Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microeco
Microeco
Uploaded by
Karen RearioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Applied Economics Module 1Document16 pagesApplied Economics Module 1Natalie Serrano90% (31)
- Chapter 1: Overview of AccountingDocument79 pagesChapter 1: Overview of AccountingJayar80% (5)
- Econ 100.1 - ReviewerDocument34 pagesEcon 100.1 - ReviewerLianne Angelico Depante100% (1)
- Economics ReviewerDocument7 pagesEconomics ReviewerLANANo ratings yet
- APECO Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesAPECO Midterms ReviewerSOLEDAD LONo ratings yet
- Economics RevisionsDocument11 pagesEconomics Revisionsboysteacherevening003No ratings yet
- Module 3 Diss ReviewDocument4 pagesModule 3 Diss ReviewRayhanah AndiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Reading MaterialDocument154 pagesMicroeconomics Reading MaterialZoya Farah HussainNo ratings yet
- Extension Unit 6Document123 pagesExtension Unit 6Mann PandyaNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 1Document8 pagesEconomics Unit 1dhadhi payaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Core Concepts in MicroeconomicsDocument1 pageUnit 1 Core Concepts in MicroeconomicsML CreationsNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerAevan Joseph100% (1)
- NatrDocument17 pagesNatrVikasDBZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76Document34 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76riteshhpatel0945No ratings yet
- Economics For EngineersDocument5 pagesEconomics For EngineersSrivikashini KNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity CostDocument4 pagesCircular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity Costadam_barrettoNo ratings yet
- What A EconomiaDocument2 pagesWhat A EconomiaScybiz GamingNo ratings yet
- Micro 1to3 English ColourDocument13 pagesMicro 1to3 English Colourhanoonaa786No ratings yet
- P4 - Economics - FT - Books @CAFoundationLegendsDocument419 pagesP4 - Economics - FT - Books @CAFoundationLegendsMr.Aditya NibeNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Diss MidtermsDocument9 pagesReviwer Diss MidtermsLJ FamatiganNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Document18 pagesCa Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Alexander SoniNo ratings yet
- Economics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDocument11 pagesEconomics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDo KyungsoooooNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical Economic...Document15 pagesNeoclassical Economic...Misha KosiakovNo ratings yet
- Introduction Main Key PointsDocument3 pagesIntroduction Main Key Pointsmohitbm28No ratings yet
- Classical Liberal Political Economy: Context: Adam Smith and David RicardoDocument5 pagesClassical Liberal Political Economy: Context: Adam Smith and David RicardoHanna Mhel DionisioNo ratings yet
- Microecon NotesDocument22 pagesMicroecon NotesDahlia OjalesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Module 1Document16 pagesApplied Economics Module 1Kathyleen RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Introductory Microeconomics BBA, BCIS, BBA-BIDocument42 pagesIntroductory Microeconomics BBA, BCIS, BBA-BISubash Khatiwada63% (8)
- Econ 1-3Document46 pagesEcon 1-3i'm lightNo ratings yet
- ECONOMIC WAY OF THINKING - Module 1Document22 pagesECONOMIC WAY OF THINKING - Module 1shekNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Economics Ch1 Introduction To Micro EconomicsDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Economics Ch1 Introduction To Micro EconomicsgauryNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument7 pagesModule IElaine EscobanezNo ratings yet
- Economics ReadingDocument162 pagesEconomics ReadingAnne CamantigueNo ratings yet
- Wa0014.Document168 pagesWa0014.Aman hacksNo ratings yet
- Investing in Mutual FundsDocument22 pagesInvesting in Mutual FundsIan PatrickNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts - AgEconDocument21 pagesLecture Handouts - AgEconMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceDocument58 pagesLesson 1 Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceCarolina PangilinanNo ratings yet
- 1st CEC ReviewerDocument3 pages1st CEC ReviewerFeiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Nature and Scope of EconomicsDocument25 pagesLesson 2: The Nature and Scope of EconomicsRea Mariz JordanNo ratings yet
- Basic Econ Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesBasic Econ Midterm ReviewerJasmine OrijuelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Economicsadyasha padhyNo ratings yet
- Economics Short NotesDocument10 pagesEconomics Short Notesclass xNo ratings yet
- Economics Quiz ReviewerDocument5 pagesEconomics Quiz ReviewerCrystal MercadoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Economic History & Tools of AnalysisDocument11 pagesWeek 1 - Economic History & Tools of AnalysisSebastian BistranNo ratings yet
- EDNO SAARTHI Business Economics - Jun'24Document248 pagesEDNO SAARTHI Business Economics - Jun'24hdheekekwjenNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Subject - Micro EconomicsDocument22 pagesSyllabus: Subject - Micro EconomicsHappy BangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Economics DefinedDocument95 pagesChapter 1 Economics DefinedWayne Logronio SevandalNo ratings yet
- Basic Problems in Micro Economics - Advanced EconomicsDocument3 pagesBasic Problems in Micro Economics - Advanced Economicsaravind_91No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Klysh SalvezNo ratings yet
- Economics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsPatricia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics: What Is Economics? Methods of EconomicsDocument5 pagesBasic Microeconomics: What Is Economics? Methods of EconomicsJersey SNo ratings yet
- Economic ReviewerDocument3 pagesEconomic ReviewerJhea May CatapiaNo ratings yet
- Economics Module - I-1Document66 pagesEconomics Module - I-1Neet 720No ratings yet
- 202004201521034278madhurima App Economics ScopeDocument18 pages202004201521034278madhurima App Economics Scopesadiq farhanNo ratings yet
- Economics 1Document25 pagesEconomics 1MerylNo ratings yet
- 1 - Classical Theory of Output, Income and Employment DeterminationDocument14 pages1 - Classical Theory of Output, Income and Employment Determinationsara.028279No ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Economics: Dr. Smita ShuklaDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Economics: Dr. Smita Shuklamanukoshy76No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document54 pagesChapter 1my Lord JesusNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ReviewDocument45 pagesEcon Dev Reviewmaxell decilloNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- 18MAB303T - RegressionDocument97 pages18MAB303T - RegressionJEMINA J (RA2011037010010)No ratings yet
- Chemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015Document96 pagesChemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015ZiyadNo ratings yet
- College of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureDocument20 pagesCollege of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureAngela V. De LunaNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Unit-2Document57 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Unit-2Moin KhanNo ratings yet
- PE 2 (Rhythmic (SyllabusDocument2 pagesPE 2 (Rhythmic (SyllabusJoseph MazoNo ratings yet
- Line Dance ModuleDocument34 pagesLine Dance ModuleKim Ignatius GianganNo ratings yet
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- BSBTWK601 - PDF HojeDocument21 pagesBSBTWK601 - PDF HojeDaniela CabralNo ratings yet
- Salaat Salaam PDFDocument44 pagesSalaat Salaam PDFSana SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Clauses of Purpose Reason and Result Fun Activities Games - 974Document3 pagesClauses of Purpose Reason and Result Fun Activities Games - 974tesslimaNo ratings yet
- Carnivoruos Lubomír Adamec 2021Document20 pagesCarnivoruos Lubomír Adamec 2021Evaldo PapeNo ratings yet
- Resume - Ricky - VivancoDocument1 pageResume - Ricky - VivancoRicky VivancoNo ratings yet
- Semantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsDocument7 pagesSemantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsgangancristinaNo ratings yet
- MBA Regular-2020 ArsiDocument3 pagesMBA Regular-2020 ArsiAsfawosen Dingama100% (3)
- LEA 5 Midterm Exam 2013Document2 pagesLEA 5 Midterm Exam 2013Ivy Maril De Guzman-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Accounting MCQsDocument12 pagesAccounting MCQsLaraib AliNo ratings yet
- Film Study Worksheet Documentary Logos Pathos EthosDocument2 pagesFilm Study Worksheet Documentary Logos Pathos EthosGerardo E. Lopez MoralesNo ratings yet
- LP Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageLP Quadratic EquationMarcus Antonio G. IsraelNo ratings yet
- The Palette Magazine 2011Document56 pagesThe Palette Magazine 2011101ThingsToDoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionAtif LiaqatNo ratings yet
- My Mbbs Choice 25-2023Document2 pagesMy Mbbs Choice 25-2023Herbal Medicine TamilNo ratings yet
- Wealth of Nations QuestionsDocument3 pagesWealth of Nations QuestionssantanaNo ratings yet
- Chinese Literature Singapore Asiapac 201Document16 pagesChinese Literature Singapore Asiapac 201Tan Zhen HuiNo ratings yet
- Subt 541 Ponencia 3Document51 pagesSubt 541 Ponencia 3Javier Cobos MoraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionRholynne Ghie Anne EstebanNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Essentials Book PDFDocument73 pagesSAP HANA Essentials Book PDFMythili DuraisamiNo ratings yet
- Qatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesDocument97 pagesQatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesMohammed BadieNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Transmission Training Material V2.0Document547 pagesHCIA-Transmission Training Material V2.0Ahmed ElseliniNo ratings yet
- JFD Alarm Manager User-Guide EN PDFDocument50 pagesJFD Alarm Manager User-Guide EN PDFANGKIONGBOHNo ratings yet
Microeco
Microeco
Uploaded by
Karen RearioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microeco
Microeco
Uploaded by
Karen RearioCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROECO
The word 'economics' comes from two Greek THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD OF
words, 'eco' meaning home and 'nomos' meaning ECONOMICS
accounts.
Data Gathering - It is the process of
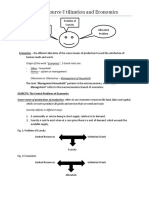
Economics is the study of the proper allocation gathering and measuring information on
and efficient use of scarce resources to produce variables of interest,
commodities for the satisfaction of unlimited Economic Analysis - Data gathered is
needs and wants of man. useless if not analyzed.
Economic Conclusions - After laying
Economic Goals down all assumptions, one proceeds to
reasoning in order to generate
Economic efficiency
conclusions.
Economic Freedom
REASONING
Economic security and predictability
Inductive Reasoning
Economic equity (particular to general}
Economic growth and innovation Deductive Reasoning
Other goals (general to the particular.)
ECONOMICS RELATED TO OTHER NORMATIVE VS. POSITIVE
SOCIAL SCIENCES
Normative economics is concerned with what
Anthropology – “Anthropos” one believes ought to be. It values judgment of
and “logus” which means the “study of what is good and bad, what is true and false. It
group or people”. describe what is happening to the economy and
why.
Political Science- “polis” which means
“city” or “sate” and science came from Positive economics has something to do with
latin word “scire” which means “to “what is’. It describes facts and data in the
know”. economy. It is concerned with the development
and testing of positive statements about the
Sociology- word “socio” and world that are objective and verifiable.
“logus” which means study of society.
Psychology- word “psyche”
and “logus” meaning soul and study.
History- It is important in studying
economics not only through systematic
recording of past events but a detailed
and in-depth interpretation of the cause
and effect of past events.
BRANCHES OF ECONOMICS
Micro Economics (Small) - Individual
Macro Economics (Large) – Economy
MICROECO
ANCIENT PERIOD: Production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graph that
shows all of the different combinations of output that
Plato – Theory of Money & Market can be produced given current resources and
Aristotle - Paradox of Value- “What is technology. Sometimes called the production
rare is greater than good than what is possibilities frontier (PPF), the PPC illustrates
plentiful” scarcity and tradeoffs.
Xenophone – Memorabilia
3 BASIC ECONOMIC PROBLEM
MIDIEVAL PERIOD:
What to produce
Thomas Aquinas – How to produce
- Lending and Interest For whom
- Just Price
4 FACTORS OF PRUDUCTION
CLASSICAL PERIOD:
Land
Adam Smith – Father of Microeconomics Labour
David Ricardo –Political economist & Capital
Businessman Enterprise
NEO-CLASSICAL PERIOD: 4 ECONOMIC SYSTEM
Alfred Marshall– Father of Neo-Classical Traditional Economic System
Carl Menger – First Austrian Economist Command Economic System
Market Economic System
MODERN PERIOD:
Mixed Economic System
John Maynard Keynes – Founder of Macro THE THREE ISM
Milton Friedman – Economist, Monetarist
CAPITALISM- private owned
SOCIALISM- community owned
COMMUNISM- government owned
CIRCULAR FLOW
- Shows connection between firms and
households in input and output market.
Law of Scarcity: cannot produce all goods and
services.
Law of Demand- the higher the price, the lower
the quantity demanded.
Law of Supply- The higher the price, the higher
quantity supplied.
Trade off- when a choice is made by two or
more options.
Opportunity Cost- choosing one option.
You might also like
- Applied Economics Module 1Document16 pagesApplied Economics Module 1Natalie Serrano90% (31)
- Chapter 1: Overview of AccountingDocument79 pagesChapter 1: Overview of AccountingJayar80% (5)
- Econ 100.1 - ReviewerDocument34 pagesEcon 100.1 - ReviewerLianne Angelico Depante100% (1)
- Economics ReviewerDocument7 pagesEconomics ReviewerLANANo ratings yet
- APECO Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesAPECO Midterms ReviewerSOLEDAD LONo ratings yet
- Economics RevisionsDocument11 pagesEconomics Revisionsboysteacherevening003No ratings yet
- Module 3 Diss ReviewDocument4 pagesModule 3 Diss ReviewRayhanah AndiNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Reading MaterialDocument154 pagesMicroeconomics Reading MaterialZoya Farah HussainNo ratings yet
- Extension Unit 6Document123 pagesExtension Unit 6Mann PandyaNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 1Document8 pagesEconomics Unit 1dhadhi payaleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Core Concepts in MicroeconomicsDocument1 pageUnit 1 Core Concepts in MicroeconomicsML CreationsNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics ReviewerDocument6 pagesApplied Economics ReviewerAevan Joseph100% (1)
- NatrDocument17 pagesNatrVikasDBZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76Document34 pagesChapter 1 Intro To Economics - 9914937e c0f1 4fa8 9418 Bb9f4270ae76riteshhpatel0945No ratings yet
- Economics For EngineersDocument5 pagesEconomics For EngineersSrivikashini KNo ratings yet
- Circular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity CostDocument4 pagesCircular Flow Diagram PPF and Opportunity Costadam_barrettoNo ratings yet
- What A EconomiaDocument2 pagesWhat A EconomiaScybiz GamingNo ratings yet
- Micro 1to3 English ColourDocument13 pagesMicro 1to3 English Colourhanoonaa786No ratings yet
- P4 - Economics - FT - Books @CAFoundationLegendsDocument419 pagesP4 - Economics - FT - Books @CAFoundationLegendsMr.Aditya NibeNo ratings yet
- Reviwer Diss MidtermsDocument9 pagesReviwer Diss MidtermsLJ FamatiganNo ratings yet
- Ca Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Document18 pagesCa Foundation - Paper 4 - Economics: Chapter-1 Nature & Scope of Business Economics (By-Jatin Lamba)Alexander SoniNo ratings yet
- Economics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDocument11 pagesEconomics, 19th Edition by Samuelson, ReviewerDo KyungsoooooNo ratings yet
- Neoclassical Economic...Document15 pagesNeoclassical Economic...Misha KosiakovNo ratings yet
- Introduction Main Key PointsDocument3 pagesIntroduction Main Key Pointsmohitbm28No ratings yet
- Classical Liberal Political Economy: Context: Adam Smith and David RicardoDocument5 pagesClassical Liberal Political Economy: Context: Adam Smith and David RicardoHanna Mhel DionisioNo ratings yet
- Microecon NotesDocument22 pagesMicroecon NotesDahlia OjalesNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Module 1Document16 pagesApplied Economics Module 1Kathyleen RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Introductory Microeconomics BBA, BCIS, BBA-BIDocument42 pagesIntroductory Microeconomics BBA, BCIS, BBA-BISubash Khatiwada63% (8)
- Econ 1-3Document46 pagesEcon 1-3i'm lightNo ratings yet
- ECONOMIC WAY OF THINKING - Module 1Document22 pagesECONOMIC WAY OF THINKING - Module 1shekNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Economics Ch1 Introduction To Micro EconomicsDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Economics Ch1 Introduction To Micro EconomicsgauryNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument7 pagesModule IElaine EscobanezNo ratings yet
- Economics ReadingDocument162 pagesEconomics ReadingAnne CamantigueNo ratings yet
- Wa0014.Document168 pagesWa0014.Aman hacksNo ratings yet
- Investing in Mutual FundsDocument22 pagesInvesting in Mutual FundsIan PatrickNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts - AgEconDocument21 pagesLecture Handouts - AgEconMicah Porcal ArelladoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceDocument58 pagesLesson 1 Revisiting Economics As A Social ScienceCarolina PangilinanNo ratings yet
- 1st CEC ReviewerDocument3 pages1st CEC ReviewerFeiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Nature and Scope of EconomicsDocument25 pagesLesson 2: The Nature and Scope of EconomicsRea Mariz JordanNo ratings yet
- Basic Econ Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesBasic Econ Midterm ReviewerJasmine OrijuelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Economicsadyasha padhyNo ratings yet
- Economics Short NotesDocument10 pagesEconomics Short Notesclass xNo ratings yet
- Economics Quiz ReviewerDocument5 pagesEconomics Quiz ReviewerCrystal MercadoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Economic History & Tools of AnalysisDocument11 pagesWeek 1 - Economic History & Tools of AnalysisSebastian BistranNo ratings yet
- EDNO SAARTHI Business Economics - Jun'24Document248 pagesEDNO SAARTHI Business Economics - Jun'24hdheekekwjenNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Subject - Micro EconomicsDocument22 pagesSyllabus: Subject - Micro EconomicsHappy BangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Economics DefinedDocument95 pagesChapter 1 Economics DefinedWayne Logronio SevandalNo ratings yet
- Basic Problems in Micro Economics - Advanced EconomicsDocument3 pagesBasic Problems in Micro Economics - Advanced Economicsaravind_91No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Klysh SalvezNo ratings yet
- Economics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsDocument6 pagesEconomics Is A Science: Applied Economics Nature of EconomicsPatricia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics: What Is Economics? Methods of EconomicsDocument5 pagesBasic Microeconomics: What Is Economics? Methods of EconomicsJersey SNo ratings yet
- Economic ReviewerDocument3 pagesEconomic ReviewerJhea May CatapiaNo ratings yet
- Economics Module - I-1Document66 pagesEconomics Module - I-1Neet 720No ratings yet
- 202004201521034278madhurima App Economics ScopeDocument18 pages202004201521034278madhurima App Economics Scopesadiq farhanNo ratings yet
- Economics 1Document25 pagesEconomics 1MerylNo ratings yet
- 1 - Classical Theory of Output, Income and Employment DeterminationDocument14 pages1 - Classical Theory of Output, Income and Employment Determinationsara.028279No ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial Economics: Dr. Smita ShuklaDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Economics: Dr. Smita Shuklamanukoshy76No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document54 pagesChapter 1my Lord JesusNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ReviewDocument45 pagesEcon Dev Reviewmaxell decilloNo ratings yet
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- 18MAB303T - RegressionDocument97 pages18MAB303T - RegressionJEMINA J (RA2011037010010)No ratings yet
- Chemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015Document96 pagesChemistry PG 2015 Admn On05sept2015ZiyadNo ratings yet
- College of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureDocument20 pagesCollege of Health & Allied Sciences: Review of Related LiteratureAngela V. De LunaNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Unit-2Document57 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Unit-2Moin KhanNo ratings yet
- PE 2 (Rhythmic (SyllabusDocument2 pagesPE 2 (Rhythmic (SyllabusJoseph MazoNo ratings yet
- Line Dance ModuleDocument34 pagesLine Dance ModuleKim Ignatius GianganNo ratings yet
- Tekin Iftar2017 PDFDocument21 pagesTekin Iftar2017 PDFVictor Martin CobosNo ratings yet
- BSBTWK601 - PDF HojeDocument21 pagesBSBTWK601 - PDF HojeDaniela CabralNo ratings yet
- Salaat Salaam PDFDocument44 pagesSalaat Salaam PDFSana SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Clauses of Purpose Reason and Result Fun Activities Games - 974Document3 pagesClauses of Purpose Reason and Result Fun Activities Games - 974tesslimaNo ratings yet
- Carnivoruos Lubomír Adamec 2021Document20 pagesCarnivoruos Lubomír Adamec 2021Evaldo PapeNo ratings yet
- Resume - Ricky - VivancoDocument1 pageResume - Ricky - VivancoRicky VivancoNo ratings yet
- Semantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsDocument7 pagesSemantic Configuration of Sexist Idioms: Radical Networks and Cultural ScriptsgangancristinaNo ratings yet
- MBA Regular-2020 ArsiDocument3 pagesMBA Regular-2020 ArsiAsfawosen Dingama100% (3)
- LEA 5 Midterm Exam 2013Document2 pagesLEA 5 Midterm Exam 2013Ivy Maril De Guzman-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Accounting MCQsDocument12 pagesAccounting MCQsLaraib AliNo ratings yet
- Film Study Worksheet Documentary Logos Pathos EthosDocument2 pagesFilm Study Worksheet Documentary Logos Pathos EthosGerardo E. Lopez MoralesNo ratings yet
- LP Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageLP Quadratic EquationMarcus Antonio G. IsraelNo ratings yet
- The Palette Magazine 2011Document56 pagesThe Palette Magazine 2011101ThingsToDoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Test: Make Circle Around A), B), C) or D) According To The Asked QuestionAtif LiaqatNo ratings yet
- My Mbbs Choice 25-2023Document2 pagesMy Mbbs Choice 25-2023Herbal Medicine TamilNo ratings yet
- Wealth of Nations QuestionsDocument3 pagesWealth of Nations QuestionssantanaNo ratings yet
- Chinese Literature Singapore Asiapac 201Document16 pagesChinese Literature Singapore Asiapac 201Tan Zhen HuiNo ratings yet
- Subt 541 Ponencia 3Document51 pagesSubt 541 Ponencia 3Javier Cobos MoraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 The Teaching ProfessionRholynne Ghie Anne EstebanNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Essentials Book PDFDocument73 pagesSAP HANA Essentials Book PDFMythili DuraisamiNo ratings yet
- Qatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesDocument97 pagesQatar National Physical Activity GuidelinesMohammed BadieNo ratings yet
- HCIA-Transmission Training Material V2.0Document547 pagesHCIA-Transmission Training Material V2.0Ahmed ElseliniNo ratings yet
- JFD Alarm Manager User-Guide EN PDFDocument50 pagesJFD Alarm Manager User-Guide EN PDFANGKIONGBOHNo ratings yet