Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE Mat Higher2
GCSE Mat Higher2
Uploaded by
JayCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- GCSE Mat (Higher)Document1 pageGCSE Mat (Higher)renekah ghhiNo ratings yet
- Hagseed + TempestDocument3 pagesHagseed + Tempesteve4binetNo ratings yet
- Hcia RSDocument131 pagesHcia RSZveZ100% (1)
- Signal Urchin Rostrum ASCII TABDocument6 pagesSignal Urchin Rostrum ASCII TABTmitch81No ratings yet
- ITBIS373 Database Development: Guide To Oracle 10gDocument73 pagesITBIS373 Database Development: Guide To Oracle 10gdesitorontoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing ProcessDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing Processjessa barbosaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 FormulaeDocument16 pagesGrade 10 FormulaeRITIN A.C.RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Multiple IntegralsDocument33 pagesChapter 5 Multiple Integrals物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument12 pagesLesson 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsmeisukeyumeNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSAT Math Formula SheetvanbutnotavanNo ratings yet
- M2 Adv. AlgebraDocument5 pagesM2 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Solving Neutrosophic Travelling Salesaman Problem in Triangular Fuzzy Number Using Ones Assignment MethodDocument7 pagesSolving Neutrosophic Travelling Salesaman Problem in Triangular Fuzzy Number Using Ones Assignment MethodScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionDocument4 pagesExponential FunctionErica Mamauag100% (1)
- Complex Number, Binomial & PolinomialsDocument2 pagesComplex Number, Binomial & PolinomialsTalha Ash SharkɪNo ratings yet
- (Hal 1) RUMUS MPSL UTS ST Utak AtikDocument2 pages(Hal 1) RUMUS MPSL UTS ST Utak AtikR. RR APRIANI SOFIANANo ratings yet
- All Important Curves Sketching (P1) : Name Shape Shortcut Remark ExampleDocument1 pageAll Important Curves Sketching (P1) : Name Shape Shortcut Remark ExampleNacon ProNo ratings yet
- Summary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيDocument7 pagesSummary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيLilian AlkordyNo ratings yet
- Formule Statistica Descriptiva 2021Document1 pageFormule Statistica Descriptiva 2021Florentina GutanuNo ratings yet
- Math IgcseDocument13 pagesMath IgcseminthantphoneNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 11 Revision and Final Exam Prep Paper 1 What You Need To Know Algebra 2020Document4 pagesMathematics Grade 11 Revision and Final Exam Prep Paper 1 What You Need To Know Algebra 2020simamkelsmncubeNo ratings yet
- Exercise: 2.7 Linear Approximations and DifferentialsDocument14 pagesExercise: 2.7 Linear Approximations and Differentialsazyan yusraNo ratings yet
- Acst356 Class Test 1 FinalDocument1 pageAcst356 Class Test 1 FinalJoshua AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Required Formulas: Number Line: Sign NumbersDocument2 pagesRequired Formulas: Number Line: Sign Numberszahed83No ratings yet
- Formulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Document3 pagesFormulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Eduardo Torres PinoNo ratings yet
- Formulas de DerivacionDocument3 pagesFormulas de DerivacionESTEFANIA AMATONNo ratings yet
- HL AA Complex Number Notes RMSDocument14 pagesHL AA Complex Number Notes RMSTanish BenganiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Maths Chapter 3 Soulution NOTESPKDocument48 pages2nd Year Maths Chapter 3 Soulution NOTESPKFaisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- 4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationDocument23 pages4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationKamran BabarNo ratings yet
- ACTMath Formula Sheet 2Document2 pagesACTMath Formula Sheet 2Stu PotNo ratings yet
- Ch4 NumDocument13 pagesCh4 Numahmed ramadanNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 Two Hinge ArchDocument3 pagesEx 1 Two Hinge ArchchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- 7.4 NotesDocument2 pages7.4 NotesSahar SayedNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Module Week14Document3 pagesMath 9 Module Week14Destiny Fiona Peralta PilarNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Formulae Sheet 3 PDFDocument6 pagesSAT Math Formulae Sheet 3 PDFAryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- Mecanica de FluidosDocument6 pagesMecanica de FluidosAndrés sanchezNo ratings yet
- Math 156 Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMath 156 Final Cheat SheetshreyaNo ratings yet
- Xi - Mat - Vol I & II - RRDocument57 pagesXi - Mat - Vol I & II - RRSpedNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - NovDocument1 pageFormula Sheet - NovMegan SenekalNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document27 pagesWeek 314mervekaya01No ratings yet
- Week 11Document76 pagesWeek 11snaaaoNo ratings yet
- ESO209A Notes TutorialDocument14 pagesESO209A Notes TutorialDinesh Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Alves 2018 PDFDocument20 pagesAlves 2018 PDFAvelleo PantaleoNo ratings yet
- Functions Ws 1Document6 pagesFunctions Ws 1Farishta SNo ratings yet
- Laju ReaksiDocument2 pagesLaju ReaksiIzma YulianaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet 34521Document3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet 34521Francis AngtudNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo IntegralDocument2 pagesFormulario Calculo Integralaleeeeeeelopez669No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument2 pagesMathematicsronneil joy obinaNo ratings yet
- Sheet #1 - SolutionDocument14 pagesSheet #1 - SolutionEslam KandeilNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument2 pagesFormula RiololoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-MeasurementDocument1 pageChapter 1-MeasurementantonstefanbiehlerNo ratings yet
- Manual 6to 2020Document14 pagesManual 6to 2020Graci OliveraNo ratings yet
- 30 Selected Notes Two PopulationsDocument1 page30 Selected Notes Two Populationssminatozaki762No ratings yet
- Rumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorDocument2 pagesRumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorAhmad Nur HadieNo ratings yet
- Regularization and Feature Selectio NDocument102 pagesRegularization and Feature Selectio NEhab EmamNo ratings yet
- Formulas 2 T3 AY2020-21Document9 pagesFormulas 2 T3 AY2020-21deanNo ratings yet
- SATMath Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSATMath Formula SheetMuntaha LolNo ratings yet
- 6应用机器学习的建议Document79 pages6应用机器学习的建议836328948No ratings yet
- Formula Scanner Class 10 New PatternDocument1 pageFormula Scanner Class 10 New Patternnitesh kotianNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Paramont NVR - User Manual - v1.2Document119 pagesParamont NVR - User Manual - v1.2Bsm GwapuNo ratings yet
- Data Base Managment SystemDocument14 pagesData Base Managment Systempratham PandeyNo ratings yet
- BA English IdiomsDocument4 pagesBA English IdiomsUmar Zahid100% (2)
- Chuyên Anh Lào Cai 2019-2020Document8 pagesChuyên Anh Lào Cai 2019-2020Tuấn TrầnNo ratings yet
- Excellence in English Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideDocument138 pagesExcellence in English Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideLUIS FERNANDO VARGAS PEÑANo ratings yet
- Gunter Part 1Document9 pagesGunter Part 1api-364531747No ratings yet
- Patrice Pavis - Languages of The StageDocument89 pagesPatrice Pavis - Languages of The StageYİĞİT SÜMBÜLNo ratings yet
- Schutz, On Multiple Realities PDFDocument42 pagesSchutz, On Multiple Realities PDFCarlos ManoelNo ratings yet
- Creating A RFID Door Latch With Arduino: InstructablesDocument15 pagesCreating A RFID Door Latch With Arduino: InstructablesVENOM LYNo ratings yet
- GP 300Document2 pagesGP 300Darya Russ100% (1)
- 0548 w09 Ms 1 PDFDocument7 pages0548 w09 Ms 1 PDFCatherine WreyfordNo ratings yet
- Live Music: Video UK - Exercises: Preparation: MatchingDocument3 pagesLive Music: Video UK - Exercises: Preparation: MatchingFlorijan DjerdjiNo ratings yet
- White Box CryptoDocument60 pagesWhite Box CryptoRaahul SenNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument27 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderFrenstan Tan100% (2)
- Basic HTML CommandsDocument36 pagesBasic HTML CommandsVedamurthy J100% (10)
- Poetry TermsDocument2 pagesPoetry TermstchristianberwicksdoNo ratings yet
- Program Detail - Mastering AI Bootcamp v3Document21 pagesProgram Detail - Mastering AI Bootcamp v3vandal liciousNo ratings yet
- (Learnjapaneseaz - Com) - List of Kanji For JLPT n4 1 10Document10 pages(Learnjapaneseaz - Com) - List of Kanji For JLPT n4 1 10jayihid308No ratings yet
- Презентація 1Document2 pagesПрезентація 1Ніка НаконечнаNo ratings yet
- Qualys Cloud Agent Mac Install GuideDocument23 pagesQualys Cloud Agent Mac Install GuideSalvatore SorrientoNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp6 17l238 RepDocument12 pagesDC Lab Exp6 17l238 RepRakesh VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Going To-Future - English GrammarDocument2 pagesGoing To-Future - English GrammarRicardo Patricio Salazar JijónNo ratings yet
- Sure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Document316 pagesSure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Arthanari Vaidyanathan100% (1)
- Sanskrit Daily ConversationDocument32 pagesSanskrit Daily Conversationapi-370612195% (20)
- Literature in English SyllabusDocument35 pagesLiterature in English SyllabusOmega Joy B. DacayananNo ratings yet
- Excel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterDocument34 pagesExcel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterMariz PacilanNo ratings yet
GCSE Mat Higher2
GCSE Mat Higher2
Uploaded by
JayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Mat Higher2
GCSE Mat Higher2
Uploaded by
JayCopyright:
Available Formats
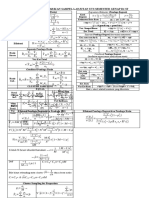
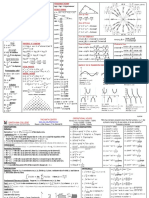
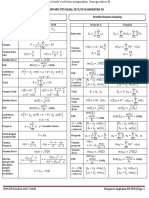
GCSE Mathematics Higher Tier Here is pretty much all the Higher Tier content we could fit onto
Here is pretty much all the Higher Tier content we could fit onto an A3 sheet of paper, including all the formulae you are
required to know for GCSE. An points to an illustrative example. The codes refer to the DfE subject content. Pin this
Number Algebra Ratio, proportion and rates of change Geometry & measures Probability Statistics to a wall, keep it on your desk, carry it in your bag, make notes on it (sorry, don’t take it into the examination)…
Listing strategies N5 Laws of indices A4 Standard graphs A12 Iteration A20 Percentages: multipliers R9, R16
•
Product rule for counting: For any value a: You will be given the formula to use: Percentage increase or decrease; use
𝟒 × 𝟑 × 𝟐 × 𝟏 = 𝟐𝟒 ways to 𝑎 𝑥 × 𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥+𝑦 Solve 𝒙𝟑 + 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟒 = 𝟎 by using a multiplier (powers for repetition)
arrange the letters P, I, X and L. 𝑎𝑥 the iteration 𝒙𝒏+𝟏 = 𝟑√𝟔𝒙𝒏 − 𝟒. Initially there were 20 000 fish
= 𝑎 𝑥−𝑦
𝑎𝑦 in a lake. The number decreases by
Powers and roots N6, N7 Start with 𝒙𝟏 = −𝟐. 𝟖.
(𝑎 𝑥 )𝑦 = 𝑎 𝑥𝑦 15% each year. Estimate the
Special indices: for any value a: 𝟑 𝒙𝟐 = 𝟑√𝟔 × (−𝟐. 𝟖) − 𝟒 = −𝟐. 𝟕𝟓𝟎 … number of fish after 6 years.
𝟐𝒑𝒒𝟒 𝟖𝒑𝟑 𝒒𝟏𝟐 𝟖𝒒𝟗
𝑎0 = 1 ( ) = = or 𝟖𝒒𝟗 𝒑−𝟔 𝟑 𝟐𝟎 𝟎𝟎𝟎 × 𝟎. 𝟖𝟓𝟔 = 𝟕 𝟓𝟎𝟎 (2sf)
1 𝒑𝟑 𝒒 𝒑 𝟗 𝒒𝟑 𝒑𝟔 𝒙𝟑 = √𝟔 × (−𝟐. 𝟕𝟓𝟎 … ) − 𝟒 = ⋯
𝑎−𝑛 = 𝑛 1 Repeat until you know the solution, or
𝑎 𝑦 = 𝑥2 𝑦= 𝑥3 𝑦= 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑥 𝑦 = sin(𝑥°) 𝑦 = cos(𝑥°) 𝑦 = tan(𝑥°) Formula for compound interest
𝑝 Difference of two squares A4 𝑥 you do as many as the question says.
( )
𝑎𝑞
𝑞
= √𝑎𝑝 𝑟 𝑛
𝑎2 − 𝑏 2 = (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 − 𝑏) Total accrued = 𝑃 (1 + )
Quadratics A11, A18 Right angled triangles G20 100
𝟏 𝟏 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟐𝟓 = (𝒙 + 𝟓)(𝒙 − 𝟓) I invest £600 at 3% compound
𝟑−𝟒 = 𝟒= If a quadratic equation cannot be Pythagoras Theorem. Trigonometry. interest. What is my account worth
𝟑 𝟖𝟏 Rearrange a formula A5
factorised, use the formula Links all three sides. Links two sides and one angle.
opposite
c after 5 years?
𝟐 The subject of a formula is the term −𝑏 ± √𝑏 2 − 4𝑎𝑐 No angles. SOH│CAH│TOA 𝟑 𝟓
𝟖
( )
𝟑
𝟑
= √𝟖𝟐 = 4 on its own. Rearrange to 𝑥= 2
𝑎 +𝑏 =𝑐2 2 a £𝟔𝟎𝟎 × (𝟏 + ) = £𝟔𝟗𝟓. 𝟓𝟔
2𝑎 opp adj opp 𝟏𝟎𝟎
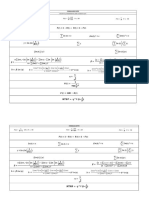
Make 𝒙 the subject of sin𝜃 = cos𝜃 = tan𝜃 =
Solve 𝟐𝒙𝟐 + 𝟑𝒙 − 𝟕 = 𝟎 hyp hyp θ
adj
Direct & inverse proportion R10
Surds N8 𝟐𝒙 + 𝒂𝒚 = 𝒚 − 𝒃𝒙
𝟐𝒙 + 𝒃𝒙 = 𝒚 − 𝒂𝒚 −𝟑−√𝟗−(−𝟓𝟔)
b Use “2ndF” or “SHIFT” key to find a missing angle adjacent
Look for the biggest square number 𝒙= = −𝟐. 𝟕𝟑 𝑦 is directly proportional to 𝑥:
𝒙(𝟐 + 𝒃) = 𝒚 − 𝒂𝒚 𝟐×𝟐 The longest side of any right angled triangle is the hypotenuse; check that your answer is consistent with this. 𝑦 = 𝑘𝑥 for a constant 𝑘
factor of the number: 𝒚 − 𝒂𝒚
√𝟖𝟎 = √𝟏𝟔 × 𝟓 = 𝟒√𝟓 𝒙= or 𝒙 =
−𝟑+√𝟗−(−𝟓𝟔)
= 𝟏. 𝟐𝟑 Advanced trigonometry G21, G22 𝒃 is directly proportional to 𝒂𝟐 ;
𝟐+𝒃 𝟐×𝟐 a = 6 when 𝒃 = 90. Find 𝒃 if a = 8.
Rationalise the denominator N8 Sine Rule Special values of sin, cos, tan 𝑏 = 𝑘𝑎2 ; 𝑎 = 6 and 𝑏 = 90 for 𝑘;
Functions A7
Complete the square to find the 𝟗𝟎 = 𝒌 × 𝟔𝟐 𝐬𝐨 𝒌 = 𝟐. 𝟓, 𝒃 = 𝟐. 𝟓𝒂𝟐
Multiply the numerator and Use if you are given an angle-side pair Learn (or be able to find
Combining functions: turning point of a quadratic graph. B 𝒃 = 𝟐. 𝟓 × 𝟖𝟐 = 𝟏𝟔𝟎
denominator by an expression that 𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 without a calculator)…
𝑓𝑔(𝑥) = 𝑓(𝑔(𝑥)) 𝒚 = 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟐 c Missing side: = = 𝑦 is inversely proportional to 𝑥:
makes the denominator an integer:
If 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝒙 + 𝟑 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝒈(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟐 𝒚 = (𝒙 − 𝟑)𝟐 − 𝟗 + 𝟐 sin𝐴 sin𝐵 sin𝐶
sin0° = 0, cos0° = 1, tan0° = 0
𝟒 𝟒 × √𝟕 𝟒√𝟕 A 𝑘
= = 𝒇𝒈(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟑 𝒚 = (𝒙 − 𝟑)𝟐 − 𝟕 𝑦𝑥 = 𝑘 or 𝑦 = for a constant 𝑘
𝟕 𝒈𝒇(𝒙) = (𝒙 + 𝟑)𝟐 Turning point is at (3 , −7) a sin𝐴 sin𝐵 sin𝐶 1 √3 1 𝑥
√𝟕 √𝟕 × √𝟕 Missing angle: = = sin30° = , cos30° = , tan30° =
b 𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 2 2 √3 Probability rules P8, P9
𝟐 Equation of a circle A16
The inverse of 𝑓 is 𝑓 −1
𝟒 + √𝟓 If 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟓 then 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 = 𝑟 2 is a circle with centre 1 1 Multiply for independent events
C Cosine Rule sin45° = , cos45° = , tan45° = 1 P(6 on dice and H on coin)
𝒙−𝟓 (0 ,0) and radius 𝑟. √2 √2
𝟐 𝟒 − √𝟓 𝟐(𝟒 − √𝟓) 𝒇−𝟏 (𝒙) = Use if you can’t use the sine rule 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏
= × = 𝟐 𝒙𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐 = 𝟐𝟓 has centre A is opposite a × =
𝟒 − √𝟓 𝟒 − √𝟓 𝟏𝟏 (0 , 0) and radius 5. B is opposite b √3 1 𝟔 𝟐 𝟏𝟐
𝒚 = 𝐦𝒙 + 𝐜 A9 Missing side: 𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑏𝑐cos𝐴 sin60° = , cos60° = , tan60° = √3
C is opposite c 2 2 Add for mutually exclusive events
Standard form N9 Simultaneous equations A19 P(5 or 6 on dice)
Equation of straight line 𝑦 = m𝑥 + c 𝑏2 + 𝑐 2 − 𝑎2
Missing angle: cos𝐴 = sin90° = 1, cos90° = 0 𝟏 𝟏 𝟐
Standard form numbers are of the m is the gradient; c is the 𝑦 intercept: One linear, one quadratic; 2𝑏𝑐 + =
form 𝑎 × 10𝑛 , where 1 ≤ 𝑎 < 10 and Find the equation of the line 𝒙 + 𝟑𝒚 = 𝟏𝟎 𝟔 𝟔 𝟔
Solve { 𝟐 Circle theorems G10 Apply these rules to tree diagrams.
𝑛 is an integer. that joins (0 , 3) to (2 , 11) 𝒙 + 𝒚𝟐 = 𝟐𝟎
Find its gradient… Rearrange the linear, and substitute
Recurring decimals N10 𝟏𝟏 − 𝟑 𝟖 In general…
into the quadratic
= =𝟒 P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A and B)
Make a recurring decimal a fraction: 𝟐−𝟎 𝟐 𝒙 = 𝟏𝟎 − 𝟑𝒚 𝑎 𝑏 𝑐 𝑒
𝒏 = 𝟎. 𝟐𝟑̇𝟔̇ …and its y intercept… so (𝟏𝟎 − 𝟑𝒚)𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐 = 𝟐𝟎 P(A and B) = P(A given B) × P(B)
𝑏
(two digits are in the recurring Passes through (0 , 3), so c = 3. Expand and solve the quadratic 2𝑎 Histograms S3
𝑑
pattern, so multiply by 100) Equation is 𝒚 = 𝟒𝒙 + 𝟑. 𝟏𝟎𝟎 − 𝟔𝟎𝒚 + 𝟗𝒚𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐 = 𝟐𝟎 𝑒
𝟏𝟎𝟎𝒏 = 𝟐𝟑̇. 𝟔̇ 𝟏𝟎𝒚𝟐 − 𝟔𝟎𝒚 + 𝟖𝟎 = 𝟎 Frequency = frequency density
(this is the same as 23.63̇6̇) Parallel lines: gradients are equal; 𝒚 = 𝟐 𝐨𝐫 𝒚 = 𝟒 multiplied by class width. This means
𝟗𝟗𝒏 = 𝟐𝟑. 𝟔𝟑̇𝟔̇ − 𝟎. 𝟐𝟑̇𝟔̇ = 𝟐𝟑. 𝟒 perpendicular lines: gradients are Finally, substitute into the linear and Angle in a Angle at the centre Angles in the Opposite angles in a Alternate Tangent and that bars with the same frequency
𝟐𝟑. 𝟒 𝟐𝟑𝟒 𝟏𝟑 “negative reciprocals”. solve, pairing values… semicircle is 90° is double the angle same segment cyclic quadrilateral segment radius are have the same area.
𝒏= = =
𝟗𝟗 𝟗𝟗𝟎 𝟓𝟓 𝒚 = 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟑 and 𝒚 = 𝟐𝒙 − 𝟓 are 𝒙 + 𝟑 × 𝟐 = 𝟏𝟎 𝐬𝐨 (𝒙 , 𝒚) = (4 , 2) at the circumference are equal total 180° theorem perpendicular
frequency density
parallel to each other; 𝒚 = 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟑 𝒙 + 𝟑 × 𝟒 = 𝟏𝟎 𝐬𝐨 (𝒙 , 𝒚) = (−2 , 4)
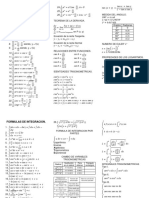
Error intervals N15
smallest frequency
𝟏 Areas and volumes G16, G17, G18, G23
and 𝒚 = − 𝒙 + 𝟑 are perpendicular Sequences A24, A25
Find the range of numbers that will 𝟐 1
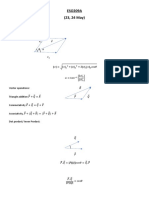
Circumference of circle = 𝜋 × 𝐷 Area of triangle = 𝑎𝑏sin𝐶 a
round to a given value: 𝑛th term of an arithmetic (linear) 2
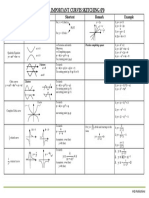
Transformations of curves A13 Area of circle = 𝜋 × 𝑟 2 cone
𝒙 = 𝟓. 𝟖𝟑 (2 decimal places) sequence is 𝑏𝑛 + 𝑐
𝟓. 𝟖𝟐𝟓 ≤ 𝒙 < 𝟓. 𝟖𝟑𝟓 Starting with the curve 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥): n𝐭𝐡 term of 5,8,11,14,… is 3𝒏+2 equal areas;
𝒚 = 𝟒𝟔 (2 significant figures) (always increases by 3; first term is h equal frequencies
0
Translate ( ) for 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) + 𝑎 θ a cross
𝟒𝟓. 𝟓 ≤ 𝒚 < 𝟒𝟔. 𝟓 𝟑 × 𝟏 + 𝟐 = 𝟓.) frustum
𝑎 section
Note use of ≤ and <, and that the last −𝑎 𝑛th term of a quadratic sequence is C b
Translate ( ) for 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥 + 𝑎) 𝜃 b Box plots S4
significant figure of each is 5. 0 𝑎𝑛2 + 𝑏𝑛 + 𝑐 Arc length = ×𝜋×𝐷 1
Area of trapezium = (𝑎 + 𝑏) × ℎ
Reflect in 𝑥 axis for 𝑦 = −𝑓(𝑥) First three terms of 360° 2 Interquartile range (IQR) = UQ − LQ
Equations and identities A3 𝜃
Reflect 𝑦 axis for 𝑦 = 𝑓(−𝑥) 𝒏𝟐 + 𝟑𝒏 − 𝟏 are 3, 9, 17, … Area of sector = × 𝜋 × 𝑟2 Volume of prism = area of cross section × length Volume of cone = 𝜋𝑟 2 ℎ
1
An equation is true for some Geometric sequence; multiply each 360° 3
Velocity - time graph A15 Volume of frustum is difference between the volumes of two cones
particular value of 𝑥… term by a constant ratio
𝟐𝒙 + 𝟏 = 𝟕 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐞 𝐢𝐟 𝒙 = 𝟑 Gradient = acceleration (you may 3, 6, 12, 24, … (ratio is 2)
minimum
maximum
median
(LQ)
lower quartile
upper quartile
(UQ)
Transformations G7, G8 Similar shapes G19
…but an identity is true for every need to draw a tangent to the curve at Fibonacci sequence; make the next
value of 𝑥 a point to find the gradient); term by adding the previous two … Reflection Rotation Enlargement Ratios in similar shapes and solids:
(𝒙 + 𝒂)𝟐 ≡ 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟐𝒂𝒙 + 𝒂𝟐 Area under curve = distance travelled. 2, 4, 6, 10, 16, 26, 42, … • Line of reflection • Centre of rotation • Centre of enlargement • Length/perimeter 1: 𝑛 𝑎: 𝑏
(note the use of the symbol ≡) Translation • Angle of rotation • Scale factor (if −1 < SF < 1 • Area 1: 𝑛2 𝑎2: 𝑏2
• Vector • Clockwise or anticlockwise the shape will get smaller). • Volume 1: 𝑛3 𝑎3: 𝑏3
You might also like
- GCSE Mat (Higher)Document1 pageGCSE Mat (Higher)renekah ghhiNo ratings yet
- Hagseed + TempestDocument3 pagesHagseed + Tempesteve4binetNo ratings yet
- Hcia RSDocument131 pagesHcia RSZveZ100% (1)
- Signal Urchin Rostrum ASCII TABDocument6 pagesSignal Urchin Rostrum ASCII TABTmitch81No ratings yet
- ITBIS373 Database Development: Guide To Oracle 10gDocument73 pagesITBIS373 Database Development: Guide To Oracle 10gdesitorontoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing ProcessDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing Processjessa barbosaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 FormulaeDocument16 pagesGrade 10 FormulaeRITIN A.C.RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Multiple IntegralsDocument33 pagesChapter 5 Multiple Integrals物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument12 pagesLesson 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsmeisukeyumeNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSAT Math Formula SheetvanbutnotavanNo ratings yet
- M2 Adv. AlgebraDocument5 pagesM2 Adv. AlgebraAngel Von Heart PandesNo ratings yet
- Solving Neutrosophic Travelling Salesaman Problem in Triangular Fuzzy Number Using Ones Assignment MethodDocument7 pagesSolving Neutrosophic Travelling Salesaman Problem in Triangular Fuzzy Number Using Ones Assignment MethodScience DirectNo ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionDocument4 pagesExponential FunctionErica Mamauag100% (1)
- Complex Number, Binomial & PolinomialsDocument2 pagesComplex Number, Binomial & PolinomialsTalha Ash SharkɪNo ratings yet
- (Hal 1) RUMUS MPSL UTS ST Utak AtikDocument2 pages(Hal 1) RUMUS MPSL UTS ST Utak AtikR. RR APRIANI SOFIANANo ratings yet
- All Important Curves Sketching (P1) : Name Shape Shortcut Remark ExampleDocument1 pageAll Important Curves Sketching (P1) : Name Shape Shortcut Remark ExampleNacon ProNo ratings yet
- Summary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيDocument7 pagesSummary (ES) أ. احمد الزريعيLilian AlkordyNo ratings yet
- Formule Statistica Descriptiva 2021Document1 pageFormule Statistica Descriptiva 2021Florentina GutanuNo ratings yet
- Math IgcseDocument13 pagesMath IgcseminthantphoneNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 11 Revision and Final Exam Prep Paper 1 What You Need To Know Algebra 2020Document4 pagesMathematics Grade 11 Revision and Final Exam Prep Paper 1 What You Need To Know Algebra 2020simamkelsmncubeNo ratings yet
- Exercise: 2.7 Linear Approximations and DifferentialsDocument14 pagesExercise: 2.7 Linear Approximations and Differentialsazyan yusraNo ratings yet
- Acst356 Class Test 1 FinalDocument1 pageAcst356 Class Test 1 FinalJoshua AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Required Formulas: Number Line: Sign NumbersDocument2 pagesRequired Formulas: Number Line: Sign Numberszahed83No ratings yet
- Formulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Document3 pagesFormulario MTBF Calcular La Probabilidad de Falla Estadística Por: . + .Eduardo Torres PinoNo ratings yet
- Formulas de DerivacionDocument3 pagesFormulas de DerivacionESTEFANIA AMATONNo ratings yet
- HL AA Complex Number Notes RMSDocument14 pagesHL AA Complex Number Notes RMSTanish BenganiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Maths Chapter 3 Soulution NOTESPKDocument48 pages2nd Year Maths Chapter 3 Soulution NOTESPKFaisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- 4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationDocument23 pages4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationKamran BabarNo ratings yet
- ACTMath Formula Sheet 2Document2 pagesACTMath Formula Sheet 2Stu PotNo ratings yet
- Ch4 NumDocument13 pagesCh4 Numahmed ramadanNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 Two Hinge ArchDocument3 pagesEx 1 Two Hinge ArchchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- 7.4 NotesDocument2 pages7.4 NotesSahar SayedNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Module Week14Document3 pagesMath 9 Module Week14Destiny Fiona Peralta PilarNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Formulae Sheet 3 PDFDocument6 pagesSAT Math Formulae Sheet 3 PDFAryan MahajanNo ratings yet
- Mecanica de FluidosDocument6 pagesMecanica de FluidosAndrés sanchezNo ratings yet
- Math 156 Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesMath 156 Final Cheat SheetshreyaNo ratings yet
- Xi - Mat - Vol I & II - RRDocument57 pagesXi - Mat - Vol I & II - RRSpedNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - NovDocument1 pageFormula Sheet - NovMegan SenekalNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document27 pagesWeek 314mervekaya01No ratings yet
- Week 11Document76 pagesWeek 11snaaaoNo ratings yet
- ESO209A Notes TutorialDocument14 pagesESO209A Notes TutorialDinesh Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Alves 2018 PDFDocument20 pagesAlves 2018 PDFAvelleo PantaleoNo ratings yet
- Functions Ws 1Document6 pagesFunctions Ws 1Farishta SNo ratings yet
- Laju ReaksiDocument2 pagesLaju ReaksiIzma YulianaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet 34521Document3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet 34521Francis AngtudNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo IntegralDocument2 pagesFormulario Calculo Integralaleeeeeeelopez669No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument2 pagesMathematicsronneil joy obinaNo ratings yet
- Sheet #1 - SolutionDocument14 pagesSheet #1 - SolutionEslam KandeilNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument2 pagesFormula RiololoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-MeasurementDocument1 pageChapter 1-MeasurementantonstefanbiehlerNo ratings yet
- Manual 6to 2020Document14 pagesManual 6to 2020Graci OliveraNo ratings yet
- 30 Selected Notes Two PopulationsDocument1 page30 Selected Notes Two Populationssminatozaki762No ratings yet
- Rumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorDocument2 pagesRumus MPC Uts Gasal 2017/2018 Angkatan 58: Standar ErrorAhmad Nur HadieNo ratings yet
- Regularization and Feature Selectio NDocument102 pagesRegularization and Feature Selectio NEhab EmamNo ratings yet
- Formulas 2 T3 AY2020-21Document9 pagesFormulas 2 T3 AY2020-21deanNo ratings yet
- SATMath Formula SheetDocument2 pagesSATMath Formula SheetMuntaha LolNo ratings yet
- 6应用机器学习的建议Document79 pages6应用机器学习的建议836328948No ratings yet
- Formula Scanner Class 10 New PatternDocument1 pageFormula Scanner Class 10 New Patternnitesh kotianNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Paramont NVR - User Manual - v1.2Document119 pagesParamont NVR - User Manual - v1.2Bsm GwapuNo ratings yet
- Data Base Managment SystemDocument14 pagesData Base Managment Systempratham PandeyNo ratings yet
- BA English IdiomsDocument4 pagesBA English IdiomsUmar Zahid100% (2)
- Chuyên Anh Lào Cai 2019-2020Document8 pagesChuyên Anh Lào Cai 2019-2020Tuấn TrầnNo ratings yet
- Excellence in English Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideDocument138 pagesExcellence in English Senior Secondary 2 Teachers GuideLUIS FERNANDO VARGAS PEÑANo ratings yet
- Gunter Part 1Document9 pagesGunter Part 1api-364531747No ratings yet
- Patrice Pavis - Languages of The StageDocument89 pagesPatrice Pavis - Languages of The StageYİĞİT SÜMBÜLNo ratings yet
- Schutz, On Multiple Realities PDFDocument42 pagesSchutz, On Multiple Realities PDFCarlos ManoelNo ratings yet
- Creating A RFID Door Latch With Arduino: InstructablesDocument15 pagesCreating A RFID Door Latch With Arduino: InstructablesVENOM LYNo ratings yet
- GP 300Document2 pagesGP 300Darya Russ100% (1)
- 0548 w09 Ms 1 PDFDocument7 pages0548 w09 Ms 1 PDFCatherine WreyfordNo ratings yet
- Live Music: Video UK - Exercises: Preparation: MatchingDocument3 pagesLive Music: Video UK - Exercises: Preparation: MatchingFlorijan DjerdjiNo ratings yet
- White Box CryptoDocument60 pagesWhite Box CryptoRaahul SenNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument27 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderFrenstan Tan100% (2)
- Basic HTML CommandsDocument36 pagesBasic HTML CommandsVedamurthy J100% (10)
- Poetry TermsDocument2 pagesPoetry TermstchristianberwicksdoNo ratings yet
- Program Detail - Mastering AI Bootcamp v3Document21 pagesProgram Detail - Mastering AI Bootcamp v3vandal liciousNo ratings yet
- (Learnjapaneseaz - Com) - List of Kanji For JLPT n4 1 10Document10 pages(Learnjapaneseaz - Com) - List of Kanji For JLPT n4 1 10jayihid308No ratings yet
- Презентація 1Document2 pagesПрезентація 1Ніка НаконечнаNo ratings yet
- Qualys Cloud Agent Mac Install GuideDocument23 pagesQualys Cloud Agent Mac Install GuideSalvatore SorrientoNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp6 17l238 RepDocument12 pagesDC Lab Exp6 17l238 RepRakesh VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Going To-Future - English GrammarDocument2 pagesGoing To-Future - English GrammarRicardo Patricio Salazar JijónNo ratings yet
- Sure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Document316 pagesSure Ways of Success - Compressed 2Arthanari Vaidyanathan100% (1)
- Sanskrit Daily ConversationDocument32 pagesSanskrit Daily Conversationapi-370612195% (20)
- Literature in English SyllabusDocument35 pagesLiterature in English SyllabusOmega Joy B. DacayananNo ratings yet
- Excel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterDocument34 pagesExcel Hacks Workshop Exercises - Harry PotterMariz PacilanNo ratings yet