNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus B.tech 1stDocument12 pagesUG Syllabus B.tech 1stRaunak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanDocument8 pagesStruktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanSri FamilasariNo ratings yet
- #5 Conservation of EnergyDocument2 pages#5 Conservation of Energyaruzhankarabala98No ratings yet
- ORIGINALDocument2 pagesORIGINALKristel Joy ManceraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Effective CommunicationtaherzamanratherNo ratings yet
- Reservoir EngineeringDocument13 pagesReservoir EngineeringhasanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- 18-19 HỌC SINH GIỎI CẤP TỈNH CHO HSDocument6 pages18-19 HỌC SINH GIỎI CẤP TỈNH CHO HStien leNo ratings yet
Informative Digital Poster Sample
Informative Digital Poster Sample
Uploaded by
kcx6g8dzdj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageThis document discusses quantitative research methods. It defines quantitative research as using numerical data and statistical analysis, and notes its strengths are objectivity and generalizability while weaknesses can include oversimplification. It provides guidelines for choosing a good quantitative research problem, including topics that are relevant, specific, researchable and have a clear research question addressing numerical data. It also outlines characteristics of variables, levels of measurement, qualities of a good research title, and different kinds of quantitative research.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses quantitative research methods. It defines quantitative research as using numerical data and statistical analysis, and notes its strengths are objectivity and generalizability while weaknesses can include oversimplification. It provides guidelines for choosing a good quantitative research problem, including topics that are relevant, specific, researchable and have a clear research question addressing numerical data. It also outlines characteristics of variables, levels of measurement, qualities of a good research title, and different kinds of quantitative research.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageInformative Digital Poster Sample
Informative Digital Poster Sample
Uploaded by
kcx6g8dzdjThis document discusses quantitative research methods. It defines quantitative research as using numerical data and statistical analysis, and notes its strengths are objectivity and generalizability while weaknesses can include oversimplification. It provides guidelines for choosing a good quantitative research problem, including topics that are relevant, specific, researchable and have a clear research question addressing numerical data. It also outlines characteristics of variables, levels of measurement, qualities of a good research title, and different kinds of quantitative research.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
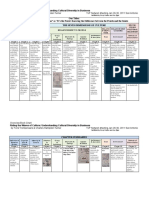
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
Caadan, Ainbelle Leoveras
How to choose a good quantitative research
problem;
To choose a good quantitative research problem,
consider selecting a topic that is relevant, specific,
researchable, and has a clear research question that
can be addressed using numerical data and
statistical analysis.
Characteristics, Strengths, and Variables in Quantitative Research in
Weakness of Quantitative Research terms of Roles and Level of
Qualities of a Good Measurement
Quantitative Research Title
> Concise and descriptive of the
Quantitative research is characterized by research topic. Roles of Variables
its use of numerical data and statistical > Includes key variables or concepts.
analysis, its strengths include objectivity ➢ Independent Variable – The variable
and generalizability, but its weaknesses > Avoids jargon and acronyms.
manipulated by the researcher.
may include limited depth of > Engages the reader’s interest. ➢ Dependent Variable – The outcome
understanding and the potential for or effect being studied.
> Indicates the research approach
oversimplification.
(quantitative).
Levels of Measurement
➢ Characteristic:
Involves the collection and analysis of
➢ Nominal – Categorical data with no
numerical data. Focuses on objective,
inherent
measurable phenomena. Often
➢ Ordinal – Categorical data with a
structured and standarsized.
meaningful order
➢ Interval – Numerical data with equal
➢ Strengths:
intervals but no true zero point
Provides precise and reliable data. Allows
➢ Ratio – Numerical data with equal
for generalization of findings.
Kinds of Qualitative intervals and a true zero point
➢ Weaknesses: Research
Limited in addressing complex social
phenomena. Potential for researcher
bias in data collection. Time consuming
➢ Descriptive Research – Aims to
describe a phenomenon without
manipulating it 6
➢ Correlational Research – Examines 5
relationships between variables
➢ Experimental Research – Involves
4
manipulating variables to establish
6
3
5 causation 2
➢ Survey Research – Collects data
through questionnaires
4 1
3 ➢ Longitudinal Research – Studies 0
Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4
2
changes over time
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJenie Espino100% (9)
- Difference Between Service and Product QualityDocument3 pagesDifference Between Service and Product Qualityferreirae100% (3)
- Yarn EvennessDocument30 pagesYarn EvennessMd Ahasan HabibNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Reviewernd555100% (12)
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Persuasive Speech On Limiting The Production and Use of PlasticDocument2 pagesA Persuasive Speech On Limiting The Production and Use of PlasticKemberly Semaña Penton100% (1)
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerMarlian ElgincolinNo ratings yet
- pr2 NotesDocument8 pagespr2 Notesjclmaeramonal23No ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerJhea May CatapiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Document4 pagesReviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Jv OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument8 pagesResearch Notestessamay0982No ratings yet
- Crim 7Document6 pagesCrim 7Al FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJenie EspinoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Lesson 1Document5 pagesPractical Research 2 - Lesson 1Chin KwonNo ratings yet
- Research Reviewer Q2Document3 pagesResearch Reviewer Q2senjiNo ratings yet
- PR2 ExamreviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ExamreviewerLeonah VelascoNo ratings yet
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaDocument2 pagesLESSON 5.1: Introduction To Research Methodologies: 2nd SEMESTER S.Y 2022-2023 Lecturer: Mr. Eric PalmerolaBIANCA LEONA MARIE PUNONo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research (PR 3)Document3 pagesQuantitative Research (PR 3)leibnagNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch ReviewerEliza MaeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Lesson 1Document2 pagesPractical Research Lesson 1Reinn DionisioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Quincy Joy SarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- Handouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Document3 pagesHandouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Alvin Ray GarciaNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument24 pagesResearch DesignNeza MAe Bulat-ag SalutanNo ratings yet
- Research HandoutsDocument14 pagesResearch HandoutsMichelle Manibale R.N100% (2)
- 1ST QT Research ReviewerDocument12 pages1ST QT Research ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Q1 PR2 Notes 2Document14 pagesQ1 PR2 Notes 2ericka khimNo ratings yet
- NCMB315 MidtermDocument19 pagesNCMB315 Midterm2 - GUEVARRA, KYLE JOSHUA M.No ratings yet
- RESEARCH ReviewerDocument4 pagesRESEARCH ReviewerCARDO SegumaNo ratings yet
- Eda - Module 1Document4 pagesEda - Module 1Zane TitaniumNo ratings yet
- Qualitative-Research IntroductionDocument7 pagesQualitative-Research Introductionmblanco.dchNo ratings yet
- PR For PTDocument3 pagesPR For PTAbbyjane MadlangsakayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR 2Document2 pagesReviewer PR 2jet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument8 pagesPractical Researchsrd9g6jj58No ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch ReviewerZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Research Approaches and DesignsDocument5 pagesResearch Approaches and Designsmahmoudmustapha93No ratings yet
- Practical Research II Grade 12 (1st Quarter)Document5 pagesPractical Research II Grade 12 (1st Quarter)gallegos.elijahjerome.belenNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument6 pagesResearch ReviewerChristyl Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Overview of Research Process in EducationDocument27 pagesOverview of Research Process in Educationkkeng9570No ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument69 pagesResearch MethodologyEa ShaNo ratings yet
- Research 1ST QuarterDocument3 pagesResearch 1ST QuarterSandara MarieNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument29 pagesNotesB12. Lacorte, Daniel Ross R.No ratings yet
- Research Intervention, Planning Data Analysis and Research Methodology (W2) Quarter 2Document2 pagesResearch Intervention, Planning Data Analysis and Research Methodology (W2) Quarter 2Blaise CañonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document4 pagesPractical Research 2Vinluan, Kaye Andrei P.No ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerRyan GañaNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-11Document15 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-11030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- Study Guide First QuarterDocument3 pagesStudy Guide First QuarterValNo ratings yet
- PR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Document7 pagesPR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Jasmin MasaNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument11 pagesStatsAkirha SoNo ratings yet
- NRES Review201Document223 pagesNRES Review201Jenny BalocatingNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-4Document5 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-4030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- ResprojDocument11 pagesResprojlovelykat728No ratings yet
- Respondent (Random) Respondent (Nonrandom) : Systematically Collect DataDocument3 pagesRespondent (Random) Respondent (Nonrandom) : Systematically Collect DataJasmine Joy LopezNo ratings yet
- Research MethodDocument20 pagesResearch MethodMarchelino Devan WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Practical Research 2Document3 pagesReviewer in Practical Research 2Elmo Vincent Bernardo MurosNo ratings yet
- PracRes - 1st Quarter Notes-MinDocument10 pagesPracRes - 1st Quarter Notes-Minlalla.lilli026No ratings yet
- ECD415 Project Preliminary SyllabusDocument7 pagesECD415 Project Preliminary Syllabuslakshmivs23No ratings yet
- How To Write A Thesis StatementDocument8 pagesHow To Write A Thesis StatementNgọc Quân TrươngNo ratings yet
- About The Job Smelter Operation ReadinessDocument4 pagesAbout The Job Smelter Operation Readinessmuhammad ridwanNo ratings yet
- Proc No 548 Multimodal TransportDocument19 pagesProc No 548 Multimodal TransportasdfNo ratings yet
- TD13 enDocument12 pagesTD13 enkiyong namNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing PartsDocument14 pagesEssay Writing PartsPAK JANNo ratings yet
- Material Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)Document4 pagesMaterial Inspection Request - CIVIL - QF - R-MIR-C-Q-281 (23 - 10 - 2023)krishanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflDocument7 pagesNumerical Study On Application of CuO-Water NanoflvinodNo ratings yet
- Conclusion PolymersDocument1 pageConclusion Polymershuong louNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Resorcinol in Presence of PhenolDocument2 pagesQuantitative Determination of Resorcinol in Presence of Phenolראול אפונטהNo ratings yet
- Riding The Waves of CultureDocument3 pagesRiding The Waves of CultureWaqar Akbar KhanNo ratings yet
- EPP E2 Activity 2Document2 pagesEPP E2 Activity 2Hannah Nore TalingtingNo ratings yet
- HSE Calendar 2023 - 221230 - 112723Document13 pagesHSE Calendar 2023 - 221230 - 112723Mkd OfficialNo ratings yet
- Bioethics-UNIT 2Document81 pagesBioethics-UNIT 2Bea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Matlab Sheet 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesMatlab Sheet 1 SolutionLonardo WajihNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 109Document3 pagesProf Ed 109Nadnad DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Observation Grade 12 PhysicsGerald BaculnaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Different Heights and Angles of EnerDocument10 pagesThe Effect of Different Heights and Angles of EnersaiNo ratings yet
- The Awesome Classroom Design CommitteeDocument3 pagesThe Awesome Classroom Design CommitteeVatamanu ValeriaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry CalculationsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry CalculationsasyaroesNo ratings yet
- UG Syllabus B.tech 1stDocument12 pagesUG Syllabus B.tech 1stRaunak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanDocument8 pagesStruktur Anatomi Dan Kualitas Serat Kayu Parashorea Malaanonan (Blanco) Merr. (Anatomical Structure and Fiber Quality of Parashorea MalaanonanSri FamilasariNo ratings yet
- #5 Conservation of EnergyDocument2 pages#5 Conservation of Energyaruzhankarabala98No ratings yet
- ORIGINALDocument2 pagesORIGINALKristel Joy ManceraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Effective CommunicationtaherzamanratherNo ratings yet
- Reservoir EngineeringDocument13 pagesReservoir EngineeringhasanuzzamanNo ratings yet
- 18-19 HỌC SINH GIỎI CẤP TỈNH CHO HSDocument6 pages18-19 HỌC SINH GIỎI CẤP TỈNH CHO HStien leNo ratings yet