Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Brief History of The Age of Exploration
A Brief History of The Age of Exploration
Uploaded by
Remmuel SantiagoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Brief History of The Age of Exploration
A Brief History of The Age of Exploration
Uploaded by
Remmuel SantiagoCopyright:
Available Formats
MENTARI INTERCULTURAL SCHOOL JAKARTA
IB Primary Years Programme (PYP)
Grade 5 SY 2023 – 2024
Unit of Inquiry: Where We Are in Place and Time
Central Idea: Exploration leads to discovery and develops new understanding.
Directions: Read the following expository text.
A Brief History of the Age of Exploration
The Age of Exploration brought about discoveries and advances.
By Amanda Briney
The era known as the Age of Exploration, sometimes called the Age of Discovery, officially began in
the early 15th century and lasted through the 17th century. The period is characterized as a time when
Europeans began exploring the world by sea in search of new trading routes, wealth, and knowledge. The
impact of the Age of Exploration would permanently alter the world and transform geography into the modern
science it is today.
WHEN DID THE AGE OF EXPLORATION BEGIN?
Many nations were looking for goods such as silver and gold, but one of the biggest reasons for
exploration was the desire to find a new route for the spice and silk trades. When the Ottoman Empire took
control of Constantinople in 1453, it blocked European access to the area, severely limiting trade. In addition,
it also blocked access to North Africa and the Red Sea, two very important trade routes to the Far East.
The first of the journeys associated with the Age of Discovery were conducted by the Portuguese.
Although the Portuguese, Spanish, Italians and others had been plying the Mediterranean for generations,
most sailors kept well within sight of land or traveled known routes between ports. Prince Henry the
Navigator changed that, encouraging explorers to sail beyond the mapped routes and discover new trade
routes to West Africa. Portuguese explorers discovered the Madeira Islands in 1419 and the Azores in 1427.
Over the coming decades, they would push farther south along the African coast, reaching the coast
of present-day Senegal by the 1440s and the Cape of Good Hope by 1490. Less than a decade later, in
1498, Vasco da Gama would follow this route all the way to India.
THE DISCOVERY OF THE NEW WORLD
While the Portuguese were opening new sea
routes along Africa, the Spanish also dreamed of
finding new trade routes to the Far East.
Have you heard the name Christopher
Columbus? He is an Italian working for the Spanish
monarchy who made his first journey in 1492, but
instead of reaching India, he instead found the island
of San Salvador in what is known today as the
Bahamas. He also explored the island of Hispaniola,
home of modern-day Haiti and the Dominican
Republic.
Columbus would lead three more voyages to
the Caribbean; he explored parts of Cuba and the Central American coast. The Portuguese also reached the
New World when explorer Pedro Alvares Cabral explored Brazil, setting off a conflict between Spain and
Portugal in terms of the newly claimed lands. As a result, the Treaty of Tordesillas officially divided the world
in half in 1494.
Columbus’s journeys opened the door for the Spanish conquest of the Americas, and during the next
century, men like Hernan Cortes and Francisco Pizarro would decimate the Aztecs of Mexico, the Incas of
Peru and other indigenous peoples of the Americas. By the end of the Age of Exploration, Spain would rule
from the southwestern United States to the southernmost reaches of Chile and Argentina.
Other important voyages of exploration that took place during the Age of Exploration were Ferdinand
Magellan’s attempted circumnavigation of the globe, the search for a trade route to Asia through
the Northwest Passage, and Captain James Cook’s voyages that allowed him to map various areas and
travel as far as Alaska.
WHEN DID THE AGE OF EXPLORATION END?
The Age of Exploration ended in the early 17th century after technological advancements and
increased knowledge of the world allowed Europeans to travel easily across the globe by sea. The creation
of permanent settlements and colonies created a network of communication and trade, therefore ending the
need to search for trade routes.
It is important to note that the exploration did not cease entirely at this time. Eastern Australia was not
officially claimed for Britain by Capt. James Cook until 1770, while much of the Arctic and Antarctic were not
explored until the 19th century. Much of Africa also was also unexplored by Westerners until the early 20th
centuries.
WHAT ARE THE CONTRIBUTIONS TO SCIENCE?
The Age of Exploration had a significant impact on geography; by traveling to different regions around
the globe, explorers were able to learn more about areas like Africa and the Americas. In learning more about
such places, explorers were able to bring knowledge of a larger world back to Europe.
Methods of navigation and mapping improved as a result of the travels of people like Prince Henry
the Navigator. Prior to his expeditions, navigators used traditional portolan charts, which were based on
coastlines and ports of call, keeping sailors close to shore.
The Spanish and Portuguese explorers who journeyed into the unknown created the world's first
nautical maps, delineating not just the geography of the lands they found but also the seaward routes and
ocean currents that led them there. As technology advanced and territory explored, maps and mapmaking
became more and more sophisticated.
These explorations also introduced a whole new world of flora and fauna to Europeans. Corn, now a
staple of much of the world's diet, was unknown to Westerners until the time of the Spanish Conquest, as
were sweet potatoes and peanuts. Likewise, Europeans had never seen turkeys, llamas or squirrels before
setting foot in the Americas.
The Age of Exploration served as a stepping stone for geographic knowledge. It allowed more people
to see and study various areas around the world which increased geographic study, giving us the basis for
much of the knowledge we have today.
Do you know other contributions of the Age of Explorations? Please share them with the class. Can you
connect the concept of Gold, Glory and God (3Gs) as reasons for their explorations?
Source: https://www.thoughtco.com/age-of-exploration-1435006
You might also like
- The Path of Ascension Book 1 Final Edit - TM1 DONEDocument470 pagesThe Path of Ascension Book 1 Final Edit - TM1 DONELeonardo Cruz Garcia100% (1)
- Age of ExplorationDocument20 pagesAge of Explorationdaf4tee100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Summary Europeans Encounter The New World 1492 1600 PP 2753Document36 pagesChapter 2 Summary Europeans Encounter The New World 1492 1600 PP 2753sering15ukayNo ratings yet
- Contributions To GeographyDocument1 pageContributions To Geographyapi-224225781No ratings yet
- Performance of A High-Solidity Wells Turbine For An OWC Wave Power PlantDocument6 pagesPerformance of A High-Solidity Wells Turbine For An OWC Wave Power PlantAna Elisa Rodrigues do CoutoNo ratings yet
- The Docks of Big Lake 376pags PDFDocument376 pagesThe Docks of Big Lake 376pags PDFPablo Iglesias100% (2)
- Matthews Ridge Pre Feasibility Study W App FinalDocument975 pagesMatthews Ridge Pre Feasibility Study W App FinalIsaac VisualNo ratings yet
- Strut BucklingDocument9 pagesStrut BucklingWai Sheng75% (4)
- A Brief History of The Age of ExplorationDocument2 pagesA Brief History of The Age of ExplorationxenogodNo ratings yet
- Age of Exploration 1435006Document6 pagesAge of Exploration 1435006Priya PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Age of Exploration Grade 6THDocument18 pagesChapter 4 Age of Exploration Grade 6THKaren BalonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33 Age of ExplorationDocument13 pagesChapter 33 Age of ExplorationSelenai Selenai100% (2)
- PU HisDocument12 pagesPU Hisabhinavjaspal143No ratings yet
- Ageofexploration StudentDocument20 pagesAgeofexploration Studentapi-259177253No ratings yet
- Age of Exploration and Discovery (Spain and Portugal)Document8 pagesAge of Exploration and Discovery (Spain and Portugal)Rafleah RiojaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Final His1055Document5 pagesQ1 Final His1055Trann TtuyetNo ratings yet
- 1/ The Mid To The Late 15th Century Is Known To History As The Age ofDocument1 page1/ The Mid To The Late 15th Century Is Known To History As The Age ofALIBABANo ratings yet
- 1 History of The Slave Trade Unit ReadingDocument19 pages1 History of The Slave Trade Unit ReadingSiddharth MahendranNo ratings yet
- Topic: Age of Exploration and Its ImpactDocument13 pagesTopic: Age of Exploration and Its ImpactSakib MhmudNo ratings yet
- Final Adam Sullinger NTI Days May 18-22Document7 pagesFinal Adam Sullinger NTI Days May 18-22Jorge YanovskyNo ratings yet
- Age of ExplorationDocument10 pagesAge of ExplorationJoshua San JoseNo ratings yet
- Europe Enters Modern AgeDocument54 pagesEurope Enters Modern AgeVic Shah100% (1)
- Age of Exploration: Garcia 1Document5 pagesAge of Exploration: Garcia 1api-301949750No ratings yet
- EDocument61 pagesEDjura JovanovicNo ratings yet
- The Geographical Discoveries of The 15th and 16th CenturiesDocument2 pagesThe Geographical Discoveries of The 15th and 16th CenturiesPatrick dcosta67% (3)
- GEHI 03 Block 02Document35 pagesGEHI 03 Block 02Yaar Jigree Season 3No ratings yet
- Age of ExplorationDocument6 pagesAge of ExplorationEric James AbarroNo ratings yet
- World HistoryDocument5 pagesWorld HistoryRobinsonLuis100% (1)
- A New Continent, a New World: Discovery and Conquest During the Age of ExplorationFrom EverandA New Continent, a New World: Discovery and Conquest During the Age of ExplorationNo ratings yet
- Transcript - Docu - The Age of ExplorationDocument4 pagesTranscript - Docu - The Age of ExplorationLeiNo ratings yet
- Expedition and Discoveries of EuropeanDocument10 pagesExpedition and Discoveries of EuropeanHimanshu LahotiNo ratings yet
- The Age of ExplorationDocument2 pagesThe Age of Explorationكنابست جيجلNo ratings yet
- Age of DiscoveryDocument38 pagesAge of DiscoveryAlexfunnyNo ratings yet
- Age of Discovery: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument45 pagesAge of Discovery: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaajonas69No ratings yet
- The Age of DiscoveryDocument2 pagesThe Age of DiscoveryGladys ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Research On The Age of Exploration (Portugal & Spain)Document9 pagesResearch On The Age of Exploration (Portugal & Spain)SheilaJoyJuarezNo ratings yet
- Time Allotment: 1 Week Instructor: Robert S. Pardillo Contact DetailsDocument11 pagesTime Allotment: 1 Week Instructor: Robert S. Pardillo Contact DetailsCarl Ryan G. VillaNo ratings yet
- The Age of Discovery and Exploration (With Answers)Document11 pagesThe Age of Discovery and Exploration (With Answers)Zat Lan MyarNo ratings yet
- Age of ExplorationDocument8 pagesAge of Explorationapi-282001671No ratings yet
- Age of DiscoveryDocument7 pagesAge of DiscoveryFrance FuertesNo ratings yet
- The Age of Exploration - DelacruzDocument15 pagesThe Age of Exploration - DelacruzIKevin DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Age of DiscoveryDocument1 pageAge of DiscoveryMc Khan TabamoNo ratings yet
- First Global AgeDocument12 pagesFirst Global Ageapi-235209117100% (2)
- The First Stage of Western Imperialism 3Document5 pagesThe First Stage of Western Imperialism 3Danielle Rose Maglacion JalagatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 TextDocument11 pagesChapter 32 TextHimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. The Age of Discovery, Humanism and ReformationDocument15 pagesUnit 1. The Age of Discovery, Humanism and ReformationyasminaahdidnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 VocabularyDocument23 pagesChapter 14 VocabularyNicholas FarratNo ratings yet
- Outline Age of ExplorationDocument10 pagesOutline Age of ExplorationMilena KarolinaNo ratings yet
- Encounter With The West (1400 - 1600)Document9 pagesEncounter With The West (1400 - 1600)lagari lee100% (1)
- Introduction First VoyageDocument1 pageIntroduction First VoyageJoseph CabailoNo ratings yet
- Conditions in Europe Which Led To The VoyagesDocument16 pagesConditions in Europe Which Led To The VoyagesMatthew MorrisNo ratings yet
- Why Europe Has To Come To Asia?Document28 pagesWhy Europe Has To Come To Asia?Frenzie Mae Vasquez RiveraNo ratings yet
- WHII.4 Age of Exploration NarrativeDocument4 pagesWHII.4 Age of Exploration Narrativeniabae15No ratings yet
- Age of Exploration & Age of Discovery of SPAIN and PORTUGAL (TERM PAPER) HISTORY 101Document6 pagesAge of Exploration & Age of Discovery of SPAIN and PORTUGAL (TERM PAPER) HISTORY 101Mike Andrew ZambalesNo ratings yet
- 15th Century EuropeansDocument10 pages15th Century EuropeansMelissa AlexanderNo ratings yet
- SocialDocument3 pagesSocialhappywithyoutineNo ratings yet
- History of OceanographyDocument4 pagesHistory of OceanographyMarko DesnicaNo ratings yet
- Economic and Political Motives: Factors That Motivated European Kingdoms To Explore The WorldDocument7 pagesEconomic and Political Motives: Factors That Motivated European Kingdoms To Explore The WorldHaru HaruNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - European Colonization in America - HistoryDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - European Colonization in America - HistoryAlifa CantikaNo ratings yet
- History NosDocument8 pagesHistory NosDavid SolisNo ratings yet
- History NoesDocument8 pagesHistory NoesDavid SolisNo ratings yet
- Outlining - Info Map - Work SheetDocument3 pagesOutlining - Info Map - Work SheetRemmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in OutliningDocument1 pageGuidelines in OutliningRemmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Basic Outlining WorksheetDocument1 pageBasic Outlining WorksheetRemmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Whales OutliningDocument1 pageWhales OutliningRemmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IBD Reading Log 4 - Chapters 16-20Document5 pagesIBD Reading Log 4 - Chapters 16-20Remmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IBD Reading Log 5 - Chapters 21-25Document5 pagesIBD Reading Log 5 - Chapters 21-25Remmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IBD Reading Log 3 - Chapters 11-15Document5 pagesIBD Reading Log 3 - Chapters 11-15Remmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IBD Reading Log 2 - Chapters 6-10Document5 pagesIBD Reading Log 2 - Chapters 6-10Remmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- IBD Reading Log 1 - Chapters 1-5Document5 pagesIBD Reading Log 1 - Chapters 1-5Remmuel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document28 pagesLecture 3Lovely ZahraNo ratings yet
- SINPACDocument32 pagesSINPACFV AllanNo ratings yet
- Ifedc 2022 Rock TypingDocument17 pagesIfedc 2022 Rock TypingpetrolognewsNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument17 pagesIUPAC Nomenclaturesurya kant upadhyay100% (3)
- Optimal Solution Using MODI - MailDocument17 pagesOptimal Solution Using MODI - MailIshita RaiNo ratings yet
- Me8595 Iq R17Document2 pagesMe8595 Iq R17Narayanan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Culinary ArtsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Culinary ArtsNico Urieta De AdeNo ratings yet
- Project On Production Process OFDocument15 pagesProject On Production Process OFtarun-neha100% (2)
- Outdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24Document4 pagesOutdoor Commander Series Evacuation Signals WGEC24/ WGES24osamamaeNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument301 pagesPDFEddy TriyonoNo ratings yet
- The Cotton Industry in The Philippines: ' Country StatementDocument8 pagesThe Cotton Industry in The Philippines: ' Country StatementJocelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- DOPO - Productivity Meets PrecisionDocument4 pagesDOPO - Productivity Meets PrecisionRamakrishna MamidiNo ratings yet
- BakerHughes BruceWright NewCokerDefoamer CokingCom May2011Document9 pagesBakerHughes BruceWright NewCokerDefoamer CokingCom May2011Anonymous UoHUagNo ratings yet
- Dinner MenuDocument2 pagesDinner MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- Discussion 1 NPNDocument53 pagesDiscussion 1 NPNFaith TambongNo ratings yet
- Energy Snapshot: American SamoaDocument4 pagesEnergy Snapshot: American SamoaSr. RZNo ratings yet
- 04a. Quadratics - The Quadratic Formula and The DiscriminantDocument1 page04a. Quadratics - The Quadratic Formula and The Discriminantjingcong liuNo ratings yet
- Axis TechnologyFct en-USDocument342 pagesAxis TechnologyFct en-USClaudiu GogoseanuNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 Notes - FinalsDocument21 pagesPhysics 71 Notes - FinalsCris Reven GibagaNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Gever-2020 ASTM B819Document2 pagesBrochure-Gever-2020 ASTM B819sahriNo ratings yet
- List of Courses-SemV VIIDocument2 pagesList of Courses-SemV VIIAakash VermaNo ratings yet
- Is 9259 1979 PDFDocument15 pagesIs 9259 1979 PDFsagarNo ratings yet
- Hitler's Priestess: Savitri Devi, The Hindu-Aryan Myth, and Occult Neo-Nazism:Hitler's Priestess: Savitri Devi, The Hindu-Aryan Myth, and Occult Neo - NazismDocument14 pagesHitler's Priestess: Savitri Devi, The Hindu-Aryan Myth, and Occult Neo-Nazism:Hitler's Priestess: Savitri Devi, The Hindu-Aryan Myth, and Occult Neo - NazismVassilis PagratisNo ratings yet
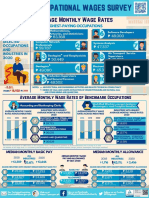
- 2020 OWS InfographicsDocument1 page2020 OWS InfographicsElisha PaloNo ratings yet
- EC8491 Communication Systems - Notes 1Document138 pagesEC8491 Communication Systems - Notes 1Kaniha KNo ratings yet