Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14th Lecture Cataract
14th Lecture Cataract
Uploaded by
Muhammad Khalil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesCataract is defined as a lens opacity or cloudiness that commonly affects people over age 40. It is the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Cataracts develop from various causes such as smoking, corticosteroid use, sunlight exposure, diabetes, and eye injuries. The three main types are nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular cataracts. Symptoms include blurry vision, sensitivity to light and glare, and reduced visual acuity. Diagnosis involves visual acuity testing, ophthalmoscopy, and slit-lamp examination to determine lens opacity. While no treatment can cure or prevent cataracts, glasses or lenses may improve vision in early stages.
Original Description:
Original Title
14th Lecture Cataract (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCataract is defined as a lens opacity or cloudiness that commonly affects people over age 40. It is the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Cataracts develop from various causes such as smoking, corticosteroid use, sunlight exposure, diabetes, and eye injuries. The three main types are nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular cataracts. Symptoms include blurry vision, sensitivity to light and glare, and reduced visual acuity. Diagnosis involves visual acuity testing, ophthalmoscopy, and slit-lamp examination to determine lens opacity. While no treatment can cure or prevent cataracts, glasses or lenses may improve vision in early stages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pages14th Lecture Cataract
14th Lecture Cataract
Uploaded by
Muhammad KhalilCataract is defined as a lens opacity or cloudiness that commonly affects people over age 40. It is the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Cataracts develop from various causes such as smoking, corticosteroid use, sunlight exposure, diabetes, and eye injuries. The three main types are nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular cataracts. Symptoms include blurry vision, sensitivity to light and glare, and reduced visual acuity. Diagnosis involves visual acuity testing, ophthalmoscopy, and slit-lamp examination to determine lens opacity. While no treatment can cure or prevent cataracts, glasses or lenses may improve vision in early stages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Shekhan Technical College and Institute
Department of Nursing
Grade : 2nd Stage
2nd Semester 2022 – 2023
Adult Nursing
14th Lecture Title
“Cataract ”
Subject Lecturer : Dr. Saad Hussein Murad
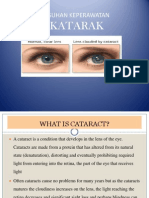
Definition: A cataract is a lens opacity or cloudiness.
Background :
1. Cataracts rank behind only arthritis and heart disease as a leading cause of
disability in older adults.
2. Cataracts affect who are 40 years of age or older, or about one in six people
in this age range.
3. Cataract is the leading cause of blindness in the world
Pathophysiology
1. Cataracts can develop in one or both eyes at any age as a result of a variety
of causes such as Cigarette smoking, long-term use of corticosteroids,
especially at high doses, sunlight and ionizing radiation, diabetes, obesity,
and eye injuries can increase the risk of cataracts.
2. The three most common types of senile (age-related) cataracts are defined by
their location in the lens: nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular.
3. The extent of visual impairment depends on their size, density, and location
in the lens.
Risk Factors for Cataract Formation
1. Aging
2. Associated Ocular Conditions
3. Toxic Factors
4. Nutritional Factors
5. Physical Factors
6. Systemic Diseases and Syndromes
Clinical Manifestations
1. Painless, blurry vision is characteristic of cataracts.
2. The person perceives that surroundings are dimmer, as if his or her glasses
need cleaning.
3. Light scattering is common, and the person experiences reduced contrast
sensitivity, sensitivity to glare, and reduced visual acuity.
4. Other effects include myopic shift (return of ability to do close work [eg,
reading fine print] without eyeglasses), astigmatism, monocular diplopia
(double vision), color shift (the aging lens become progressively more
absorbent at the blue end of the spectrum), brunescens (color values shift to
yellow-brown), and reduced light transmission.
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings
1. Decreased visual acuity is directly proportionate to cataract density.
2. The Snellen visual acuity test, ophthalmoscopy, and slit-lamp
biomicroscopic examination are used to establish the degree of cataract
formation.
3. The degree of lens opacity does not always correlate with the patient’s
functional status.
Medical Management
1. No nonsurgical (medications, eyedrops, eyeglasses) treatment cures cataracts
or prevents age-related cataracts.
2. In the early stages of cataract development, glasses, contact lenses, strong
bifocals, or magnifying lenses may improve vision.
Reference
Brunner, L. S., Suddarth, D. S., Smeltzer, S. C. O., & Bare, B. G. (2018),
Brunner & Suddarth's textbook of medical-surgical nursing (14th ed.),
Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
You might also like
- New ProposalDocument29 pagesNew ProposalBless CoNo ratings yet
- Senile Cataract (Age-Related Cataract) Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, CausesDocument4 pagesSenile Cataract (Age-Related Cataract) Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, CausesAhmad Fahrozi100% (1)
- Ophtha Quiz - Optics and RefractionDocument2 pagesOphtha Quiz - Optics and Refractionadi100% (1)
- Management of Refractive Errors PDFDocument168 pagesManagement of Refractive Errors PDFJorge Flores100% (3)
- 09 Vision Therapy Techniques PDFDocument12 pages09 Vision Therapy Techniques PDFosiris calderaNo ratings yet
- Jogi. Mcqs-1Document47 pagesJogi. Mcqs-1Fazan Gem100% (3)
- Reviews in Clinical GerontologyDocument18 pagesReviews in Clinical GerontologyRADYA PUTRA PRATAMANo ratings yet
- ABSTRAC1Document38 pagesABSTRAC1Rahid KhanNo ratings yet
- Peculiarities of Ocular and Systemic Pathology in The ElderlyDocument11 pagesPeculiarities of Ocular and Systemic Pathology in The ElderlyAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Nurses Role in The Early Detection of CataractsDocument8 pagesNurses Role in The Early Detection of Cataractsintan juitaNo ratings yet
- Learn About CataractsDocument41 pagesLearn About CataractsRizkyAgustriaNo ratings yet
- Cataract Morphology: Dip HE Rehabilitation Work (Visual Impairment)Document9 pagesCataract Morphology: Dip HE Rehabilitation Work (Visual Impairment)blinkbumbumNo ratings yet
- Cataracts: Jay Thompson,, Naheed LakhaniDocument15 pagesCataracts: Jay Thompson,, Naheed LakhaniwhiezardNo ratings yet
- Cataract in Adults - UpToDateDocument25 pagesCataract in Adults - UpToDateKevin FernandezNo ratings yet
- CataratasDocument13 pagesCataratasMacarena AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Standard Treatment Guidelines Opthalmology Author Dr. Venkatesh PrajnaDocument146 pagesStandard Treatment Guidelines Opthalmology Author Dr. Venkatesh PrajnaAriana BulaiNo ratings yet
- A Case Presentation of CataractDocument16 pagesA Case Presentation of CataractDoneva Lyn Medina100% (1)
- Catarata Relacionado Con LaedadDocument11 pagesCatarata Relacionado Con LaedadMarcos Fernando Piñas CanchanyaNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching: Era UniversityDocument14 pagesPractice Teaching: Era UniversityAru VermaNo ratings yet
- Specific Objectives Methodology Time Allotment Resources EvaluationDocument13 pagesSpecific Objectives Methodology Time Allotment Resources EvaluationTabrrett BethelNo ratings yet
- My SeminarDocument12 pagesMy SeminarAdeleye SeunNo ratings yet
- Spirovital Therapy Option For Macular DegenerationDocument6 pagesSpirovital Therapy Option For Macular DegenerationtavlarNo ratings yet
- Final TouchDocument49 pagesFinal TouchmalathiNo ratings yet
- ASKEP KATARAK m.2Document24 pagesASKEP KATARAK m.2Given MalelakNo ratings yet
- Low Vision Manuscript Group 7Document13 pagesLow Vision Manuscript Group 7Jay JimenNo ratings yet
- Article Wjpps 1533027420Document25 pagesArticle Wjpps 1533027420rahayuNo ratings yet
- Macular Degeneration: From Diagnosis to TreatmentFrom EverandMacular Degeneration: From Diagnosis to TreatmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Myopia - Incidence, Pathogenesis, Management and New Possibilities of TreatmentDocument7 pagesMyopia - Incidence, Pathogenesis, Management and New Possibilities of TreatmenthanaddulNo ratings yet
- Biology Invesigatory Project: Group MembersDocument13 pagesBiology Invesigatory Project: Group MembersNavaneeth KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Review MyopiaDocument5 pagesClinical Review MyopiaWing Yan LamNo ratings yet
- Seminar: Penny A Asbell, Ivo Dualan, Joel Mindel, Dan Brocks, Mehdi Ahmad, Seth EpsteinDocument11 pagesSeminar: Penny A Asbell, Ivo Dualan, Joel Mindel, Dan Brocks, Mehdi Ahmad, Seth EpsteinMagny DcrNo ratings yet
- Mature CataractDocument24 pagesMature CataractmethadamayNo ratings yet
- Robyn H Guymer Age Related Macular Degeneration 2023Document14 pagesRobyn H Guymer Age Related Macular Degeneration 2023frwf8j7dr4No ratings yet
- Ebook 20Document8 pagesEbook 20Eusivia PasiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Nov 2022 B213298B OPTC202Document5 pagesAssignment 1 Nov 2022 B213298B OPTC202Kudzai RusereNo ratings yet
- Cataracts Pathophysiology and Managements: Abdulrahman Zaid AlshamraniDocument4 pagesCataracts Pathophysiology and Managements: Abdulrahman Zaid AlshamraniOcha24 TupamahuNo ratings yet
- Bobbys Sensory TaskDocument13 pagesBobbys Sensory TaskbobbyNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument72 pagesCataractsKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocument46 pagesCataract: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Detection of Ocular Cataracts With Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument10 pagesDetection of Ocular Cataracts With Convolutional Neural NetworksAlejandro PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Age Related Macular DegenerationDocument60 pagesAge Related Macular DegenerationputrifitriacahyaniNo ratings yet
- Cataract, Senile: Author: Vicente Victor D Ocampo JR, MD, Head, Uveitis and Ocular ImmunologyDocument7 pagesCataract, Senile: Author: Vicente Victor D Ocampo JR, MD, Head, Uveitis and Ocular ImmunologyDicki Pratama HolmesNo ratings yet
- LTM SenseDocument6 pagesLTM SenseNabilla MerdikaNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Cataract & GlaucomaDocument26 pagesAge-Related Cataract & Glaucomasweetyeyal2002No ratings yet
- Geriatric Orthoptics and Non-Paretic Diplopia in AdultsDocument144 pagesGeriatric Orthoptics and Non-Paretic Diplopia in AdultsoptilabriberosNo ratings yet
- Senile Cataract (Age-Related Cataract) Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, Causes PDFDocument4 pagesSenile Cataract (Age-Related Cataract) Clinical Presentation - History, Physical, Causes PDFAhmad FahroziNo ratings yet
- Central Serous Chorioretinopathy Induced by Work StressDocument16 pagesCentral Serous Chorioretinopathy Induced by Work StressVincent RoorohNo ratings yet
- Paper Engish 3Document13 pagesPaper Engish 3Nurika ArvianaNo ratings yet
- Optho HXDocument5 pagesOptho HXChris KingNo ratings yet
- Wiki CataractDocument20 pagesWiki CataractUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Cataract For Medical StudentsDocument6 pagesCataract For Medical Studentsopt.atiyehmhnNo ratings yet
- Baccay Udaundo Retinoblastoma Case StudyDocument16 pagesBaccay Udaundo Retinoblastoma Case StudyCarlo BaccayNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pediatric Cataract-An UpdateDocument26 pagesApproach To Pediatric Cataract-An UpdateDayang SayalamNo ratings yet
- Managing Myopia Clinical Guide Dec 2020Document12 pagesManaging Myopia Clinical Guide Dec 2020Jorge Ivan Carcache LopezNo ratings yet
- Vitreous Floaters: Publication DetailsDocument6 pagesVitreous Floaters: Publication Detailsmithaa octoviagnesNo ratings yet
- Sensory Impairment in Older AdultsDocument22 pagesSensory Impairment in Older AdultsBethany CrusantNo ratings yet
- Cataracts - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Surgery: Southern Cross Medical LibraryDocument6 pagesCataracts - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Surgery: Southern Cross Medical Librarypuskesmas sukorejoNo ratings yet
- Assignment in HCIDocument20 pagesAssignment in HCIJanheshNo ratings yet
- Blue Light Roundtable White PaperDocument12 pagesBlue Light Roundtable White PaperDaniel KarasaniNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument10 pagesCataractPrakash DeubaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Eye Syndrome in Aortic Arch DiseaseDocument3 pagesIschemic Eye Syndrome in Aortic Arch DiseaseCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics of CataractDocument12 pagesMolecular Genetics of Cataractshaheena ahmedNo ratings yet
- Macular Degeneration: A Complete Guide for Patients and Their FamiliesFrom EverandMacular Degeneration: A Complete Guide for Patients and Their FamiliesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Occupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthFrom EverandOccupational Health Tips On Eye Protection For Good Visual HealthNo ratings yet
- Psychology Notes Class 11thDocument2 pagesPsychology Notes Class 11thSheeraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Consumer PerceptionDocument41 pagesLecture 5 - Consumer PerceptionSalman AtherNo ratings yet
- Fall Color by Number Worksheet: NameDocument1 pageFall Color by Number Worksheet: NamePacopaqueteNo ratings yet
- 05 PPT Persepsi VisualDocument13 pages05 PPT Persepsi VisualMBayuTejoSNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorders Bio ProjectDocument9 pagesEye Disorders Bio Projectmadhav laningiriNo ratings yet
- Pre-School Permanent Record: San Agustin Schoolyard Montessori, IncDocument2 pagesPre-School Permanent Record: San Agustin Schoolyard Montessori, IncMelbienNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase Studyapi-354288920No ratings yet
- Strab Research Proposal TGDocument9 pagesStrab Research Proposal TGHenok TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Dummy Interview MAx FreshDocument5 pagesDummy Interview MAx FreshArsalanAhmadNo ratings yet
- InTech - ElectroretinogramsDocument250 pagesInTech - ElectroretinogramsriveliNo ratings yet
- SNA-Davis-Chapter 15 NoiseDocument23 pagesSNA-Davis-Chapter 15 NoiseShanthini KaurNo ratings yet
- 6 CurriculumDocument1 page6 Curriculumapi-237183310No ratings yet
- Original Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationDocument7 pagesOriginal Article: The Effect of Experimentally Induced Anisometropia On Binocularity and Bifoveal FixationNurul Falah KalokoNo ratings yet
- Categories of Disabilities: (A Compilation)Document120 pagesCategories of Disabilities: (A Compilation)Diana Zamoras100% (1)
- Ophthalmology VIBEDocument78 pagesOphthalmology VIBEDinesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Tongziliao Gb-1: Pupil CreviceDocument1 pageTongziliao Gb-1: Pupil Creviceray72roNo ratings yet
- Poetry WorksheetDocument3 pagesPoetry WorksheetLpt Ashley OlbinarNo ratings yet
- AcrySof IQ PanOptix IOLDocument7 pagesAcrySof IQ PanOptix IOLKBOI 2NewsNo ratings yet
- Tabela de Marcacoes de Lentes ProgressivasDocument10 pagesTabela de Marcacoes de Lentes ProgressivasneicapelNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception Review PacketDocument16 pagesSensation and Perception Review Packetapi-421695293No ratings yet
- Homoeopathy Treatment of Vitreous OpacitiesDocument4 pagesHomoeopathy Treatment of Vitreous OpacitiesVitorio VenturiniNo ratings yet
- Cortical Deafness: Oleh: Dr. Laila Fajri Pembimbing: Dr. Novina Rahmawati, M.Si, Med, SP - THT-KL, FICSDocument18 pagesCortical Deafness: Oleh: Dr. Laila Fajri Pembimbing: Dr. Novina Rahmawati, M.Si, Med, SP - THT-KL, FICSzikral hadiNo ratings yet
- 22468Document66 pages22468manonmaniNo ratings yet
- 2010 NRN2833 Keysers Kaas GazzolaDocument12 pages2010 NRN2833 Keysers Kaas GazzolaRenzo LanfrancoNo ratings yet
- Objective RefractionDocument12 pagesObjective RefractionWendy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IOL PowerDocument273 pagesIOL Powermarlon García100% (3)