Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
Uploaded by
Sameh MostafaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Standard Operating Procedure Pharmaceutical Quality Risk Management ToolsDocument15 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Pharmaceutical Quality Risk Management ToolsPharma Life-cycle Consultancy100% (1)
- Iso13485 QOP4101 RiskMng PDFDocument4 pagesIso13485 QOP4101 RiskMng PDFQuality and Safety Consultants Co.No ratings yet
- Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment GuidelineDocument81 pagesHazard Identification & Risk Assessment Guidelinebahaa mostafa100% (5)
- Risk and OpportunityDocument5 pagesRisk and OpportunityQualityproNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringDocument8 pagesStructural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringHema Chandra Reddy KarimireddyNo ratings yet
- QMS-135 Quality Risk Management Techniques SampleDocument14 pagesQMS-135 Quality Risk Management Techniques Samplefaisal abbas100% (1)
- Rely On Laboratory Recognition by Conformity Assessment BodiesDocument4 pagesRely On Laboratory Recognition by Conformity Assessment BodiesANU M ANo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management Plan: ApprovalsDocument8 pagesQuality Risk Management Plan: Approvalsnsk79in@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management PlanDocument9 pagesQuality Risk Management Plansakib445No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarDocument23 pagesRisk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarsanthoshkurvaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Document For LAFDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment Document For LAFLaraib BhattiNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Testing TechniquesDocument8 pagesRisk Based Testing TechniquesLucian CNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management-ICH Q9Document38 pagesQuality Risk Management-ICH Q9Pharma DataNo ratings yet
- Wa0007Document6 pagesWa0007gujjar786badshah786No ratings yet
- Selection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques in Oil & Gas and Petrochemical Industries For Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesSelection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques in Oil & Gas and Petrochemical Industries For Risk AssessmentMohammad NadimNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & ManagementDocument51 pagesRisk Assessment & ManagementBelkacem AchourNo ratings yet
- 6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixDocument7 pages6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixWelma JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 15JF Brady PDFDocument8 pages15JF Brady PDFitung23No ratings yet
- 1 PurposeDocument4 pages1 PurposeBryan DyNo ratings yet
- HirarcDocument9 pagesHirarcMohammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management ProcessDocument4 pagesRisk Management ProcessMelody M ChocolateNo ratings yet
- The Risk Matrix: Jenmark John F. Jacolbe Gapor TahaDocument14 pagesThe Risk Matrix: Jenmark John F. Jacolbe Gapor TahaJheonology Fernando100% (1)
- Example Quality Risk Management Application To Identify Deviations Vs Event SampleDocument4 pagesExample Quality Risk Management Application To Identify Deviations Vs Event SampleNarine MardirossianNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Bra Procedure With MethodologyDocument4 pages4.2 Bra Procedure With MethodologyaceNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment and ManagementMudassar Bin ZaheerNo ratings yet
- RAR FormDocument7 pagesRAR Formdpaul.mbNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Chapter 2Document25 pagesRisk Management Chapter 2Nayle aldrinn LuceroNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentMosfer Al kerdemNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk ManagementDocument25 pagesLecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk Managementeladio30No ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Process Procedure QPP-061-1 Risks and OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesISO 9001 Process Procedure QPP-061-1 Risks and Opportunitiesimran shaukatNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentShadeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Risk Management For Human ErrorDocument81 pagesRisk Management For Human Errorbasit.000No ratings yet
- Case For Quality Company B: Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesCase For Quality Company B: Risk ManagementRakeshNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Bra Procedure With MethodologyDocument4 pages3.1. Bra Procedure With MethodologyaceNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Building ConstructioDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment For Building ConstructioLei Angielin Romulo DurwinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document29 pagesLecture 3seham alshehhiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Treatment MethodologyDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment & Treatment MethodologySeni OkeNo ratings yet
- Antonio Regadio Regulatory Affairs (RMP) PAPPI 15th BiCon 11 Mar 2016Document52 pagesAntonio Regadio Regulatory Affairs (RMP) PAPPI 15th BiCon 11 Mar 2016Kim Cyrelle Samson Umbalin100% (2)
- Method Statement and Risk Analysis GuidelinesDocument69 pagesMethod Statement and Risk Analysis GuidelinesVJ Geo100% (1)
- Risk Assessment GuidelinesDocument29 pagesRisk Assessment GuidelinesGerald88% (26)
- Whs Risk Management ProceduresDocument10 pagesWhs Risk Management Procedurespizixi11No ratings yet
- Risk Management SopDocument8 pagesRisk Management SopLi QiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management SopDocument8 pagesRisk Management SopLi QiNo ratings yet
- CM 659 Risk Management-IntroductionDocument27 pagesCM 659 Risk Management-IntroductionjbjuanzonNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument54 pagesRisk Assessment and ManagementDika Rahayu Widiana100% (1)
- A Guide On Quality Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesA Guide On Quality Risk Managementisrael afolayan mayomiNo ratings yet
- Case For Quality Company A: Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesCase For Quality Company A: Risk ManagementRakeshNo ratings yet
- 02.00MSHEM - Specific Awareness 02.00Document209 pages02.00MSHEM - Specific Awareness 02.00ShadifNo ratings yet
- Sitxwhs002 Whs PlanDocument6 pagesSitxwhs002 Whs PlanNish MigrationNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)Document24 pagesRisk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)ardesh abdille100% (1)
- Risk MatrixDocument3 pagesRisk MatrixGhanta Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- QSP - 08 - Risk Assessment, Management and Contingency Planning Rev 0 PDFDocument11 pagesQSP - 08 - Risk Assessment, Management and Contingency Planning Rev 0 PDFPhuong Huynh100% (2)
- Assingment OSHADocument23 pagesAssingment OSHAFikri HaziqNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Procedures - Step To Prepare Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment Procedures - Step To Prepare Risk AssessmentaneethavilsNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveDocument25 pagesRisk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveParth RavalNo ratings yet
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Mastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesFrom EverandMastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-Knowledge of Risk AssessmentFrom EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-Knowledge of Risk AssessmentRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Risk Management Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical ManufacturingFrom EverandRisk Management Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical ManufacturingHamid MollahNo ratings yet
- CompTIA CASP+ Certification The Ultimate Study Guide To Master the Advanced Security Practitioner ExamFrom EverandCompTIA CASP+ Certification The Ultimate Study Guide To Master the Advanced Security Practitioner ExamNo ratings yet
- TEM 250 Cleaning Vaidationl Interim Report Template SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 250 Cleaning Vaidationl Interim Report Template SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 255 Cleaning Validation Camapign Length Increase Protocol SampleDocument3 pagesTEM 255 Cleaning Validation Camapign Length Increase Protocol SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 305 Electronic Records and Signatures Compliance Assessment SampleDocument4 pagesTEM 305 Electronic Records and Signatures Compliance Assessment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Nexis GC-2030: SpecificationsDocument8 pagesNexis GC-2030: SpecificationsSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 230 Project Definition SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 230 Project Definition SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 180 Installation Qualification Operating Environment SampleDocument3 pagesTEM 180 Installation Qualification Operating Environment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 160 Periodic Review of Systems and Processes SampleDocument2 pagesVAL 160 Periodic Review of Systems and Processes SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- QMS 020 Documentation Rule For GMP Documents SampleDocument1 pageQMS 020 Documentation Rule For GMP Documents SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Microwave DigestionDocument8 pagesMicrowave DigestionSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- 2022 SphereFlash - Promotional - Leaflet-3 LogosDocument4 pages2022 SphereFlash - Promotional - Leaflet-3 LogosSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 285 Packaging Validation Report Template SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 285 Packaging Validation Report Template SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 095 Facility and Utility Validation Guideline SampleDocument1 pageVAL 095 Facility and Utility Validation Guideline SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 220 Cleaning Validation Master Plan Veterinary BiologicalsDocument7 pagesVAL 220 Cleaning Validation Master Plan Veterinary BiologicalsSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 035 in House Trial Procedure SampleDocument1 pageVAL 035 in House Trial Procedure SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 215 Cleaning Validatio Master Plan Non Sterile Solid SampleDocument5 pagesVAL 215 Cleaning Validatio Master Plan Non Sterile Solid SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 150 Conducting An Electronic Record and Signature Assessment SampleDocument3 pagesVAL 150 Conducting An Electronic Record and Signature Assessment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 055 Design Qualification Guidelines SampleDocument3 pagesVAL 055 Design Qualification Guidelines SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 210 Computer Validation Master Plan SampleDocument4 pagesVAL 210 Computer Validation Master Plan SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- 23.H Document and Record ControlDocument4 pages23.H Document and Record ControlSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Validation ReviewDocument2 pagesValidation ReviewSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- SopDocument3 pagesSopSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- PlanDocument1 pagePlanSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Else Tows 55Document19 pagesElse Tows 55Sameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Iso 22519 2019 en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 22519 2019 en PDFSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Hydroforce Olympus M200 ManualDocument44 pagesHydroforce Olympus M200 ManualNestor Marquez-DiazNo ratings yet
- Roll No. ...................... Total Pages: 3: GSM/D-21Document3 pagesRoll No. ...................... Total Pages: 3: GSM/D-21Pankaj KaushikNo ratings yet
- Mkomagi Et Al 2023. Relationship-Between-Project-Benefits-And-Sustainability-Of-Activities-A-Comparative-Analysis-Of-Selected-Donor-Funded-Agriculture-Related-Projects-In-TanzaniaDocument23 pagesMkomagi Et Al 2023. Relationship-Between-Project-Benefits-And-Sustainability-Of-Activities-A-Comparative-Analysis-Of-Selected-Donor-Funded-Agriculture-Related-Projects-In-TanzaniaJeremiah V. MkomagiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing - MCQsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Marketing - MCQsMaxwell;100% (1)
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityTunWin NaingNo ratings yet
- C A PerryDocument17 pagesC A PerryInfanta mary33% (3)
- IGCSE Computer by Inqilab Patel-Paper 2 PDFDocument208 pagesIGCSE Computer by Inqilab Patel-Paper 2 PDFJawad hossainNo ratings yet
- Psicothema 0214-9915: Issn: Psicothema@cop - EsDocument8 pagesPsicothema 0214-9915: Issn: Psicothema@cop - EsangeNo ratings yet
- Eng 121 NotesDocument7 pagesEng 121 Notesproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- Analisis Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Wilayah Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Tahun 2007-2011Document17 pagesAnalisis Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Wilayah Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Tahun 2007-2011Septyy RizqillahhNo ratings yet
- Homework: Name DateDocument24 pagesHomework: Name DateboysNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Electricals Limited: Job Title Job Code Department/ BU LocationDocument3 pagesBajaj Electricals Limited: Job Title Job Code Department/ BU LocationabhijitNo ratings yet
- Kahrs - Indian Semantic Analysis The Nirvacana Tradition - Kashmir - SaivismDocument318 pagesKahrs - Indian Semantic Analysis The Nirvacana Tradition - Kashmir - SaivismRalphNo ratings yet
- Datatool Alarm ManualDocument20 pagesDatatool Alarm ManualMark AustinNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Population 2011: Object 2Document5 pagesJharkhand Population 2011: Object 2niraj1947No ratings yet
- Walter Fales - Historical FactsDocument11 pagesWalter Fales - Historical FactsCésarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Preparation & Meshing Techniques Using HYPERMESH: Module HM 1Document7 pagesGeometry Preparation & Meshing Techniques Using HYPERMESH: Module HM 1Rahul ChowdariNo ratings yet
- Klaus-Michael Fortmann-Fundamentals of LogisticsDocument143 pagesKlaus-Michael Fortmann-Fundamentals of LogisticsHéctor MendozaNo ratings yet
- August Lock Installation ManualDocument12 pagesAugust Lock Installation ManualeyaoNo ratings yet
- Robert 5Document440 pagesRobert 5로헬No ratings yet
- SAP SD - CertifiedDocument3 pagesSAP SD - Certifiedamit25feb.guptaNo ratings yet
- Sales Document StructureDocument5 pagesSales Document StructureShashi RayappagariNo ratings yet
- Multimedia ICON+ As A Services PJBDocument18 pagesMultimedia ICON+ As A Services PJBHafidz MalkanNo ratings yet
- A REPORT OF SIX-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesA REPORT OF SIX-WPS OfficeAjay KNo ratings yet
- Revised RFQ Kochi OceanariumDocument90 pagesRevised RFQ Kochi OceanariumEjas Halu Mohammed100% (1)
- PROGRAM 1: Write A Program To Check Whether A Given Number Is Even or OddDocument45 pagesPROGRAM 1: Write A Program To Check Whether A Given Number Is Even or OddShobhita MahajanNo ratings yet
- Resume Tracy 2018 Portfolio2Document2 pagesResume Tracy 2018 Portfolio2api-418542159No ratings yet
- Tender Text: HYDRUS Ultrasonic Water Meter DN 15Document4 pagesTender Text: HYDRUS Ultrasonic Water Meter DN 15Anselmo LimaNo ratings yet
- Aaron Kipngeno - 1061200425-Trade ProjectDocument21 pagesAaron Kipngeno - 1061200425-Trade ProjectEvansNo ratings yet
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
Uploaded by
Sameh MostafaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
VAL 185 Guidance For The Use of Risk Assessment in Validation Sample
Uploaded by
Sameh MostafaCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Operating Procedure
Title: Guidance for the use of Risk Assessment in Validation
Department Validation/Technical Services Document no VAL-185
Prepared by: Date: Supersedes:
Checked by: Date: Date Issued:
Approved by: Date: Review Date:
1. APPLICATION
This procedure details the standard methodology used to perform GMP/Quality Risk Assessments during
Validation activities.
2. RESPONSIBILITITY AND AUTHORITY
The Validation Supervisor is responsible for appointing personnel to and coordinating Risk
Assessments. The Validation Momager will be responsible for the development of the Validation Risk
Management plan, the implementation/execution of the plan and the documentation of the activities
associated with the plan.
3. SAFETY AND PROCESS SPECIFIC INFORMATION
All safety requirements for relevant areas at any GMP facility must be followed at all times.
4. PROCEDURE
4.1 Risk Assessment
The Risk Assessment shall be conducted to determine the level of inherit risk within a given process or
product. The Risk assessment should be developed to suit the type of Validation undertaken and should
be used to determine the level at which Validation is performed. Validation should not be conducted
where steps in a process do not impact the safety or quality of the final product and no perceivable risks
are identified.
4.2 Describe the product and process
A full description of the product and the process should be drawn up, including relevant quality
information such as the composition, physical/chemical properties, structure, pH, temperatures, method
of cleaning, bactericidal/bacteriostatic treatments (e.g. heat-treatment), drying, screening, mixing,
blending, packaging, and the storage conditions. The method of distribution and transport should also be
described.
4.3 Describe the intended use of the product
The intended use should be based on the expected uses of the product by the end user or consumer.
The end use of the product can have a significant impact on the severity of any hazards that are
identified and the extent to which Validation may be applied.
4.4 Construct a flow diagram
A flow diagram should be constructed and should cover all operations and decisions in a process. When
applying risk assessment to a given operation, the steps preceding and following that operation should
also be considered. A block-type diagram may be sufficiently descriptive.
4.5 Identify steps in the process that may impact on safety and product quality
List all the hazards that may be reasonably expected to occur at each step from production, testing and
distribution up to the point of use. A hazard analysis should then be conducted to identify which hazards
are of such a nature that their elimination or reduction to acceptable levels is essential.
A thorough hazard analysis is required to ensure an effective assessment of all potential risks. A list of
the potential hazards which may be introduced, increased or controlled in each step should be drawn
up.
Copyright©www.gmpsop.com. All rights reserved
Unauthorized copying, publishing, transmission and distribution of any part of the content by electronic means are strictly
prohibited. Page 1 of 5
Standard Operating Procedure
Title: Guidance for the use of Risk Assessment in Validation
Rate as MEDIUM if the hazard relates to situations where:
The hazard may be identified through in process checks
Rate as LOW if the hazard relates to situations where:
The hazard is not likely to be easily identified.
4.5.2 Defining the class and priority of the hazard
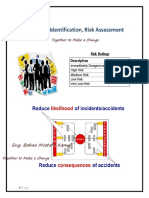
The hazard can then be assigned a Risk Class number. To determine the risk class the severity rate
and the probability rate are multiplied (See Figure 1 – Risk Class). Once the Risk Class has been
assessed the Risk Priority can be determined. The Risk Priority is derived by multiply the Risk Class
with the likely hood of hazard detectability (See Figure 2 – Risk Priority).
At the completion of the Hazard assessment process each Hazard should be rated as HIGH,
MEDIUM and LOW priority. The following actions should then be conduction for each of the following
priorities:
HIGH – Where the hazard has been assessed as high for a given step a Critical Control (CC) should
be established and the control Validated or Verified (each time the step is performed).
MEDIUM - Where a hazard has been assessed as medium for a given step a Critical Control (CC)
should be considered and the control may be Validated or Verified (each time the step is performed).
LOW – Where a hazard has been assessed as low for a given step procedures the development of
procedures to handle the risk should be considered.
Probability
Medium
High
Low
Risk Class 1
High
Risk Class 2
Severity
Medium Risk Class 3
Low
Severity = Impact on Patient Safety and Product Quality.
Probability = Likely hood of Hazard occurrence
Risk Class = Severity X Probability
Figure 1: Risk Class
Copyright©www.gmpsop.com. All rights reserved
Unauthorized copying, publishing, transmission and distribution of any part of the content by electronic means are strictly
prohibited. Page 3 of 5
Standard Operating Procedure
Title: Guidance for the use of Risk Assessment in Validation
Figure 4: Validation – Critical Control Point Decision Tree
Copyright©www.gmpsop.com. All rights reserved
Unauthorized copying, publishing, transmission and distribution of any part of the content by electronic means are strictly prohibited. Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Standard Operating Procedure Pharmaceutical Quality Risk Management ToolsDocument15 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Pharmaceutical Quality Risk Management ToolsPharma Life-cycle Consultancy100% (1)
- Iso13485 QOP4101 RiskMng PDFDocument4 pagesIso13485 QOP4101 RiskMng PDFQuality and Safety Consultants Co.No ratings yet
- Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment GuidelineDocument81 pagesHazard Identification & Risk Assessment Guidelinebahaa mostafa100% (5)
- Risk and OpportunityDocument5 pagesRisk and OpportunityQualityproNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringDocument8 pagesStructural Dynamics & Earthquake EngineeringHema Chandra Reddy KarimireddyNo ratings yet
- QMS-135 Quality Risk Management Techniques SampleDocument14 pagesQMS-135 Quality Risk Management Techniques Samplefaisal abbas100% (1)
- Rely On Laboratory Recognition by Conformity Assessment BodiesDocument4 pagesRely On Laboratory Recognition by Conformity Assessment BodiesANU M ANo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management Plan: ApprovalsDocument8 pagesQuality Risk Management Plan: Approvalsnsk79in@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management PlanDocument9 pagesQuality Risk Management Plansakib445No ratings yet
- Risk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarDocument23 pagesRisk Assesment in Microbiology: Presented by K. Santosh KumarsanthoshkurvaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Document For LAFDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment Document For LAFLaraib BhattiNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Testing TechniquesDocument8 pagesRisk Based Testing TechniquesLucian CNo ratings yet
- Quality Risk Management-ICH Q9Document38 pagesQuality Risk Management-ICH Q9Pharma DataNo ratings yet
- Wa0007Document6 pagesWa0007gujjar786badshah786No ratings yet
- Selection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques in Oil & Gas and Petrochemical Industries For Risk AssessmentDocument8 pagesSelection of Hazard Evaluation Techniques in Oil & Gas and Petrochemical Industries For Risk AssessmentMohammad NadimNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & ManagementDocument51 pagesRisk Assessment & ManagementBelkacem AchourNo ratings yet
- 6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixDocument7 pages6.SHEPROC001. SHE Risk Assessment Procedure and MatrixWelma JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 15JF Brady PDFDocument8 pages15JF Brady PDFitung23No ratings yet
- 1 PurposeDocument4 pages1 PurposeBryan DyNo ratings yet
- HirarcDocument9 pagesHirarcMohammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management ProcessDocument4 pagesRisk Management ProcessMelody M ChocolateNo ratings yet
- The Risk Matrix: Jenmark John F. Jacolbe Gapor TahaDocument14 pagesThe Risk Matrix: Jenmark John F. Jacolbe Gapor TahaJheonology Fernando100% (1)
- Example Quality Risk Management Application To Identify Deviations Vs Event SampleDocument4 pagesExample Quality Risk Management Application To Identify Deviations Vs Event SampleNarine MardirossianNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Bra Procedure With MethodologyDocument4 pages4.2 Bra Procedure With MethodologyaceNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk Assessment and ManagementMudassar Bin ZaheerNo ratings yet
- RAR FormDocument7 pagesRAR Formdpaul.mbNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Chapter 2Document25 pagesRisk Management Chapter 2Nayle aldrinn LuceroNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentMosfer Al kerdemNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk ManagementDocument25 pagesLecture Notes:: Risk Assessment & Risk Managementeladio30No ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Process Procedure QPP-061-1 Risks and OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesISO 9001 Process Procedure QPP-061-1 Risks and Opportunitiesimran shaukatNo ratings yet
- OHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesOHS-PR-02-03 HIRA Hazard ID & Risk AssessmentShadeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Risk Management For Human ErrorDocument81 pagesRisk Management For Human Errorbasit.000No ratings yet
- Case For Quality Company B: Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesCase For Quality Company B: Risk ManagementRakeshNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Bra Procedure With MethodologyDocument4 pages3.1. Bra Procedure With MethodologyaceNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Building ConstructioDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment For Building ConstructioLei Angielin Romulo DurwinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document29 pagesLecture 3seham alshehhiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Treatment MethodologyDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment & Treatment MethodologySeni OkeNo ratings yet
- Antonio Regadio Regulatory Affairs (RMP) PAPPI 15th BiCon 11 Mar 2016Document52 pagesAntonio Regadio Regulatory Affairs (RMP) PAPPI 15th BiCon 11 Mar 2016Kim Cyrelle Samson Umbalin100% (2)
- Method Statement and Risk Analysis GuidelinesDocument69 pagesMethod Statement and Risk Analysis GuidelinesVJ Geo100% (1)
- Risk Assessment GuidelinesDocument29 pagesRisk Assessment GuidelinesGerald88% (26)
- Whs Risk Management ProceduresDocument10 pagesWhs Risk Management Procedurespizixi11No ratings yet
- Risk Management SopDocument8 pagesRisk Management SopLi QiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management SopDocument8 pagesRisk Management SopLi QiNo ratings yet
- CM 659 Risk Management-IntroductionDocument27 pagesCM 659 Risk Management-IntroductionjbjuanzonNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and ManagementDocument54 pagesRisk Assessment and ManagementDika Rahayu Widiana100% (1)
- A Guide On Quality Risk ManagementDocument10 pagesA Guide On Quality Risk Managementisrael afolayan mayomiNo ratings yet
- Case For Quality Company A: Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesCase For Quality Company A: Risk ManagementRakeshNo ratings yet
- 02.00MSHEM - Specific Awareness 02.00Document209 pages02.00MSHEM - Specific Awareness 02.00ShadifNo ratings yet
- Sitxwhs002 Whs PlanDocument6 pagesSitxwhs002 Whs PlanNish MigrationNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)Document24 pagesRisk Assessment: Dr. Khidir Faisal Abu Bakr MD (DPH)ardesh abdille100% (1)
- Risk MatrixDocument3 pagesRisk MatrixGhanta Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- QSP - 08 - Risk Assessment, Management and Contingency Planning Rev 0 PDFDocument11 pagesQSP - 08 - Risk Assessment, Management and Contingency Planning Rev 0 PDFPhuong Huynh100% (2)
- Assingment OSHADocument23 pagesAssingment OSHAFikri HaziqNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Procedures - Step To Prepare Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment Procedures - Step To Prepare Risk AssessmentaneethavilsNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveDocument25 pagesRisk Assessment & Risk Management: Topic FiveParth RavalNo ratings yet
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementFrom EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Mastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesFrom EverandMastering Safety Risk Management for Medical and In Vitro DevicesNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-Knowledge of Risk AssessmentFrom EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-Knowledge of Risk AssessmentRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Risk Management Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical ManufacturingFrom EverandRisk Management Applications in Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical ManufacturingHamid MollahNo ratings yet
- CompTIA CASP+ Certification The Ultimate Study Guide To Master the Advanced Security Practitioner ExamFrom EverandCompTIA CASP+ Certification The Ultimate Study Guide To Master the Advanced Security Practitioner ExamNo ratings yet
- TEM 250 Cleaning Vaidationl Interim Report Template SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 250 Cleaning Vaidationl Interim Report Template SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 255 Cleaning Validation Camapign Length Increase Protocol SampleDocument3 pagesTEM 255 Cleaning Validation Camapign Length Increase Protocol SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 305 Electronic Records and Signatures Compliance Assessment SampleDocument4 pagesTEM 305 Electronic Records and Signatures Compliance Assessment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Nexis GC-2030: SpecificationsDocument8 pagesNexis GC-2030: SpecificationsSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 230 Project Definition SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 230 Project Definition SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 180 Installation Qualification Operating Environment SampleDocument3 pagesTEM 180 Installation Qualification Operating Environment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 160 Periodic Review of Systems and Processes SampleDocument2 pagesVAL 160 Periodic Review of Systems and Processes SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- QMS 020 Documentation Rule For GMP Documents SampleDocument1 pageQMS 020 Documentation Rule For GMP Documents SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Microwave DigestionDocument8 pagesMicrowave DigestionSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- 2022 SphereFlash - Promotional - Leaflet-3 LogosDocument4 pages2022 SphereFlash - Promotional - Leaflet-3 LogosSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- TEM 285 Packaging Validation Report Template SampleDocument2 pagesTEM 285 Packaging Validation Report Template SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 095 Facility and Utility Validation Guideline SampleDocument1 pageVAL 095 Facility and Utility Validation Guideline SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 220 Cleaning Validation Master Plan Veterinary BiologicalsDocument7 pagesVAL 220 Cleaning Validation Master Plan Veterinary BiologicalsSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 035 in House Trial Procedure SampleDocument1 pageVAL 035 in House Trial Procedure SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 215 Cleaning Validatio Master Plan Non Sterile Solid SampleDocument5 pagesVAL 215 Cleaning Validatio Master Plan Non Sterile Solid SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 150 Conducting An Electronic Record and Signature Assessment SampleDocument3 pagesVAL 150 Conducting An Electronic Record and Signature Assessment SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 055 Design Qualification Guidelines SampleDocument3 pagesVAL 055 Design Qualification Guidelines SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- VAL 210 Computer Validation Master Plan SampleDocument4 pagesVAL 210 Computer Validation Master Plan SampleSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- 23.H Document and Record ControlDocument4 pages23.H Document and Record ControlSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Validation ReviewDocument2 pagesValidation ReviewSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- SopDocument3 pagesSopSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- PlanDocument1 pagePlanSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Else Tows 55Document19 pagesElse Tows 55Sameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Iso 22519 2019 en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 22519 2019 en PDFSameh MostafaNo ratings yet
- Hydroforce Olympus M200 ManualDocument44 pagesHydroforce Olympus M200 ManualNestor Marquez-DiazNo ratings yet
- Roll No. ...................... Total Pages: 3: GSM/D-21Document3 pagesRoll No. ...................... Total Pages: 3: GSM/D-21Pankaj KaushikNo ratings yet
- Mkomagi Et Al 2023. Relationship-Between-Project-Benefits-And-Sustainability-Of-Activities-A-Comparative-Analysis-Of-Selected-Donor-Funded-Agriculture-Related-Projects-In-TanzaniaDocument23 pagesMkomagi Et Al 2023. Relationship-Between-Project-Benefits-And-Sustainability-Of-Activities-A-Comparative-Analysis-Of-Selected-Donor-Funded-Agriculture-Related-Projects-In-TanzaniaJeremiah V. MkomagiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing - MCQsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Marketing - MCQsMaxwell;100% (1)
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityTunWin NaingNo ratings yet
- C A PerryDocument17 pagesC A PerryInfanta mary33% (3)
- IGCSE Computer by Inqilab Patel-Paper 2 PDFDocument208 pagesIGCSE Computer by Inqilab Patel-Paper 2 PDFJawad hossainNo ratings yet
- Psicothema 0214-9915: Issn: Psicothema@cop - EsDocument8 pagesPsicothema 0214-9915: Issn: Psicothema@cop - EsangeNo ratings yet
- Eng 121 NotesDocument7 pagesEng 121 Notesproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- Analisis Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Wilayah Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Tahun 2007-2011Document17 pagesAnalisis Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Wilayah Di Kabupaten Wonogiri Tahun 2007-2011Septyy RizqillahhNo ratings yet
- Homework: Name DateDocument24 pagesHomework: Name DateboysNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Electricals Limited: Job Title Job Code Department/ BU LocationDocument3 pagesBajaj Electricals Limited: Job Title Job Code Department/ BU LocationabhijitNo ratings yet
- Kahrs - Indian Semantic Analysis The Nirvacana Tradition - Kashmir - SaivismDocument318 pagesKahrs - Indian Semantic Analysis The Nirvacana Tradition - Kashmir - SaivismRalphNo ratings yet
- Datatool Alarm ManualDocument20 pagesDatatool Alarm ManualMark AustinNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand Population 2011: Object 2Document5 pagesJharkhand Population 2011: Object 2niraj1947No ratings yet
- Walter Fales - Historical FactsDocument11 pagesWalter Fales - Historical FactsCésarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Preparation & Meshing Techniques Using HYPERMESH: Module HM 1Document7 pagesGeometry Preparation & Meshing Techniques Using HYPERMESH: Module HM 1Rahul ChowdariNo ratings yet
- Klaus-Michael Fortmann-Fundamentals of LogisticsDocument143 pagesKlaus-Michael Fortmann-Fundamentals of LogisticsHéctor MendozaNo ratings yet
- August Lock Installation ManualDocument12 pagesAugust Lock Installation ManualeyaoNo ratings yet
- Robert 5Document440 pagesRobert 5로헬No ratings yet
- SAP SD - CertifiedDocument3 pagesSAP SD - Certifiedamit25feb.guptaNo ratings yet
- Sales Document StructureDocument5 pagesSales Document StructureShashi RayappagariNo ratings yet
- Multimedia ICON+ As A Services PJBDocument18 pagesMultimedia ICON+ As A Services PJBHafidz MalkanNo ratings yet
- A REPORT OF SIX-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesA REPORT OF SIX-WPS OfficeAjay KNo ratings yet
- Revised RFQ Kochi OceanariumDocument90 pagesRevised RFQ Kochi OceanariumEjas Halu Mohammed100% (1)
- PROGRAM 1: Write A Program To Check Whether A Given Number Is Even or OddDocument45 pagesPROGRAM 1: Write A Program To Check Whether A Given Number Is Even or OddShobhita MahajanNo ratings yet
- Resume Tracy 2018 Portfolio2Document2 pagesResume Tracy 2018 Portfolio2api-418542159No ratings yet
- Tender Text: HYDRUS Ultrasonic Water Meter DN 15Document4 pagesTender Text: HYDRUS Ultrasonic Water Meter DN 15Anselmo LimaNo ratings yet
- Aaron Kipngeno - 1061200425-Trade ProjectDocument21 pagesAaron Kipngeno - 1061200425-Trade ProjectEvansNo ratings yet