Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet - 1
Worksheet - 1
Uploaded by
Santanu DasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet - 1
Worksheet - 1
Uploaded by
Santanu DasCopyright:
Available Formats
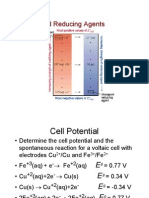
WORKSHEET - 1
Q1. The standard electrode potential of zinc ions is 0.76V. What will be the potential of a
2M solution at 300K?
Solution:
The Nernst equation for the given conditions can be written as follows;
EMn+/M = Eo – [(2.303RT)/nF] × log 1/[Mn+]
Here,
E° = 0.76V
n=2
F = 96500 C/mole
[Mn+] = 2 M
R =8.314 J/K mole
T =300 K
Substituting the given values in Nernst equation we get,
EZn2+/Zn = 0.76 – [(2.303×8.314×300)/(2×96500)] × log 1/2 = 0.76 – [0.0298 × (-0.301)]
= 0.76 + 0.009 = 0.769V
Therefore, the potential of a 2M solution at 300K is 0.769V.
For any doubt contact on whatsApp 9045693981 Page 1
Page 1
Q2. From the following standard potentials, arrange the metals in the order of their
increasing reducing power.
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s): E° = -0.76 V
Ca2+(aq) + 2e– → Ca(s): E° = -2.87 V
Mg2+(aq) + 2e– → Mg(s): E° = -2.36 V
Ni2+(aq) + 2e– → Ni(s): E° = -0.25 V
Ni(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2e– : E° = +0.25 V
Reducing power of a metal increases with its ability to give up electrons ie lower standard
potentials. Arranging the reduction potentials in the decreasing order gives the increasing order
of reducing power of metals.
Increasing order of reduction potentials is Ni (-0.25V) < Zn (-0.76V) < Mg(-2.36V) < Ca(-2.87).
Q3. What is the Cell Potential of the electrochemical cell in Which the cell reaction
is: Pb2+ + Cd → Pb + Cd2+ ; Given that Eocell = 0.277 volts, temperature = 25oC, [Cd2+]
= 0.02M, and [Pb2+] = 0.2M.
Solution
Since the temperature is equal to 25oC, the Nernst equation can be written as follows;
Ecell = E0cell – (0.0592/n) log10Q
Here, two moles of electrons are transferred in the reaction. Therefore, n = 2. The reaction
quotient (Q) is given by [Cd2+]/[Pb2+] = (0.02M)/(0.2M) = 0.1.
The equation can now be rewritten as:
For any doubt contact on whatsApp 9045693981 Page 2
Page 2
Ecell = 0.277 – (0.0592/2) × log10(0.1) = 0.277 – (0.0296)(-1) = 0.3066 Volts
Thus, the cell potential of this electrochemial cell at a temperature of 25oC is 0.3066 volts.
Q4. The Cu2+ ion concentration in a copper-silver electrochemical cell is 0.1M. If
Eo(Ag+/Ag) = 0.8V, Eo(Cu2+/Cu) = 0.34V, and Cell potential (at 25oC) = 0.422V, find the
silver ion concentration.
Solution
Here, the silver electrode acts as a cathode whereas the copper electrode serves as the anode.
This is because the standard electrode potential of the silver electrode is greater than that of the
copper electrode. The standard electrode potential of the cell can now be calculated, as shown
below.
Eocell = Eocathode – Eoanode = 0.8V – 0.34V = 0.46V
Since the charge on the copper ion is +2 and the charge on the silver ion is +1, the balanced cell
reaction is:
2Ag+ + Cu → 2Ag + Cu2+
Since two electrons are transferred in the cell reaction, n = 2. Now, the Nernst equation for this
electrochemical cell can be written as follows.
Ecell = E0cell – (0.0592/2) × log(0.1/[Ag+]2)
0.422V = 0.46 – 0.0296 × (-1 – 2log[Ag+])
Therefore, -2log[Ag+] = 1.283 + 1 = 2.283
For any doubt contact on whatsApp 9045693981 Page 3
Page 3
Or, log[Ag+] = -1.141
[Ag+] = antilog(-1.141) = 0.0722 M
For any doubt contact on whatsApp 9045693981 Page 4
Page 4
You might also like
- Exp 2 Electrochemistry - Electrochemical Cell and Thermodynamic FunctionsDocument8 pagesExp 2 Electrochemistry - Electrochemical Cell and Thermodynamic FunctionsMuhammad Amirul AfifiNo ratings yet
- ENG-TIPS de Vessel Circular Section Single Diametral Staying Member Rev 000c-3Document1 pageENG-TIPS de Vessel Circular Section Single Diametral Staying Member Rev 000c-3RomeoMendozaNo ratings yet
- CSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and QuestionsDocument133 pagesCSWIP Welding Inspection Notes and Questionslram70100% (20)
- Electro Chemistry Part-1Document2 pagesElectro Chemistry Part-1Santpal KalraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 2 PDFDocument1 pageChapter 1 - 2 PDFMadan panditNo ratings yet
- Nernst Equation.Document13 pagesNernst Equation.15 Kabir Sharma 10 HNo ratings yet
- CHE1000 & 1010 - Tutorial Sheet 5 Marking KeyDocument10 pagesCHE1000 & 1010 - Tutorial Sheet 5 Marking Keychimfwembeemmanuel712No ratings yet
- Q1) Calculate The Electrode Potential of Cu, If The Conc. of Cuso Is 0.206 M at 23.1°C. Given That E° 0.34 VDocument17 pagesQ1) Calculate The Electrode Potential of Cu, If The Conc. of Cuso Is 0.206 M at 23.1°C. Given That E° 0.34 Votherwork3757No ratings yet
- Electro SulDocument4 pagesElectro SulChutvinder LanduliyaNo ratings yet
- Nernst EquationDocument22 pagesNernst EquationAnishah ChaudheryNo ratings yet
- 3 Electrochemistry NCERT Soln.Document20 pages3 Electrochemistry NCERT Soln.hulkahsanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2electrochemical Cells EditedDocument50 pagesChapter 2electrochemical Cells EditedAdugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- Laily Jannati - 193010208001 - Elektrokimia Exp 6,7,8,9Document4 pagesLaily Jannati - 193010208001 - Elektrokimia Exp 6,7,8,9Anas Tasya GultomNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry NotesDocument83 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notess. EswarNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 3) (Electrochemistry)Document18 pages(Chapter 3) (Electrochemistry)Yuvraj Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Quiz 2Document2 pagesMarking Scheme Quiz 2NOR ZARINA BT MOHAMAD MoeNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY Worksheet With AnswersG.D. Pranav.LaskhminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Document13 pagesModule 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Steven LeeNo ratings yet
- EC Tutorial Sheet-2 II SEM 2023-24Document2 pagesEC Tutorial Sheet-2 II SEM 2023-24annofelia431No ratings yet
- CHM143 Answer For Tutorial 6Document5 pagesCHM143 Answer For Tutorial 62023502121No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ProblemsDocument14 pagesElectrochemistry ProblemsExporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Galvanic CellsDocument13 pagesActivity 1 - Galvanic Cellskarina gayosNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYExporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry LabDocument6 pagesElectrochemistry LabnahNo ratings yet
- Term - 2 Chemistry: Mahendra KalraDocument28 pagesTerm - 2 Chemistry: Mahendra KalraNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Revision 2022Document2 pagesElectrochemistry Revision 2022HARSH KHILARINo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry AssignmentDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry AssignmentSulekha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Additional Numerical Galvanic CellDocument2 pagesAdditional Numerical Galvanic CellPrahlad Das0% (1)
- Electrochemistry Complete NCERTDocument20 pagesElectrochemistry Complete NCERTNitesh YadavNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesElectrochemistryradheyNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYISLAM I. Fekry100% (2)
- Electrochemistry 12Document19 pagesElectrochemistry 12Manas ChhabraNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDocument17 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: e So Conventional Current K PotentiometerDocument9 pagesElectrochemistry: e So Conventional Current K PotentiometerRica Janelle Rioflorido MarticioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Galvanic Cell (Student Version)Document3 pagesExperiment 1 Galvanic Cell (Student Version)Husna Insyirah Bt SamadNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesElectrochemistryinstasafe424No ratings yet
- Recommended Exercises and ProblemsDocument92 pagesRecommended Exercises and ProblemsDan TranNo ratings yet
- Malate + NAD Oxaloacetate + NADH + HDocument14 pagesMalate + NAD Oxaloacetate + NADH + HRonaldNo ratings yet
- CHEM1101 Week 13 AnswersDocument6 pagesCHEM1101 Week 13 AnswersUnknown GamerNo ratings yet
- 2 MS ElectrochemistryDocument7 pages2 MS ElectrochemistrysachinNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Applications of RedoxDocument29 pagesElectrochemistry: Applications of RedoxrachelelkinNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry (QB)Document4 pagesElectro Chemistry (QB)Akshith ReddyNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument1 pageELECTROCHEMISTRYbriefcinemablitzNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 Postlab ReportDocument8 pagesPractical 4 Postlab Reportgracebrewster123No ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (Chem 111A) Laboratory Activity 7: University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesDocument3 pagesChemistry For Engineers (Chem 111A) Laboratory Activity 7: University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesMoguri OwowNo ratings yet
- Penugasan Pertemuan Ke 14Document1 pagePenugasan Pertemuan Ke 1421BELLAPERMATASARI kimiaNo ratings yet
- L2 - Daniell - Jacobi CellDocument6 pagesL2 - Daniell - Jacobi CellIuliana CovaliuNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Assignment 5Document2 pages12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Assignment 5sansharmajsNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12th Electrostatic NotesDocument2 pagesPhysics Class 12th Electrostatic Notespankaj singhNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesElectrochemistryHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 3 Electrochemical CellDocument5 pagesLab Report Exp 3 Electrochemical CellYe Woon LimNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyDocument3 pagesModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- 22CHE22-notesModule 1Document24 pages22CHE22-notesModule 1Vinay AdariNo ratings yet
- Nernst Equation 3Document20 pagesNernst Equation 3KasunBuddikaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of CellsDocument11 pagesThermodynamics of Cellsjonathan_raimanNo ratings yet
- Brady Solution Chapter 20Document31 pagesBrady Solution Chapter 20NurrahmisrNo ratings yet
- Solved QuestionsDocument11 pagesSolved Questionspankaj16fbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 BQDocument10 pagesChapter 18 BQTarek GhaddarNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- af18d208-8d38-4f29-b074-c56c0115e712Document11 pagesaf18d208-8d38-4f29-b074-c56c0115e712Santanu DasNo ratings yet
- Halogen DerivativeDocument6 pagesHalogen DerivativeSantanu DasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Second-YearDocument5 pagesChemistry Second-YearSantanu DasNo ratings yet
- Scan 13 Jun 2023Document1 pageScan 13 Jun 2023Santanu DasNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mass SpectrometryDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Mass SpectrometryFatma Zorlu100% (2)
- Physics HL IA - Viscosity - FINAL DRAFTDocument8 pagesPhysics HL IA - Viscosity - FINAL DRAFTDavid Sendín LloredaNo ratings yet
- JIS G3131 Hot Roll Mild Steel Plates Sheet and StripDocument9 pagesJIS G3131 Hot Roll Mild Steel Plates Sheet and StripAnonymous uYGle1vucNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Exo and EndoDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Exo and Endoapi-385539760No ratings yet
- Elasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WADocument12 pagesElasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- Astm-D751 06Document19 pagesAstm-D751 06Jeff Gaje100% (1)
- Rubens' TubeDocument3 pagesRubens' Tubem_a_nevesNo ratings yet
- E 101Document21 pagesE 101EberVelazquezChantacaNo ratings yet
- Ecss Q ST 70 01cDocument75 pagesEcss Q ST 70 01cspaceengineering0815No ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Technology, AASTU, Hydropower, Lect 6Document45 pagesSustainable Energy Technology, AASTU, Hydropower, Lect 6Desta MotbaynorNo ratings yet
- Leica Flexline Ts03 Ts07 Ds 876721 1018 en LRDocument2 pagesLeica Flexline Ts03 Ts07 Ds 876721 1018 en LRGreg LimNo ratings yet
- UST - PHD Program PDFDocument60 pagesUST - PHD Program PDFhp2020No ratings yet
- Latent and Specific Heat - QPDocument17 pagesLatent and Specific Heat - QPCUonline OfficeNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 Rotational InertiaDocument8 pagesLAB 2 Rotational Inertiamohdiqbal93No ratings yet
- Aerodynamics CFD ProjectDocument10 pagesAerodynamics CFD ProjectBrehndenNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHDocument39 pagesMaintenance Procedure For Switchyard Equipment Volume-II (EHbisas_rishiNo ratings yet
- SSD 2119Document95 pagesSSD 2119Leonardo1498100% (1)
- Evaporation: (I) Vapour PressureDocument15 pagesEvaporation: (I) Vapour Pressurevenka07No ratings yet
- CAR 66 Module 5.12 Electrostatics Sensitive DeviceDocument12 pagesCAR 66 Module 5.12 Electrostatics Sensitive Devicepontoo100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics - ProblemsDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics - ProblemsClement Chima50% (2)
- 05020-250-090-MDS-116-01-01 Rev.2 (090TK-001,002) DCU FEED TANKSDocument5 pages05020-250-090-MDS-116-01-01 Rev.2 (090TK-001,002) DCU FEED TANKSSelim SelimNo ratings yet
- The Adventures of Tom Sawyer EssayDocument6 pagesThe Adventures of Tom Sawyer Essayb725c62j100% (2)
- VertiMill - Preparing The Feed Within Flotable Regime at Lower Specific EnergyDocument9 pagesVertiMill - Preparing The Feed Within Flotable Regime at Lower Specific EnergyYesi CeballosNo ratings yet
- 2D Electron GasDocument16 pages2D Electron GastridevmishraNo ratings yet
- ConferencePaper AB2019 04 FADocument18 pagesConferencePaper AB2019 04 FAMito ManNo ratings yet
- MIT Math Correl 2nd Term AY 2014 2015 RetakeDocument9 pagesMIT Math Correl 2nd Term AY 2014 2015 RetakeJhera Ku100% (1)
- DNV Rule Ship DesinDocument12 pagesDNV Rule Ship DesinRWTWWNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetics by UlabyDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Electromagnetics by UlabyhistandNo ratings yet