Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JA2 Post412 Validity
JA2 Post412 Validity
Uploaded by
OscarDavidGordilloGonzalezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JA2 Post412 Validity
JA2 Post412 Validity
Uploaded by
OscarDavidGordilloGonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
Validity of a Group Intermittent-High-Intensity
Test for Repeated Sprint Ability: A pilot study (2) CORSO DI LAUREA IN SCIENZE
MOTORIE
(1) DEPARTAMENT OF SPORTS AND FACOLTA’ DI MEDICINA E CHIRURGIA
PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Universita’ di Tor Vergata – Roma
(1) BARBERO- (2)
FACULTY OF HUMANITY AND EDUCATION
OF MELILLA. UNIVERSITY OF GRANADA.
BARBERO-ÁLVAREZ, JOSÉ C. and CASTAGNA, CARLO
1. INTRODUCTION.
Many team sports as soccer require participants to repeatedly
produce maximal or near maximal sprints of short duration The aim of this study was to examine the
(1-7s) with brief recovery periods, over an extended period of
time (60-90 min). Repeated sprint ability (RSA) has been
validity of a new field intermittent high-
high-
suggested as an important component of team sports intensity group test developed to assess
performance (Spencer et al., 2005). RSA (GRSA) in soccer players.
RSA tests are specifically designed to assess the athlete's
ability to perform short bursts of high intensity exercise over
a series of multiple efforts. However the RSA assessment
requires testing protocols that are difficult to implement
(photocells) and are time consuming.
2. METHODS.
Participants: Eighteen amateur soccer players (mean ± sd: age
21.8±4.8 years, height 1.76±0.2 m, body mass 69.0±7.8 kg) were 3. RESULTS.
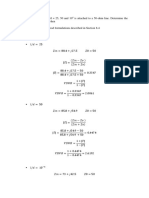
tested in a random order for RSA and GRSA at least two days RSA Total Time and best sprint performance were
apart. significantly correlated with GRSA performance (r=-0.83, and
r=-0.77, respectively p=0.002).
RSA test: The RSAT consisted in 8 bouts of 2 x 15 m shuttle run
Post tests Blood Lactate concentrations were not significantly
sprints (30-m per bout) with 30-s of passive recovery. Sprint
different (13.25±3.14 and 13.57±4.34 mmol L-1 for GRSA and
scores were assessed using custom-made infrared light sensors
RSA respectively.
connected to a personal computer.
Peak HR were 93±3.4 and 93±3.0% of HRmax for GRSA and
GRSA test: Group RSA test consisted in progressive speed RSA, respectively.
2x15m shuttle running bouts with 30s of passive recovery. Starting 6.4
speed was 18 km·h-1 with 0.5 km·h-1 increments every 8 bouts.
52.0
y = -0.0012x + 6.2916 y = -0.0097x + 51.716
6.2 R2 = 0.5899 51.0
R2 = 0.6816
50.0
GRSA performance was considered as the total distance covered
6.0
Best Time RSAT (s)
Total Time RSAT (s)
49.0
5.8
48.0
during the test. 5.6
5.4
47.0
46.0
5.2 45.0
5.0 44.0
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Distance GRSAT (m) Distance GRSAT (m)
102 20
Blood Lactate (mmol L-1) post
100 18
16
HR peak RSAT (% HRmax)
98
14
96
12
94
.
10
92
8
90
6
88
y = 0.939x + 6.7506 4 y = 0.939x + 6.7506
86 R2 = 0.6519 2 R2 = 0.6519
84 0
88 90 92 94 96 98 100 0 5 10 15 20 25
HR peak GRSAT (%HRmax) Blood Lactate (mmol L-1) postRSAT .
Fingertip blood lactate concentration was assessed at rest and
three minutes after the end of both tests. Heart rate was monitored
throughout the tests using short range telemetry.
4. DISCUSSION.
Significance level was set to P<0.05. Values are presented as means
± sd. This study results showed that GRSA test may be
considered as an interesting test to assess RSA
5. CONCLUSIONS. performance in groups of amateur soccer players
without the operative limitation usually encountered
The results of this study showed the criterion during usual running RSA protocols.
validity of a team sport specific high-
high-intensity test In fact GRSA is easy to administer and allows mass
in estimating players’ repeated sprint ability. testing.
In this regard coaches and fitness trainers may
use GRSA for a fast and economical, evaluation
of their players ability to reiterate sprints over 6. REFERENCES.
time. 1. Spencer, M., Bishop, D., Dawson, B. and Goodman, C. (2005).
Physiological and Metabolic Responses of Repeated-Sprint Activities
Specific to Field-Based Team Sports. Sports Medicine, 35(12), 1025-
1044.2.
You might also like
- PyGMTSAR: Sentinel-1 Python InSAR. An Introduction: Python InSAR, #1From EverandPyGMTSAR: Sentinel-1 Python InSAR. An Introduction: Python InSAR, #1No ratings yet
- Insert P2 - XIC - Out PDFDocument4 pagesInsert P2 - XIC - Out PDFAbbas Ali MirzaNo ratings yet
- Rubber Burn Test SpecsDocument1 pageRubber Burn Test SpecsTushar BagdeNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Vikings - Jonathan ClementsDocument1,459 pagesA Brief History of The Vikings - Jonathan ClementsRodrigo Hky100% (2)
- Validity of The Running Anaerobic Sprint Test (Rast) For Assess Anaerobic Power and Predicting Performances: 2138Document9 pagesValidity of The Running Anaerobic Sprint Test (Rast) For Assess Anaerobic Power and Predicting Performances: 2138Nur CahyoNo ratings yet
- Repeated-Sprint Performance in Team Sport Players: Associations With Measures of Aerobic Fitness, Metabolic Control and Locomotor FunctionDocument12 pagesRepeated-Sprint Performance in Team Sport Players: Associations With Measures of Aerobic Fitness, Metabolic Control and Locomotor FunctionMarko TrofenikNo ratings yet
- Rampinini 2007Document9 pagesRampinini 2007Dylan VenegasNo ratings yet
- NAVEDTRA 14339 Aviation Electricity and Electronics - RadarDocument54 pagesNAVEDTRA 14339 Aviation Electricity and Electronics - Radarhackbrian003No ratings yet
- Capacidade de Sprints Repetidos - Onde EstamosDocument5 pagesCapacidade de Sprints Repetidos - Onde EstamosSheilani MartinsNo ratings yet
- Velocity-IsAR On The Application of ISAR Techniques To Multichannel SAR ImagingDocument6 pagesVelocity-IsAR On The Application of ISAR Techniques To Multichannel SAR ImagingsanuroybhsNo ratings yet
- 2012 UWB Radar System IMSDocument5 pages2012 UWB Radar System IMSShayan aminNo ratings yet
- Barrey Et Al. 2001Document5 pagesBarrey Et Al. 2001Bruno Junior dos SantosNo ratings yet
- RPE V R B S, B P, D P: AND Elocity Elationships For The ACK Quat Ench Ress AND Eadlift in OwerliftersDocument6 pagesRPE V R B S, B P, D P: AND Elocity Elationships For The ACK Quat Ench Ress AND Eadlift in OwerliftersBatta ZahranNo ratings yet
- MSS 0000000000002412Document9 pagesMSS 0000000000002412SportsciencesNo ratings yet
- Pre-Season Fitness Testing in Elite Soccer: Integrating The 30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test Into The Weekly MicrocycleDocument3 pagesPre-Season Fitness Testing in Elite Soccer: Integrating The 30-15 Intermittent Fitness Test Into The Weekly MicrocycleCherbiti Mohammed AmineNo ratings yet
- Test of The Classic Model For Predicting Endurance.20Document7 pagesTest of The Classic Model For Predicting Endurance.20Gust AvoNo ratings yet
- Deinterlaving TeziDocument50 pagesDeinterlaving TeziFurkan KahramanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modeling of SCARA Robot Based On Udwadia-Kalaba TheoryDocument12 pagesDynamic Modeling of SCARA Robot Based On Udwadia-Kalaba TheoryCchh UuyyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Jumping Ability and Running.1-1Document5 pagesRelationship Between Jumping Ability and Running.1-1j120200018No ratings yet
- The Relation Between Running Speed and Measures Of.9Document6 pagesThe Relation Between Running Speed and Measures Of.9Nemanja DjordjevicNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Jumping Ability and Running.1Document5 pagesRelationship Between Jumping Ability and Running.1j120200018No ratings yet
- Optimization of Performance Through Kinematic Analysis of The Different Phases of The 100 MDocument10 pagesOptimization of Performance Through Kinematic Analysis of The Different Phases of The 100 MChristine BrooksNo ratings yet
- 2018 ACSM ANPL Poster-MagriniDocument1 page2018 ACSM ANPL Poster-MagriniTaryn BlackstockNo ratings yet
- Purnawan 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 890 012056Document7 pagesPurnawan 2017 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 890 012056ANUKARAN KHANNANo ratings yet
- Noakes 1990Document12 pagesNoakes 1990Einar Cumplido MartínezNo ratings yet
- Caracteristicas Antropometricas en RugbyDocument12 pagesCaracteristicas Antropometricas en RugbyRosaNo ratings yet
- "All-Out" Tethered Running As An Alternative To Wingate Anaerobic TestDocument8 pages"All-Out" Tethered Running As An Alternative To Wingate Anaerobic TestorcaNo ratings yet
- EE602 AssignmentDocument10 pagesEE602 AssignmentRajat SoniNo ratings yet
- A New Short Track Test To Estimate The Vo2max And.7Document6 pagesA New Short Track Test To Estimate The Vo2max And.7fqyquinta12345No ratings yet
- Gasto EnergeticoDocument6 pagesGasto EnergeticoJúnior Alvacir CamargoNo ratings yet
- Spie2008 ADC PosterDocument1 pageSpie2008 ADC PostergastromonoNo ratings yet
- Critical Speed Thresholds For Vo2max and BoundarieDocument6 pagesCritical Speed Thresholds For Vo2max and BoundarieHannah JanawaNo ratings yet
- Control RT Design Naclerio 2588650423Document25 pagesControl RT Design Naclerio 2588650423Vicente Ignacio Ormazábal MedinaNo ratings yet
- Gear Crack Detection Using Modified TSA and Proposed Fault Indicators For Fluctuating Speed ConditionsDocument16 pagesGear Crack Detection Using Modified TSA and Proposed Fault Indicators For Fluctuating Speed ConditionsPradeep KunduNo ratings yet
- Optimal Control For Balancing A Rotary Inverted Pendulum: An Experimental SettingDocument6 pagesOptimal Control For Balancing A Rotary Inverted Pendulum: An Experimental SettingnestorGNo ratings yet
- Abhinav Pratap Singh, Divakar Vashisth, Shalivahan SrivastavaDocument1 pageAbhinav Pratap Singh, Divakar Vashisth, Shalivahan SrivastavaSakshi MalhotraNo ratings yet
- DesignGuidelinesfortheSelectionandUseofStainlessSteels 9014Document7 pagesDesignGuidelinesfortheSelectionandUseofStainlessSteels 9014gusiNo ratings yet
- A Fuzzy Graph-Based Segmentation For Marine and Maritime Applications in SAR ImagesDocument4 pagesA Fuzzy Graph-Based Segmentation For Marine and Maritime Applications in SAR ImagesMiqueias AmorimNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Performance of Simplified RANS Formulations For Velocity Distributions Against Full 3D RANS ModelDocument10 pagesComparison of Performance of Simplified RANS Formulations For Velocity Distributions Against Full 3D RANS Modelqwertyytrewq251931No ratings yet
- Physiological Determinants of Three Kilometer.8Document6 pagesPhysiological Determinants of Three Kilometer.8premtimNo ratings yet
- On 8-Bus Test System For Solving Challenges in Relay CoordinationDocument5 pagesOn 8-Bus Test System For Solving Challenges in Relay CoordinationDaniel Felipe Macias GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Band Selection For Hyperspectral Images Based On Parallel Particle Swarm Optimization SchemesDocument4 pagesBand Selection For Hyperspectral Images Based On Parallel Particle Swarm Optimization SchemesMojtaba SabooriNo ratings yet
- JA2 Post412 RelationshipDocument1 pageJA2 Post412 RelationshipOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Our Visit Today: Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Task ForceDocument5 pagesOur Visit Today: Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Task ForceAndresNo ratings yet
- Repeat Sprint Ability: Ó National Strength and Conditioning AssociationDocument5 pagesRepeat Sprint Ability: Ó National Strength and Conditioning AssociationJürgen HennNo ratings yet
- Ynthetic Aperture Radar On Low PowerDocument6 pagesYnthetic Aperture Radar On Low Powerharsha vardhanNo ratings yet
- PhysRevLett 131 053803Document6 pagesPhysRevLett 131 053803Marco SIMONENo ratings yet
- Use of MSCR To Replace PG Plus TestsDocument2 pagesUse of MSCR To Replace PG Plus TestsDevesh Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Waveform Design To Improve Performance of An Existing Radar SystemDocument7 pagesWaveform Design To Improve Performance of An Existing Radar SystemArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Smart Materials and Structures: International WorkshopDocument10 pagesSmart Materials and Structures: International WorkshopDavid CristhianNo ratings yet
- Predictors of Performance in A 4-h Mountain-Bike RaceDocument8 pagesPredictors of Performance in A 4-h Mountain-Bike RaceDanilo Lessa BernardineliNo ratings yet
- EASA Mod 2 BK 2 Physics PDFDocument69 pagesEASA Mod 2 BK 2 Physics PDFrameshneupaneNo ratings yet
- TB 5Document15 pagesTB 5Ismail AlfarugiNo ratings yet
- Velocity ParadigmDocument8 pagesVelocity ParadigmJames WalshNo ratings yet
- Molecular ModelingDocument22 pagesMolecular ModelingHely PatelNo ratings yet
- A Survey and Experimental Evaluation of Proximity Sensors For Space RoboticsDocument8 pagesA Survey and Experimental Evaluation of Proximity Sensors For Space RoboticsmohammedNo ratings yet
- ML Report-P21035Document2 pagesML Report-P21035Hari NarayananNo ratings yet
- Vaisala Solid State RadarsDocument14 pagesVaisala Solid State RadarsKadekNo ratings yet
- 2023 RUL Interaction Models For Remaining Useful Life Estimation Dmitry RussiaDocument33 pages2023 RUL Interaction Models For Remaining Useful Life Estimation Dmitry RussiaRachit SinghNo ratings yet
- Summary of Critical Speeds For Simple Rotors Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesSummary of Critical Speeds For Simple Rotors Cheat SheetJagan TnNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Resisted Sled Training (RST) For Sprint Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument24 pagesThe Effectiveness of Resisted Sled Training (RST) For Sprint Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisabcsouzaNo ratings yet
- Signal Processing Methods in Human Motion Path Analysis: A Use Case For Karate KataDocument6 pagesSignal Processing Methods in Human Motion Path Analysis: A Use Case For Karate KataTaregh KaramiNo ratings yet
- GSA For DOCRDocument14 pagesGSA For DOCRNguyễn Thị Bích TuyềnNo ratings yet
- Efectos Del Ejercicio en La Funcion EndotelialDocument21 pagesEfectos Del Ejercicio en La Funcion EndotelialOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease and Exercise 2008Document5 pagesCardiovascular Disease and Exercise 2008OscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Enfermos Psiquiatricos EsDocument11 pagesEjercicio Enfermos Psiquiatricos EsOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- JA2 Post412 DemandsDocument7 pagesJA2 Post412 DemandsOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- JA2 Post412 FatigueDocument7 pagesJA2 Post412 FatigueOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- JA2 Post412 PerformanceDocument10 pagesJA2 Post412 PerformanceOscarDavidGordilloGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Real Time Road Sign Recognition System For Autonomous CarDocument14 pagesReal Time Road Sign Recognition System For Autonomous CarVipul MistryNo ratings yet
- Smoke Alarm User's Guide: For Model: PI2010Document16 pagesSmoke Alarm User's Guide: For Model: PI2010goawayNo ratings yet
- Fliqlo - Mobile AppDocument1 pageFliqlo - Mobile AppJon BaerNo ratings yet
- Railway Ballast PerformanceDocument27 pagesRailway Ballast PerformanceSamuel Carlos Sanjuán TorresNo ratings yet
- BWB BrochureDocument5 pagesBWB BrochureUswatul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Abstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZDocument6 pagesAbstracts: IAFRI Metaldehyde Conference - 13 September - Fera Science LTD, York YO41 1LZbendel_boyNo ratings yet
- 2012 Training Materials PDFDocument32 pages2012 Training Materials PDFWisam Ankah100% (1)
- Ejercicios PruerbaDocument5 pagesEjercicios PruerbaGato LliviNo ratings yet
- 561566642977unit-3 - TextilesDocument11 pages561566642977unit-3 - TextilesGaganpreet Kaur Fashion DesigningNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationDocument92 pages07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationKristhian GalárragaNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- Are Urbanization, Industrialization and CO2 Emissions Cointegrated?Document30 pagesAre Urbanization, Industrialization and CO2 Emissions Cointegrated?doctshNo ratings yet
- Global Stability Analysis of Eccentric Taylor Couette FlowDocument28 pagesGlobal Stability Analysis of Eccentric Taylor Couette FlowSreekanth MenonNo ratings yet
- Product Requirements Specification Process in ProdDocument12 pagesProduct Requirements Specification Process in ProdemmyNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument41 pagesLab Manualprojectapply2023No ratings yet
- Worksheet - Orbital Diagrams - TeacherDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Orbital Diagrams - Teacherdela2100% (3)
- Euthenics 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesEuthenics 2 ReviewerSun Tea SeguinNo ratings yet
- Acute Hepatitis ADocument1 pageAcute Hepatitis ACJMALNo ratings yet
- Min Pin Sweater Paradise - Autumn Stripes Crochet Min Pin SweaterDocument6 pagesMin Pin Sweater Paradise - Autumn Stripes Crochet Min Pin SweaterNathalyaNo ratings yet
- Uasin Gishu - 2Document77 pagesUasin Gishu - 2peeteoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2222Document16 pagesPaper 2222Abhijeet GholapNo ratings yet
- Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced Resins: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesIgnition Loss of Cured Reinforced Resins: Standard Test Method ForElida SanchezNo ratings yet
- Fire Water Curtain DesignDocument2 pagesFire Water Curtain Designkb_pramod89% (9)
- GCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperDocument24 pagesGCSE-Biology-7-Summer2019-Foundation Tier, Unit 1-PaperjramatlhakolaneNo ratings yet
- CPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingDocument11 pagesCPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 - ScienceDocument228 pagesClass 9 - ScienceYashwanth KasturiNo ratings yet