Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AM
VESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AM
Uploaded by
basitcontent0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesThis document summarizes various vesiculobullous diseases including their viral, immunological, and hereditary causes. Key features covered include pathogenesis, clinical presentation, histopathology, differential diagnosis, and treatment options. The diseases discussed include herpes simplex, varicella zoster, hand foot and mouth disease, herpangina, rubella, pemphigus vulgaris, mucous membrane pemphigoid, bullous pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and epidermolysis bullosa.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes various vesiculobullous diseases including their viral, immunological, and hereditary causes. Key features covered include pathogenesis, clinical presentation, histopathology, differential diagnosis, and treatment options. The diseases discussed include herpes simplex, varicella zoster, hand foot and mouth disease, herpangina, rubella, pemphigus vulgaris, mucous membrane pemphigoid, bullous pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and epidermolysis bullosa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesVESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AM
VESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE by AM
Uploaded by
basitcontentThis document summarizes various vesiculobullous diseases including their viral, immunological, and hereditary causes. Key features covered include pathogenesis, clinical presentation, histopathology, differential diagnosis, and treatment options. The diseases discussed include herpes simplex, varicella zoster, hand foot and mouth disease, herpangina, rubella, pemphigus vulgaris, mucous membrane pemphigoid, bullous pemphigoid, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and epidermolysis bullosa.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
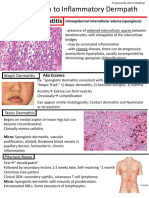
VESICULOBULLOUS DISEASE
Viral Pathogenesis Clinical features Histopathology DD /
Treatment
Herpes simplex Primary herpetic Intraepithelial vesicles Tzanck smear
gingivostomatitis Inflammatory cells Serology
Vesicles on Skin oral Exudate Viral culture
mucosa Virus infected epithelial Immunohistoch
Fever cells have emistry
Malaise Glassy homogeneous PCR
Arthralgia nucleus
Lymphadenopathy
Headache
Heal without scar Acyclovir 400
Secondary herpes mg TDS
infection Rest
Vesicles on Lips hard Fluids
palate gingiva Analgesics
Pain Antipyretics
Burning
Map like ulcers
Heal without scar
Herpes labialis (lips )
Herpetic whitlow (
fingers)
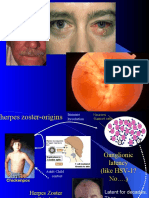
Varicella zoster Varicella (child) Virus infected epithelial DNA
Fever cells have homogenous hybridization
Chills nucleus Immuno
Malaise Multinucleated cells histochemistry
Headache No scaring Virus antigen
Rash ( trunk head neck ) typing
Rash–> vesicles–> ulcers
Self limiting
Healing with scar Acyclovir
Encephalitis Vaccine
Pneumonitis available
Zoster (adult)
Pain
Paresthesia of involved
dermatome
Unilateral Rash ( trunk
head neck )
Unilateral lesion ( oral
facial ocular )
Ramsay hunt syndrome
( facial paralysis
External ear vesicles
Tinnitus
Deafness
Vertigo )
Rash → vesicle → ulcers
Ocular inflammation
Post herpetic neuralgia
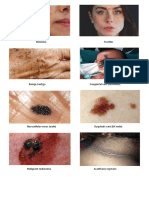
HFM disease Children Intraepithelial vesicles Virus culture
Fever Virus infected epithelial Virus antigen
Malaise cells typing
Sore mouth Inflammatory cells
Lymphadenopathy
Pain
Vesicles → ulcers Analgesics
Ulcers are covered by a
yellow fibrinous membrane
and have surrounded
erythematous area
(palate tongue buccal
mucosa )
(feet toes hands )
Heal without scar
Herpangina Childrens Virus antigen
Fever typing
Malaise Throat culture
Dysphagia PCR
Sore throat
Vesicles Antipyretic
( palate buccal mucosa )
Erythematous pharyngitis
Self limiting
Rubella Childrens Virus infected epithelial Serological test
(german Fever cells become necrotic Viral culture
measles ) Malaise Dilated blood vessels PCR
Conjunctivitis and generalized
Photophobia inflammation
Cough Inflammatory cells Rest
Lymphadenopathy Multinucleated Fluids
Small erythematous macrophages ( warthin Analgesics
macules with white finkeldey giant cells )
necrotic centers on buccal
mucosa ( koplik's spot )
Maculopapular skin rash
( head and trunk )
Encephalitis
Thrombocytopenic purpura
Otitis media
Pneumonia
Immunolog Clinical features Histopathology Immunopatholog DD /
ic disease y Treatment
Pemphigus Autoimmune disease Intraepithelial vesicles Positive IgG type C3 Topical steroids
vulgaris Fragile vesicle → Acantholysis Antigens ; desmoglein Systemic
ulcers Tzanck cells present 1 and 3 corticosteroids
P vulgaris Painfull (prednisone )
P vegetans Ulcers have ragged Azathioprine
P foliaceus borders Dapsone
igA pemphigus Gentle rubbing on
Paraneoplastic unaffected site produce Rituximab
pemphigus strippling of epithelium
( nikolsky sign ) Physician
Dermatologist
MMP Adults Subepithelial Linear pattern Topical steroids
Bullae → ulcers No acantholysis Positive IgG C3 Systemic
( conjunctiva genitals steroids
oral cavity) Prednisone
Blindness Azathioprine
Hoarseness of voice
Genital itching Chlorhexidine
Pain mouthwash
Desquamative gingivitis
Heal with scar Rituximab
BP Elderly Subepithelial Linear pattern Systemic
Rash → bullae→ ulcers No acantholysis Positive IgG C3 steroids
( trunk limbs ) Antigens ; Prednisone
( buccal mucosa BP 230 and BP 180
palate) Antibiotics
Tetracycline
Rituximab
Dermatitis Adults Papillae of dermis ( Granular pattern Gluten free diet
herpetiformis Vesicles connective tissue involved) Positive IgA C3 on Dapsone
(elbow knees buttocks) Inflammatory cells connective tissue
( oral mucosa ) papilla
Linear IgA Bullae Subepithelial Linear pattern Dapsone
bullous disease ( oral mucosa ) No acantholysis Positive IgA antibodies
( trunk limbs ) At basement membrane Antigen BP180
Two types Collection of bulla
1. Children called rosettes
2. Adult
Hereditary Clinical features Histopathology Immunopatholog DD /
disease y Treatment
Epidermolysis Blister formation at site Subepithelial Linear pattern Systemic
bullosa of trauma No acantholysis Positive IgA C3 steroids
Simplex Antigen type 7 collagen
Two types Less severe type Dapsone
Hereditary Bulla on oral mucosa
Simplex Soles of feet Vitamin E
Dystrophic
Junctional Junctional and Avoid trauma
dystrophic
Acquired Lethal type
Epidermolysis Severe blisters on oral
bullosa mucosa
acquisita Blisters → erosions
Scar formation
You might also like
- Pathognomonic Signs of DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathognomonic Signs of Diseasesblacknurse75% (8)
- Pediatrics: Compilation of Tables From Topnotch Pedia HandoutDocument6 pagesPediatrics: Compilation of Tables From Topnotch Pedia HandoutCielo Lomibao0% (1)
- Case Summary FamilyMedicine29 72-YDocument9 pagesCase Summary FamilyMedicine29 72-YAndrea Kristin Origenes100% (1)
- Justine Jackson Capstone AatDocument29 pagesJustine Jackson Capstone AatJuliana IshakNo ratings yet
- Non-Sporing Anaerobic: InfectionsDocument14 pagesNon-Sporing Anaerobic: InfectionsZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum ORR Derma ImagesDocument25 pagesCerebellum ORR Derma Imagessubramaniam krishnamoorthiNo ratings yet
- 4) Conjunctival DiseasesDocument47 pages4) Conjunctival DiseasesAlhanouf AlasmariNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Patho Quick GuideDocument3 pagesHead and Neck Patho Quick GuideTMC PGI GENER MICKONo ratings yet
- Fever in Infants and Children - Pediatrics - Merck Manuals Professional EditionDocument5 pagesFever in Infants and Children - Pediatrics - Merck Manuals Professional Editionlokita_opdNo ratings yet
- PathogDocument3 pagesPathogJhey MalanyaonNo ratings yet
- Fever With RashDocument2 pagesFever With RashzahraaNo ratings yet
- L3 Conjunctival DiseaseDocument70 pagesL3 Conjunctival DiseaseAlhNo ratings yet
- Top Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingDocument3 pagesTop Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- Skin PDFDocument13 pagesSkin PDFLanaAmerieNo ratings yet
- PigmantosumDocument5 pagesPigmantosumHunter BannaNo ratings yet
- Gram-Negative: NeisseriaDocument26 pagesGram-Negative: NeisseriaZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Dermatology PDFDocument57 pagesDermatology PDFSheikhEras100% (1)
- Virology TableDocument6 pagesVirology TablejeffdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Cims Case 1 - SGD A4Document16 pagesCims Case 1 - SGD A4SGD A4No ratings yet
- Pedia Resident's CompetencyDocument12 pagesPedia Resident's CompetencyElizabeth MaderazoNo ratings yet
- ConjungtivitisDocument86 pagesConjungtivitisIvo AfianiNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisdheeneshNo ratings yet
- Eyes and Ears Disease Other Name Causative Agent Pathognomonic Sign Conjuctivitis: Acute ConjunctivitisDocument1 pageEyes and Ears Disease Other Name Causative Agent Pathognomonic Sign Conjuctivitis: Acute ConjunctivitisWiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Infection DiseaseDocument1 pageOdontogenic Infection Diseasealvarez.sofiadennieceNo ratings yet
- Derm StuffDocument7 pagesDerm StuffSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- DR - Gaurav Shukla DR - Jyoti Batra DR - Uma SridharDocument101 pagesDR - Gaurav Shukla DR - Jyoti Batra DR - Uma SridharGaurav shuklaNo ratings yet
- RashDocument3 pagesRashNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Notes EntDocument43 pagesNotes Entadriana azmanNo ratings yet
- Cims Case 1Document14 pagesCims Case 1SGD A4No ratings yet
- CervixDocument8 pagesCervixyaraabdulkaderaliNo ratings yet
- Rashes: Paediatric Dermatology: Ellis HonDocument95 pagesRashes: Paediatric Dermatology: Ellis HonB AuNo ratings yet
- Kul Mata Merah PDFDocument56 pagesKul Mata Merah PDFMuhammad HasanNo ratings yet
- Herpes SimpexDocument1 pageHerpes Simpexmkct111No ratings yet
- JAMURDocument53 pagesJAMURFikri PutroNo ratings yet
- Benign Skin LegionsDocument14 pagesBenign Skin LegionsTahani AlmagrhiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Middle EarDocument32 pagesDiseases of Middle EarDr Sravya M VNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Lab AnimalsDocument45 pagesDiseases of Lab AnimalsvetpathforumNo ratings yet
- 12 KULIT KELAMIN Viral Diseases of The Oral Cavity-1Document79 pages12 KULIT KELAMIN Viral Diseases of The Oral Cavity-1NAOMI SINAGANo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic SignsDocument1 pagePathognomonic SignsRodessa Mandac TarolNo ratings yet
- Adult I Study Guide Exam 1Document23 pagesAdult I Study Guide Exam 1Christopher JamesNo ratings yet
- InfectionsDocument7 pagesInfectionsMaliha Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Normal Body FloraDocument1 pageNormal Body FloraJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- Blistering Disorders TableDocument1 pageBlistering Disorders TableDylan RastoNo ratings yet
- Review Lecture KIPS Unit 4 (CRTS)Document33 pagesReview Lecture KIPS Unit 4 (CRTS)Huzaifa ImranNo ratings yet
- Rare VesiculopustularDocument23 pagesRare VesiculopustularcebadawitNo ratings yet
- Male Genital DermDocument112 pagesMale Genital DermVũ CaoNo ratings yet
- Impetigo, Erysipela S, Cellulitis: Rasay, Joana Mikee DDocument48 pagesImpetigo, Erysipela S, Cellulitis: Rasay, Joana Mikee DJoana Mikee RasayNo ratings yet
- Key To PATH 202 PracticalDocument5 pagesKey To PATH 202 Practicalzain hassanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dermatology - 2021 - Jordens - Acral Manifestations Associated With Infection-1Document13 pagesPediatric Dermatology - 2021 - Jordens - Acral Manifestations Associated With Infection-1silviaNo ratings yet
- Viral Eye Infections and Treatment 2342 2342Document22 pagesViral Eye Infections and Treatment 2342 2342Sarthak KabiNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of OphthalmologyDocument1,998 pagesEncyclopedia of OphthalmologySmara100% (3)
- Oral Manifestation of HivDocument1 pageOral Manifestation of HivDurva JainNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument3 pagesMeningitisSuhana JahangeerNo ratings yet
- Spongiotic Dermatitis: Aka EczemaDocument8 pagesSpongiotic Dermatitis: Aka EczemafadoNo ratings yet
- Derma Transcribed Table FormDocument9 pagesDerma Transcribed Table FormGerlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis Differential Diagnoses: Diagnostic ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesAtopic Dermatitis Differential Diagnoses: Diagnostic ConsiderationsjesusNo ratings yet
- HPV Benign Lesions SummaryDocument2 pagesHPV Benign Lesions SummaryzainNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument76 pagesFungal InfectionsHrishikesh NachinolkarNo ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument8 pagesHead and Neckstudy with maineNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris Acne Rosacea Acne Disorders: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument19 pagesAcne Vulgaris Acne Rosacea Acne Disorders: Systemic Lupus Erythematosusapi-26938624No ratings yet
- Skin PathologyDocument42 pagesSkin PathologykateNo ratings yet
- AspergillusDocument13 pagesAspergillusangelNo ratings yet
- Circulo Code: OrganotherapyDocument2 pagesCirculo Code: OrganotherapyHomer SimpsonNo ratings yet
- ParaphrasingDocument12 pagesParaphrasingFaridawati FiayNo ratings yet
- Eob RemittanceDocument2 pagesEob RemittanceAndres ChavarrioNo ratings yet
- MDCG 2022-9 enDocument9 pagesMDCG 2022-9 enmd edaNo ratings yet
- Arnica Montana - FayazuddinDocument13 pagesArnica Montana - FayazuddinMohammad AtaNo ratings yet
- Communicable and Non-Communicable DiseaseDocument44 pagesCommunicable and Non-Communicable DiseaseSajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument26 pagesAcute Rheumatic FeverAshvanee sharma100% (1)
- Concept and Mapping For Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument5 pagesConcept and Mapping For Rheumatic Heart DiseaseAilyne A. CleofeNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial Changes and Coping Strategies in Home Quarantined University Students of Pakistan During COVID-19 PandemicDocument6 pagesPsychosocial Changes and Coping Strategies in Home Quarantined University Students of Pakistan During COVID-19 PandemicSyed Shafqat ShahNo ratings yet
- Lactose Intolerance Patient Education Handout 8th GradeDocument2 pagesLactose Intolerance Patient Education Handout 8th Gradeapi-368093620No ratings yet
- Obstetrics 4Document27 pagesObstetrics 4denekeNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document45 pagesGroup 4Nicole Juliette CCNo ratings yet
- Radiotherapy For Colorectal CancerDocument28 pagesRadiotherapy For Colorectal CancerIndonesian Journal of CancerNo ratings yet
- Clinical Rotation Handbook 2021Document22 pagesClinical Rotation Handbook 2021Tony Allday0% (1)
- Kidney PainDocument2 pagesKidney PainAulia Abdillah RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Myocardial Infarction: TimeDocument17 pagesLesson Plan On Myocardial Infarction: TimeRio Rio100% (1)
- Radiation Therapy For Sarcomas and Skin CancersDocument376 pagesRadiation Therapy For Sarcomas and Skin CancersAr-pardo RogerNo ratings yet
- IELTS SpeakingDocument11 pagesIELTS SpeakingAna Cristina SilvaNo ratings yet
- MetamizoleDocument15 pagesMetamizoleFahri AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Preseptorship KDGN 3N 3S UMB Jan 20Document83 pagesPreseptorship KDGN 3N 3S UMB Jan 20Rayantinilailagmail.com MahasiswaNo ratings yet
- schc321 in Chicago Style FinalDocument19 pagesschc321 in Chicago Style Finalapi-737290876No ratings yet
- FOLK MEDICINE ExtraDocument22 pagesFOLK MEDICINE ExtraPaul SavvyNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Oral AntidiabeticsDocument24 pagesInsulin and Oral AntidiabeticsMirza Shaharyar Baig100% (1)
- Erectile Dysfunction Can Be A Sign of A Physical or Intellectual Condition Otoee PDFDocument2 pagesErectile Dysfunction Can Be A Sign of A Physical or Intellectual Condition Otoee PDFlandsteam52No ratings yet
- Activity # 2 NAME - DATEDocument4 pagesActivity # 2 NAME - DATEJamie Haravata100% (1)
- Artesunate For The Treatment of Severe Falciparum Malaria: Philip J. Rosenthal, M.DDocument7 pagesArtesunate For The Treatment of Severe Falciparum Malaria: Philip J. Rosenthal, M.DbadshahytNo ratings yet
- Association of The Chantix Recall With US Prescribing of Varenicline and Other Medications For Nicotine DependenceDocument4 pagesAssociation of The Chantix Recall With US Prescribing of Varenicline and Other Medications For Nicotine DependenceAndrade GuiNo ratings yet